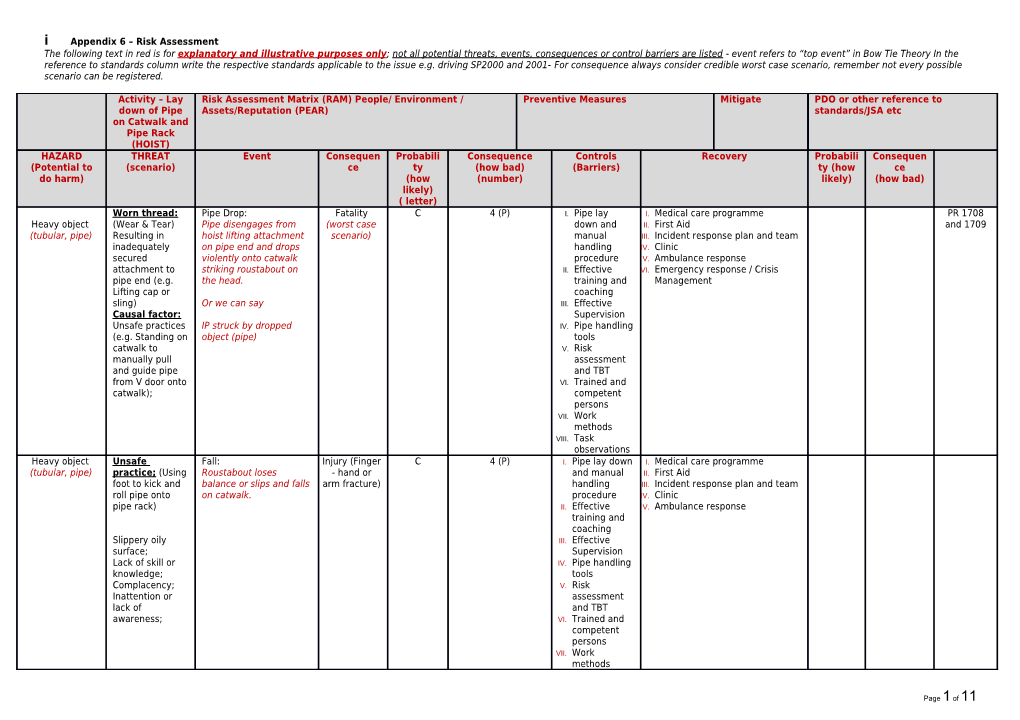
i Appendix 6 – Risk Assessment The following text in red is for explanatory and illustrative purposes only; not all potential threats, events, consequences or control barriers are listed - event refers to “top event” in Bow Tie Theory In the reference to standards column write the respective standards applicable to the issue e.g. driving SP2000 and 2001- For consequence always consider credible worst case scenario, remember not every possible scenario can be registered.
Activity – Lay Risk Assessment Matrix (RAM) People/ Environment / Preventive Measures Mitigate PDO or other reference to down of Pipe Assets/Reputation (PEAR) standards/JSA etc on Catwalk and Pipe Rack (HOIST) HAZARD THREAT Event Consequen Probabili Consequence Controls Recovery Probabili Consequen (Potential to (scenario) ce ty (how bad) (Barriers) ty (how ce do harm) (how (number) likely) (how bad) likely) ( letter) Worn thread: Pipe Drop: Fatality C 4 (P) I. Pipe lay I. Medical care programme PR 1708 Heavy object (Wear & Tear) Pipe disengages from (worst case down and II. First Aid and 1709 (tubular, pipe) Resulting in hoist lifting attachment scenario) manual III. Incident response plan and team inadequately on pipe end and drops handling IV. Clinic secured violently onto catwalk procedure V. Ambulance response attachment to striking roustabout on II. Effective VI. Emergency response / Crisis pipe end (e.g. the head. training and Management Lifting cap or coaching sling) Or we can say III. Effective Causal factor: Supervision Unsafe practices IP struck by dropped IV. Pipe handling (e.g. Standing on object (pipe) tools catwalk to V. Risk manually pull assessment and guide pipe and TBT from V door onto VI. Trained and catwalk); competent persons VII. Work methods VIII. Task observations Heavy object Unsafe Fall: Injury (Finger C 4 (P) I. Pipe lay down I. Medical care programme (tubular, pipe) practice; (Using Roustabout loses - hand or and manual II. First Aid foot to kick and balance or slips and falls arm fracture) handling III. Incident response plan and team roll pipe onto on catwalk. procedure IV. Clinic pipe rack) II. Effective V. Ambulance response training and coaching Slippery oily III. Effective surface; Supervision Lack of skill or IV. Pipe handling knowledge; tools Complacency; V. Risk Inattention or assessment lack of and TBT awareness; VI. Trained and competent persons VII. Work methods
Page 1 of 11 VIII. Task observations IX. Competence assessments X. Critical task analysis Activity - Food Risk Assessment Matrix (RAM) People/ Environment / Preventive Measures Mitigate PDO or other reference to Management Assets/Reputation (PEAR) standards/JSA etc HAZARD THREAT Event Consequen Probabili Consequence Controls Recovery Probabili Consequen (Potential to (scenario) ce ty (how bad) (Barriers) ty (how ce do harm) (how (number) likely) (how bad) likely) ( letter) Mould; Toxins Unhygienic food Food poisoning: Fatality C 4 (p) I. HACCP I. Medical care programme B 3 SP1232 Contaminants storage and Toxins ingested by (worst case standards and II. First Aid Parasites - handling eating contaminated scenario) inspections III. Incident response plan and team (Protozoa, practices food resulting in Abdominal II. Effective food IV. Clinic roundworms, (Causal factors diarrhoea cramps, control V. Ambulance response and tapeworms.) may be due to nausea, management VI. Emergency response/Crisis Viruses, lack of vomiting, III. Storage and Management Bacteria, mould knowledge or and handling etc. awareness or diarrhoea standards and lack of procedures compliance with IV. Proper food a standards e.g. storage HACCP 22000) facilities e.g. (dry goods store, metal shelving, containers, ventilation control, refrigeration, segregation, temp control and monitoring, cleaning etc) V. Proper cleaning of facilities with proper chemicals and steam VI. Pest control and waste disposal VII. Cleaning materials e.g. sanitised wet wipes VIII. Food purchasing standards IX. Supplier agreements
Page 2 of 11 and SLA’s X. Personal hygiene standards (food handlers) XI. Adequate standards for food preparation and cooking Activity – Risk Assessment Matrix (RAM) People/ Environment / Preventive Measures Mitigate PDO or other reference to Manual Assets/Reputation (PEAR) standards/JSA etc Handling HAZARD THREAT Event Consequen Probabili Consequence Controls Recovery Probabili Conseque (Potential to (scenario) ce ty (how bad) (Barriers) ty (how nce do harm) (how (number) likely) (how bad) likely) (letter) Heavy Object Assuming wrong Overexertion Back Injury I. Manual I. Medical care programme B 2 PR2111 body posture (Due to weight of object (due to Handling II. First Aid during manual exceeding physical muscle training III. Incident response plan handling of capability of individual) strain or II. Awareness IV. Clinic heavy material slipped disc) training on V. Ambulance response (Causal Factors ergonomics in might be lack of the workplace awareness or III. Provision of training - unsafe correct lifting practice) equipment for C 3 (P) manual handling IV. Job hazard analysis V. Supervision VI. Workplace layout and design VII. Manual Handling procedure Activity - Risk Assessment Matrix (RAM) People/ Environment / Preventive Measures Mitigate PDO or other reference to Driving Assets/Reputation (PEAR) standards/JSA etc HAZARD THREAT Event Consequen Probabili Consequence Controls Recovery Probabili Consequen (Potential to (scenario) ce ty (how bad) (Barriers) ty (how ce do harm) (how (number) likely) (how bad) likely) (letter) Vehicle in motion Driver fatigue Loss of control of the Fatality/ies D 5 (P) I. Shift pattern I. Radio facility. B 4P SP2000 (Causal Factors vehicle resulting in a (Maybe 4 management II. Vehicle Recovery Unit. (Kinetic energy) might be lack of rollover occupants II. Coaching and III. Emergency response plans. sleep, excessive (Due to driver falling killed) training on IV. Trained responders. driving hours or asleep behind the health hazards V. Medics. excessive steering wheel while III. Medical VI. Effective Incident management overtime or use driving resulting in roll examination VII. Clinics of medication) over and serious IV. Journey VIII. Ambulance service injuries) management
Page 3 of 11 V. Advanced defensive driver training VI. IVMS VII. Sp 2000 specs Vehicle in motion Substandard or Loss of control of the Fatality/ies I. Purchasing I. Radio facility. B 4P SP2000 badly worn Tyres vehicle resulting in a (Maybe 4 standards and II. Vehicle Recovery Unit. (Kinetic energy) (Causal factors rollover occupants policy III. Emergency response plans. may be (Due to a blow out while killed) II. Coaching and IV. Trained responders. inadequate driving) training on V. Medics. inspections, vehicle VI. Effective Incident management inadequate inspections standards, III. Standards for inadequate tyres (only use maintenance, new tyres and substandard all the same manufacturing brand and etc) spec) IV. Robust maintenance programme D 5 (P) V. Defensive driver training (reduce excessive acceleration or braking) VI. Fleet management audits VII. SP 2000 Specs
Activity - Risk Assessment Matrix (RAM) People/ Environment / Preventive Measures Mitigate PDO or other reference to Driving Assets/Reputation (PEAR) standards/JSA etc HAZARD THREAT Event Consequen Probabili Consequence Controls Recovery Probabili Consequen (Potential to (scenario) ce ty (how bad) (Barriers) ty (how ce do harm) (how (number) likely) (how bad) likely) (letter) Vehicle in motion Stray animals Loss of control of the Fatality/ies C 5(P) I. Journey I. Radio facility. e.g. camels, vehicle resulting in a (Maybe 4 management II. Vehicle Recovery Unit. (Kinetic energy) goats, donkeys rollover occupants II. Advanced III. Emergency response plans. or horses (Due to trying to avoid killed) defensive IV. Trained responders. (These animals collision with animals) driver training V. Medics. may cause the (how to be VI. Effective Incident management driver to react alert for VII. Ambulance service suddenly to wild/domestic avoid colliding animals along with them route and resulting in loss practical
Page 4 of 11 of control of the collision vehicle) avoidance techniques) Pedestrians III. IVMS can also IV. SP2000 specs represent a V. Roll over cage threat VI. Cargo and passenger segregation Vehicle in motion Foreign object Loss of control of the Fatality/ies I. Journey I. Radio facility. debris lying in vehicle resulting in a (Maybe 4 management II. Vehicle Recovery Unit. (Kinetic energy) road rollover occupants II. Advanced III. Emergency response plans. (This could be (Due to tyre bursting as killed) defensive IV. Trained responders. any object lying a consequence of driver training V. Medics. on the road such striking the object while (how to be VI. Effective Incident management as a concrete travelling at high speed) alert for debris VII. Ambulance service block, a metal in the road pipe or drive along route shaft) C 5(P) and practical collision avoidance techniques) III. IVMS IV. SP2000 vehicle standards VII. Roll over cage
Vehicle in motion Third party Head on collision with Fatality/ies I. Journey I. Radio facility. drivers (trucks, other vehicles (Maybe 4 management II. Vehicle Recovery Unit. (Kinetic energy) tankers, buses, (Due to other oncoming occupants II. Advanced III. Emergency response plans. cars, HGV’s) vehicles drifting into the killed) defensive IV. Trained responders. (These vehicles path of your vehicle) (Could be driver training V. Medics. on the road pose more (how to be VI. Effective Incident management a threat due to fatalities if alert for VII. Ambulance service their drivers for example oncoming VIII. Civil defence unsafe driving a bus is C 5(P) vehicles and practices) struck by a practical HGV) collision avoidance techniques) III. IVMS IV. SP2000 vehicle standards Vehicle in motion Sub standard or Loss of control of the As above C 5(P) I. Journey As above poor road vehicle due to sub management (Kinetic energy) surface condition standard road surface II. Advanced (This may resulting in a rollover defensive include potholes driver training or very rough (how to be dirt road) alert for substandard road conditions along route and practical
Page 5 of 11 collision avoidance techniques) III. IVMS IV. SP2000 vehicle standards VIII. Roll over cage Vehicle in motion Adverse weather Loss of control of the As above As above As above conditions – vehicle due to lack of (Kinetic energy) Heavy rain, visibility resulting in a flooding, high rollover or head on wind causing collision dust clouds, ice conditions, C 5(P) extreme heat (This may affect vehicle control due to rain or high dust levels restricting visibility) Activity - Risk Assessment Matrix (RAM) People/ Environment / Preventive Measures Mitigate PDO or other reference to Maintaining Assets/Reputation (PEAR) standards/JSA etc high voltage electrical equipment HAZARD THREAT Event Consequen Probabili Consequence Controls Recovery Probabili Consequen (Potential to (scenario) ce ty (how bad) (Barriers) ty (how ce do harm) (how (number) likely) (how bad) likely) (letter) Electricity Bare insulation Contact with live Fatality D 5 (P) I. Inspection I. Practiced emergency response C 4P PR1076 exposing live electrical circuit schedule II. Trained first aiders PR1948 electrical wiring resulting in electrocution II. Wiring III. Effective Incident management (conductors) or (I.e. the electrical standards IV. Emergency response plans. terminals conductors were III. Maintenance V. Trained responders. Other threats exposed or safeguards IV. Trained and VI. Medics. I. Lack of such as isolators were certified VII. Clinic. maintenance missing) operators and (electricians) inspections; V. Isolation II. Lack of procedure awareness; VI. Communicatio III. Lack of n knowledge; VII. Permit to work IV. Lack of VIII. JSP supervision IX. Lock out tag V. Inadequate out communicatio n; VI. Inadequate application of PTW process; VII. Sub standard equipment; VIII. Poor design or
Page 6 of 11 construction;
Activity - Risk Assessment Matrix (RAM) People/ Environment / Preventive Measures Mitigate PDO or other reference to Working on Assets/Reputation (PEAR) standards/JSA etc Scaffolding (i.e. working at height) HAZARD THREAT Event Consequen Probabili Consequence Controls Recovery Probabili Consequen (Potential to (scenario) ce ty (how bad) (Barriers) ty (how ce do harm) (how (number) likely) (how bad) likely) (letter) Height Missing guard Fall through opening Fatality I. Scaffold I. Practiced emergency response – B 2P SP1257 (distance of fall, rail on open side (Due to inattention and (Due to Inspections stabilise the greater the (Causal Factors stepping out where blunt force (qualified II. Incident management - including distance the may be lack of guard rail is missing trauma and competent effective communication more severe the competence in Resulting in fall from internal safety officer) III. First aid responder, injuries) scaffold erection height) injuries) II. Compliance IV. Paramedic, and lack of with scaffold V. Medical centre etc (Potential standards) erection and energy) design Other threats standards can be: III. Certified I. Defective competent D 4(P) scaffolding scaffold components erectors or IV. Effective II. Sub standard supervision erection of V. Training and Scaffolding certification on III. Inadequate working at scaffold height inspection VI. Working at process height procedure
Page 7 of 11 Activity - Risk Assessment Matrix (RAM) People/ Environment / Preventive Measures Mitigate PDO or other reference to Mechanical Assets/Reputation (PEAR) standards/JSA etc Lifting HAZARD THREAT Event Consequen Probabili Consequence Controls Recovery Probabili Consequen (Potential to (scenario) ce ty (how bad) (Barriers) ty (how ce do harm) (how (number) likely) (how bad) likely) (letter) Suspended Load Damaged or Dropped load Fatality I. Standards for I. Practiced emergency response B 1(P) PR1708 (Heavy object) worn lifting sling (Due to sling or chain and/or rigging; lifting II. Effective Incident management PR1709 or weak chain breakage or mechanical Asset slings, chains III. Emergency response plans. PR1710 (Potential link; failure resulting in damage etc IV. Trained responders. energy) (Causal Factors serious injury) II. Trained and V. Medics. might be certified overuse of sling riggers i.e. worn, or sub III. Correct storage standard of slings, equipment or chains with failed inspection inspections or register substandard IV. Inspection of audits, or slings, chains poor V. Correct management slinging practices etc) D 4(P) methods VI. Competent and Other threats: effective I. Inadequate lift supervision planning & VII. Compliance execution; with lifting and II. Overloading; rigging III. Poor load procedure securing VIII. Inspected and methods; certified lifting IV. Incompetent equipment or IX. Load chart inexperienced banks man / rigger / crane operators;
Activity - Risk Assessment Matrix (RAM) People/ Environment / Preventive Measures Mitigate PDO or other reference to Confined Assets/Reputation (PEAR) standards/JSA etc Space Entry HAZARDS THREAT Event Consequenc Probabili Consequence Controls Recovery Probabili Consequen (Potential to (scenario) e ty (how bad) (Barriers) ty (how ce do harm) (how (number) likely) (how bad) likely) (letter) Absence of Unauthorised Worker asphyxiated Fatality I. Permit to work I. Practiced emergency response B 1(P) PR1172 oxygen, (Oxygen entry, due to inhalation of II. Demarcation, II. Trained first aiders PR1148 deficient life Uncontrolled toxic gas or oxygen signs and III. Effective Incident management threatening access, deficient air. barriers IV. Emergency response plans. C 4P atmosphere) Workers without III. Confined V. Trained responders. training or space entry VI. Medics. Too much awareness, procedure VII. Clinic oxygen, Non approved IV. Standby man VIII. Confined space rescue plan and
Page 8 of 11 (Oxygen work method, V. Breathing equipment enriched) Work areas not apparatus identified as VI. Gas testing Presence of toxic confined space VII. Venting - gases (H2S, or high hazard Forced air carbon dioxide, area in risk circulation nitrogen assessment, VIII. Training and enriched, argon etc competence etc) evaluation IX. Authorised access and control
Activity - Use Risk Assessment Matrix (RAM) People/ Environment / Preventive Measures Mitigate PDO or other reference to of Electrical Assets/Reputation (PEAR) standards/JSA etc Hand Tools HAZARDS THREAT Event Consequenc Probabili Consequence Controls Recovery Probabili Consequen (Potential to (scenario) e ty (how bad) (Barriers) ty (how ce do harm) (how (number) likely) (how bad) likely) (letter) Electricity Tools with Contact with electrical Fatality I. Equipment I. Practiced emergency response B 1(P) PR 1947 damaged source resulting in purchasing II. Trained first aiders 1948 electrical plugs, electrocution standards III. Effective Incident management Tools without II. Equipment IV. Emergency response plans. electrical plugs, inspections V. Trained responders. (just bare wires) III. Equipment VI. Medics. Damaged maintenance VII. Clinic. insulation i.e. IV. Training on C 4P worn electrical proper use of cables, electrical exposed wiring, hand tools non earthed V. Effective wiring, supervision etc VI. Equipment tag out if damaged Activity - Risk Assessment Matrix (RAM) People/ Environment / Preventive Measures Mitigate PDO or other reference to Operating Assets/Reputation (PEAR) standards/JSA etc Forklift – Rig Operation HAZARDS THREAT Event Consequenc Probabili Consequence Controls Recovery Probabili Consequen (Potential to (scenario) e ty (how bad) (Barriers) ty (how ce do harm) (how (number) likely) (how bad) likely) (letter) Forklift in motion Incompetent Loss of control of the Fatality C 4P I. Assignment of I. Practiced emergency response B 1 (P) (driving too fast inexperienced forklift causing a tip licensed II. Trained first aid responders with load at top operator over forklift III. Effective Incident management of mast) operators IV. Emergency response plans. II. Competence V. Qualified Medics. training for VI. Communication set Thuraya forklift VII. Ambulance and Clinic. operators III. Testing and verification by
Page 9 of 11 an accredited training provider IV. Effective supervision and management V. Control of allocation of forklift keys VI. Competent Rigger Banks man VII. Effective load management
Note: Incorporating lessons learned and findings from safety observations should be a major part of TBT & JHA, it promotes awareness, thus improving safety performance and prevention of injuries. The above examples are for illustrative purposes only - purely examples to illustrate the principle Activity = Hazardous activity due to the “hazards associated with the activity” Threat is that thing that can release, unleash or cause the hazard to be realised examples: Threats are issues like Corrosion, over pressurisation, hot surfaces, alcohol, fatigue, sub standard practices, lack of attention or experience, poor visibility, speed etc Not all control barriers have been included in the above examples Determination of residual risk is dependent on contractor’s assessment
RISK ASSESSMENT MATRIX
Consequences Increasing Likelihood S ev A B C D E er it Has happened in Has happened at Environ Reputati Has happened y People Assets the Company or the location or ment on Never heard of Heard of in the more than once more than once more than once in the Industry Industry per year at the per year in the per year in the Location Industry Company
Page 10 of 11 No injury or No No No 0 health damage effect impact effect Slight injury Slight Slight Slight 1 or health damage effect impact effect Minor injury Minor Minor Minor 2 or health damage effect impact effect Major injury Moderat Moderate Moderate 3 or health e effect impact effect damage Permanent or total Major Major Major 4 disability or damage effect impact up to 3 fatalities More than 3 Massive Massive Massive 5 fatalities damage effect impact
Page 11 of 11