Name: ______Date: ______Class: ______Diffusion Practice Worksheet
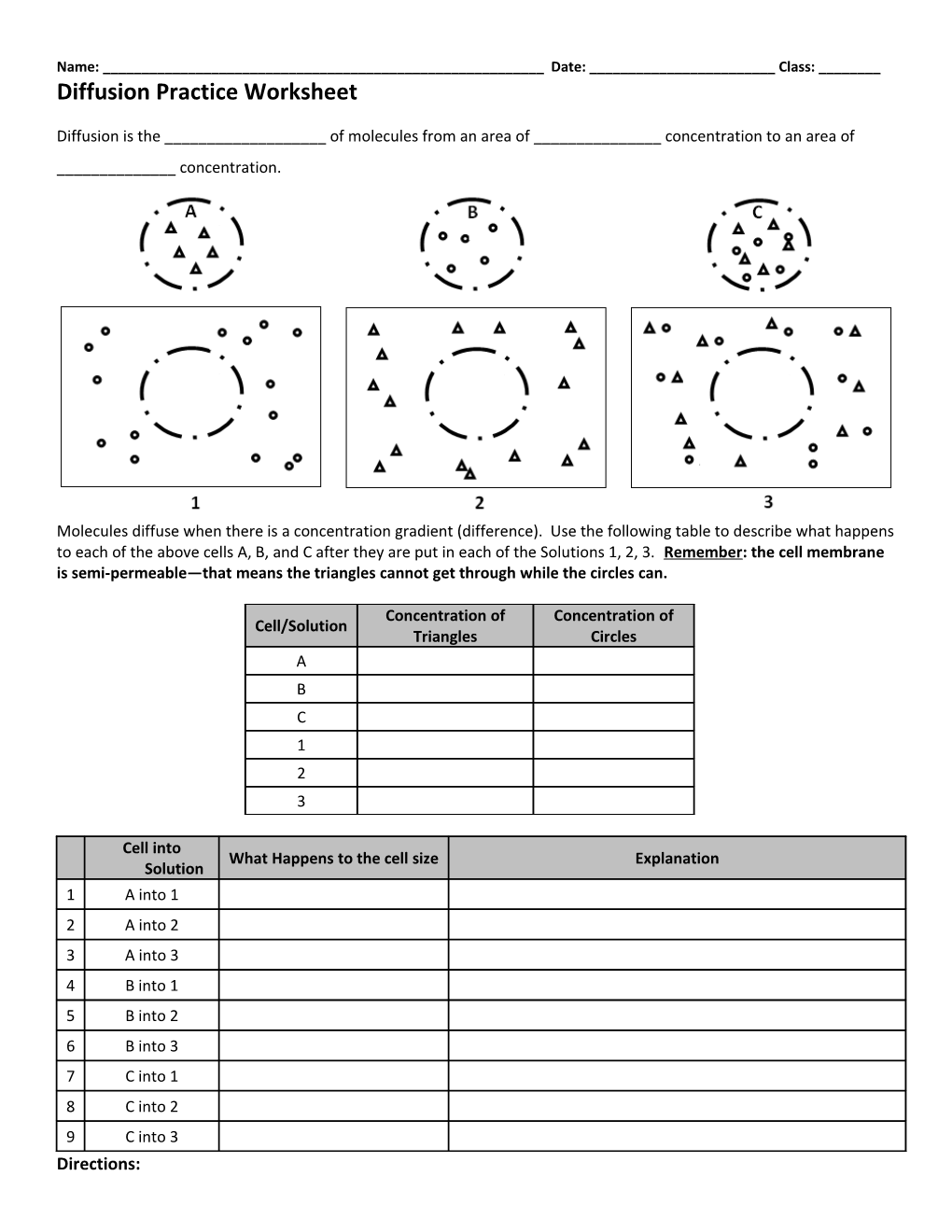
Diffusion is the ______of molecules from an area of ______concentration to an area of ______concentration.
Molecules diffuse when there is a concentration gradient (difference). Use the following table to describe what happens to each of the above cells A, B, and C after they are put in each of the Solutions 1, 2, 3. Remember: the cell membrane is semi-permeable—that means the triangles cannot get through while the circles can.
Concentration of Concentration of Cell/Solution Triangles Circles A B C 1 2 3
Cell into What Happens to the cell size Explanation Solution 1 A into 1 2 A into 2 3 A into 3 4 B into 1 5 B into 2 6 B into 3 7 C into 1 8 C into 2 9 C into 3 Directions: Name: ______Date: ______Class: ______1. Cut and paste the cells pictured in section A into each of the solutions in section B. 2. Draw an arrow using a color pencil to show the direction in which molecules will diffuse across the membrane. 3. Cut and paste your final copy into your journal under the title “Diffusion of Molecules.” Section A
Section B Name: ______Date: ______Class: ______Cell Membrane Movement Worksheet
Directions: Complete the table comparing the types of movement across a membrane. Facilitated Passive Transport Diffusion Osmosis Active Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Diffusion
Uses energy?
Y or N
Types of Molecules
Movement through phospholipid bilayer? Y or N Uses transport proteins?
Y or N
Direction:
In, Out, Both
Concentration Gradient?
Down or Against
Words to help you remember Name: ______Date: ______Class: ______Diffusion Practice Worksheet Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Molecules diffuse when there is a concentration gradient (difference). Use the following table to describe what happens to each of the above cells A, B, and C after they are put in each of the Solutions 1, 2, 3. Remember: the cell membrane is semi-permeable—that means the triangles cannot get through while the circles can.
Concentration of Concentration of Cell/Solution Triangles Circles A 5 0 B 0 5 C 5 5 1 0 15 2 16 0 3 10 10
Cell into Sol What Happens to Explanation utio the cell size n 1 A into 1 Cell gets bigger Circles diffuse into cell because its concentration is higher outside the cell. 2 A into 2 Cell is unchanged Triangles cannot pass across the membrane. 3 A into 3 Cell gets bigger Circles diffuse into cell because its concentration is higher outside the cell. 4 B into 1 Cell gets bigger Circles diffuse into cell because its concentration is higher outside the cell. 5 B into 2 Cell gets smaller Circles diffuse out of cell because its concentration is lower outside the cell. 6 B into 3 Cell gets bigger Circles diffuse into cell because its concentration is higher outside the cell. 7 C into 1 Cell gets bigger Circles diffuse into cell because its concentration is higher outside the cell. 8 C into 2 Cell gets smaller Circles diffuse out of cell because its concentration is lower outside the cell. 9 C into 3 Cell gets bigger Circles diffuse into cell because its concentration is higher outside the cell. Name: ______Date: ______Class: ______Directions: 4. Cut and paste the cells pictured in section A into each of the solutions in section B. 5. Draw an arrow using a color pencil to show the direction in which molecules will diffuse across the membrane. 6. Cut and paste your final copy into your journal under the title “Diffusion of Molecules.” Name: ______Date: ______Class: ______Cell Membrane Movement Worksheet
Directions: Complete the table comparing the types of movement across a membrane. Facilitated Passive Transport Diffusion Osmosis Active Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Diffusion
Uses energy? N N Y and N N Y Y Y Y or N
LARGER Types of SMALL, MOLECULES LARGER, CAN BE WASTE MOLECULES WATER FOOD Molecules UNCHARGED NEEDING HELP CHARGED PRODUCTS OF CELL GETTING ACROSS Movement through phospholipid Y Y Y Y N N N bilayer? Y or N Uses transport proteins? N Y N N N Y or N
Direction: BOTH BOTH BOTH BOTH BOTH IN OUT In, Out, Both
Concentration Gradient? DOWN DOWN DOWN DOWN AGAINST AGAINST AGAINST
Down or Against
When you are Words to help Action needs passive no energy Molecules move Proteins help Water moves Endo- means “in” Exo – means “out” energy you remember is required