AP Bio March Through the Kingdoms Due 3/13
List and describe the three domains of living things and list some major organisms belonging to each domain.
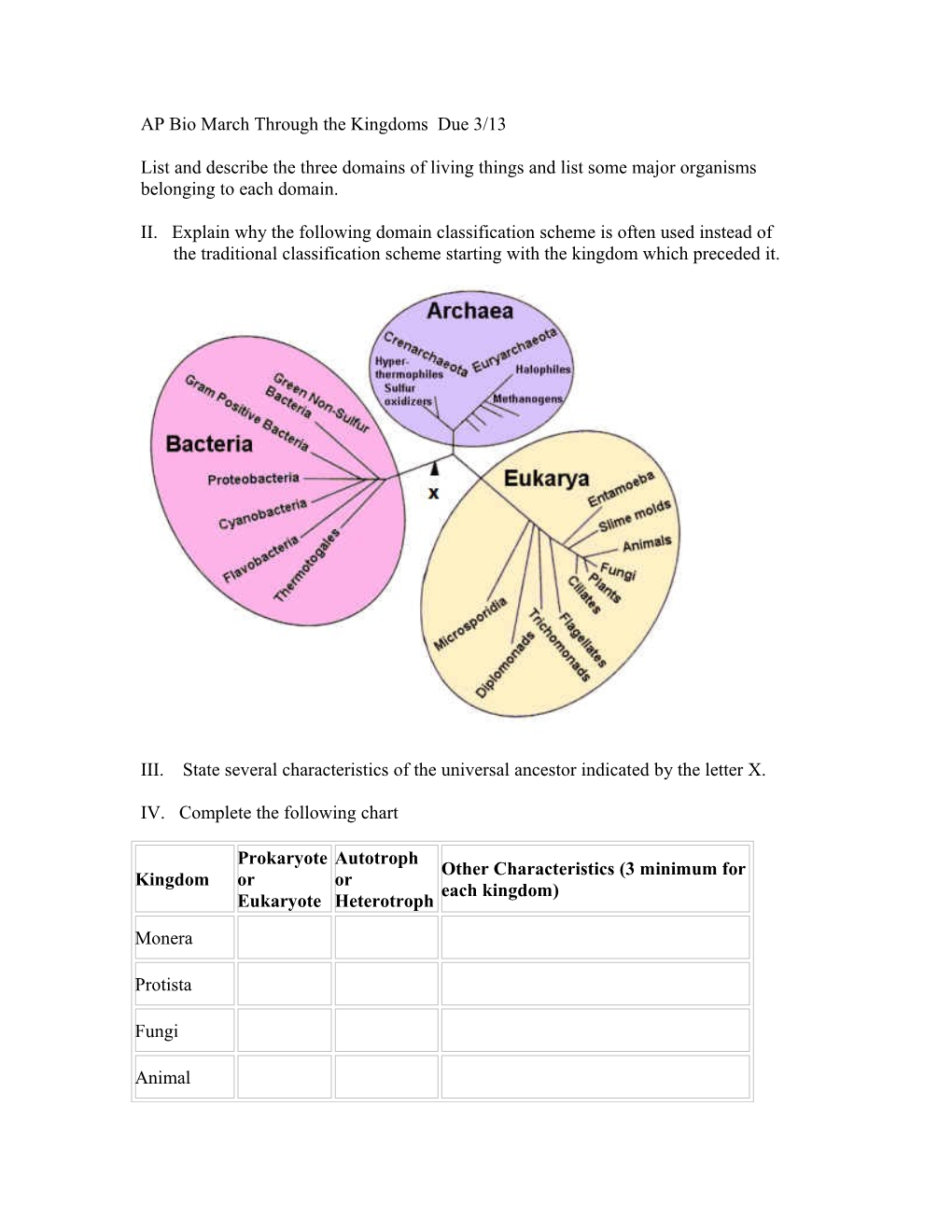
II. Explain why the following domain classification scheme is often used instead of the traditional classification scheme starting with the kingdom which preceded it.
III. State several characteristics of the universal ancestor indicated by the letter X.
IV. Complete the following chart
Prokaryote Autotroph Other Characteristics (3 minimum for Kingdom or or each kingdom) Eukaryote Heterotroph Monera
Protista
Fungi
Animal Plant
Animal Characteristics Define these terms on another sheet of paper: Parazoa, Eumetazoa, protostome, deuterostome, diploblastic, triploblastic, radial, bilateral, asymmetry, acoelomate, schizocoelous, & enterocoelous Using the meanings of the above terms, complete the following chart for animal characteristics:
Animal Phylum Higher Tissues Symmetry Coelom Coelomic taxa type formation
Human
Portuguese man-of- war
Brittle star
Squid
Planarian
Rotifer
Horseshoe crab
Roundwor m
Sponge Earthworm
V. Describe the differences between the terms in each of the following pairs.
(a.) Coelomate versus psuedocoelomate versus acoelomate body plan (b.) Protostome versus deuterostome development (c.) Radial versus bilateral symmetry
VI. Discuss how the characteristics listed in parts a and b of question number V were involved in the construction of the phylogenetic tree of the animal kingdom below. Also discuss the significance of the hardly visible letter at the bottom of the phylogenetic tree.
VII. Classify each of the following phyla of the Animal Kingdom according to the characteristics listed in part one above. Record your information in a chart like fashion. The phyla to be assessed are as follows; Porifera, Cnidaria, Echinodermata, Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, Annelida, Arthropoda, Mollusca, and Chordata. (Note: A phylum which is acoelomate or psuedocoelomate is obviously not either protostome or deuterostome.)
Acoelomate, Psuedocoelomate, or Protostome or Animal Phylum Coelomate Deuterostome Porifera xxxxxxxxxxx Cnidaria xxxxxxxxxxx Rotifera xxxxxxxxxxx Platyhelminthes xxxxxxxxxxx Nematoda xxxxxxxxxxx Annelida Mollusca Echinodermata Arthropoda Chordata
For each of the following, choose the response which best completes each of the following statements or answers each of the following questions.
Utilize the following key to select the correct answers for questions 1-5.
(a.) phylum Chordata (b.) phylum Cnidaria (c.) phylum Mollusca (d.) phylum Echinodermata (e.) phylum Annelida (f.) phylum Platyhelminthes (g.) phylum Nematoda (h.) phylum Porifera (i.) none of these
1. Includes spiders, crabs, millipedes, and insects. 2. Includes snakes, toads, and bony fishes. 3. Includes hydra, corals, jellyfish, and sea anemones 4. Includes clams, squid, and octopus 5. Includes blood and liver flukes, tapeworms, and planaria 6. Includes the saltwater and freshwater sponges. 7. Includes the earthworm. 8. Includes the paramecium, euglena, and ameoba. Animal Systems Define these terms on another sheet: Gastrovascular cavity, gut, simple diffusion, open circulation, closed circulation, flame cells, nephridia, malpighian tubules, green glands, flame cells, kidneys, endoskeleton, exoskeleton, shell, limestone case, hydrostatic skeleton, spongin & spicules, gills, lungs, book lungs
Using the meanings of the above terms, complete the following chart for animal systems:
Animal Phylum Digestion Respiration Circulation Excretion Support
Deer
Crayfish
Nautilus
Scallop
Hydra
Rotifer
Coral
Tapeworm
Sponge
Spider
Earthworm Starfish