Scientific method
1. colored light 2. plant growth 3. plant with white light 4. comparison group 5. plant type
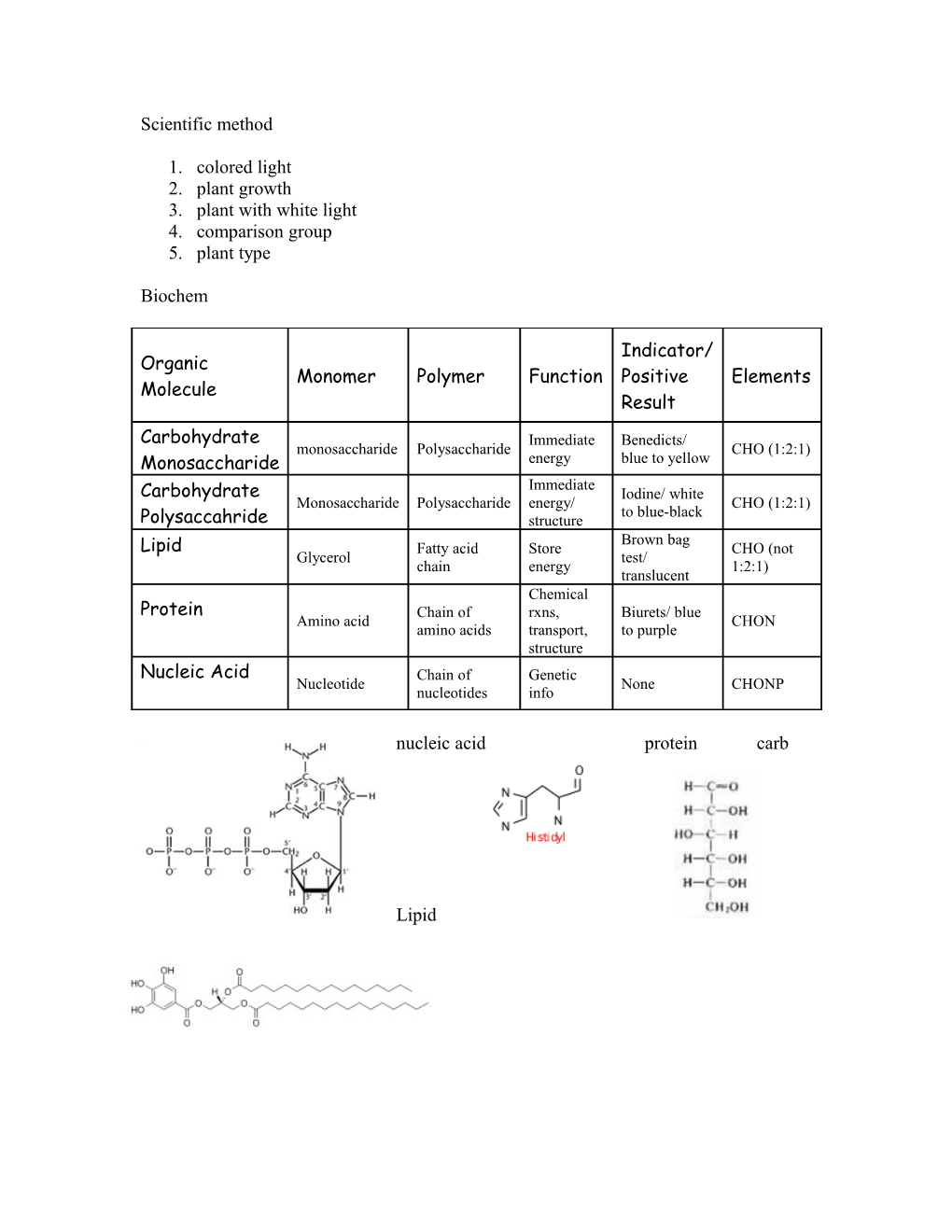
Biochem
Indicator/ Organic Monomer Polymer Function Positive Elements Molecule Result
Carbohydrate Immediate Benedicts/ monosaccharide Polysaccharide CHO (1:2:1) Monosaccharide energy blue to yellow Immediate Carbohydrate Iodine/ white Monosaccharide Polysaccharide energy/ CHO (1:2:1) to blue-black Polysaccahride structure Brown bag Lipid Fatty acid Store CHO (not Glycerol test/ chain energy 1:2:1) translucent Chemical Protein Chain of rxns, Biurets/ blue Amino acid CHON amino acids transport, to purple structure Nucleic Acid Chain of Genetic Nucleotide None CHONP nucleotides info
nucleic acid protein carb
Lipid Enzymes A. reactant/ substrate B. active site C. enzyme D. enzyme-substrate complex E. product
1. speed up chemical rxns 2. temperature, denatured, shape 3. proteins 4. ends in –ase 5. fructose 6. ATP synthase C 40۫~ .7 C 63۫~ .8 9. the enzyme was denatured
Ecology 1. organism population community ecosystem biosphere 2. ecosystem 3. mutualism +/+ buffalo/bird; commensalism, +/0, shark/remora; parasitism, +/-, dog/flea 4. a. rabbit, b. coyote, c. it goes up when rabbit goes up; it goes down when rabbits go down, d. dependent because one population is affected by the other population 5. biotic: flower, fungus, apple; abiotic: rock, water, rust
Growth 1. S, J 2. carrying capacity 3. there are no limiting factors 4. space, food, resources 5. bacteria 6. disease, competition, natural disasters
Age-Structure Diagrams 1. Nigeria 2. Germany 3. United States 4. exponential 5. Nigeria: developing; US: developed
Carbon Cycle 1. respiration, combustion 2. photosynthesis 3. increased by of industrialization 4. increase levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere because of decreased photosynthesis
Food Webs 1. oak tree 2. bees, deer, mice, rabbit, insects 3. decomposers; bacteria 4. 5 5.
Red fox
skunk
toad
insects
leaves
6. leaves (tree); sun (photosynthesis) 7. red fox; life processes 8. 10% 9. red fox; biological magnification
Human Impact Impact Cause Effect Population Size Lack of education Overpopulation Population Density Too many people Disease; pollution; smog Resource Use Too many people Depletion of resources; pollution Acid Rain Pollution Building damage Habitat Destruction Too many people Loss of biodiversity Invasive Species Humans Disruption of ecosystems Pesticide Use Humans Loss of biodiversity Deforestation Humans Loss of biodiversity; increased amount of carbon dioxide in atmosphere Cells
Eukaryote: nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, more recent, unicellular or multicellular Prokaryote: no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, most primitive, unicellular, ex: bacteria Both: ribosomes, cell membrane, DNA (eu: double helix, pro: circular)
Plant: cell wall, central vacuole, chloroplasts Animal: centrioles Both: all other organelles are present in both
Organelle Picture Function Plant/Animal/Both Nucleus Controls cell both function
Plasma Controls what both membrane goes in and out
Cell wall Structure and plant protection
mitochondria INCLUDEPICTURE Energy both "http://www.kathleensworld.com/mitoch ondria.jpg" \* MERGEFORMATINET Central vacuole Storage Central only in plants; animal cell contains several smaller vacuoles
chloroplast INCLUDEPICTURE Site for plant "http://www.helpsavetheclimate.com/chl photosyntheis oroplast1.gif" \* MERGEFORMATINET
Ribosome INCLUDEPICTURE Protein synthesis both "http://www.bothbrainsandbeauty.com/w p- content/uploads/2009/12/ribosome1.jpg" \* MERGEFORMATINET
1. osmosis 2. active transport 3. energy 4. shrink; outside 5. proteins 6. endocytosis; exocytosis 7. Photosynthesis/ Cellular Respiration 1. chloroplasts; plant 2. absorb sunlight 3. 6CO2 + 6 H2O + light C6H12O6 + 6O2 4. glucose, glycolysis, mitochondria 5. fermentation, alcoholic, carbon dioxide, lactic acid, lactic acid 6. krebs cycle, pyruvic, mitochondria 7. electron transport chain, ATP 8. adenosine triphosphate, ADP, phosphate, breaking bonds
DNA/Protein Synthesis 1. deoxyribonucleic acid; nuclei 2. nucleotide 3. adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine 4. double helix, sugar, phosphate 5. helicase, DNA polymerase 6. RNA: single strand, ribose sugar, uracil instead of thymine 7. mRNA, tRNA, rRNA 8. transcription, nucleus 9. translation, ribosome 10. mRNA 11. codon 12. tRNA 13. amino acids 14. mRNA: AUGCCCUAAAGAUGA amino acids: MET-PRO-STOP-ARG-STOP
Biotechnology: Individual B is the father