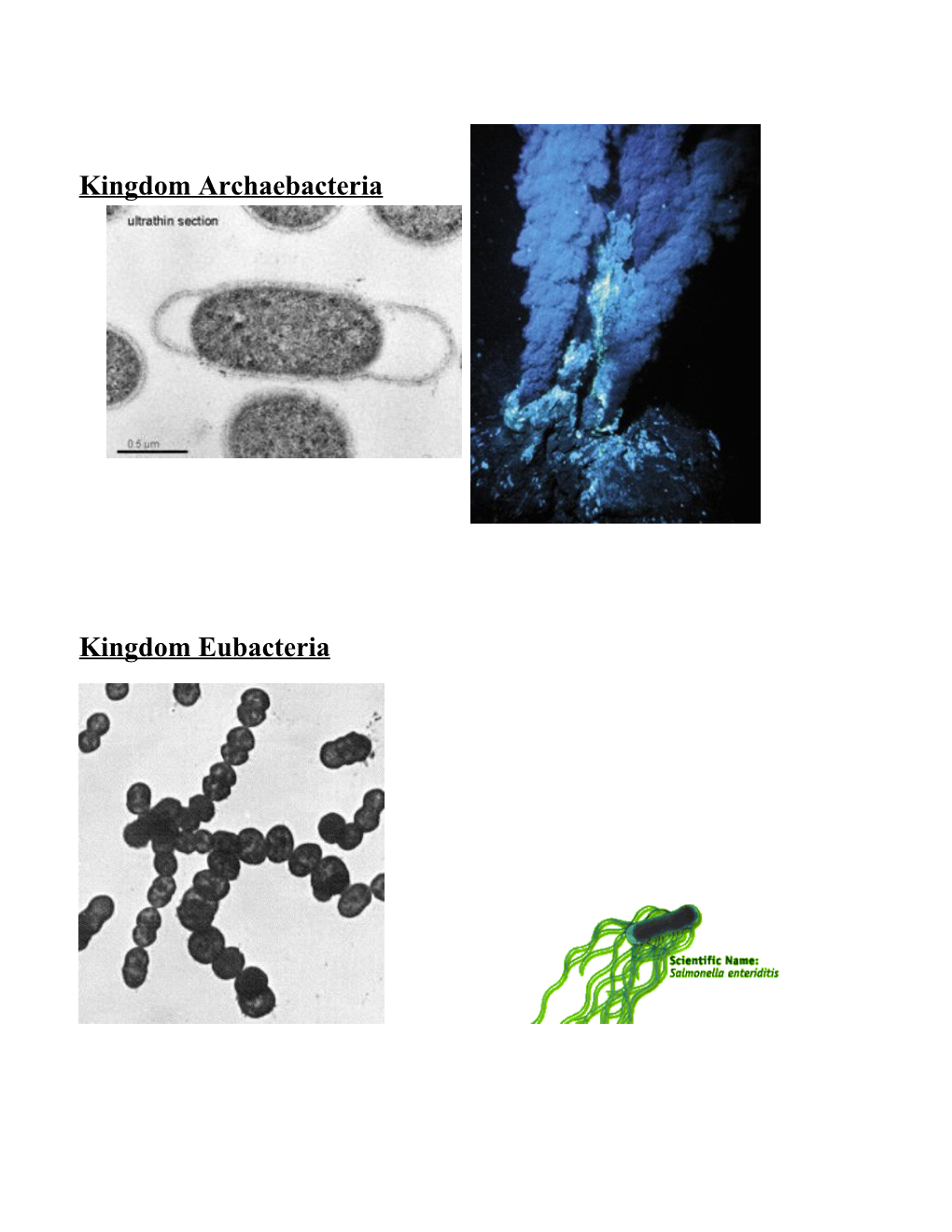
Kingdom Archaebacteria
Kingdom Eubacteria
Kingdom Protista
Kingdom fungi Kingdom Plantae
Phylum coelenterata
Jelly fish Coral
Phylum Annelida
Earthworm
Phylum mollusca
Phylum anthropoda
Tarantula Butterfly
Phylum Porifera
Sponge Live Sponges
Phylum Echinodermata
Sand Dollar Sea Star
Phylum: Chordata
The entire phylum Chordata is made up of the animals in the subphylum Vertebrata. The two main hallmarks of this phylum are a skull and a backbone containing vertebrae.
Class Amphibia
Class Aves
Class Osteichthyes
Class Reptilia
Class mammalia
Text for the back of these six Kingdom pictures: Kingdom Fungi (4) Kingdom Archaebacteria (1) Characteristics: Most are Characteristics: Microscopic multicellular and complex celled. one cell (unicellular) organisms. Fungi cannot make their own food. Found in extreme environments They absorb food from parts of with no oxygen, such as the hot plants that are decaying in the soil. springs of Yellowstone National Some can be eaten and some are Park or deep ocean vents poisonous. Examples: mushrooms, mold (shower curtain, bread), yeast, blue Kingdom Eubacteria (2) cheese Characteristics: microscopic single cell organism. Most bacteria Kingdom Plantae (5) are in this kingdom. Characteristics: Plants are Examples: yogurt, multicellular and complex celled. streptococci (strep throat) They make their own food (autotrophs) through a process called photosynthesis. It is the second largest kingdom with over Kingdom Protista (3) 250,000 species. Characteristics: Most are Examples: Mosses, ferns, unicellular, microscopic, complex fruits and vegetables, flowering cell organisms. This kingdom plants, grasses, trees includes all microscopic organisms that are not bacteria, not animals, not plants and not fungi Examples: algae, giant kelp Kingdom Animalia (6) Phylum Annelida (9) Characteristics: All animals Characteristics: Segmented consist of many complex cells. They bodies, well-developed internal are organisms that eat other organs. Tube within a tube organisms (heterotrophs). The Examples: worms, leeches animal kingdom is the largest kingdom with over one million known species and is divided into two phylums: chordata (vertebrate or backbone) and invertebrate. 98% of Phylum Molusca (10) the animal species are Characteristics: soft body invertebrates. often covered by a hard shell. Examples: from ant to zebra Mollusks that live on land move on a Phylum Protozoa (7) flat sole called a foot. Mollusks Characteristics: The that live in the ocean propel or smallest of all animals. Most can move themselves by ejecting water only be seen under a microscope. from their body. Some ocean Single-celled animals that live in mollusks attach themselves to rocks water, they eat tiny algae and and can’t move. bacteria. Examples: snails, slugs, Examples: amoebas, octopus, clams, squid, oyster, mussel flagellates Phylum Arthropoda (11) Characteristics: Over 75% of the world’s animal species are Phylum Coelenterata (Cnidaria) (8) arthropods. They have an Characteristics: Radial exoskeleton (a hard external symmetry, mouth surrounded by skeleton) and joints that help them tentacles with stinging cells; move. They molt (shed their captures prey with tentacles exoskeleton) as they grow. Examples: jellies, coral, Examples: insects, crustaceans sea anemones, hydrozoans (lobsters, crabs), arachnids (spiders, ticks) centipedes and millipedes. Phylum Porifera (12) Characteristics: Most are • Class Reptilia (15) found in the ocean. A hollow tube Characteristics: Reptiles have with many pores or openings, it scales that cover their body. Their takes in food via water that flows body temperature depends on the through its pores. environment. Examples: Sponges Examples: Crocodiles, alligators, snakes, lizards,
Phylum Echinodermata (13) • Class Osteichthyes (16) Characteristics: marine Characteristics: Bony fish, (ocean) animals that have arms or cold-blooded, breath through gills, spines that radiate from the center paired fins, scales, many teeth of their body. 90% of the ocean Examples: salmon, tuna, trout animals on the sea floor are echinoderms. Spiny skinned Examples: Sea stars, sea urchins • Class Aves (19) Characteristics: Birds have wings for flight, feathers, and a beak instead of teeth. They also have claws Phylum Chordata (Vertebrates) Examples: ñandú, eagle, hawk, parrot, seagull • Class Mammalia (14) Characteristics: Most mammals have hair or fur covering • Class Amphibia (20) their bodies. They can regulate Characteristics: Most their body temperature. They give amphibians can walk and swim in birth to fully formed babies and water. Their body temperature produce milk to feed their babies. changes with the environment. Examples: humans, lions, They lay their eggs in water monkeys, marsupials, rodents, Examples: frogs, toads whales, dolphins, seal