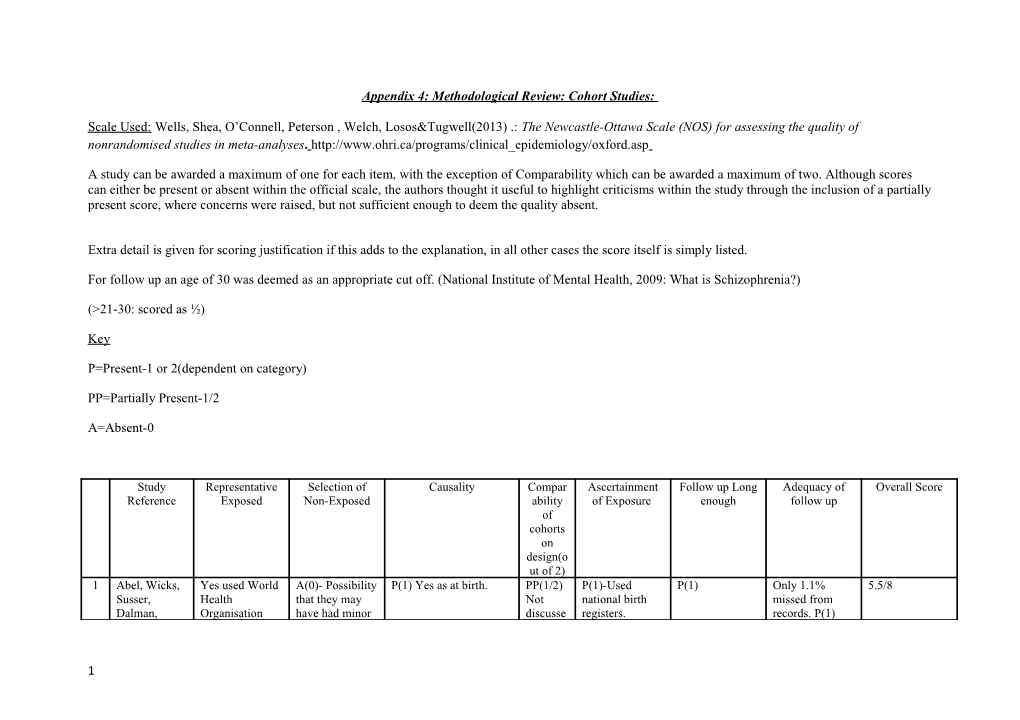
Appendix 4: Methodological Review: Cohort Studies:
Scale Used: Wells, Shea, O’Connell, Peterson , Welch, Losos&Tugwell(2013) .: The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp
A study can be awarded a maximum of one for each item, with the exception of Comparability which can be awarded a maximum of two. Although scores can either be present or absent within the official scale, the authors thought it useful to highlight criticisms within the study through the inclusion of a partially present score, where concerns were raised, but not sufficient enough to deem the quality absent.
Extra detail is given for scoring justification if this adds to the explanation, in all other cases the score itself is simply listed.
For follow up an age of 30 was deemed as an appropriate cut off. (National Institute of Mental Health, 2009: What is Schizophrenia?)
(>21-30: scored as ½)
Key
P=Present-1 or 2(dependent on category)
PP=Partially Present-1/2
A=Absent-0
Study Representative Selection of Causality Compar Ascertainment Follow up Long Adequacy of Overall Score Reference Exposed Non-Exposed ability of Exposure enough follow up of cohorts on design(o ut of 2) 1 Abel, Wicks, Yes used World A(0)- Possibility P(1) Yes as at birth. PP(1/2) P(1)-Used P(1) Only 1.1% 5.5/8 Susser, Health that they may Not national birth missed from Dalman, Organisation have had minor discusse registers. records. P(1)
1 Pedersen, Guidelines P(1) Psychiatric d Mortensen& disorders. complet Webb (2010) ely but study did control for appropri ate confoun ders 2 Allebeck, P(1) P(1)Control PP(1/2) Do not know A(0) P(1) Used P(1)- 10 year PP(1/2) Missing 5/8 Adamsson , Representative selection not that pre-morbid phase Not cannabis follow up data=10% Engstrom, of Stockholm explicitly did not come before discusse dependence as a Rydberg County discussed but cannabis use. However d. Other diagnosis for (1993) only.Only a few drawn from did look at temporal drug use ascertainment. % of cases same records of whether present missed. community. cannabis or psychosis discusse Those who used reported first. d but not cannabis but controlle didn’t develop d for. schizophrenia were in effect the control group. 3 Andreasson, P(1) But males P(1) Same as A(0) Causality difficult- P(2)To A(0) From 2 P(1) P(1)Follow up 6/8 Engstrom, only (eligible for cases Of 730 high consumers control anonymous through medical Allebeck, conscription.) of cannabis in this study, for questionnaires. records Rydebeck(198 430 had potential 7% refused to 7) a psychiatric diagnosis confoun answer other than psychosis at ders, 11 questions on conscription, variable drugs so were mainly neurosis and s were excluded. personality disorder. selected, reflectin g social and psychol
2 ogical characte ristics. The effect on the end- point admissio n with a diagnosi s of schizoph renia- was first evaluate d by stratifica tion of each backgro und variable separatel y. 4 Andreasson, A(0) Subsample P(1) There was PP(1/2) Cannabis abuse P(2)Neg P(1)The medical P(1) P(1) All 6.5/8 Allebeck of national no major present at conscription, ative records were followed up &Rydebeck(1 cohort. Only 8 difference before a diagnosis. social scrutinized - 989) cases. between However, again do not backgro with the users and know if due to und researcher blind nonusers in premorbid phase. Other factors to the level of heredity for drug abuse was present were cannabis schizophrenia or before. more abuse at other mental common conscription - disorder. among focusing on: cannabis evidence of abusers. cannabis abuse Analyse in case records
3 d through medical records, which confoun ders present. 5 Andréasson,& P(1) Yes but P(1) P(1) Alcohol abuse at P(2) The A(0)2 P(1) 15 year Not discussed 6/8 Allebeck, only male’s as conscription. Controlled conscrip questionnaires follow up. A(0) (1991). conscripts(about for other Psychiatric ts were and Psychiatric 5% missing) morbidity at stratified interview. conscription both Similar to self accordin report g to presence or absence of depressi on at conscrip tion and level of alcohol consum ption. 6 Cederlof, P(1) P(1) A(0) Not discussed P(2) P(1) ICD P(1)Comparativ NA P(1) 7/8 Bergen, individu Diagnosis. e to relatives in Langstrom, als another cohort. Larsson , matched Not a follow up Boman, on birth Craddock year, , Ostberg , sex, and Lundstrom county Sjolander, of Nordlind , residenc Landen e were
4 Lichtenstein randoml (2014). y selected from the Multi- Generati on Register 7 Class, Abel, P(1) P(1) P(1) Death of relative P(1) P(1) P(1) Childhood Number who 6/8 Khashan, before and Adulthood dropped out not Rickert, Psychiatric reported A(0). Dalman, outcomes Larsson, Hultman, Långström, Lichtenstein and. D‘Onofrio(20 14) 8 Dalman and P(1)Yes but P(1)Each of the P(1) P(1) P(1) P(1) P(1)There was 8/8 Allebeck only those from subjects with information (2002) Stockholm schizophrenia about paternal was matched age in the birth with two records of 420 subjects from (80.2%) of the the parish 524 subjects register who 1) with were born schizophrenia immediately and 857 (82.2%) after the subject of the 1,043 with comparison schizophrenia, subjects. Thus, 2) were matched the distribution for sex and of dropouts was hospital of birth, even. and 3) resided in Stockholm at the time the cases
5 were selected. 9 Dalman,Alleb P(1) From same P(1) PP(1) P(1) PP(1/2) Until A(0)No 5.5/8 eck, Cullberg, register(1) Not 22. discussion Grunewald& stratified Koster(1999) . But adjusted for appropri ate confoun ders. 10 Dalman, P(1) Yes but P(1) Eighty-nine P(1) Yes as factor P(2) A(0) A(0) P(1) Up to 34 A(0)No 6/8 Thomas, Stockholm birth records occurred at birth. Indicators of years. discussion David, Gentz, County only- (7.9%) could not asphyxia were Lewis and (6.5%) birth be retrieved. obtained from Allebeck records could retrospective (2001) not be retrieved. records 11 David, P(1) Yes but P(1) P(1) A(0) No A(0) A(0)Age not A(0)No 3/8 Malmberg male conscripts mention Handedness discussed. discussion Lewis,Brandt, only. of based on self Allebeck compara report and one (1995) bility. task. Howeve r both cases and controls would have received the same tests on conscrip tion. 12 David, P(1) Yes but P(1) PP(1/2) Yes as at 18 but PP(1) PP(1/2) IQ tests P(1) Up to 34. A(0) No 5/8 ,Malmberg, male conscripts difficult that may reflect Included most reliable discussion Brandt, only. premorbid stage, at this all thing for this. Allebeck age. conscrip But
6 &Lewis ts so controversies (1997) indirectl with y yes. generalising to Also intelligence; controlle culturally bound d for etc. what previous ly found to be different in the conscrip ts. 13 Ek, P(1) P(1) P(1) P(2) P(1) P(1) A(0) Not 7/8 Wicks,Magnu discussed sson &Dalman, (2012)
14 Ek, Wicks, P(1) P(1) PP(1/2)Yes but was this P(2) P(1) P(1) Time at P(1) 91% no 7/8 Svensson, relevant? More Stratifie risk was defined missing data. Idring, and important to control for d and as time Dalman(2014) non-shared appropri from 15 years of environment? ate age until confoun diagnosis of ders. nonaffective psychotic disorder (including schizophrenia), emigration, or death. 15 Ekeus, P(1) National P(1) P(1) Yes controlled for P(2) NA/P(1) A(0) Youngest A(0) Not 6/8 Olausson Registers appropriate and age at Age was only followed to discussed &Hjern birth(so factor exists IV plus 24. May not be (2005) before) controlle long enough to d for capture all.
7 gender. Other confoun ders appropri ate. 16 Frans P(1) P(1) P(1) age at birth. P(2)For N/A P(1) A(0)Not A(0) Not 6/8 ,McGrath , each discussed discussed Sandin, subject Lichtenstein affected Reichenberg , with Langstrom schizoph and Hultman renia, (2011) The authors randoml y selected five unaffect ed control individu als matched on birth year and sex from the populati on register 17 Fouskakis, P(1) P(1) P(1)excluded all A(0) P(1) Through A(0) Subjects A(0) Not 4/8 Gunnell subjects diagnosed with Not birth records. were followed discussed Rasmussen, schizophrenia stratified up for a mean of Tynelius,,Sipo or other non-affective 7.28 years s& Harrison psychosis before (range 1 day to (2004) 16 years of age. 11.0 years) after
8 16 years of age. 18 Gunawardana, P(1) Several P(1) P(1) As pregnancy yes. P(2) PP(1/2) For pre- A(0) Did not P(1) (3.1%) 6.5/8 Davey Smith, registers linked controlle pregnancy follow up past were excluded Zammit, d for interval yes. But very early 20’s. because of Whitley, gender, assuming this missing data. Gunnell,Lewi calendar will reliably s and year, represent Rasmussen(20 parental maternal folate. 11) age, parental socioeco nomic status, place of birth, obstetric complic ations (Caesare an section or uterine atony), birthwei ght, length of gestatio n, history of psychosi s in parents or siblings, family
9 size, and birth order. First- borns were exclude d from analyses of pre- birth inter- pregnan cy interval (167 767 exclude d leaving 183 921) and last- borns from analyses of post- birth inter- pregnan cy interval (168 831 exclude d leaving
10 182 857). 19 Gunnell P(1)Conscripts P(1) P(1)Authors excluded PP(1) P(1) Medical A(0) 3.4 year A(0) 5/8 Rasmussen only from analysis 389 records follow up from A total of Fouskakis subjects with aged 18. 87,533 (26 Tynelius, schizophrenia or other percent) &Harrison(20 nonaffective psychosis subjects, of 03) diagnosed at either the whom 26 (0.030 time of or prior to their percent) conscription developed medical examination. schizophrenia and 49 (0.056 percent) developed other nonaffective psychoses, were excluded from the main analyses because data were missing for one or more of the factors investigated. 20 Gunnell, P(1) P(1) P(1)Subjects were PP(1) P(1) A(0) A(0)Not 5/8 Harrison, excluded Though discussed Whitley, if they had been through Lewis, admitted to hospital with controlli Tynelius, a diagnosis ng Rasmussen(20 of psychosis prior to 16 factors. 05) years of age or if data for variables of interest were incomplete or implausible 21 Gunnell, P(1) But P(1) P(1) Authors controlled PP(1) P(1) Testing was PP(1/2) 5 years A(0) 109 643 5.5/8 Harrison, military for this : To assess From carried out in six from 18. subjects had
11 Rasmussen, conscripts only. whether intellectual same regional complete Fouskakis&T function may have been register conscription data>from ynelius (2002) affected by early, pre- and centres. Central cohort 197 613. diagnostic disease controlle training and Doesn’t mention processes (reverse d for instruction of number of cases causality) the authors appropri the vs controls. investigated whether the ate psychologists strength of the confoun who carry out association with ders. the tests, and the intellectual function Howeve use of a standard varied in cases r more manual, help to diagnosed soon after officers ensure conscription, compared were consistency with those admitted to controls hospital several years than later For most of the cases. tests examined, associations were some- what weaker in later- onset than early-onset cases, although confidence intervals were wide. 22 Gunnell P(1) Yes but P(1) P(1) All subjects with PP(1) P(1) Foetal A(0) Mean 3.4 A(0)Those with 5/8 Rasmussen males only. psychoses at Did not based measures year follow up missing data Fouskakis conscription excluded. take into by clinician. from aged 18. tended to be of Tynelius, Additionally to assess account Diagnoses from May have lower &Harrison(20 possible selection psychoti registers. missed those birth weight 03) biases, the authors c illness who develop at (101 g lighter) ; repeated all age adjusted in the a later stage. shorter at birth analyses separately for parents (0.4 cm shorter), each variable based on of cases. were more likely those Controll to be born subjects for whom data ed for before 36 weeks were available for that age. gestation (7.69% variable. Those v. 3.97%); with were more likely Schizop to have been
12 hrenia born in the more winter likely to (December– have February: parent 26.15% v. 23 . with 54%); to lowest be male or (52.02% v. 51 . highest 32%); and to bands of have a educatio lower level of n. maternal education (<9 years, 19.70% v. 13 . 00%). Authors made no adjustments to check whether this made a difference to any emerging results from the analysis. 23 Harrison, P(1) P(1) PP(1/2)Babies P(2)Use P(1)9 categories PP(1/2)Follow P(1)Those with 7/8 Fouskakis, born in main cities and d same used for up from age 16 missing data Rasmussen, suburbs were more samplin definitions of for up to 9.8 tended to be of Tynelius, likely g urbanicity;took years. Mean of lower Sipos& to have lower birth methods into account 5.1years follow birth weight Gunnell( 2003 weight, shorter birth , industrialisation up. (101 g lighter) ; ) length, exclude of area. shorter at birth lower APGAR scores d those Diagnosis of (0.4 cm shorter), and increased risk of with a schizophrenia were more likely birth diagnosi from registers. to be born by Caesarean section. s of before 36 weeks And more cases of schizoph gestation (7.69% schizophrenia within renia on v. 3.97%); urban areas. But entry to were more likely
13 controlling for these the to have been factors did not result in study. born in the any differences. winter (December– February: 26.15% v. 23 . 54%); to be male (52.02% v. 51 . 32%); and to have a lower level of maternal education (<9 years, 19.70% v. 13 . 00%). However when the authors restricted the analysis to only those with complete data; only marginally different Hazard ratios emerged. 24 Hjern, Wicks P(1) P(1) P(1) Yes as country of PP(1) P(1) Yes by P(1) A(0) 6/8 &Dalman birth. However the Yes but various (2004) social drift hypothesis whether registers. may come into play using here. immigra tion as a proxy for another factor is unclear . For
14 example controls/ those born elsewher e were shown to be more likely to have single parent househo ld and more likely to reside in an urban area. 25 Johansson, P(1) Yes but co- P(1) P(1) Analysed using 3 P(2) For P(1) P(1)Follow up A(0) Number 7/8 Lundholm, morbidity or different time periods to each 1973 or 1987- lost in follow up Hillert, sibling cohort see which was the most sibling 2009. not discussed. Masterman, created. appropriate fit. pair Lichtenstein, exposed Landén & Authors Hultman randoml (2014) y selected 10 unexpos ed sibling pairs, matched for birth year and sex (for
15 both individu als in the pair). 26 Larsson, Ryde P(1) Used P(1) From total A(0) Measuring P(2) PP(1/2) Non PP(1/2)More A(0) Not 5/8 ´n, Marcus psychiatric population association. control standardised retrospective but discussed within Langstrom, symptom data register Schizophrenia; was not group register used for could have paper, other than Lichtenstein from 20 000 necessarily following participa diagnoses but ADHD people enter and and twins (born ADHD. Looking at a nts were used psychiatric diagnosis up to leave the Lande(2013) 1992–2001) shared genetic aetiology alive symptom data 65. inpatient register from the instead. and from 20 000 at different ages. Swedish Twin living in twins (born Register to Sweden 1992–2001) explore the and not from the validity diagnose Swedish Twin of the register- d with Register to based ADHD ADHD explore the diagnosis. at the validity time of of the register- the first based ADHD ADHD diagnosis. diagnosi s of the proband. ) For each case, we randoml y selected 10 control group member s matched by birth
16 year and gender. 27 Leao, P(1) P(1) All A(0) Authors PP(1) P(1) Selected by PP(1/2) P(1) Because of 5.5/8 Sundquist, individuals quote :”our study sheds Age, the Immigration Youngest 20 and the Frank, were followed no light on the gender Register and the then followed up unique Swedish Johansson, until first causation-selection and Register of the for 9 years. identification Johansson& hospital issue, the difference income Total However it number, the Sundquist, admission for between causation and looked Population. would have been authors stated it (2006) schizophrenia selection at. more suitable to was possible to or other should be mentioned in start from aged follow each psychoses, the context of 18. Oldest was individual death, socioeconomic also only up to during the whole emigration, or status and psychiatric 39. So could follow-up end of study disorders. The only include period. on December “causation” hypothesis early onset Data from the 31, 1999. states that adversities psychoses cases. national linked to low database were socioeconomic status highly complete cause psychiatric for all disorders, while the variables. “selection” hypothesis states that individuals with psychiatric disorders are unable to reach higher socioeconomic strata.”
28 Lewis, David, P(1) But male P(1) PP(1/2) Although non- P(2)Adj PP(1/2) P(1) 13 years A(0) From 6/8 Malmberg and conscripts Psychotic diagnosis at usted for Although ICD until 31/32.) registers only Allebeck 18 happened before other diagnosis, 70-83% (2000) diagnosis of sympto questionnaires followed up in schizophrenia the ms and regarding family full(depended causality of whether diagnosi background and on year) shared environment or s at behaviour genetic or aetiology is conscrip during still unclear. tion, adolescence personal were self- ity administered
17 variable and so s, IQ, vulnerable to drug bias. taking, family econom y, place of upbringi ng. 29 Li, Sundquist, P(1) P(1) PP(1/2) Can partially P(2) P(1) Used multi- P(1)All patients P(1) 7.5/8 Hemminki control for Gender, generation younger &Sundquist,2 environmental age, register. than 72 years 009 influences and show occupati hospitalized for genetic effects. But still onal psychotic doesn’t fully explain status, disorders or why genetic risk may be geograp schizophrenia increased in siblings. hical between 1987 Time period taken into region, and 2004 were consideration in time included. analyses. period 30 Ludvigsson, P(1) P(1) P(1) All study PP(1) P(1) ICD A(0) Not A(0) Missing 5/8 Osby, participants were free of The Diagnosis for discussed in full. data 38% for Ekbom& previous schizophrenia authors Coeliac Disease. Except those cases and 47% Montgomery( or any other psychosis at identifie less than a year controls. 2007) the d five in follow up start of follow-up. referenc time excluded. e individu als matched for age and calendar year at diagnosi s, gender
18 and county. But did not match for Socio- economi c status. 31 MacCabe , P(1) P(1) P(1) Found for all P(2) P(1) National A(0) Some A(0) Missing 6/8 Lambe , subjects. Controll School register follow up only test scores only Cnattingius, No diagnosis at 16. ed for until aged 22. 0.3%. However Torrång , migrant May not have doesn’t fully Björk , Sham , status, been long discuss whether David , low enough. Though any not followed Murray , birthwei mean follow up up. Hultman ght, until 24.5 (2008) hypoxia, parental educatio n level or socio- economi c group. 32 MacCabe, P(1) Yes but P(1) P(1) To minimize the P P(1) P(1) Follow up P(1) Amount of 8/8 Wicks, only male effect of reverse (2)Samp Standardised itself was over missing data Lofving, students (as later causality, the authors les timed tests at 13, 25 years listed as small. David, conscript data) excluded from the stratified then again at 18 Berndtsson, analysis individuals who by birth and 19. Gustafsoon, had already experienced date. Allbeck a psychotic disorder by Adjuste &Dalman the time of conscription, d for (2013) individuals who other received a diagnosis at variable conscription s, falling within the set of urbanicit ICD codes included and y, individuals parental
19 who were admitted to history the hospital with such a of diagnosis psychiat before the first ric anniversary of their disorder conscription. and parental educatio nal level. 33 Malmberg, P(1) Yes but P(1) PP(1/2) Diagnosis at PP(1) A(0) PP(1/2) 10 P(1) Data on 30 5/8 Lewis and male conscripts conscription excluded. Adjuste Questionnaire years/up to 28. of the variables Allebeck However do not know d for was self report. were available (1998) whether what capturing family Not validated by for more than was a premorbid phase history teachers, 93% of the of the disorder. of significant sample. psychiat others etc. ric illness (But self report) diagnosi s of a non- psychoti c illness at conscrip tion, IQ and city upbringi ng. Would have been helpful to addition
20 ally have adjusted for Socio Econom ic Status and stratified by age. Only male sample so gender was controlle d for here. 34 Manrique- P(1) But male P(1) PP(1/2) Alcohol and PP(1) A(0) Self report P(1) Follow up A(0) Not 4.5/8 Garcia, sample only. drug use was measured Psychiat questionnaire on until 2007 from discussed. Zammit, only at one time. Also ric cannabis and 1970. Dalman, arguments for self- diagnosi other drugs. Hemmingsson medication are not s However ,Andreasson& completely resolved by at authors argue Allebeck, the chosen methodology conscrip any limitations (2012) of the study. tion, IQ of this would However a dose score, only response relationship ‘disturbe underestimate was present. d the risk. behavio ur’, having been brought up in a city and cigarette
21 smoking are associat ed with schizoph renia. But socioeco nomic status and age not controlle d for. 35 Manrique- P(1) But male P(1) P(1) excluded those P(2) A(0) Self report P(1) One of P(1) Apart from 7/8 Garcia,. conscripts subjects who received a Controll questionnaire on longest follow subjects who Zammit, diagnosis of psychiatric ed for cannabis and ups available. emigrated (four Dalman, disorder at conscription, substanti other drugs. persons) or died Hemmingsson in order to minimize al However (82 persons), no ,Andreasson possibility of reverse number authors argued participants and causality of any limitations were lost to Allebeck(201 confoun of this would follow-up. 4) ders only proven underestimate to the risk. impact risk. 36 Nilsson, PP(1/2) Twin P(1)Unaffected A(0) Not able to P(2) P(1) P(1) P(1)Analyses 6.5/8 Stålberg, Registry but unrelated and subdivide the analysis Design were restricted Lichtenstein, only 85% related twins with Monozygotic and adjusts to pairs where Cnattingius, delivery records Dyzygotic twin pairs to for birth order was Olausson and available elucidate whether there many confirmed in Hultman(2005 are genetic or shared factors. written (Cohort and environmental factors Shared documents (i.e., Case Control that explain the familial gender, baptized and Study) mediation of the age, named at birth). association between Socioec 4 missing foetal growth restriction onomic Schizophrenia
22 and schizophrenia status records. 858 etc. missing Same controls. sex twins. 37 Nosarti, P(1) A(0) controls P(1), individuals who PP(1) P(1) PP(1/2) Only up P(1) 95% in 5.5/8 Reichenberg, would (first) developed Adjuste to 29. records Murray, have included depressive disorder and d for Cnattingius, individuals not thereafter nonaffective majority Lambe, Yin, hospitalized for psychosis of MacCabe, the psychiatric were not included in the importa Rifkin& disorders we analysis of nonaffective nt Hultman studied and psychosis. confoun (2012) those with ders but psychiatric authors disorders that did not often do not adjust require for hospitalization, measure such s of as anxiety and social mood disorders. adversit y(only educatio nal level) 38 Sariaslan, P(1) P(1) P(1) Participants who P(2) All P(1) Used P(1) The median A(0)A total of 7/8 Larsson, had died (n = statistica national follow-up time 993 820 (58%) D’Onofrio, 23 359), migrated (n = l models registers was 16.5 years. cousins and 317 Långström, 116 998), or been adjusted Authors used 535 (19%) Fazel, and diagnosed with for sex, exposure data siblings were Lichtenstein(2 schizophrenia (n = 72) birth from the end of living in 014) or depression (n = 1121) year the year the case different before (categori or control neighbourhoods the age of 16 were zed into subject turned at age 15 within excluded. 5-year 15. the study follow intervals up. Difficult to ), and measure if
23 birth substantial order number in (categori different zed as neighbourhoods. first, second, third, and fourth or more). When looking at neighbo urhood factors this is likely to be enough. 39 Sipos, P(1) P(1) P(1) Excluded cases if P(2) P(1) PP(1/2) Subjects P(1) Overall, 42 7.5/8 Rasmussen, developed schizophrenia Controll were followed 316 (5.6%) Harrison, (68 cases) or other non- ed for up for a mean of people were Tynelius, affective relevant nine years after excluded from Lewis, Leon, psychosis (141 cases) number the age the main Gunnell(2004 before the age of 16 demogra of 16 years. analysis because ) years. phics. of missing data for one or more of the variables examined 40 Song, Bergen, P(1) P(1) A(0) Co-occurrence not P(2) As P(1) P(1) Follow up A(0) Not 6/8 Kuja-Halkola, as an aetiological factor family from 1973 to discussed. Larsson, measured. study 2009. Landen , could Lichtenstein control (2014) by looking
24 at estimate s heritabil ity, shared and non shared environ ment. Addition ally to increase compara bility, only selected the eldest siblings born within five years of each other. 41 Stålberg PP(1/2) Largely P(1) Hospitals A(0) Was not clear P(2) P(1) Divided P(1/2) Yes PP(1/2) Large 5.5/8 Haglund from Malmo that didn’t use within the study. The Controll into exposed or however amount of Axelsson Hospital records ultrasound authors quote” It seems ed for not exposed. If Maximum age sample couldn’t Cnattingius only. that factors related to sig mothers of follow up was be included : Of Hultman, place of birth, rather number were registered 31. 593,917 and than ultrasound of as residents of singleton live Kieler(2007) exposure, may have variable Malmo¨, in births in Sweden influenced the results for s which case they between both men and women.” includin were excluded 1973 and 1978, g from the study. we could maternal include 370,945 influenc individuals
25 es, age (62.5%) with of reliable follow exposure up and information, of hospital whom . 190,405 were men and 180,540 were women(but equal genders). 42 Sundquist, Li, P(1) P(1) A(0) Not discussed PP(1) P(1) P(1) The follow- A(0) Not 5/8 Hemminki,& Stratifie up varied discussed) Sundquist, d by considerably (2008) male was categorized and as less than 1, 1 female to 4, 5 to 9, and but 10 or more years otherwis and e only subsequently controlle controlled for d for within the geograp analyses. hic region and age at follow up. 43 Svensson, P(1) P(1) .Relatives P(1)Other variables P(2)Mat P(1) Used P(1) Looked at A(0) Not 7/8 Lichtenstetin, so multi- were from ched on registers. age of onset into discussed Sandin generation birth)Matched relative age, those a lot later: O¨Berg, register had no diagnosis. birth e.g. over 40. Sullivan & cohort Hultman and (2012)(Also gender. case control To design) ensure equal
26 follow- up time for schizoph renia, authors addition ally required that the proband was matched to individu als who were alive and had not been admitted to psychiat ric care for. schizoph renia in Sweden at the date the proband was first hospitali zed. 44 Svensson P(1) Yes but 18 P(1) P(1/2) All factors A(0) P(1) P(1) Follows A(0) Not 4.5/8 ,Rogvin, to 45 only. present at time of birth Factors population for discussed. Hultman, but difficult to conclude controlle 30 years.
27 Reichborn from design whether d for not Kjennerud,Sa other moderators are discusse ndin, influencing the results in d (could Moger(2013) some cases e.g. with argue urbanicity is this a however proxy? co- variates within design would be confoun ders in another design e.g. gender) 45 Van der Ven. P(1) But P(1) P(1) P(1) PP(1/2) Mainly P(1) Tested both P(1) 4.1% lost in 6.5/8 Dalman,. military Matched from official narrow and follow up due to Wicks, conscripts on records but broad definition death Allebeck, appropri some self report. of IV: “Since Magnusson, ate some men van Os, confoun develop Non and ders but affective Selten(2014) not by psychotic age. disorder at a later age, we also included a broad definition referring to all individuals who lived abroad for at least 2 years during the period between conscription and
28 the age of 40 years. “ 46 Westman, PP(1/2) 25-64 P(1) A(0) Before study P(2) P(1) Registers A(0) Only one P(1) 5.5/8 Johansson, years old. period not discussed. Age and official year follow up Sundquist(200 adjusted records.. 6) rates, adjusted for income and marital status stratified by gender and country of birth. 47 Wicks, Hjern P(1)Adoptees P(1) Non A(0) Before study PP(1) P(1) Registers P(1) Youngest A(0) Not 5/8 and Dalman from register adoptees period not discussed. Confoun and official follow up would discussed. (2010) ders not records.. have been 36. discusse Majority ok. d but design largely controlle d for this. Age and gender taken into consider ation 48 Wicks, Hjern, P(1) P(1) PP(1/2) Dose response P(1 ) P(1) PP(1/2) P(1) Children 6/8 Gunnell,Lewi relationship but it is Signific Youngest follow without s and Dalman likely that there is a ant up 29 not identifiable (2005) strong correlation factors necessarily parents and
29 between exposure for enough. foreign adopted in early childhood and schizoph children were exposure in utero so renia excluded don’t know routes to taken because of such a path. into missing data for consider biological ation but parents. didn’t adjust for maternal complic ations. Age and gender addition ally taken into consider ation by design. 49 Zammit, P(1) Conscripts P(1) P(1/2)Dose response P(2) P(1/2) Some P(1) P(1) Data on 7/8 Allebeck, relationship found but Importa self-report drug use etc Andreasson, self medication nt measures only missing in Lundberg& hypothesis. confoun a small number Lewis(2002) ders of cases. consider ed. Stratifie d by time of diagnosi s 50 Zammit, P(1) Conscripts P(1) P(1) Those with P(1) P(1) Parental P(1)Up to 45 for P(1/2) As with 6.5/8 Allebeck, , psychosis excluded at Importa age at birth of male population registers Dalman, conscription. nt subjects this is largely :authors state Lundberg, confoun was obtained enough for EOP. over 83% follow
30 Hemmingson, ders from the up at least. They Owen shown Statistics of argue that this is &Lewis(2003 to be Sweden enough. ) associat Registers, blind Data missing on ed to to diagnosis. paternal age not schizoph sig. renia consider ed. Only men. Howeve r did not take age develop ed Schizop hrenia into account. 51 Zammit, P(1) Conscripts P(1) P(1) Those with P(2) P(1/2) Some self P(1)Up to 45 for A(0)83-95% 6.5/8 Allebeck,Davi psychosis excluded at Took report measures. male population coverage. d; Dalman, conscription age at Authors argue Hemmingsson first significant. IQ ,Lundberg&L admissio test scores ewis, (2004) n into missing not account. discussed. Gender covered for by design. Importa nt confoun ders consider ed. 52 Zammit, P(1) Conscripts P(1) P(1) Those with PP(1) P(1/2) Some self P(1) 27 year A(0) Not 5.5/8 Lewis, psychosis excluded at Did not report measures. follow up discussed
31 Dalman and conscription discuss period. Allebeck(201 confoun 0) ders but design itself largely controls for this. 53 Zammit,Lewis P(1) P(1) P(1) Those with P(2)Too P(1) National A(0) Not A(0)Of those 6/8 , Rasbash . psychosis excluded at k birth registers discussed never having Dalman, conscription year into been admitted Gustafsson&. account. with a psychotic Allebeck . Design illness (2010) itself before the end took of follow-up, into 1414 individuals account, had emigrated, individu while 1156 had al(e.g. died. Of the sex) and remaining neighbo sample, 6996 urhood had missing data level on school variable attended or s.. municipality lived in at age 16 years and were also excluded, leaving a sample of 203 829 individuals. Missing data for any of the exposure variables or covariates
32 ranged from 0 to 21 299, and in total 40 908 had missing data for at least 1 of the variables included in the final model (final model n=169 910). 54 Zammit, P(1)Male P(1) P(1) As it was possible P(2) P(1) A(0) Last P(1) Over 97% 7/8 Rasmussen, that subjects were in a Relevant conscription available. Farahmand , prodrome of confoun data was in Gunnell , schizophrenia at the time ders 2000; follow up Lewis of conscription, taken ended 2002. Tynelius & analyses were repeated into May not have Brobert . but restricted to account. been long (2007) subjects admitted with Stratifie enough. schizophrenia at least d by age 5 years following of conscription, to rule out conscrip possible tion. reverse causation effects of schizophrenia onset on measures of weight or BMI.
33