LINCOLNSHIRE AGREED SYLLABUS FOR RELIGIOUS EDUCATION KEY STAGE ONE (Years 1 & 2) Overview of Medium Term Planned Units
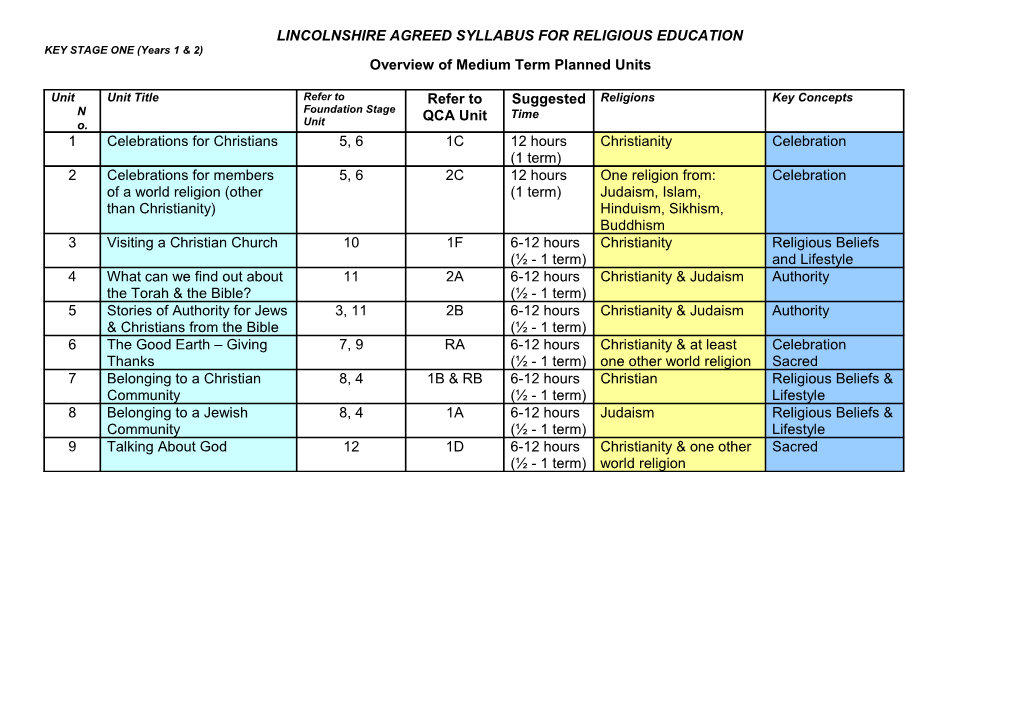
Unit Unit Title Refer to Refer to Suggested Religions Key Concepts N Foundation Stage QCA Unit Time o. Unit 1 Celebrations for Christians 5, 6 1C 12 hours Christianity Celebration (1 term) 2 Celebrations for members 5, 6 2C 12 hours One religion from: Celebration of a world religion (other (1 term) Judaism, Islam, than Christianity) Hinduism, Sikhism, Buddhism 3 Visiting a Christian Church 10 1F 6-12 hours Christianity Religious Beliefs (½ - 1 term) and Lifestyle 4 What can we find out about 11 2A 6-12 hours Christianity & Judaism Authority the Torah & the Bible? (½ - 1 term) 5 Stories of Authority for Jews 3, 11 2B 6-12 hours Christianity & Judaism Authority & Christians from the Bible (½ - 1 term) 6 The Good Earth – Giving 7, 9 RA 6-12 hours Christianity & at least Celebration Thanks (½ - 1 term) one other world religion Sacred 7 Belonging to a Christian 8, 4 1B & RB 6-12 hours Christian Religious Beliefs & Community (½ - 1 term) Lifestyle 8 Belonging to a Jewish 8, 4 1A 6-12 hours Judaism Religious Beliefs & Community (½ - 1 term) Lifestyle 9 Talking About God 12 1D 6-12 hours Christianity & one other Sacred (½ - 1 term) world religion LINCOLNSHIRE AGREED SYLLABUS FOR RELIGIOUS EDUCATION KEY STAGE 1 (Years 1 & 2) Scheme of work planning sheet Unit Theme: (suggested time: hours) (Refer also to Foundation Stage Units ( term) & QCA Unit ) Intended teaching outcomes & Religions Content: Teaching and learning Key questions Assessment learning outcomes suggestions. Opportunities Pupils will be taught:
Key Concepts
Suggested Resources
Pupils will be enabled to:
Skills to be taught
Attitudes to be developed
Unit 1 Theme: Celebrations for Christians (suggested time: 12 hours - 1 term) (Refer also to Foundation Stage Units 5 & 6
Intended teaching outcomes & Religions Content: What pupils will be taught Key questions Assessment learning outcomes Opportunities Learning About Religions & Christianity - How do Christians celebrate Retell the Christmas or Exploring Human Experience - Discuss all the celebrations they have special days eg. Christmas, Easter, Easter story and explain Key Concepts experienced – using cards, photographs, possibly also Saints’ days, why Christians celebrate Acquire and develop knowledge and pictures, clothes, artefacts etc baptisms, wedding. at this time of year. Give understanding of Christianity and the Celebration - Share the Christian stories of Easter and - What stories are celebrated by examples of some of the other principal religions represented in Christmas from the Bible including the lead up Christians? eg. stories of Jesus’ activities undertaken as Great Britain and their associated Suggested to these stories birth, Easter stories, stories of part of this celebration. beliefs, experiences and practices. Resources - To be aware of the variety of ways Christians Saints (does good win over evil in (AT1, level 1.) Nativity set prepare for Christmas and that this period is these stories – if so how?) Draw a picture of a Learning From Religions & Responding Celebration cards called Advent. Explore three or more ways - What special food do Christians special celebration they to Human Experience Family celebration children know Christmas is coming eg. Advent eat at times of celebration? have experienced (eg. photographs calendars, Christmas cards, Advent wreath, - How can different types of music birthday party, christening, Reflect on their own beliefs, values, Special decorations, choosing presents, preparing food, help Christians to celebrate? eg wedding) and relate how perceptions and experiences in the celebration clothes specific school celebrations carols, hymns, choirs, chants, they felt on this occasion light of their study of religion. eg. Christening robe, - To understand why Easter is a special time for prayers and poems to music. What (verbal or written), wedding dress, Christians and how Christians prepare for do the words say? detailing their favourite or Develop positive attitudes of respect bridesmaid dress Easter in the period known as ‘Lent’. Explore - What are the special days in my most interesting part of the towards other people who hold views Advent calendar three or more ways children know that Easter is life? What happens? How do I day. (AT2, level 1.) and beliefs that are different from their Advent ring coming eg. Easter eggs in the shops, Spring feel? How do others feel at these own. time activities, hot-cross buns, Palm Sunday, special times? eg. birthdays, Palm cross Skills to be taught school-based learning about Easter baptisms, weddings. Range of light Pupils will be enabled to: celebrations - What special clothes have you sources used in Reflection - What happens at the Christian celebrations worn at an important celebration celebrations eg. Expression Understand that religion is a way of studied and why? Additional examples might and how did you feel when you Baptism candle, Empathy life for believers and that festivals & include. baptisms, weddings, Christingle were wearing them? Advent candle Discernment celebrations are one part of a range of services, St George’s Day, Mothering Sunday - How do Christians prepare for Interpretation Range of experiences and occasions. etc specific festivals? Investigation celebratory food eg. Retell stories of the Christian - Investigate the importance of light(s) used in For Christmas:- advent candles, Easter egg, hot- festivals or celebrations studied. music/dance/songs associated with the festival calendars, Christmas shopping, Attitudes to be developed cross buns, - Stories associated with the chosen festivals – cards etc Connect the idea of celebrating in Christmas cake their own lives with those of others. does good triumph over evil, if so how? For Easter:- Shrove Tuesday, Lent, Respect Range of - Learn about the use of light in the celebrations. hot cross buns, palm crosses etc Fairness Understand the concept of a celebration music precious gift and relate the ideas of - How is light used within the giving and receiving gifts to their own festival? experience. - Why is it important to have some celebrations in life? Unit 2 Theme: Celebrations for members of a world religion (other than Christianity) (suggested time: 12 hours - 1 term) (Refer also to Foundation Stage Units 5 & 6)
Intended teaching outcomes & Religions Content Key questions Assessment learning outcomes Opportunities Learning About Religions & Exploring One religion from: From the religion you have chosen: Refer to the one religion you Pupils to retell the story Human Experience have chosen, and the relevant to the festival or Judaism Children will learn about a festival relevant to the time children’s experiences: celebration chosen A1 Islam of year this unit is being taught in: explaining what the story Acquire and develop knowledge and Hinduism - What makes people want teaches members of that understanding of Christianity and the Sikhism Judaism – Hanukkah (Festival of Lights), Sukkot to celebrate? religious faith and how they other principal religions represented in Buddhism (Harvest), Rosh Hashanah (New Year), Pesach - What events are might be able to put the Great Britain and their associated beliefs, (Passover), Yom Kippur (day of Atonement) celebrated through the teaching into practice. experiences and practices. Key Concepts Islam – Id ul Fitr (end of Ramadan) year? Can we make a (AT1, level 2). Hinduism – Holi (Spring festival of colours in honour calendar? Celebration Ask pupils to draw or Learning From Religions & Responding of Krishna), Diwali (Festival of Lights & New Year) - How are special days paint, and choose words to to Human Experience Sikhism – Baisakhi (the founding of the Sikh Khalsa celebrated? Suggested Resources describe, a specially happy community), Guru Nanak’s birthday, Diwali (Sikh New - What stories are told as moment. (AT2, level 2) B1:2 Year & Festival of Lights) part of the celebrations? Artefacts, including light Observe pupils Responding to such questions with Buddhism – Wesak (Buddha Day, May), Kathina Does good win over evil? responses (in discussion) to reference to the teachings and practices sources and uses Day (monks are presented with cloth for robes, If so how? associated with your visitors beliefs about of religions, and to their own October / November). - Is there special food their religion and the understanding and experience. celebrations from the associated with the chosen religion. celebration activities. (AT2, What happens at these festivals? celebration? level 2). B2 Photographs/ pictures Prauyer, worship, special food eaten, clothes worn, - How do you think the Develop positive attitudes of respect of festivals and jewellery worn, artefacts used, music, dance, songs children feel on their celebrations. towards other people who hold views associated with the festival. special celebration day? Skills to be taught and beliefs that are different from their Examples of food, - What special clothes are clothes, jewellery, music, own. Invite a follower of your chosen religion to talk to the worn for particular Reflection video clips of chosen children about a religious festival of celebration which celebrations and why? Expression festival celebration. Pupils will be enabled to: has been important to them, bringing in photographs Are there cards, presents, Empathy Understand that religion is a way of A Visitor to recount why and relevant artefacts (eg. clothes, food, jewellery special gatherings of Interpretation life for believers and that festivals and a particular religious etc). people? Analysis celebrations are one part of a range of festival or celebration has - What preparations are Investigation experiences and occasions. been important to them. Tell the stories associated with your chosen festival. made for specific Retell the stories of the chosen NB: Many publishers Discuss whether good triumphs over evil. celebrations? festival. provide detailed resources - How is light used within Attitudes to be developed Connect the idea of celebrating in for KS1 on religious Learn about the uses of light in the celebrations for your chosen celebration? their own lives with those of others. festivals. There are some your chosen festival. What does light mean in these - Why is it important to Fairness good broadcast resources Begin to understand the symbolism celebrations? have some celebrations in Respect from BBC and independent of the use of light in religious festivals. life? TV.. Discuss the other forms of celebration practised eg. birth celebrations, weddings, seasonal celebrations. Unit 3: Theme: Visiting a Christian Church (suggested time: 6-12 hours ½ - 1 term) (See also Foundation Stage Unit 10) Intended teaching outcomes & Religions Content Key questions Assessment learning outcomes Opportunities Learning About Religions & Exploring Christianity - Start by discussing places that are special to the - Where is your special place and Draw some of Human Experience children and why they are special what do you like to do there? the symbols and - Look at pictures, paintings or videos of different - Is it important for people to have artefacts seen in A1 Key Concepts types/denominations/styles of Christian churches, special places? the church and Acquire and develop knowledge and Religious Beliefs and chapels and other sacred buildings. - Do you like being in church? explain their understanding of Christianity and the Lifestyle - Discuss the similarities and differences How does it make you feel? religious purpose other principal religions represented in - Visit at least one Christian place of worship - Who uses the building? and significance to Great Britain and their associated - Teach the children the correct vocabulary for church - What furniture do you find in Christian worship. beliefs experiences and practices. Suggested furniture, artefacts and specific areas eg. altar, pulpit, church and what is it used for? (AT1, level 2). Resources lectern, font, pews, aisle, nave, chalice etc - What do different symbols Prepare a set of Learning From Religions & Responding - Talk about how symbols are used mean eg. light and water questions to ask to Human Experience Pictures, - Use silence and time for reflection to appreciate the - What happens in a church? eg. the church leader paintings, videos of atmosphere of the place of worship. weekly services, baptisms, about their role and B2 different types of - Discuss children’s own experiences of church weddings, funerals, special responsibilities or a Develop positive attitudes of respect Christian churches. attendance for worship and any use of the church hall school events, festivals. church goer about towards other people who hold views A Church visit. eg. cubs, brownies, sports groups, coffee mornings, - Does the church have a hall? their reasons for and beliefs that are different from their Christian charity sales etc What activities take place going to church own. interviewees. - Based on their own experiences, children suggest there? and why they think Artefacts used in why people go to church, what they do there and - Who has a special job to do in church is a special church worship eg. why. church? place. (AT2, level Pupils will be enabled to: cross, candle, Bible, - Introduce the vicar/leader of the church to the - Are the windows in church 2). Communion utensils, children and find out the special jobs he/she does special? Do they tell a story? Know that a church is a special bread and wine, - Children compile questions to ask at least one - Why is a church building special place for Christians and consider some hymn books, regular Christian church worshipper who could be to Christians? Skills to be taught reasons why. service / prayer invited into school to be interviewed - What makes a holy building Recognise some of the artefacts and books, hassock. - Children to draw something they have seen and liked different from other buildings? Investigation symbols found in a church and know in the church building - How should we behave in Interpretation the purpose of some of them. - Explore the reasons why churches are special places church? Discernment Reflect on their own feelings and for Christians - Is it a good idea to go to a Evaluation responses to the atmosphere of a holy - Children could draw up a simple code of conduct for special place, to praise, thank, building. visitors to a church say sorry or be calm? Why? Attitudes to be - Children to be told stories associated with the local developed church: stained glass window stories, carvings, commemorative plaques, stories about past or Commitment present leaders/members, eg Lincoln Cathedral, St. Respect Hugh, Edward King, The Lincoln Imp. Unit 4 Theme: What Can We Find Out About the Torah and the Bible [suggested time: 6 –12 hours or ½ - 1 term) (it is suggested that Units 4 & 5 be delivered in consecutive ½ terms) (See Foundation Stage Unit 11)
Intended teaching outcomes & learning Religions Content: what pupils will be taught Key questions Assessment outcomes Opportunities Learning About Religions & Exploring Human Christianity & - Start off with books that are special to the - Do you have a special Name the books Experience Judaism children, discuss why they are special. book and why is it which are very special in - Ask a number of adults (parents, staff, special? the Jewish faith and the A1 grandparents etc) about their favourite book – - How do you look after Christian faith. Describe Acquire and develop knowledge and understanding of Key Concepts display. your special book? ways in which these Christianity and the other principal religions Authority - Make a class special book and together - What is the Torah? books are handled, represented in Great Britain and their associated suggest ways of treating, storing, handling it. - Where in a synagogue treated and used by beliefs, experiences and practices. Suggested - Show the children the Torah scroll and the is the Torah kept? followers of the two Resources Bible and give an overview of their content:- - How is the Torah faiths. (AT1, level 2). Jewish Torah – teachings and instructions special to Jewish Compile a list of ‘dos Learning From Religions and Responding to Human Special books to (law) for Jews – 1st five books of the Jewish people? and don’ts’ about how to Experience the children and Bible. - What is the Bible? treat a) their own special adults in their life Christian Bible – Collection of books divided - Where in a church book, b) their friend’s or B1:2 eg. favourite story into 2 sections, Old & New Testament would you find a Bible? family member’s special Responding to core questions with reference to the books, photograph Old – Jewish sacred writings and history - Do you have a Bible at book and c) the Bible or teachings and practices of religions, and to their own albums, books New – stories of Jesus and his followers. home/school? Where is the Torah. (AT2, level understanding and experience. given to them by - Show the children how the Torah and the it kept? 2). special people, a Bible should be handled – with respect. - How is the bible special B2 religious book. - What signs of respect do Jews and Christians to Christian people? Skills to be taught Develop positive attitudes of respect towards other A Bible. use? Where is the Torah kept? How is it - Who uses the Torah Investigation people who hold views and beliefs that are different A Torah scroll handled? Why do Bibles often have a gold and the Bible in places Discernment from their own. and a Yad leaf edge, or a leather cover? of worship? Empathy (pointer). - Discuss where the Torah is kept in a - How should the Torah Pupils will be enabled to: Protective synagogue and where the Bible is kept in a and the Bible be covers for books. church. handled? Attitudes to be Know that some books are special to them and that Some story - Invite a Jew and a Christian in to tell children - What do the children developed other people also have very special books. books for telling why the Torah/Bible are special to them. think makes words Know that the Torah is a Holy Book for the Jews sacred stories to - Hear some stories from the Jewish Torah and special, favoured, Commitment and explain how it is treated. young Jews and the Christian Bible (link to unit 5). important or holy? Respect Know that the Christian Holy Book is the Bible and Christians (link to that it comprises of the Old & New Testament. unit 5). Understand some of the ways the Torah and the Bible are used and handled by Jews and Christians in the synagogue, the church and at home, eg for stories, guidance, meanings and teaching about God and goodness. Unit 5 Theme: Stories of Authority about Jews & Christians from the Bible (suggested time: 6 - 12 hours or ½ - 1 term] (It is suggested that this unit be delivered immediately after unit 4) (Refer also to Foundation Stage Units 3 & 11)
Intended teaching outcomes & Religions Content Key questions Assessment learning outcomes Opportunities Learning About Religions & Exploring Human Christianity & - Start off by discussing authority figures in their - Who tells you what to do at Retell in their own Experience Judaism lives and why they must listen and do as they home? At school? The wider words one of the are told. community? (Police, club parables of Jesus and A2 - Devise a set of rules for the classroom / leaders, doctor, crossing patrol say what they can learn Acquire and develop knowledge and Key Concepts playground and discuss how they will be kept etc). from the story. (AT1, understanding of some of the influences of life Authority - Tell stories from the Jewish Bible (Jewish Old - Why do they tell you what to level 1). experiences, beliefs, values and faith Testament) and the Christian New Testament do? Devise a set of rules traditions upon individuals, communities, which illustrate the concept of authority :- - Why do we have rules? for the classroom / societies and cultures. Suggested eg: - What are the stories telling us? playground / home life Resources Jewish – Abraham & Isaac, Joseph & his - Why do these stories matter? and discuss how they will Learning From Religions & Responding to family, Moses & the Exodus from Egypt – - Who loves these stories? be kept. (AT2, level 1). Human Experience Sets of rules for Moses & the 10 Commandments, - What meaning or message can classroom, the Boy Samuel, Jonah, Solomon & the baby be found in a story? B1:2 playground, Skills to be taught Responding to core questions with reference school. Christian – parables of Jesus, (eg. the Good to the teachings and practices of religions, and Rules in society Samaritan, the lost sheep, the prodigal son, the Investigation to their own understanding and experience. eg. Highway Code, sower, the parable of the talents). Reflection Countryside Code Empathy B2 etc. Note: Put the parables of Jesus in context ie. as Interpretation Develop positive attitudes of respect towards A Bible (Old & a response to questions asked of him. Expression other people who hold views and beliefs that New Testament). are different from their own. Collections of Set activities which enable children to work with the stories from Jewish stories, such as painting, singing, illustrating, Attitudes to be Pupils will be enabled to: Old Testament and sequencing or re telling. developed Christian New Begin to realise the need for rules in Testament, Discuss the meaning of the stories to Jews and to Commitment society including those Christians. Do they have a meaning or a message Fairness Recognise the authority figures in their life retold for young for us today? at home and in school, and think about children. how they respond. ‘The Miracle Explore the idea that stories tell us something about Know that the Christian Bible is divided Maker’ (video of ourselves, or give us a message or meaning. into two parts - the Old and New life of Jesus using Testaments puppetry) Ask children to write simple stories of their own with Know that the Jews revere the Torah. ‘Testament’ a meaning or a message. Know that the Bible is an important book (Puppet re tellings for Christians and Jews as it gives them of Biblical story). guidance about how to live and about God. Unit 6 Theme: The Good Earth – Giving Thanks (suggested time: 6–12 hours ½ - 1 term) (Refer also to Foundation Stage Units 7 & 9)
Intended teaching outcomes & Religions Content: What pupils will be taught Key questions Assessment learning outcomes Opportunities Learning About Religions & Exploring Christianity & at least - Look at seasonal changes and highlight the - What special things happen Pupils describe a Human Experience one other world beauty of each season: What do the children in each individual season? Harvest Festival and its religion like best about each of the four seasons? - What is your favourite season meaning and purpose to A2 - Discuss the meaning of thanks and praise and why? Christians. Describe Acquire and develop knowledge and drawing initially from children’s own - How can we help our natural another festival understanding of some of the influences of Key Concepts experiences. world? celebrated by a different life experiences, beliefs, values and faith Celebration - Allow the children to express how they would - How do we harm our world? religion which is aimed at traditions upon individuals, communities, Sacred give thanks and / or praise for our world eg. - Why do some Christians say giving thanks for our societies and cultures. thank you letters/cards, prayers, poems, thank you to God at Harvest good earth. (AT1, level artistic expression. Who is to be thanked for time? 2). Suggested the world’s beauty? - In what other ways can Create a poster or Learning From Religions & Responding to Resources - Learn about some of the various ways people people say thank you for our information leaflet Human Experience throughout the world give thanks for our Good world? designed to inform others Photographs, video Earth, including religious thanksgivings. - When do you say thank you? how to look after the B1:1 clips of seasonal - Through festivals:- - Has anyone ever said thank school grounds, giving Developing awareness of some of the changes. Christian – Harvest Festival you to you? How did it make consideration to the fundamental questions of life raised by Natural objects eg. - Jewish Sukkot (harvest), you feel? feelings of others if their human experiences, and of how religious flowers, leaves, fruits - Hindu Holi (Spring festival) - How do you feel when advice is not followed. teachings can relate to them. and nuts. - Through prayer, poetry, songs, stories, art and someone says ‘well done’ to (AT2, level 2). Videos/ music you? B1:3 photographs/ pictures - Emphasise the importance of looking after our - How do you believe the world Reflecting on their own beliefs, values, of religious seasonal world because of our dependence on it. was created? Skills to be taught perceptions and experiences in the light of festivals. - Explore practical ways of caring for our own - What can you do to look after their study of religion. Creation stories. school grounds and local environment our beautiful earth? Investigation An environment - Tell and discuss simple versions of creation - How did the world get to be Reflection Pupils will be enabled to walk. stories, eg from Genesis and other traditions. so beautiful? Expression - Consider with pupils what they like best about - Do you think the world feels Empathy Identify changes within the seasons. the natural world, its weather, fruits, animals, like a specially made home Interpretation Know that different religions have special plants and wonders. Make a ‘thank you’ for for humans? In what ways? Analysis festivals to say thank you to God for our their favourite beauties of nature, and consider natural world. how these can be passed on into the future. Attitudes to be Appreciate the importance of saying developed thank you. Begin to realise their responsibilities in Respect caring for the world. Self-understanding Enquiry Unit 7: Theme: Belonging To A Christian Community (suggested time: 6 – 12 hours ½ - 1 term) (Refer also to Foundation Stage Units 4 & 8) Intended teaching outcomes & learning Religions Content. What pupils will be taught. Key questions Assessment outcomes Opportunities Learning About Religions & Exploring Human Christian - Write about themselves and their family. - Who belongs to my family? Retell the story of Experience - List the times when whole families meet together - When was the last time lots of the Baptism of Jesus A1 eg. birthdays, anniversaries, festivals, New Year, your family members met in the River Jordan by Acquire and develop knowledge and Key Concepts welcoming a new baby, weddings etc) together? John the Baptist – understanding of Christianity and the other Religious Beliefs - Draw upon children’s experiences of new babies. - At what other times do they relating the use of principal religions represented in Great Britain and and Lifestyle - Gather together a selection of ‘new baby cards’ – all meet and why? water to a Baptism their associated beliefs, experiences and look at greetings – design a welcome card for a - How do families respond to service or practices. new baby the birth of a new baby? Christening. Children A2 Suggested - Find out what happens at a Christian Christening - Why is your name special? to say why John was Acquire and develop knowledge and Resources or dedication using accounts from children or Who chose it for you? given the title ‘The understanding of some of the influences of life Artefacts visitors, videos, books and role play activities - What does your name mean? Baptist’. (AT1, level experiences, beliefs, values and faith traditions associated with - Display Christian artefacts related to - How does the Church 1). upon individuals, communities, societies and belonging. Christenings – eg. photographs, shawl / robe, welcome a new member? Draw a picture of cultures. Video clips/ baptismal candle, order of service, cards, font, - Why do Christians light a a family celebration photographs of water etc. candle at the Christening of a they have Learning From Religions & Responding to Human Christening. - Tell the story from the Bible of the Baby Jesus new baby? experienced and Experience Christening being dedicated to God in the Temple and - What special job do explain (written or B1:1 artefacts (eg. welcomed in the Jewish family by Simeon and Godparents have? verbal) why the family Developing awareness of some of the shawl, cards, Anna (Luke chapter 2) - How and why do people give gathered together and fundamental questions of life raised by human candle). - Tell the story of how Jesus was baptised by John thanks in the family? how they felt about experiences, and of how religious teachings can the Baptist in the River Jordan, signifying the - How do Christians give taking part. (AT2, relate to them. New baby cards. start of his special work or ministry (Mark chapter thanks in a chosen religious level 1). B1:2 1). ceremony? Responding to such questions with reference to Names book - - Look at the meaning of Christian/first names and - How do you know which Skills to be taught the teachings and practices of religions, and to to show definitions find out why they were so named. Conduct school a child belongs to? Investigation their own understanding and experience. and meanings of survey of most popular names in school, look at - What sort of things do Application B2 names. the meanings of some of those names. Tell Christians do together to Reflection Develop positive attitudes of respect towards appropriate stories of name origins (Biblical – show that they belong to Expression other people who hold views and beliefs that are Saints names) God’s family? Interpretation different from their own. - Explore ways in which children show they belong - If you belonged nowhere and Synthesis Pupils will be enabled to: to their school (eg. uniform, badge, daily to no one, what would that be attendance, responsibilities and privileges etc). like? Write about where they belong, and who and Attitudes to be - Introduce the idea that people who believe in - Could humans be happy in what they belong to. developed God belong to a ‘family’ too and explain that they life without belonging? Commitment Draw on their own experiences to identify what do things together to show that they belong (eg. - Do we choose to belong, or Respect is involved in belonging to a family or school. worship, attend a church, raise money, have a do other people choose us? Self understanding Retell what happens at a Christian Christening special meal (Communion), pray, take action and explain some of the symbolism used. together). Talk about what belonging means for Christians. Unit 8 Theme: Belonging To A Jewish Community (suggested time: 6 – 12 hours ½ - 1 term) (Refer also to Foundation Stage Units 8 & 4)
Intended teaching outcomes & learning Religions Content: what pupils will be taught Key questions Assessment outcomes Opportunities Learning About Religions & Exploring Human Experience Judaism - Begin by looking at simple reference books - Who are the family Make a simple book A1 on Jewish family life members? about either the Acquire and develop knowledge and understanding of - Retell what happens at a Jewish baby’s - When do the family Hanukkah festival or the Christianity and the other principal religions represented Key Concepts initiation ceremony focussing on the meet together? Shabbat meal, explaining in Great Britain and their associated beliefs, experiences Religious Beliefs importance of welcoming the baby into the - What are the special what happens and why and practices. & Lifestyle Jewish family (teachers will want to prepare occasions Jewish light is used as part of the A2 carefully what they will say about male families celebrate in celebration / ceremony. Acquire and develop knowledge and understanding of Suggested circumcision). their homes? (AT2, level 2). some of the influences of life experiences, beliefs, values Resources - Remind children of the Bible story of Jesus' - Why are they so Write some questions and faith traditions upon individuals, communities, Jewish dedication in the Temple by Simeon special to them? for a Jewish boy or girl societies and cultures. artefacts used at - Identify the family members - What special foods are (hypothetical or real if special family - Highlight special family occasions at home eaten? possible) to explore the Learning From Religions & Responding to Human occasions. e.g. weekly Shabbat meal, Rosh Hashanah - What special artefacts significance of either the Experience Pictures / (New Year) are used on these Shabbat meal or B1:1 videos of - Bring in food eaten at special Jewish occasions? Hanukkah festival Developing awareness of some of the fundamental synagogues . occasions - Are special clothes activities to them. (AT2, questions of life raised by human experiences, and of A Hanukiah - Find out how and why the food is used worn? level 2). how religious teachings can relate to them. (special candle - Show and explain uses of artefacts used in - What special stories B1:2 holder used at special Jewish family occasions eg. are remembered? Are Skills to be taught Responding to such questions with reference to the the Hanukkah candles, spice box, tallit or prayer shawl, there prayers? Investigation teachings and practices of religions, and to their own celebrations), kippah or yamulkah (skull-cap), shofar or - How do you think a Application understanding and experience. tallit (prayer ram’s horn Jewish boy/girl might Reflection B2 shawl), kippah - Role play of the Jewish Sabbath (Shabbat) feel at a special Expression Develop positive attitudes of respect towards other or yamulkah meal at home occasion? Empathy people who hold views and beliefs that are different from (skull cap), - Discuss how a Jewish person might feel on - How does the family Interpretation their own. miniature Torah such an occasion worship at the Synthesis scroll (sacred - Use a reference book or pictures to illustrate synagogue? Pupils will be enabled to Attitudes to be writings), shofar what happens at the synagogue on the - How does the Write about where they belong, and who and what developed (rams horn), Jewish Sabbath (Shabbat) synagogue welcome they belong to. spice box. - Explain the role of a Rabbi, if possible invite new members? Commitment Know how a baby is welcomed in to the Jewish a Rabbi in to talk about his work - What do we call a Fairness religion. - Explain the importance of the festival of Jewish leader in the Respect Know what is special about belonging to a Jewish Hanukkah – a family festival which uses synagogue? community and explain some of the practices which light to celebrate the survival of Judaism. - Why is Hanukkah an Jews share in the home and at the synagogue. - Consider what the children see as the value important festival for Explain the significance of some of the artefacts and and purposes of these signs of belonging, Jews? symbols used by members of the Jewish community. and how they might be enjoyed by Jewish - What do Jews do to Talk about what belonging means for Jews. children. celebrate Hanukkah? Unit 9 Theme: Talking About God (suggested time: 6 – 12 hours ½ - 1 term) (Refer also to Foundation Stage Unit 12) Intended teaching outcomes & Religions Content Key questions Assessment Opportunities learning outcomes Learning About Religions & Exploring Christianity and one - Explore children’s ideas of God at the start of this - Who do you think Pupils to make a simple Human Experience other world religion unit through discussion, writing, pictures God is? three part book on prayer – - Ask children to make up, in pairs, ten questions they - Where can you focussing on a) an occasion in A1 Key Concepts would like to ask God / the person who knows find God? the Bible when Jesus prayed to Acquire and develop knowledge and Sacred everything. Use the questions in the rest of the unit. - What is God like? God understanding of Christianity and the other - Find out what other people (known to them) think - What would you b) in their experience when a principal religions represented in Great Suggested about God – use discretion! like to ask God? prayer has been said Britain and their associated beliefs, Resources - Introduce children to some Christian beliefs and - Does everyone c) a way or ways in which experiences and practices. ideas about God (including the idea of God in Jesus) think the same something can be used to help Art depicting and the beliefs of at least one other religion and things about God? people from a particular religion Learning From Religions & Responding to God(s) throughout ideas of their God(s) (eg. God of Love, God the - What do other to pray. (AT1, level 2). Human Experience the ages. carer, God is one, God has the truth). This can be people say God Compile a list of important Artefacts used B1:2 done through stories, art, symbols, artefacts does? ingredients for an act of in different religious Responding to core questions with reference - Explore different ways in which Christians worship - How do people talk collective worship (school or worship eg Hindu to the teachings and practices of religions, God eg Christian worship in a church, other buildings to God? other occasion for children who shrine items, and to their own understanding and and places, in school - How do people withdraw) giving reasons for Muslim prayer mat, experience. - Explore ways in which members of another world worship their God? their choices. (AT2, level 3). Buddhist eight religion worship their God(s) eg Hindu shrines in the - Why is it important spoked wheel. B1:3 home (a simple model shrine can be created in the to sometimes be Skills to be taught Reflecting on their own beliefs, values, Resources used classroom) or the way in which a Muslim prayer mat quiet and still? Investigation perceptions and experiences in the light of in worship which will is used - Why might a Hindu Reflection their study of religion. allow children first - Discuss the importance of prayer to Christians and family have a Expression hand sensory members of another world religion. shrine in their Empathy B2 experiences (see - Look at artefacts which help people to pray eg. house? Interpretation Develop positive attitudes of respect towards content). prayer beads, candles, pictures, icons. - How does a Analysis other people who hold views and beliefs that Aids to prayer - Find examples in the Christian New Testament of Muslim use a are different from their own. from more than one occasions when Jesus prayed to God eg. temptation prayer mat? Attitudes to be developed religion eg. prayer in the wilderness, blessing of children, prayer to heal - Do you know the Fairness Pupils will be enabled to: beads, candles, the sick, the Last Supper, in the Garden of words of any Respect pictures, icons Gethsemane, on the cross. prayers? Self understanding Explore their own ideas about God and - Introduce the ‘Lord’s Prayer’ explaining why it is - Why is the Lord’s Enquiry begin to understand and appreciate some important for Christians. Prayer important beliefs that other people (Christians and - Introduce a few simple prayers used by Christians for Christians? members of another religion) have about (school prayer, grace, blessing) and discuss when - What do you think God(s). they would be used. about God? Begin to appreciate the many ways - Introduce a simple prayer used by members of - What puzzles you people worship and the range of artefacts another religion, eg the Jewish Shema or the Muslim about God? used to aid worship. Al-Fatihah. Begin to understand the importance of - Explore use of senses in worship:- sights, sounds, prayer to many people. smells, taste using a variety of artefacts - incense, a range of music, candles, flowers, food, art, bells - Give children periods of silence to absorb the sensory experiences being offered to them, and opportunities to talk about the questions that puzzle them and the beliefs they are sure of about God. NB. Many teachers find this unit difficult, but are pleased with the responses of pupils. In general, teaching need not be troubled by the big questions pupils ask. The best teacher replies root and ground the ‘God talk’ in particular communities (eg ‘many Christians believe God is best seen in Jesus, but Muslims find God in their holy book, the Qur’an’)