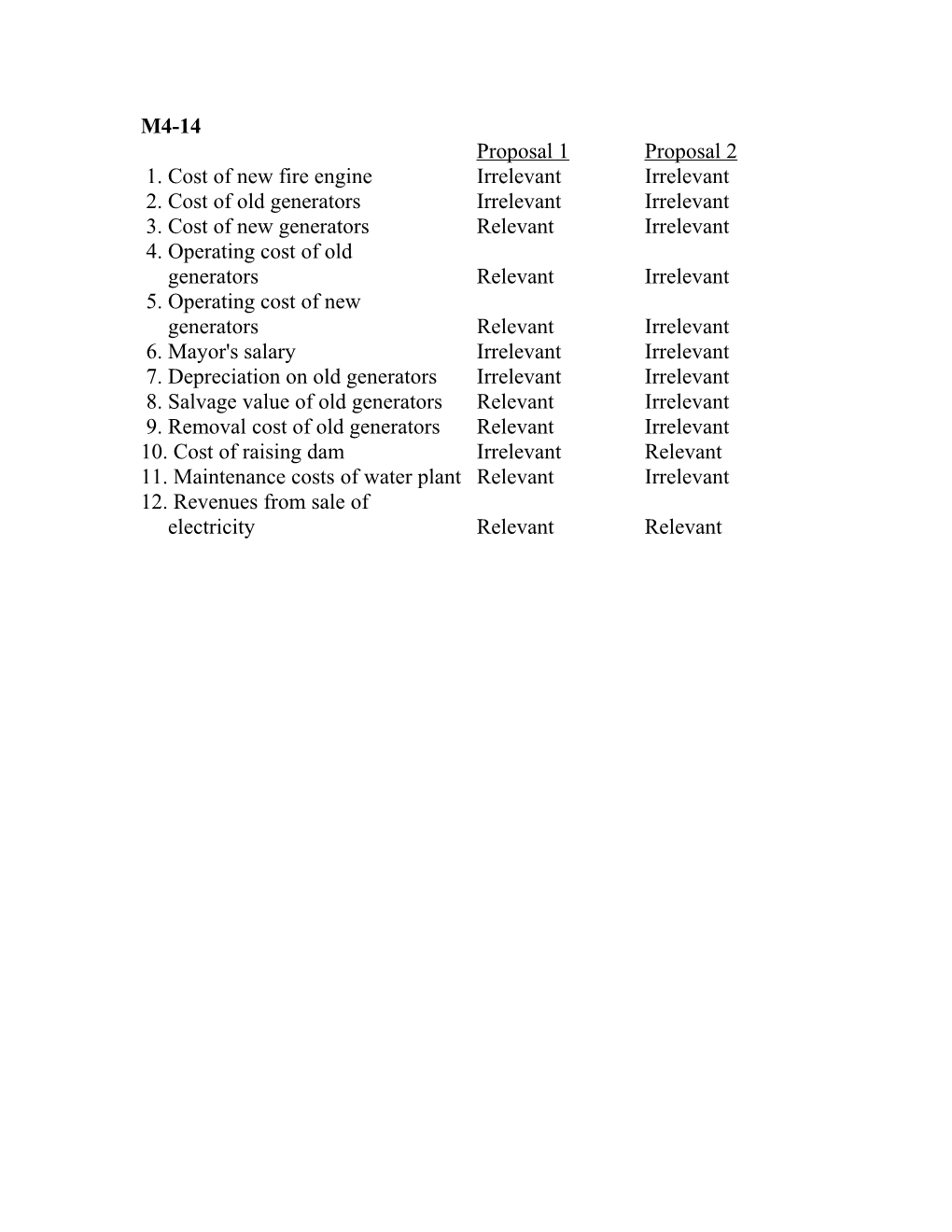
M4-14 Proposal 1 Proposal 2 1. Cost of new fire engine Irrelevant Irrelevant 2. Cost of old generators Irrelevant Irrelevant 3. Cost of new generators Relevant Irrelevant 4. Operating cost of old generators Relevant Irrelevant 5. Operating cost of new generators Relevant Irrelevant 6. Mayor's salary Irrelevant Irrelevant 7. Depreciation on old generators Irrelevant Irrelevant 8. Salvage value of old generators Relevant Irrelevant 9. Removal cost of old generators Relevant Irrelevant 10. Cost of raising dam Irrelevant Relevant 11. Maintenance costs of water plant Relevant Irrelevant 12. Revenues from sale of electricity Relevant Relevant M4-15 Relevant Costs Irrelevant Costs Opportunity Outlay Outlay Sunk 1. The case will require three attorneys to stay four nights in a Washington hotel. The predicted hotel bill is $1,200. X 2. Taylor, Taylor, and Tower's professional staff is paid $2,000 per day for out-of-town assignments. X 3. Last year, depreciation on Taylor, Taylor, and Tower's office was $12,000. X 4. Round-trip transportation to Washington is expected to cost $250 per person. X 5. The firm has recently accepted an engagement that will require partners to spend two weeks in Atlanta. The predicted out-of-pocket costs of this engagement are $8,500. X 6. The firm has a maintenance contract on its computer equipment that will cost $2,200 next year. X 7. If the firm accepts the engagement in Washington, it will have to decline a conflicting engagement in Hilton Head that would have provided a net cash flow of $15,000. X 8. The firm's variable overhead is $80 per client hour. X 9. The firm pays $250 per year for Tower's subscription to a law journal. X X 10. Last year, the firm paid $3,500 to increase the insulation in its building. X M4-18
Relevant cost analysis Increase in revenues: Sell complete sailboats $6,000 Sell sailboat hulls (5,000 ) $ 1,000 Costs of masts, sales, and rigging (1,500 ) Advantage (disadvantage) of further processing $ (500)
An alternative analysis treats the selling price of the uncompleted hulls as an opportunity cost:
Revenues from complete sailboats $ 6,000 Costs: Outlay costs of masts, sails, and rigging$1,500 Opportunity cost of not selling hull 5,000 (6,500) Advantage (disadvantage) of further processing $ (500)
M4-19 a. Contribution from special order (($18 - ($16 - $1.50 + $2.00)) 2,500 bags $3,750 Opportunity cost ($20 - $16) 400 bags -1,600 Profit from accepting order $2,150 b. Expansion into a new area Larger market share Lost sales to regular customers Pressure from regular customers to receive the same price Unhappy regular customers c.
For a long-term relationship, management must consider all of the factors raised in (b).
They must also realize that in the long run all costs are variable. Hence, the profitability of the order might better be based on current average costs with an adjustment for shipping expenses. When this is done, the long-run average cost of $18 ($17.50 -$1.50 + $2.00) equals the selling price. It appears that the order is not desirable in the long run.
Other considerations include the possibility of small crops in future years and the risk of changes in costs.
E4-22
Cost to make: Variable costs (10,000 units $24.00) $240,000
Fixed costs (10,000 units $5.00) 50,000 Rent income (opportunity cost) 25,000 $315,000
Cost to buy (10,000 units $32.00) 320,000 Advantage (disadvantage) of buying $ (5,000)
Making has an advantage of $5,000.