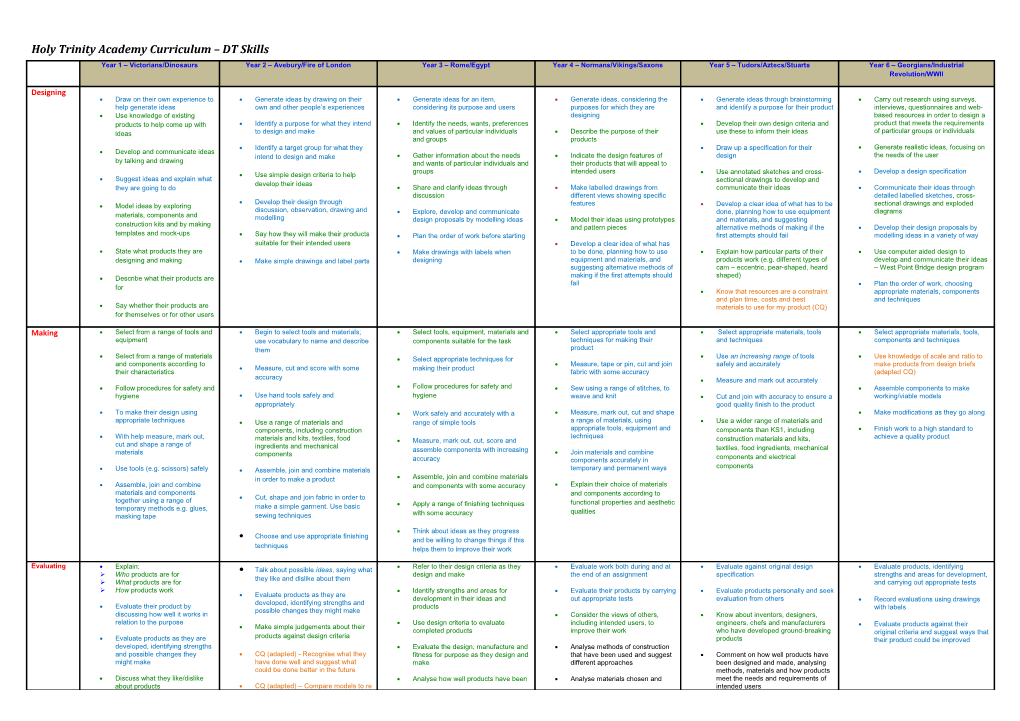
Holy Trinity Academy Curriculum – DT Skills Year 1 – Victorians/Dinosaurs Year 2 – Avebury/Fire of London Year 3 – Rome/Egypt Year 4 – Normans/Vikings/Saxons Year 5 – Tudors/Aztecs/Stuarts Year 6 – Georgians/Industrial Revolution/WWII
Designing Draw on their own experience to Generate ideas by drawing on their Generate ideas for an item, Generate ideas, considering the Generate ideas through brainstorming Carry out research using surveys, help generate ideas own and other people’s experiences considering its purpose and users purposes for which they are and identify a purpose for their product interviews, questionnaires and web- Use knowledge of existing designing based resources in order to design a products to help come up with Identify a purpose for what they intend Identify the needs, wants, preferences Develop their own design criteria and product that meets the requirements ideas to design and make and values of particular individuals Describe the purpose of their use these to inform their ideas of particular groups or individuals and groups products Identify a target group for what they Draw up a specification for their Generate realistic ideas, focusing on Develop and communicate ideas intend to design and make Gather information about the needs Indicate the design features of design the needs of the user by talking and drawing and wants of particular individuals and their products that will appeal to groups intended users Develop a design specification Use simple design criteria to help Use annotated sketches and cross- Suggest ideas and explain what sectional drawings to develop and develop their ideas they are going to do Share and clarify ideas through Make labelled drawings from communicate their ideas Communicate their ideas through discussion different views showing specific detailed labelled sketches, cross- Develop their design through Model ideas by exploring features Develop a clear idea of what has to be sectional drawings and exploded discussion, observation, drawing and diagrams materials, components and Explore, develop and communicate done, planning how to use equipment modelling design proposals by modelling ideas Model their ideas using prototypes and materials, and suggesting construction kits and by making and pattern pieces alternative methods of making if the Develop their design proposals by templates and mock-ups Say how they will make their products Plan the order of work before starting first attempts should fail modelling ideas in a variety of way suitable for their intended users Develop a clear idea of what has State what products they are Make drawings with labels when to be done, planning how to use Explain how particular parts of their Use computer aided design to designing and making Make simple drawings and label parts designing equipment and materials, and products work (e.g. different types of develop and communicate their ideas suggesting alternative methods of cam – eccentric, pear-shaped, heard – West Point Bridge design program Describe what their products are making if the first attempts should shaped) fail Plan the order of work, choosing for Know that resources are a constraint appropriate materials, components and plan time, costs and best and techniques Say whether their products are materials to use for my product (CQ) for themselves or for other users
Making Select from a range of tools and Begin to select tools and materials; Select tools, equipment, materials and Select appropriate tools and Select appropriate materials, tools Select appropriate materials, tools, equipment use vocabulary to name and describe components suitable for the task techniques for making their and techniques components and techniques them product Select from a range of materials Select appropriate techniques for Use an increasing range of tools Use knowledge of scale and ratio to and components according to Measure, tape or pin, cut and join safely and accurately make products from design briefs Measure, cut and score with some making their product their characteristics fabric with some accuracy (adapted CQ) accuracy Measure and mark out accurately Follow procedures for safety and Follow procedures for safety and Sew using a range of stitches, to Assemble components to make hygiene Use hand tools safely and hygiene weave and knit Cut and join with accuracy to ensure a working/viable models appropriately good quality finish to the product To make their design using Work safely and accurately with a Measure, mark out, cut and shape Make modifications as they go along appropriate techniques Use a range of materials and range of simple tools a range of materials, using Use a wider range of materials and components, including construction appropriate tools, equipment and components than KS1, including Finish work to a high standard to With help measure, mark out, techniques achieve a quality product materials and kits, textiles, food Measure, mark out, cut, score and construction materials and kits, cut and shape a range of ingredients and mechanical assemble components with increasing textiles, food ingredients, mechanical materials components Join materials and combine accuracy components accurately in components and electrical components Use tools (e.g. scissors) safely Assemble, join and combine materials temporary and permanent ways in order to make a product Assemble, join and combine materials Assemble, join and combine and components with some accuracy Explain their choice of materials materials and components and components according to Cut, shape and join fabric in order to together using a range of functional properties and aesthetic make a simple garment. Use basic Apply a range of finishing techniques temporary methods e.g. glues, qualities masking tape sewing techniques with some accuracy
Think about ideas as they progress Choose and use appropriate finishing and be willing to change things if this techniques helps them to improve their work
Evaluating Explain: Talk about possible ideas, saying what Refer to their design criteria as they Evaluate work both during and at Evaluate against original design Evaluate products, identifying Who products are for design and make the end of an assignment specification strengths and areas for development, they like and dislike about them What products are for and carrying out appropriate tests How products work Identify strengths and areas for Evaluate their products by carrying Evaluate products personally and seek Evaluate products as they are development in their ideas and out appropriate tests evaluation from others Record evaluations using drawings developed, identifying strengths and Evaluate their product by products with labels possible changes they might make discussing how well it works in Consider the views of others, Know about inventors, designers, relation to the purpose Use design criteria to evaluate including intended users, to engineers, chefs and manufacturers Make simple judgements about their Evaluate products against their completed products improve their work who have developed ground-breaking original criteria and suggest ways that products against design criteria Evaluate products as they are products their product could be improved developed, identifying strengths Evaluate the design, manufacture and Analyse methods of construction and possible changes they CQ (adapted) - Recognise what they fitness for purpose as they design and that have been used and suggest Comment on how well products have might make have done well and suggest what make different approaches been designed and made, analysing could be done better in the future methods, materials and how products Discuss what they like/dislike Analyse how well products have been Analyse materials chosen and meet the needs and requirements of about products CQ (adapted) – Compare models to re intended users al things they have studied designed, constructed and function comment on their fitness for purpose
Project ideas and Ideas: Ideas: Ideas: Ideas: Ideas: Ideas: technical Somerset Skills – KS1 – structures – Somerset skills – KS1 – wheels, axles… - Idea Somerset skills – KS2 – structures – Idea – Somerset skills – KS2 – Textiles – Idea - Somerset skills – KS2 – understanding - Roman Villa Saxon/Norman/Viking purse or Viking Control Mechanisms – Moving Toys – Idea – involved in each stability and fastening – Idea – assignment Homes/Castles (Links to Victorians or boots Cams that make boats or sea objects ‘bob’ Textiles – (Discovery of New World) other story based activities) Obtain ideas for their own designs by Relate the way things work to their looking at familiar products and draw intended purpose Understand that different shaped Know that a designer needs to on their investigations of _____ to cams produce different movements consider appearance, function, cost Begin to understand how to inform their own designs Understand how the working and safety when designing products make their structures more characteristics of materials relate to Use a cam to change rotary stable – e.g. by using a wide Use wheels and axles, understanding the ways materials are used movement into linear/reciprocating Know that many different materials base – and able to withstand that wheels and axles can be movement can be used on one product – e.g. greater loads – e.g. by adding assembled in two different ways: Understand how card is stiffened slipper – some to stiffen, some to Know that fabrics have different supports to their swing or Either the wheel is attached tightly to when a packet is made Identify the cam within a mechanism provide a hard-wearing surface and the axle and the axle is free to rotate, properties some for appearance climbing frame and explain how it changes movement or Identify parts of a net and can explain Recognise the role of a cam and its The axle is fixed with the wheel free to how it was assembled; understand the Understand that some joining follower in a mechanism and how Know that patterns/templates can be Investigate how materials and rotate around it need to extend the net to incorporate techniques are stronger/weaker cams produce movement used many times and that this components have been joined tabs for joining than others ensures consistency in size and have a basic idea of how Textiles: Joining fabrics and decorative Electricity, belts and pulleys – links to the items have been assembled techniques – Idea – Making a Fireman’s Understand that 3D structures can be Know that fabrics can be joined in science – grouping materials Structures – Idea – Bridges (Victorian) Jacket (Fire of London) constructed from nets temporary or permanent ways Talk about different examples of ____, Construct a model by joining Investigate and disassemble products Understand the principles of describing how they have been made Food - Sandwich snacks – Idea – Roman Use simple decorative patterns to learn how they are made/function triangulation in different structures and combining 2D and 3D food e.g. dyeing, embroidery or fabric materials in appropriate ways Discuss the advantages and Understand about the importance of paints Know there are a variety of products Recognise that under certain disadvantages of different joining hygienic food preparation and storage that incorporate a pulley/belt drive circumstances structures can fail Use simple methods for making techniques driven by a motor when loaded (become familiar with free-standing structures stronger Know that food can be divided into Structures – instruments – Viking Lyre or techniques that reinforce and and more stable (QCA/DfES) Join their fabric pieces effectively different groups pipes (links to science – sound) Know that a belt and pulley system strengthen structures) can increase or decrease the speed of Textiles – sock puppets (dinosaurs) Describe patterns in fabric and show Explain that different combinations of rotation (by using different pulley Understand that some structures are how they are repeated ingredients can affect taste and sizes) stabilised by having a wide stable texture of the product base – e.g. the use of suspension Join fabric pieces effectively How to repeat patterns Levers and Sliders – moving mouth animals cables Say what forms a healthy diet Use a simple needle and cut How to use a graphics programme to Identify simple levers and sliders in lengths of thread to some test repeated patterns Control Mechanisms – Moving Monsters – moving toys Structures – shelters WWII degree of accuracy Idea – moving mummies from the tomb Look at crank systems and how they That 2D paper patterns are used to (hydraulics)/Egyptian monsters affect rotational movement Choose materials for mark out the shape and size of pieces Identify how to strengthen paper a Investigate and understand how cams to make a 3D product Use a simple pneumatic system to nd card in different ways turn rotational movement into linear aesthetic qualities e.g. colour create movement (QCA/DfES) movement Use a template (QCA/DfES) Identify which parts support and st Food: Healthy Eating and Hygiene How air pressure can be used to rengthen simple structures – Idea - Winding Mechanisms – Idea – making a produce and control movement model well to draw water, as in prehistoric (hydraulics) Recognise and name a number times (Avebury) Food – bread – Ideas – Saxon Bread of different fruit and vegetables Talk about how a winding mechanism Know some techniques for making To weigh and measure accurately and can say which may be is made and how they work simple pneumatic systems (time, dry ingredients, liquids) peeled before being eaten Observe carefully how a winding Compare the effectiveness of different Know that ingredients have mechanism works pneumatic systems different characteristics Classify some fruit/vegetables according to colour, texture and Investigate techniques for winding Know ways of using simple pneumatic Know that the proportion of taste, how and where they are mechanisms systems in conjunction with simple ingredients will affect the product grown, what they are used for, levers to control movement how they are eaten Use a winding/winch mechanisms Using a heat source changes (DfES/QCA) ingredients Carry out simple tasting of fruit Understand the need for a stable Recipes can be adapted by adding and vegetables e.g. preference structure to support a mechanism or substituting ingredients tests and record results (QCA/DfES)
Know that fruit and vegetables are part of a healthy diet
Cooking Across KS1 Across KS2 and Know that all food comes from plants or animals Know that all food is grown, reared and caught in the UK, Europe and rest of the world Nutrition Know that food has to be farmed, grown elsewhere (e.g. home) or caught Know that seasons may affect the food available
Name and sort foods into the five groups on the Eatwell Plate How food is processed into ingredients that can be eaten or used in cooking
Know that everyone should eat five portions of fruit and vegetables everyday Know how to prepare a variety of predominantly savoury dishes safely and hygienically including, where appropriate, the use of a heat-source Know how to prepare simple dishes safely and hygienically, without a heat source Know how to use a range of techniques such as peeling, chopping, slicing, grating, mixing, spreading, kneading and baking Use techniques such as grating, peeling and cutting Demonstrate hygienic food preparation and storage Know the principles of basic food handling, hygienic practices and personal hygiene Weigh and measure accurately (time, dry goods, liquids)
KS2 TECHNICAL KNOWLEDGE
Use learning from science to help design and make products that work
Use learning from mathematics to help design and make products that work
Know that materials have both functional properties and aesthetic qualities
Know that mechanical and electrical systems have an input, process and an output
Know how mechanical systems such as levers, linkages and pneumatic systems create movement
Know how to programme a computer to control their products
Know how to make strong, stiff shell structures
Know how mechanical systems such as cams or pulleys or gears create movement
How more complex electrical circuits and components can be used to create functional products
KS1 TECHNICAL KNOWLEDGE
Know about the simple working characteristics of materials and components
Know about the movement of simple mechanisms such as levers, sliders, wheels and axles
Know how free-standing structures can be made stronger, stiffer and more stable
Know that a 3D textiles product can be assembled from two identical fabric shapes
Pan-pipes: Another type of pan-pipes can be made from plastic tubing or copper pipe . You will need a total of 41 inches of either. If using plastic, try for an opaque white (you can apply a little ochre-colored paint to make it look like bone) or an opaque black . You will also need some plasticine clay or wax, some strong cord or waxed linen thread and some wooden sticks about the thickness and width of ice cream sticks if you are using the fastening technique in Figure 3. Cut the tubes to length using a saw, knife, or pipe cutter. For tubing with an outside diameter of 1/2", the following lengths give you the notes plus a little room for tuning: 63/4" C 6" D 51/2" E 43/4" F 41/4" G 33/4" A 31/2" B 31/4" C 3" D If you are using copper, you want to file the mouthpiece ends to smooth any sharp edges. Lay the tubes side by side with one end even (this is the top) and wrap with plastic tape to hold them together. You can now tie the pipes together using one of three methods. Figure 2 shows the traditional Chinese method of tying pipes. Wrap string around two adjacent pipes and tie then wrap the second pipe to the next pipe in the series. When completed, wrap all the pipes together at the top. you want to be careful and make sure all the pipes are even at the top. Figure 3 shows another traditional method used in Europe with the pipes lashed to a wooden stick. Tie the diagonal stick first and then the top one. Figure 4 shows the African method of wrapping pipes, by far the most simple to wrap, but harder to play. Now you need to tune them. Insert clay or wax plugs in the bottom end of each pipe. Blow across the top of the pipe and add or subtract clay or wax until you get the note you want. An easy way is to take a wooden dowel that fits inside the tube, and push the clay from the inside to change the pitch. If you are using wax, you will have to warm it to make it pliable, and keep it warm through the tuning process. Play the pipes by holding in the hand and blowing across the open ends of the tubes.