Set Priorities Plan Strategically Expand Progress
8th Grade ESSENTIALS
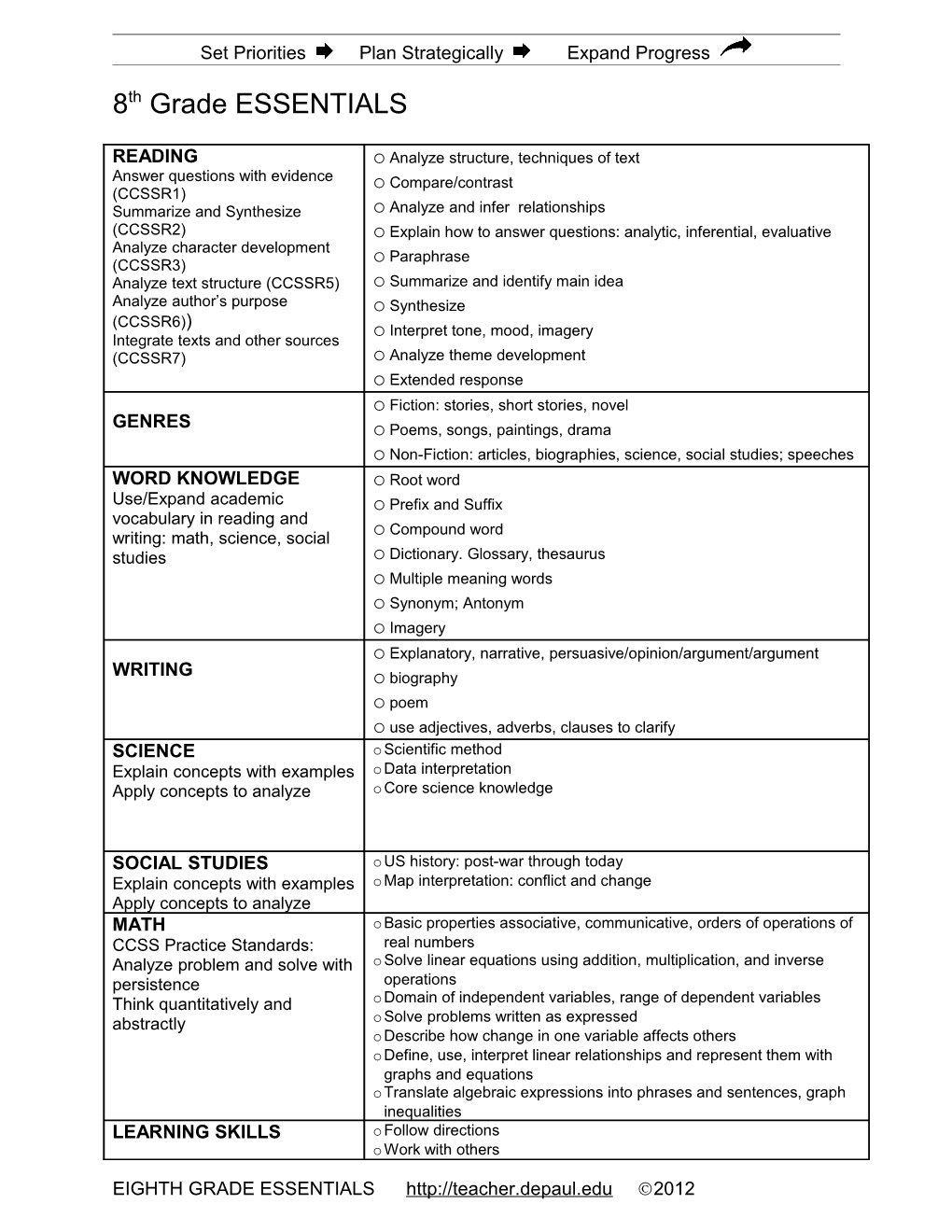
READING o Analyze structure, techniques of text Answer questions with evidence o Compare/contrast (CCSSR1) Summarize and Synthesize o Analyze and infer relationships (CCSSR2) o Explain how to answer questions: analytic, inferential, evaluative Analyze character development Paraphrase (CCSSR3) o Analyze text structure (CCSSR5) o Summarize and identify main idea Analyze author’s purpose o Synthesize (CCSSR6)) Interpret tone, mood, imagery Integrate texts and other sources o (CCSSR7) o Analyze theme development o Extended response o Fiction: stories, short stories, novel GENRES o Poems, songs, paintings, drama o Non-Fiction: articles, biographies, science, social studies; speeches WORD KNOWLEDGE o Root word Use/Expand academic o Prefix and Suffix vocabulary in reading and Compound word writing: math, science, social o studies o Dictionary. Glossary, thesaurus o Multiple meaning words o Synonym; Antonym o Imagery o Explanatory, narrative, persuasive/opinion/argument/argument WRITING o biography o poem o use adjectives, adverbs, clauses to clarify SCIENCE oScientific method Explain concepts with examples oData interpretation Apply concepts to analyze oCore science knowledge
SOCIAL STUDIES oUS history: post-war through today Explain concepts with examples oMap interpretation: conflict and change Apply concepts to analyze MATH oBasic properties associative, communicative, orders of operations of CCSS Practice Standards: real numbers Analyze problem and solve with oSolve linear equations using addition, multiplication, and inverse persistence operations Think quantitatively and oDomain of independent variables, range of dependent variables abstractly oSolve problems written as expressed oDescribe how change in one variable affects others oDefine, use, interpret linear relationships and represent them with graphs and equations oTranslate algebraic expressions into phrases and sentences, graph inequalities LEARNING SKILLS oFollow directions oWork with others
EIGHTH GRADE ESSENTIALS http://teacher.depaul.edu 2012 Set Priorities Plan Strategically Expand Progress
oLearning reports oUse graphic organizers oMake exhibits and presentations oTake notes; summarize notes
EIGHTH GRADE ESSENTIALS http://teacher.depaul.edu 2012 2 Set Priorities Plan Strategically Expand Progress CPS Mathematics Targets—EIGHTH GRADE
By the end of Grade 8, students will:
Number Sense Model, recognize, and translate among equivalent representations of numbers in meaningful contexts Represent, order, and compare rational and irrational numbers in meaningful contexts Apply rules and properties of arithmetic and perform operations with real numbers in problem-solving situations using estimation to approximate results Solve problems using proportional reasoning and relationships in problem-solving situations
Measurement Use Measurement units and Measurement tools in problem-solving situations and determine accuracy of results Solve problems involving measurable attributes
Algebra Identify a relationship, and make generalizations from linear or non-linear sequences in meaningful contexts Represent, simplify, and solve mathematical relationships and situations using expressions, equations, and inequalities Identify, interpret, represent, and solve functions in a coordinate system
Geometry Visualize, describe, and solve problems involving the characteristics, properties, and relationships between geometric figures Identify, represent, describe, and predict results of transformations of objects in a plane and on a coordinate system
Data Analysis and Probability Create, compare, and explain data displayed in a variety of representations Describe and use the measures of central tendency and spread in problem-solving situations Solve problems, make predictions, and use probability in problem-solving situations
EIGHTH GRADE ESSENTIALS http://teacher.depaul.edu 2012 3 Set Priorities Plan Strategically Expand Progress ISAT PRIORITIES: REPRESENTATIVE MATH CONTENT 8th GRADE
This chart lists terms from the Illinois Learning Standards and the ISAT sample. See the Common Core standards for national priorities.
Operations/Problem Fractions, Decimals, ALGEBRA Solving Percentages balance equation calculate determine convert denominator equivalent exponent divisible estimate fraction greater than > expression inequality factors formula improper less than < integer negative greatest inequality fraction positive represent common mixed number numerator table of values unknown factor ratio simplest form value variable absolute ascending simplify decimal additive additive value order decimal point equivalent identity inverse square root number line equivalent fraction bar property property operation sign per percent arithmetic associative sequence property probability proportion ordered value combination compound pairs inequality order of square function linear equation operations number multiplicative multiplicative descending value identity inverse order property property cube root multiplicative permutation property of zero prime rational factorization number scientific notation Analyzing Graphs Geometry Measurement and Data average circumference complementary exactly gram angles coordinate height kilometer conversion cube data gallon measure cylinder hypotenuse data point kilogram mile isosceles line segment histogram mass ounce trapezoid intersect, intersecting lines perimeter scale parallelogram perimeter pattern non-standard liter rectangular rectangular pie graph unit prism pyramid stem and leaf plot miles per hour degrees, regular right cylinder line plot Celsius, pyramid median Fahrenheit scale square prism range Measurement milliliter mode surface area three- system probability dimensional slope trapezoid triangular x axis prism y axis two- vertex scatter plot dimensional intercept vertices
EIGHTH GRADE ESSENTIALS http://teacher.depaul.edu 2012 4 Set Priorities Plan Strategically Expand Progress CPS Science Targets—EIGHTH GRADE
By the end of Grade 8, students will:
Scientific Inquiry and Technological Design Formulate hypotheses to explain observations, referencing prior knowledge and research Make testable predictions and re-evaluate hypotheses when data determine that previous ideas were incorrect Design and conduct experiments that address proposed hypotheses, controlling all but one variable and conducting multiple trials Collect both qualitative and quantitative data using metric units of measurement Represent results through the use of multiple charts and graphs Explain the existence of unexpected results in a data set and form hypotheses to explain these results Evaluate proposed hypotheses based on evidence from experiment Report the investigation using appropriate graphical displays, and defend the process used in the investigation
Matter and Energy Analyze the chemical and physical characteristics of matter, and classify materials based on these properties Explain the organization of the periodic table of elements Use quantitative data from investigations and simple chemical formulas and equations to understand the conservation of mass Understand interactions between energy and matter Identify and explain the changes of state of materials Explain energy transfer and transformations
Force and Motion Analyze how forces affect motion Explain the effect of speed and direction on motion along straight, circular, and inclined paths Explain the laws of force, mass, and inertia
Earth and Its Resources Describe Earth’s energy resources, and compare and contrast renewable and non- renewable resources
Practices of Science Demonstrate appropriate principles of safety within and beyond the classroom Evaluate sources and evidence for validity and reliability Make inferences based on data Apply scientific procedures to investigations Analyze and evaluate scientific studies and information Create a scientific investigation based upon a learned concept
Science, Technology, and Society Explain how advances in technology affect the sciences on multiple levels and explain the costs and benefits of such technological advances Describe ways to conserve and manage resources
EIGHTH GRADE ESSENTIALS http://teacher.depaul.edu 2012 5 Set Priorities Plan Strategically Expand Progress Core Reading Standards for Eighth Grade READING LITERATURE READING INFORMATIONAL TEXT/NONFICTION KEY IDEAS AND DETAILS KEY IDEAS AND DETAILS 1. Cite the textual evidence that most strongly 1. Cite the textual evidence that most strongly supports an analysis of what the text says supports an analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as inferences drawn from text. explicitly as well as inferences drawn from the text. 2. Determine a theme or central idea of a text 2. Determine a central idea of a text and analyze its and analyze its development over the course development over the course of the text, including of the text, including its relationship to the its relationship to supporting ideas; provide an characters, setting, and plot; provide an objective summary of the text. objective summary of the text. 3. Analyze how particular lines of dialogue or 3. Analyze how a text makes connections among incidents in a story or drama propel the action, and distinctions between individuals, ideas, or reveal aspects of a character, or provoke a events (e.g., through comparisons, analogies, or decision. categories). CRAFT AND STRUCTURE CRAFT AND STRUCTURE 4. Determine the meaning of words and 4. Determine the meaning of words and phrases as phrases as they are used in a text, including they are used in a text, including figurative, figurative and connotative meanings; analyze connotative, and technical meanings; analyze the the impact of specific word choices on meaning impact of specific word choices on meaning and and tone, including analogies or allusions to tone, including analogies or allusions to other other texts. texts. 5. Compare and contrast the structure of two or 5. Analyze in detail the structure of a specific more texts and analyze how the differing paragraph in a text, including the role of particular structure of each text contributes to its sentences in developing and refining a key meaning and style. concept. 6. Analyze how differences in the points of view 6. Determine an author’s point of view or purpose of the characters and the audience or reader in a text and analyze how the author (e.g., created through the use of dramatic irony) acknowledges and responds to conflicting create such effects as suspense or humor. evidence or viewpoints. INTEGRATION OF KNOWLEDGE AND IDEAS INTEGRATION OF KNOWLEDGE AND IDEAS 7. Analyze the extent to which a filmed or live 7. Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of production of a story or drama stays faithful to using different mediums (e.g., print or digital text, or departs from the text or script, evaluating the video, multimedia) to present a particular topic or choices made by the director or actors. idea. 8. (Not applicable to literature) 8. Delineate and evaluate the argument and specific claims in a text, assessing whether the reasoning is sound and the evidence is relevant and sufficient; recognize when irrelevant evidence is introduced. 9. Analyze how a modern work of fiction draws on 9. Analyze a case in which two or more texts provide themes, patterns of events, or character types conflicting information on the same topic and from myths, traditional stories, or religious identify where the texts disagree on matters of fact works such as the Bible, including describing or interpretation. how the material is rendered new. RANGE AND LEVEL OF TEXT COMPLEXITY RANGE AND LEVEL OF TEXT COMPLEXITY 10. By the end of the year, read and comprehend 10. By the end of the year, read and comprehend literature, including stories, dramas, and literary nonfiction at the high end of the grades 6– poems, at the high end of grades 6–8 text 8 text complexity band independently and complexity band independently and proficiently. proficiently.
EIGHTH GRADE ESSENTIALS http://teacher.depaul.edu 2012 6 Set Priorities Plan Strategically Expand Progress CPS Reading Targets—EIGHTH GRADE By the end of Grade 8, students will:
Comprehension Infer meaning to determine main idea and/or themes of a text and analyze theme development by citing textual evidence Analyze how an author introduces, illustrates, and elaborates two or more significant ideas in a text, including how the relationship between the ideas is expressed Explain the comparisons an author makes through metaphors, allusions, and analogies in a text and analyze how those comparisons contribute to meaning Analyze how an author or narrator uses description, dialogue, and action to suggest relationships between characters in print, or non-print sources (e.g., films, advertisements) Recognize contradictions and inconsistencies in text Examine specific language in text and propose plausible interpretations based in part on the reader’s own viewpoints and experiences Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of using different mediums (e.g., text, video, multimedia) to present a particular topic or idea
Literary Analyze how elements of a story or drama interact (e.g., how plot and setting are important to one another; how the setting affects characters) Explain how the differences in the perspective or knowledge of characters and the audience produces suspense or humor (e.g., created through the literary devices of irony, symbolism, flashback, and foreshadowing) Compare a fictional portrayal of a time, place, or character to historical sources from the same period as a means of understanding how authors use or alter history Critique an author’s use of elements of poetic style (e.g., repetition, omission, line organization/patterns and dialogue) Describe and discuss the effect of the author’s use of exaggeration, flashback, foreshadowing, diction, word choice (e.g. the choice to omit words that leave the reader with much to infer), tone, mood, exposition, action, or dialogue on the reader’s understanding of grade-appropriate text Informational Analyze the effectiveness of text organization (e.g., sequence, including chronology and enumeration; description; cause and effect; compare and contrast; problem and solution) in grade-appropriate text Evaluate, explain, and discuss how the different components of a presentation of an argument (e.g., issue definition, issue choice, stance, and relevance) affect the quality of the position Analyze how two or more authors writing about the same topic shape their presentations of key information by emphasizing different evidence or advancing different interpretations of facts Fluency Read and comprehend informational and narrative grade-appropriate texts fluently and accurately Recognize errors during reading that interfere with the meaning, use self-correcting strategies, and adjust reading rate Vocabulary Determine word meanings using structural analysis (e.g., roots, affixes, etc.) or context, whether stated directly or inferred, through use of definition, restatement, example, and compare and contrast Use grade-appropriate academic vocabulary (e.g., science, math, social science, technology) and English language arts-specific words and phrases (e.g., poetry, literature) taught directly and gained through reading and responding to text Speaking and Listening Initiate and engage actively in group discussion on Grade 8 topics and texts by: o Building on others’ ideas by asking relevant questions and contributing appropriate and essential information o Cooperating with classmates to set clear goals, deadlines, and establish roles o Explaining own ideas, thoughts, and understanding clearly and in a sequential order Prepare for discussions by reading and researching materials and explicitly drawing on that preparation in discussion Present claims and findings, using visual materials when appropriate Present information using appropriate eye contact, adequate volume, and clear pronunciation for appropriate audience, context, and task
EIGHTH GRADE ESSENTIALS http://teacher.depaul.edu 2012 7 Set Priorities Plan Strategically Expand Progress Core Writing Standards for Eighth Grade TEXT TYPES AND PURPOSES 1. Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence. Introduce claim(s), acknowledge and distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and organize the reasons and evidence logically. Support claim(s) with logical reasoning and relevant evidence, using accurate, credible sources and demonstrating an understanding of the topic or text Use words, phrases, and clauses to create cohesion and clarify the relationships among claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence. Establish and maintain a formal style. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the argument presented. 2. Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant content. Introduce a topic clearly, previewing what is to follow; organize ideas, concepts, and information into broader categories; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., charts, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. Develop the topic with relevant, well-chosen facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples. Use appropriate and varied transitions to create cohesion and clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts. Use precise language and domain-specific vocabulary to inform about or explain the topic. Establish and maintain a formal style. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented. 3. Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, relevant descriptive details, and well-structured event sequences. Engage and orient the reader by establishing a context and point of view and introducing a narrator and/or characters; organize an event sequence that unfolds naturally and logically. Use narrative techniques, such as dialogue, pacing, description, and reflection, to develop experiences, events, and/or characters. Use a variety of transition words, phrases, and clauses to convey sequence, signal shifts from one time frame or setting to another, and show the relationships among experiences and events. Use precise words and phrases, relevant descriptive details, and sensory language to capture the action and convey experiences and events. Provide a conclusion that follows from and reflects on the narrated experiences or events. PRODUCTION AND DISTRIBUTION OF WRITING 4. Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. (Grade-specific expectations for writing types are defined in standards 1–3 above.) 5. With some guidance and support from peers and adults, develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on how well purpose and audience have been addressed. 6. Use technology, including the Internet, to produce and publish writing and present the relationships between information and ideas efficiently as well as to interact and collaborate with others. RESEARCH TO BUILD AND PRESENT KNOWLEDGE 7. Conduct short research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question), drawing on several sources and generating additional related, focused questions that allow for multiple avenues of exploration. 8. Gather relevant information from multiple print and digital sources, using search terms effectively; assess the credibility and accuracy of each source; and quote or paraphrase the data and conclusions of others while avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation. 9. Draw evidence from literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. Apply grade 8 Reading standards to literature (e.g., “Analyze how a modern work of fiction draws on themes, patterns of events, or character types from myths, traditional stories, or religious works such as the Bible, including describing how the material is rendered new”). Apply grade 8 Reading standards to literary nonfiction (e.g., “Delineate and evaluate the argument and specific claims in a text, assessing whether the reasoning is sound and the evidence is relevant and sufficient; recognize when irrelevant evidence is introduced”). RANGE OF WRITING 10. Write routinely over extended time frames (time for research, reflection, and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two).
EIGHTH GRADE ESSENTIALS http://teacher.depaul.edu 2012 8 Set Priorities Plan Strategically Expand Progress CPS Writing Targets—EIGHTH GRADE
By the end of Grade 8, students will:
Process Engage in the writing process (e.g., prewriting, drafting, revision, editing, and publishing) to develop the habits of writers Use the writing process for a variety of purposes (e.g., narrative, expository and persuasive) and audiences Read and discuss the work of published authors to study what they do as writers and imitate what they noticed in an effort to strengthen their own writing Revise and edit for organization, coherence, and quality after reviewing their work through discussion and conferences, with classmates and teachers Use available resources to design, produce, and present compositions and multimedia works
Inquiry and Research Generate questions of interest around issues gained from experiences (e.g., field trips, news, discussions, text, and/or digital media) as sources of information Gather relevant information from multiple sources and assess the credibility and accuracy of sources Write explanatory texts on chosen topics utilizing relevant facts Quote, paraphrase, and cite the source of their research Use text, graphic materials, or visual aids to present information (e.g., charts, written reports, maps, artifacts, student-created games, multimedia) Present information in appropriate format that was gathered by either inquiry or research (e.g., interviews, surveys, software, presentations)
Communication through Writing Value writing as a way of expressing themselves (e.g., short story, poetry, play, song, parody, letters) Write for a variety of purposes, audiences, and time constraints Use appropriate language, detail, and format for a specified audience Use the characteristics of a well-developed narrative, expository, and persuasive piece Compose a multi-paragraph piece that presents one position of an issue with sufficient support
Organization, Coherence, and Quality Elaborate ideas through: facts and evidence, details, description, reasons, and narration Organize a coherent structure appropriate to audience and context using paragraphs while writing narrative, expository, and persuasive pieces Draft an effective introduction that provides a context for discussion Compose topic sentences while establishing and maintaining focus throughout a paragraph or writing piece Draft a conclusion that emphasizes main theme and synthesizes key points Use transition words to connect ideas within and across paragraphs Develop multi-paragraph compositions that include introduction, first- and second-level support, and a conclusion
Conventions Edit own work for grammar, punctuation, conventional spelling, and revise accordingly Demonstrate appropriate use of various parts of speech Explore and use more sophisticated sentence constructions and improve awkward or confusing structures Write paragraphs that include a variety of sentence types (e.g., declarative, interrogative, exclamatory, imperative)
EIGHTH GRADE ESSENTIALS http://teacher.depaul.edu 2012 9