8-6.1 Recall that waves transmit energy but not matter.
What is a wave? A wave is a repeating disturbance or vibration that transfers or moves energy from place to place. What causes a wave to occur? Vibration (Waves are created when a source of energy (force) causes a vibration. ) A vibration is a repeated back-and-forth or up-and-down motion.
How do waves carry energy? Waves carry energy through empty space or through a medium without transporting matter .
What is a medium? A medium is a material through which waves can travel. It can be a solid, liquid, or gas. Medium State of Matter Seismic Wave Earth’s Crust Solid Ocean Wave Water Liquid Sound Wave Air Gas
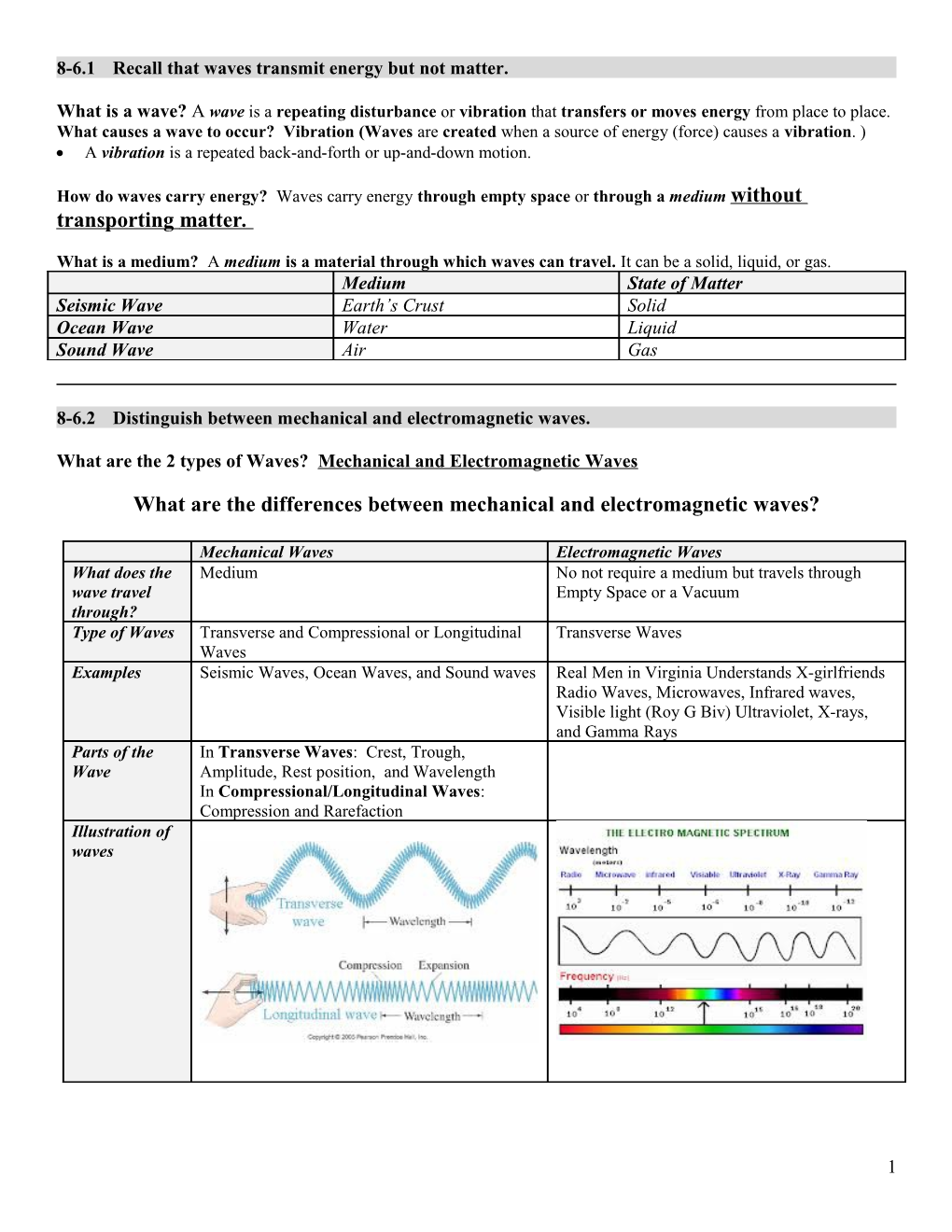
8-6.2 Distinguish between mechanical and electromagnetic waves.
What are the 2 types of Waves? Mechanical and Electromagnetic Waves
What are the differences between mechanical and electromagnetic waves?
Mechanical Waves Electromagnetic Waves What does the Medium No not require a medium but travels through wave travel Empty Space or a Vacuum through? Type of Waves Transverse and Compressional or Longitudinal Transverse Waves Waves Examples Seismic Waves, Ocean Waves, and Sound waves Real Men in Virginia Understands X-girlfriends Radio Waves, Microwaves, Infrared waves, Visible light (Roy G Biv) Ultraviolet, X-rays, and Gamma Rays Parts of the In Transverse Waves: Crest, Trough, Wave Amplitude, Rest position, and Wavelength In Compressional/Longitudinal Waves: Compression and Rarefaction Illustration of waves
1 Each line represents ENERGY
What are the 2 types of Mechanical Waves? Transverse and Compressional/Longitudinal Wave
What are the Differences between the Mechanical Waves?
Transverse Waves Compressional/Longitudinal Waves Type of Mechanical Mechanical Wave The Mechanical waves in which the particles of matter Mechanical waves in which the particles of matter in Direction in the medium vibrate by moving back and forth the medium vibrate by pushing together and the Waves and perpendicular (at right angles) to the moving apart parallel to the direction in which the Travel direction the wave travels wave travels Parts of Crest, Trough, Amplitude, Rest position, and Compression and Rarefaction the Wave Wavelength
Illustration of Wave
Main parts Crest: The highest part of a wave Compression (Compress): The part of the wave that of the Trough: The lowest part of a wave close together Wave Rarefaction: The part of the wave that are far apart
8-6.3. Summarize factors that influence the basic properties of waves (including frequency, amplitude, wavelength, and speed).
Basic properties of waves Definitions Important Facts & Illustration Frequency Frequency is a measure of how many High Frequency =Shorter Wavelengths waves pass a point in a certain amount Low Frequency = Longer Wavelengths of time.
2 Amplitude (Height of the Amplitude is a measure of the distance Sounds with greater amplitude will be louder; Wave) between a line through the middle of a Higher the wave the higher the amplitude. wave and a crest or trough. High Amplitude =High Pitch, High Frequency, & Shorter Wavelength
Low Amplitude = Low Pitch, Low Frequency, & Longer Wavelength
Wavelength Wavelength is a measure of the High Frequency =Shorter Wavelengths/Closer distance from the crest on one Low Frequency = Longer Wavelengths/Far wave to the crest on the very Apart next wave.
Speed of the Waves Speed is a measure of the distance a wave travels in an amount of time. The speed of a wave is determined by the type of wave and the nature of the medium.
Speed Other Important Facts Mechanical Wave The Speed Changes because Waves have different speeds in different mechanical waves travel through media (mediums) different mediums. Electromagnetic Wave All electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed because all electromagnetic waves travel through empty space.
3 8-6.4 Summarize the behaviors of waves (including refraction, reflection, transmission, and absorption).
Behavior of Waves Behavior of Key Definition Examples & Illustration Wave Word(s) Refraction Bending Refraction is the bending of waves Prisms, convex lens, Magnifying glass, and of a caused by a change in their speed as glasses Wave they pass from one medium to another. As waves pass at an angle from one medium to another, they may speed up or slow down.
Reflection Bouncing Reflection is the bouncing back of a Plane Mirrors, Echoes, and Ocean waves back of a wave when it meets a surface or hitting a cliff, and reflection from a lake wave boundary that does not absorb the entire wave’s energy. Transmission Waves Transmission of waves occurs when Sound waves are transmitted through solids, pass waves pass through a given point or liquids, and gases. through medium
3 Types of Transmissions 1. All Light Transparent materials allow all or Clear objects such as Glass Transparent waves most of the light waves that strikes pass them to pass through through
4 2. Translucent Some Translucent materials transmit some Light light, but cause it to be scattered so no waves clear image is seen. pass through
3. Opaque No Light Opaque materials allow no light pass waves to be transmitted through through them.
Absorption Absorbs, Absorption of certain frequencies of Takes in light occurs when the energy is not transferred through, or reflected by, the given medium.
8.6.5 Explain hearing in terms of the relationship between sound waves and the ear. The Path Sound Waves Travel Through the EAR
5 3 MAIN PARTS TO THE EAR: OUTER, MIDDLE, AND INNER EAR
The outer ear serves to collect and channel sound to the middle ear. The middle ear serves to transform the energy of a sound wave into the internal vibrations of the bone structure of the middle ear and ultimately transform these vibrations into a compressional wave in the inner ear. The inner ear serves to transform the energy of a compressional wave within the inner ear fluid into nerve impulses that can be transmitted to the brain.
The Order Sound Waves Travel Function Through the Ear OUTER EAR (RECIEVER) COLLECTS THE SOUND: The outer ear also channels sound waves that reach the ear through the ear canal to the eardrum of the middle ear. The outer ear is called the pinna and is made of ridged cartilage covered by skin. EAR CANAL Because of the length of the ear canal, it is capable of amplifying sounds with frequencies EAR DRUM Amplifies the sound 3 SMALL BONES (ANVIL, Increases the pitch of the sound wave HAMMER, AND STIRUP) IN THE MIDDLE EAR TINY HAIRS IN THE INNER Interprets sound and transfers an electrical impulse to the brain EAR NERVES AT THE END OF Interprets sound and transfers an electrical impulse to the brain THE TINY HAIRS Auditory Nerve and Cochlea BRAIN Translate or Interpret the nerve impulses as hearing
8-6.6 Explain sight in terms of the relationship between the eye and the light waves emitted or reflected by an object. The Path Light Travels Through the Eye
6 The Path Light Travels Through the Eye Functions CORNEA Responsible for refracting and bending the light rays IRIS The Color of the Eye that contains the Pupil CONVEX LENS Responsible for refracting and focusing RETINA Responsible for producing nerve impulses NERVE IMPULSES Impulses received from the Retina OPTIC NERVE Responsible for transmitting the signals to the brain BRAIN Translate or interpret the nerve impulses as sight
8-6.7 Explain how the absorption and reflection of light waves by various materials result in the human perception of color. REFLECTION VS. ABSORPTION OF LIGT
Most materials absorb light of some frequencies and reflect the rest.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION IMPORTANT INFORMATION IF A MATERIAL REFLECTS IF ALL COLORS ARE REFLECTION LIGHT OR A COLOR THEN YOU REFLECTED, THEN THE WILL BE ABLE TO SEE IT MATERIAL WILL APPEAR WHITE IF A MATERIAL ABSORBS IF ALL THE COLORS ARE ABSORBTION LIGHT OR A COLOR, YOU WILL ABSORBED, THEN THE NOT BE ABLE TO SEE IT MATERIAL WILL APPEAR BLACK
The color that we see depends on (1) the color of light that is shined on the object and (2) the color of light that is reflected by the object. For example, if an object reflects red wavelengths and absorbs all others, the object will appear red in color.
TOOLS USED TO DEMONSTATE WAVES SPECTROSCOPE, COLOR FILTERS, TUNNING FORK, SLINKY, PLANE MIRROR, PRISM, PENCIL IN A TRANSPARENT CUP
8-6.8 Compare the wavelength and energy of waves in various parts of the electromagnetic spectrum (visible light, infrared, and ultraviolet radiation).
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES (FORM OF TRANSVERSE WAVES) Electromagnetic waves have a wide range of wavelengths. The entire range of wavelengths is called the electromagnetic spectrum.
7 Electromagnetic Spectrum from Low Frequency (longer wavelengths) to High Frequency (shorter wavelengths)
Examples Radio Wave Microwaves Infrared Visible Light Ultraviolet X-Rays Gamma of Waves (Roy G Biv) Rays Rays Electromag netic Waves (Electroma gnetic Spectrum) Acronym Real Men In Virginia Understands X Girlfriends Facts Has the longest Wavelengths All objects Visible light is Ultraviolet Carries a Has the wavelength, are shorter emit the range of radiation is the lot of shorter Lowest than radio infrared electromagneti range of energy, wavelengths, frequency, waves radiation, c waves that electromagneti are given Higher and lesser and hotter can be c waves with off by frequencies, energy objects detected by frequencies stars, and and greater emit more the human higher than are also energy infrared eye. violet on the used in radiation The entire visible airport Given off by than cooler range of spectrum, security starts and objects. visible light is thereby having some Heat called the shorter radioactive energy is visible light wavelengths substances transmitte spectrum. and more d by (ROY G BIV) energy than Kill Cancer infrared RED, violet cells radiation. ORANGE, wavelengths. YELLOW, Because of the GREEN, high energy of BLUE, ultraviolet INDIGO, radiation, too AND much exposure VIOLET is damaging to (Note that red the eyes and will have the skin. longest Attracts wavelength insects, used to /less energy kill microbes, and violet used to sterilize will have products shorter wavelengths/ greater energy out of the colors) Examples Carry signals Made by Stars, Sun, Any type of Special lights X-Rays Tracers for televisions various types lamps, light or colors from the Sun machines Radiotherapy and cellular of transmitters flames, beds for (Radiation phones and (Transmitters and you tanning and Treament) bring music to are in mobile (body Light from the the radio phones, heat) Sun antennas, and microwave ovens
8