INQUIRY AND ANALYSIS STANDARDS Adapted from the AAC&U VALUE Rubrics and acknowledged with thanks. See Assuring Graduate Capabilities
Definition: Inquiry is the ability to know when there is a need for information, to be able to identify, locate, evaluate, and effectively and responsibly use and share that information for the problem at hand. – The National Forum on Information Literacy
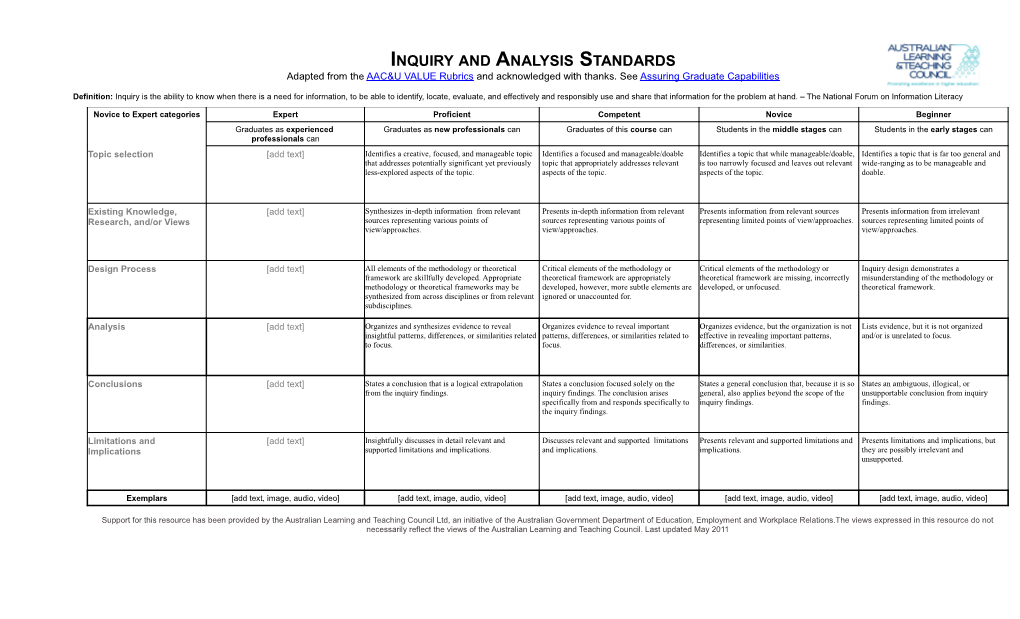
Novice to Expert categories Expert Proficient Competent Novice Beginner Graduates as experienced Graduates as new professionals can Graduates of this course can Students in the middle stages can Students in the early stages can professionals can Topic selection [add text] Identifies a creative, focused, and manageable topic Identifies a focused and manageable/doable Identifies a topic that while manageable/doable, Identifies a topic that is far too general and that addresses potentially significant yet previously topic that appropriately addresses relevant is too narrowly focused and leaves out relevant wide-ranging as to be manageable and less-explored aspects of the topic. aspects of the topic. aspects of the topic. doable.
Existing Knowledge, [add text] Synthesizes in-depth information from relevant Presents in-depth information from relevant Presents information from relevant sources Presents information from irrelevant Research, and/or Views sources representing various points of sources representing various points of representing limited points of view/approaches. sources representing limited points of view/approaches. view/approaches. view/approaches.
Design Process [add text] All elements of the methodology or theoretical Critical elements of the methodology or Critical elements of the methodology or Inquiry design demonstrates a framework are skillfully developed. Appropriate theoretical framework are appropriately theoretical framework are missing, incorrectly misunderstanding of the methodology or methodology or theoretical frameworks may be developed, however, more subtle elements are developed, or unfocused. theoretical framework. synthesized from across disciplines or from relevant ignored or unaccounted for. subdisciplines.
Analysis [add text] Organizes and synthesizes evidence to reveal Organizes evidence to reveal important Organizes evidence, but the organization is not Lists evidence, but it is not organized insightful patterns, differences, or similarities related patterns, differences, or similarities related to effective in revealing important patterns, and/or is unrelated to focus. to focus. focus. differences, or similarities.
Conclusions [add text] States a conclusion that is a logical extrapolation States a conclusion focused solely on the States a general conclusion that, because it is so States an ambiguous, illogical, or from the inquiry findings. inquiry findings. The conclusion arises general, also applies beyond the scope of the unsupportable conclusion from inquiry specifically from and responds specifically to inquiry findings. findings. the inquiry findings.
Limitations and [add text] Insightfully discusses in detail relevant and Discusses relevant and supported limitations Presents relevant and supported limitations and Presents limitations and implications, but Implications supported limitations and implications. and implications. implications. they are possibly irrelevant and unsupported.
Exemplars [add text, image, audio, video] [add text, image, audio, video] [add text, image, audio, video] [add text, image, audio, video] [add text, image, audio, video]
Support for this resource has been provided by the Australian Learning and Teaching Council Ltd, an initiative of the Australian Government Department of Education, Employment and Workplace Relations.The views expressed in this resource do not necessarily reflect the views of the Australian Learning and Teaching Council. Last updated May 2011