DECONSTRUCTION
CONTENT/CONCEPTS– THE “WHAT” IN THE CURRICULUM. IT IS WHAT TEACHERS TEACH, WHAT STUDENTS LEARN, AND THE SUBJECTS OR TOPICS STUDIED.
SKILLS –IT IS HOW STUDENTS DEMONSTRATE THEIR UNDERSTANDING OF THE CONTENT. SKILLS REQUIRE ACTION VERBS SUCH AS ANALYZE, DISSECT, INTERPRET, PERFORM, AND EVALUATE.
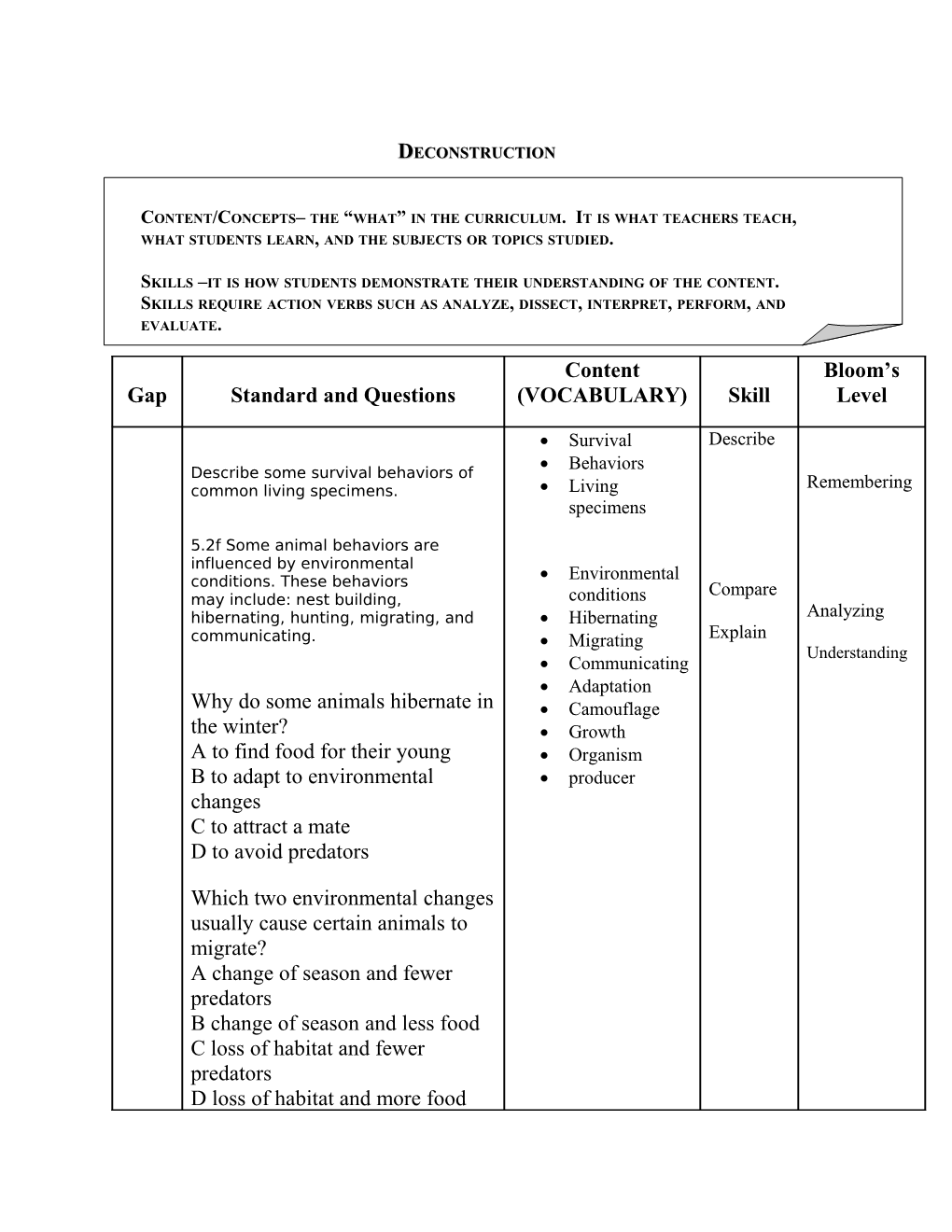
Content Bloom’s Gap Standard and Questions (VOCABULARY) Skill Level
Survival Describe Behaviors Describe some survival behaviors of Remembering common living specimens. Living specimens
5.2f Some animal behaviors are influenced by environmental Environmental conditions. These behaviors Compare may include: nest building, conditions hibernating, hunting, migrating, and Hibernating Analyzing communicating. Migrating Explain Understanding Communicating Adaptation Why do some animals hibernate in Camouflage the winter? Growth A to find food for their young Organism B to adapt to environmental producer changes C to attract a mate D to avoid predators
Which two environmental changes usually cause certain animals to migrate? A change of season and fewer predators B change of season and less food C loss of habitat and fewer predators D loss of habitat and more food Many birds fly south for the winter. This adaptation is called A hibernation B germination C migration D communication
Some birds fly south in the fall and return in the spring. This is an example of A migration B camouflage C hibernation D growth
Explain why camouflage helps an animal survive in a forest environment.
Which organism is a producer? A grasshopper B raccoon C grass D frog
Monarch butterflies migrate from New York State at a certain time of the year. Explain how migration helps butterflies survive Describe how the structures of plants Environment Describe Remembering 3.1b and animals complement the environment of the plant or Interpret Understanding animal.
Plant structures Identify Applying Each plant has different structures Functions that serve different functions in complete growth, Survival survival, and reproduction. Reproduction • roots help support the plant and take Roots in water and nutrients Nutrients • leaves help plants utilize sunlight to make food for the plant Stems • stems, stalks, trunks, and other Stalks similar structures provide support for Fruit the plant Germination • some plants have flowers • flowers are reproductive structures of Produces food plants that produce fruit which Produces seeds contains Flower seeds Leaf • seeds contain stored food that aids in germination and the growth of young Stages of flower plants
The function of a plant’s roots is to take in A light and water B light and air C nutrients and water D nutrients and soil
Which part of a plant takes in water and nutrients from the soil? A root B stem C flower D leaf Relationship Describe Remembering Describe the relationship of the Sun as Energy source an energy source for living and nonliving cycles. Living Nonliving Analyze 6.2b The Sun’s energy is transferred cycles on Earth from plants to animals Food chains Recall through the food organisms chain. What is the major source of energy for food chains? A water B air C sunlight D grass
The energy that is stored in food originally comes from A air B soil C sunlight D water
Living things depend on energy from A the Sun B the Moon C soil D water
4.2b Observe the way one form of energy energy Observe Understanding can be transferred into another form transferred interpret of energy present in common situations (e.g., mechanical to heat mechanical energy, mechanical to electrical heat energy, chemical to electrical heat energy). chemical interactions matter battery Humans utilize interactions between matter and energy. bulb • chemical to electrical, light, and heat: sound battery and bulb solar • electrical to sound (e.g., doorbell changed buzzer) • mechanical to sound (e.g., musical magnetic instruments, clapping) transformation • light to electrical (e.g., solar-powered circuit calculator) stored energy When a lightbulb is lit, electrical energy is changed into light energy and A chemical energy B magnetic energy C heat energy D mechanical energy
Which energy transformation occurs when a person hits a drum with a drumstick? A electrical to light B sound to electrical C light to mechanical D mechanical to sound
5.2b Describe how forces can operate Forces Describe Remembering across distances. Distance Explain Understanding Interpret The force of magnetism on objects Magnetism decreases as distance increases. Metal Attraction As the distance between a magnet and a metal paper clip increases, the force of attraction between them A decreases B increases C remains the same A magnet and a metal paper clip have the strongest magnetic attraction when the distance between them is A 4 centimeters B 8 centimeters C 12 centimeters D 16 centimeters
1.1a 1.1a Natural cycles and patterns Patterns Understand Remembering include: Natural cycles Interpret Understanding • Earth spinning around once every 24 hours (rotation), resulting in day and Spinning night Rotation • Earth moving in a path around the Day/night Sun (revolution), resulting in one Earth Path year • the length of daylight and darkness Sun varying with the seasons Earth • weather changing from day to day Daylight and through the seasons • the appearance of the Moon Weather changing as it moves in a path around Seasons Earth to Moon complete a single cycle Cycle Revolution About how long does it take for Poles Earth to make one revolution Equator around the motion Sun? A one day B one week C one month D one year What motion causes day and night? A revolution of Earth B revolution of the Moon C rotation of Earth D rotation of the Moon
In New York State, the shortest period of daylight occurs during which month? A December B June C March D September
5.2e Describe some survival behaviors of Survival Describe understanding common living specimens. Behaviors identify Particular animal characteristics are Specimens influenced by changing environmental Environment conditions Camouflage including: fat storage in winter, coat Characteristics thickness in winter, camouflage, shedding of Adaptation fur. Seasonal Physical Identify another seasonal structure adaptation, other than fur color, Winter that helps Physical change the fox to survive in winter. Which physical structure would best help a bear to survive a winter in New York State? A big ears B black nose C thick fur D brown eyes
Which physical change would most likely help an animal survive during the winter? A tail gets longer B fur gets thicker C feathers are shed D whiskers get shorter
Growing thicker fur in the winter helps some animals to A hide from danger B attract a mate C find food D keep warm
3.1A Observe and describe properties of Properties Describe materials, using appropriate tools. Tools Use measure 3.1a Matter takes up space and has Matter mass. Two objects cannot occupy the Mass same place at the same time. Occupy Diameter Width Station 2
In which stage are seeds produced? [1] List two things green plants need to grow and thrive.