Client Letter Rubric1
Teacher Name: Professor Burke
Student Name: ______
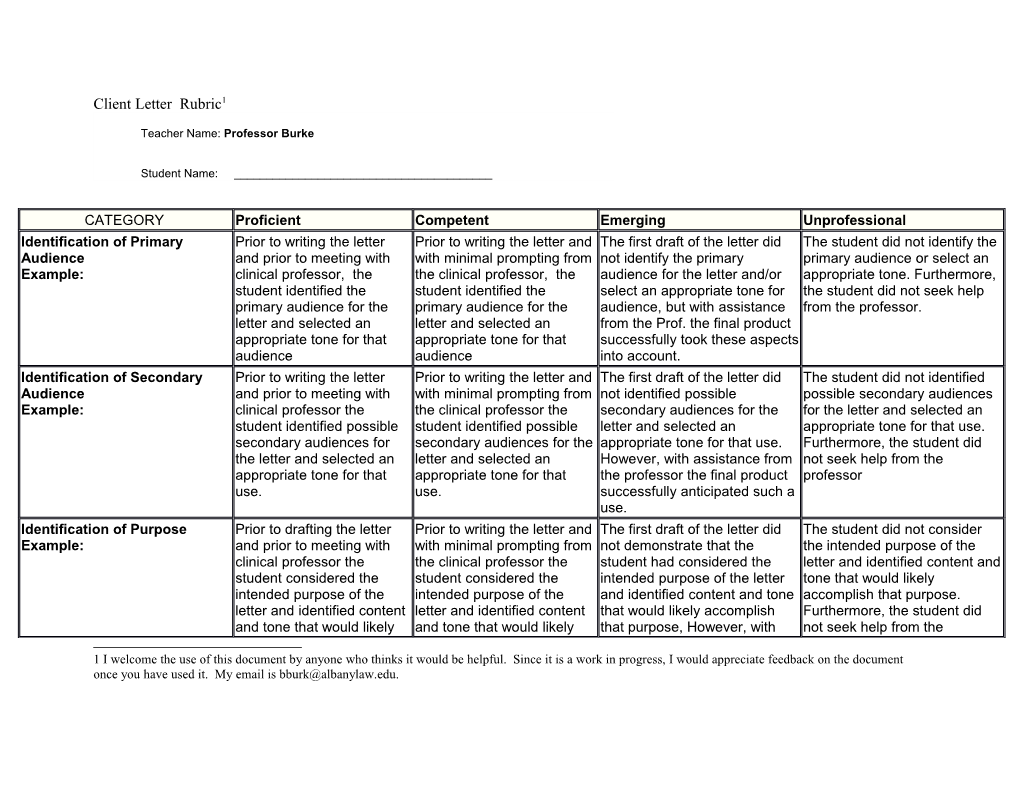
CATEGORY Proficient Competent Emerging Unprofessional Identification of Primary Prior to writing the letter Prior to writing the letter and The first draft of the letter did The student did not identify the Audience and prior to meeting with with minimal prompting from not identify the primary primary audience or select an Example: clinical professor, the the clinical professor, the audience for the letter and/or appropriate tone. Furthermore, student identified the student identified the select an appropriate tone for the student did not seek help primary audience for the primary audience for the audience, but with assistance from the professor. letter and selected an letter and selected an from the Prof. the final product appropriate tone for that appropriate tone for that successfully took these aspects audience audience into account. Identification of Secondary Prior to writing the letter Prior to writing the letter and The first draft of the letter did The student did not identified Audience and prior to meeting with with minimal prompting from not identified possible possible secondary audiences Example: clinical professor the the clinical professor the secondary audiences for the for the letter and selected an student identified possible student identified possible letter and selected an appropriate tone for that use. secondary audiences for secondary audiences for the appropriate tone for that use. Furthermore, the student did the letter and selected an letter and selected an However, with assistance from not seek help from the appropriate tone for that appropriate tone for that the professor the final product professor use. use. successfully anticipated such a use. Identification of Purpose Prior to drafting the letter Prior to writing the letter and The first draft of the letter did The student did not consider Example: and prior to meeting with with minimal prompting from not demonstrate that the the intended purpose of the clinical professor the the clinical professor the student had considered the letter and identified content and student considered the student considered the intended purpose of the letter tone that would likely intended purpose of the intended purpose of the and identified content and tone accomplish that purpose. letter and identified content letter and identified content that would likely accomplish Furthermore, the student did and tone that would likely and tone that would likely that purpose, However, with not seek help from the
1 I welcome the use of this document by anyone who thinks it would be helpful. Since it is a work in progress, I would appreciate feedback on the document once you have used it. My email is [email protected]. accomplish that purpose. accomplish that purpose. assistance from the professor professor the final product did so.
Introductory Paragraph When writing an advisory The student’s first draft, of The first draft of the advisory The advisory letter to the client Example: letter to a client the the advisory letter, prepared letter to the client did not did not include an introductory student’s first draft, with minimal prompting from include an introductory paragraph that accomplished prepared before meeting the professor, included an paragraph that accomplished the following purposes: (1) with the clinical professor, introductory paragraph that the following purposes: (1) identifies the issues the letter included an introductory accomplished the following identifies the issues the letter will address; (2) briefly answers paragraph that purposes: (1) identifies the will address; (2) briefly answers the question and (3) sets the accomplished the following issues the letter will address; the question and (3) sets the tone. Furthermore, the student purposes:(1) identifies the (2) briefly answers the tone. However, with did not seek help from the issues the letter will question and (3) sets the assistance from the professor professor address;(2) briefly answers tone. the final product did so. the question and (3) sets the tone. Factual Statements In the first draft, prepared In the first draft, prepared The factual statements in the The factual statements in the Examples: prior to meeting with the with minimal prompting from first draft of the letter did not letter did not address all the clinical professor, the the clinical professor, the address all the facts legally facts legally relevant to the factual statements in the factual statements in the relevant to the issue, and/ or issue, and/ or sufficient letter included all the facts letter included all the facts sufficient background facts background facts helpful to a legally relevant to the issue, legally relevant to the issue, helpful to a complete factual complete factual narrative. and the background facts and the background facts narrative. However with Furthermore, the student did helpful to a complete helpful to a complete factual assistance from the professor not seek help from the factual narrative. narrative the final product did so. professor Client Centered In the first draft, prepared In the first draft, prepared In the first draft the student’s The student’s description of the Examples: prior to meeting with the with minimal prompting from description of the law did not law did not match the client’s clinical professor, the the clinical professor, the match the client’s sophistication and desire for student’s description of the student’s description of the sophistication and desire for information taking into account law matched the client’s law matched the client’s information taking into account the client’s education and sophistication and desire sophistication and desire for the client’s education and familiarity with the law and for information taking into information taking into familiarity with the law and professional etiquette. account the client’s account the client’s professional etiquette. However Furthermore, the student did education and familiarity education and familiarity with assistance from the not seek help from the with the law and with the law and professor the final product did professor professional etiquette. professional etiquette. so.
Thesis Paragraph In the first draft, prepared In the first draft, prepared The first draft did not contain a The first draft did not contain a Examples: prior to meeting with the with minimal prompting from thesis paragraph to the thesis paragraph to the clinical professor, the thesis the clinical professor, the discussion of the law includes discussion of the law includes paragraph to the discussion thesis paragraph to the the following: (1) states the the following: (1) states the of the law includes the discussion of the law issue; (2) summarizes the key issue; (2) summarizes the key following: (1) states the includes the following: (1) legal principles and factors; (3) legal principles and factors; (3) issue; (2) summarizes the states the issue; (2) if complexity requires briefly if complexity requires briefly key legal principles and summarizes the key legal applies the law to the client’s applies the law to the client’s factors; (3) if complexity principles and factors; (3) if facts; and(4) states the facts; and(4) states the requires briefly applies the complexity requires briefly conclusion. However with conclusion. Furthermore, the law to the client’s facts; applies the law to the client’s assistance from the professor student did not seek help from and(4) states the facts; and(4) states the the final product did so the professor conclusion conclusion Client Centered In the first draft, prepared In the first draft, prepared In the first draft, the student’s The student’s discussion of the Legal Discussion prior to meeting with the with minimal prompting from discussion of the law did not law did not provide the client Examples: clinical professor, the the clinical professor, the provide the client with enough with enough information for the student’s discussion of the student’s discussion of the information for the client to client to understand how the law provided the client with law provided the client with understand how the law law supports the attorney’s enough information for the enough information for the supports the attorney’s conclusion. Furthermore, the client to understand how client to understand how the conclusion. However with student did not seek help from the law supports the law supports the attorney’s assistance from the professor the professor. attorney’s conclusion. conclusion. the final product did so Legal Discussion In the first draft, prepared In the first draft, prepared In the first draft, the student did The student did not explain Examples: prior to meeting with the with minimal prompting from not explain how the law applies how the law applies to the clinical professor, the the clinical professor, the to the client’s factual situation client’s factual situation nor student explained how the student explained how the nor supports the client or supports the client or law applies to the client’s law applies to the client’s appropriately identifies the appropriately identifies the factual situation and factual situation and weaknesses in the client’s weaknesses in the client’s supports the client or supports the client or case. However with assistance case. Furthermore, the student appropriately identifies the appropriately identifies the from the professor the final did not seek help from the weaknesses in the client’s weaknesses in the client’s product did so professor. case. case.
Conclusion In the first draft, prepared In the first draft, prepared In the first draft, the conclusion the conclusion portion of the Examples: prior to meeting with the with minimal prompting from portion of the letter did not letter did not include a clinical professor , the the clinical professor , the include a proposed course of proposed course of action conclusion portion of the conclusion portion of the action which: (1) clearly informs which: (1) clearly informs the letter included a proposed letter included a proposed the client of what actions the client of what actions the client course of action which: (1) course of action which: (1) client should take; and (2) should take; and (2) clearly clearly informs the client of clearly informs the client of clearly informs the client of informs the client of what action what actions the client what actions the client what action the attorney the attorney intends to take. should take; and (2) clearly should take; and (2) clearly intends to take. However with Furthermore, the student did informs the client of what informs the client of what assistance from the professor not seek help from the action the attorney intends action the attorney intends the final product did so professor. to take. to take Format In the first draft, prepared In the first draft, prepared The first draft did not included The letter did not included Examples: prior to meeting with the with minimal prompting, headers and clinic approved headers and clinic approved clinical professor, included included headers and clinic form However with assistance format. Furthermore the headers and clinic approved format. from the professor the final student did not seek approved format. product did so at. assistance.
Format In the first draft, prepared In the first draft, prepared The first draft did not identify The first draft did not identify Examples: prior to the meeting with the with minimal prompting from the other individuals who the other individuals who clinical professor, the letter the clinical professor, the received a copy of the letter received a copy of the letter identified the other letter identified the other and the enclosures included. and the enclosures included. individuals who received a individuals who received a However with assistance from Furthermore the student did not copy of the letter and the copy of the letter and the the professor the final product seek assistance. enclosures included. enclosures included. did so at. Grammar The first draft, prepared The first draft, prepared with The first draft contains incorrect The letter contained incorrect Examples: prior to the meeting with the minimal prompting from the grammar, syntax, spelling, grammar, syntax, spelling, clinical professor, contained clinical professor, contained punctuation, form and format. punctuation, form and format. correct grammar, syntax, correct grammar, syntax, However with assistance from Furthermore the student did not spelling, punctuation, form spelling, punctuation, form the professor the final product seek assistance and format. and format. did so at. Timing The student completed the The student completion of The student completion of the The student did not complete Examples: letter in a timely manner the letter was slightly letter was delayed and did not the letter in a timely manner or and provided sufficient time delayed, but provided provide much time for feedback provided time for feedback for feedback from professor sufficient time for feedback from professor and correction. from professor and correction. and correction. from professor and correction.
This rubric is based on the following resources: (1) Albany Law School Law Clinic and Justice Center’s Grading Criteria (2) The Legal Writing Handbook, Oates & Enquist, 4th edition Aspen Publishers (3) Legal Analysis and Writing, Wellford, Lexis-Nexis Electronic Authors Press (4) The Legal Research and Writing Handbook A Basic Approach for Paralegals, Yelin and Samborn, 4th edition Aspen Publishers (5) A Lawyer Writes A Practical Guide to Legal Analysis, Coughlin, Malmud & Patrick, Carolina Academic Press
1. Pre-performance/Planning: Student is expected to demonstrate competent skills in case organization, case planning, identification of client goals and short term objectives, preparation, collaboration, following office procedures and time management. Pre-performance/planning includes exercising judgment in a manner that produces the timely advancement of a case or assignment.
2. Performance: Student is expected to demonstrate competent ability in engaging in lawyering activities such as: client counseling, interviewing, fact investigation, negotiating, research, legal analysis and writing, drafting legal documents, examining witnesses, oral advocacy, and corresponding with clients and relevant parties. In performing requisite activity, student is expected to exercise professional judgment in identifying when to adjust strategies, and the manner of adjustment, without compromising firm goals. Student is expected to maintain a professional demeanor at all times. 3. Post-performance/Reflection, Correction & Judgment: Student is expected to use sound, unbiased judgment in interpreting, analyzing, and evaluating alternative courses of action and in making decisions. In order to be effective throughout this process, student should also employ a reflective, self-corrective, and purposeful thinking process.
4. Professional Responsibilities: Student is expected to behave in a professional and ethical manner at all times in dealings with clients, the legal system, the community, colleagues and opposing counsel. In fulfilling these many roles and obligations, student must demonstrate sensitivity to client needs, concerns and goals and knowledge of ethical rules. For example, the student must represent his/her other clients with diligence, preserve client confidences, respect client autonomy, and exercise independent professional judgment on a client’s behalf.
Proficient Professional: A proficient professional has good judgment and interpersonal skills, but occasionally needs prompting to complete the task at hand. At this level the professional is capable of working well independently and collaboratively, but may need assistance in identifying the most appropriate means to get a particular job done. This individual works hard to develop appropriate plans which take into account time management, organization, and their ability to implement their plan. This individual recognizes the importance of proceeding in a client centered manner and works diligently to accomplish this. The proficient professional will take advantage of appropriate readings, but will have some difficulty modifying the recommendations in the readings to suit the needs of the situation. However, with minimal prompting the proficient professional will be able to develop and execute an appropriate case plan. A professional at this level also demonstrates strong reflective and corrective skills. However, even with meaningful reflection, the individual still needs occasional prompting to achieve a meaningful understanding of the system that they are operating in and to improve their performances.
Emerging Professional: An emerging professional may lack the experience and knowledge necessary for critical judgment, but is open to feedback from others and learning from their experiences. The individual demonstrates that they value the importance of case planning, time management and organization, but may need support to perform optimally. Often, this professional can internalizes the feedback and improve his or her performance based upon the feedback, although there will be some occasions where they have difficulty with this. He or she is developing the ability to self reflect and correct performances based on his or her own reflections. This individual has good interpersonal skills and is always respectful, but may lack the experience necessary to recognize the appropriate professional behavior at all times. However, he or she shows the good judgment in seeking guidance from more experienced professionals when he or she has an experiential deficit. This individual is generally not ready to work independently to complete many tasks, but is willing and able to develop strong professional collaborations to get the necessary work done.
Unprofessional: An individual is unprofessional when they are unaware that they lack the knowledge and or experience necessary for the job or despite the awareness of the deficit, they take no meaningful action to overcome the deficit, such as reading relevant professional material, or seeking assistance from an appropriate experienced professional. They do not consistently demonstrate a reflective process and are not implementing appropriate organizational, time management or case planning activities.