Class One Curriculum Overviews - Spring Term
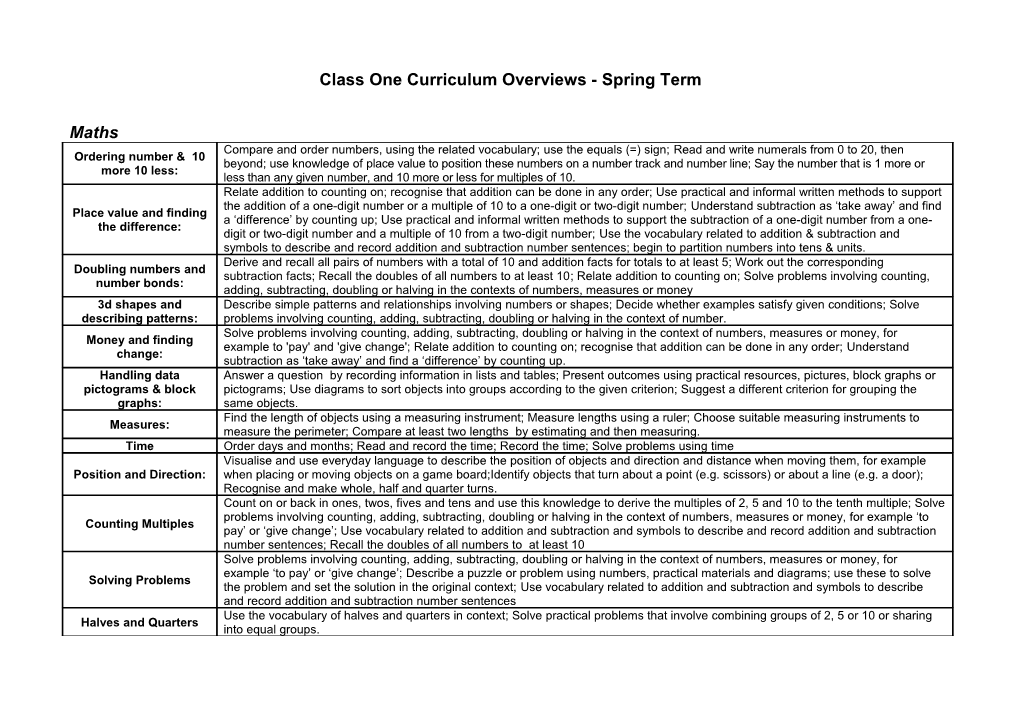
Maths Compare and order numbers, using the related vocabulary; use the equals (=) sign; Read and write numerals from 0 to 20, then Ordering number & 10 beyond; use knowledge of place value to position these numbers on a number track and number line; Say the number that is 1 more or more 10 less: less than any given number, and 10 more or less for multiples of 10. Relate addition to counting on; recognise that addition can be done in any order; Use practical and informal written methods to support the addition of a one-digit number or a multiple of 10 to a one-digit or two-digit number; Understand subtraction as ‘take away’ and find Place value and finding a ‘difference’ by counting up; Use practical and informal written methods to support the subtraction of a one-digit number from a one- the difference: digit or two-digit number and a multiple of 10 from a two-digit number; Use the vocabulary related to addition & subtraction and symbols to describe and record addition and subtraction number sentences; begin to partition numbers into tens & units. Derive and recall all pairs of numbers with a total of 10 and addition facts for totals to at least 5; Work out the corresponding Doubling numbers and subtraction facts; Recall the doubles of all numbers to at least 10; Relate addition to counting on; Solve problems involving counting, number bonds: adding, subtracting, doubling or halving in the contexts of numbers, measures or money 3d shapes and Describe simple patterns and relationships involving numbers or shapes; Decide whether examples satisfy given conditions; Solve describing patterns: problems involving counting, adding, subtracting, doubling or halving in the context of number. Solve problems involving counting, adding, subtracting, doubling or halving in the context of numbers, measures or money, for Money and finding example to 'pay' and 'give change'; Relate addition to counting on; recognise that addition can be done in any order; Understand change: subtraction as ‘take away’ and find a ‘difference’ by counting up. Handling data Answer a question by recording information in lists and tables; Present outcomes using practical resources, pictures, block graphs or pictograms & block pictograms; Use diagrams to sort objects into groups according to the given criterion; Suggest a different criterion for grouping the graphs: same objects. Find the length of objects using a measuring instrument; Measure lengths using a ruler; Choose suitable measuring instruments to Measures: measure the perimeter; Compare at least two lengths by estimating and then measuring. Time Order days and months; Read and record the time; Record the time; Solve problems using time Visualise and use everyday language to describe the position of objects and direction and distance when moving them, for example Position and Direction: when placing or moving objects on a game board;Identify objects that turn about a point (e.g. scissors) or about a line (e.g. a door); Recognise and make whole, half and quarter turns. Count on or back in ones, twos, fives and tens and use this knowledge to derive the multiples of 2, 5 and 10 to the tenth multiple; Solve problems involving counting, adding, subtracting, doubling or halving in the context of numbers, measures or money, for example ‘to Counting Multiples pay’ or ‘give change’; Use vocabulary related to addition and subtraction and symbols to describe and record addition and subtraction number sentences; Recall the doubles of all numbers to at least 10 Solve problems involving counting, adding, subtracting, doubling or halving in the context of numbers, measures or money, for example ‘to pay’ or ‘give change’; Describe a puzzle or problem using numbers, practical materials and diagrams; use these to solve Solving Problems the problem and set the solution in the original context; Use vocabulary related to addition and subtraction and symbols to describe and record addition and subtraction number sentences Use the vocabulary of halves and quarters in context; Solve practical problems that involve combining groups of 2, 5 or 10 or sharing Halves and Quarters into equal groups. English Poetry Read and respond to rhymes and verses; Use simple pattern structures to support their writing based on topic work; Create Pattern and Rhyme: brainstorms of words which rhyme and create their own rhyme following a specific pattern and within an appropriate frame. Listen to, read and respond to a range of simple poems on a shared theme; Discuss their own and others' responses to the poems; Poetry Talk about their favourite words and parts of the poems, and notice the poems' patterns; Consider obvious similarities and differences Poems on a theme: between the poems; Perform the poems in a variety of ways, including where appropriate singing, adding music, rhythms or sounds, doing actions and acting out; Use senses to build up a collection of words based on the theme and then implement using a given pattern or written within an appropriate frame. Recount and Oral recount of Educational visit involving a range of time connectives; Discussion of the school routine with recount of an event, using dictionaries: photographs to support ordering of events; Identify relevant features of a recount before planning & producing a written recount; Use of the alphabet to order items in a dictionary; Locate given words in a dictionary and find and give definition of words.
Read and tell a range of traditional stories and fairy tales, including well-known and less familiar examples; Identify basic story elements and represent outlines of plot; Talk about the reasons for events in stories; Make comparisons between stories and identify typical features, for example beginnings and endings, story language, typical characters; Use pictures, puppets and props to help remember the main events and characters through re-enactment; Retell whole stories for a group of children (include story language Traditional and Fairy and presenting events in the correct order); Look at particular story characters and identify information in the text, for example Stories appearance, behaviour, how they speak, making predictions about how they will behave in different situations; Write a character profile based on evidence from the text; Compare & contrast how a story is presented in film and in text (including playscript); Use script to develop voices for different characters; Retell a story using puppets; Plan & produce a written version of the story, retelling a traditional tale in their own written words, and orally, through speech & playscripts, using five sections to organise ideas and creating twists to different events.
Science Seasons and Weather This unit develops children’s understanding of the need for light in order to see things. Children learn that darkness is the absence of (Light & Dark) light and that in the absence of sunlight other light sources are seen more easily. observe changes across the 4 seasons with an emphasis on Winter into Spring. observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies Pupils should observe and talk about changes in the weather and the seasons. Pupils will understand that it is not safe to look directly at the sun, even when wearing dark glasses. Pupils might work scientifically by: making tables and charts about the weather; and making displays of what happens in the world around them, including day length, as the seasons change. Experimental and investigative work focuses on: making suggestions of how to investigate an idea making observations and comparisons explaining observations. Work in this unit also offers opportunities for children to relate their understanding of science to everyday experiences of light and darkness and to health and safety. Through this unit children learn about the characteristics and uses of a range of common materials and vocabulary for describing and comparing materials. Experimental and investigative work focuses on: thinking about what is expected to happen turning ideas into a form that can be tested making observations and comparisons. Children will have the opportunity to; Distinguish between an object and the material from which it s made Begin to name some common materials; making observations of these and of common objects
Sorting & Using Explore the properties of materials Materials Begin to understand that some materials are magnetic and some are waterproof Know that everyday objects are made from different materials Identify and name a variety of everyday materials, including wood, plastic, glass, cardboard , brick, metal, water, and rock Describe the simple physical properties of a variety of everyday materials Begin to sort materials by grouping Compare and group together a variety of everyday materials on the basis of their simple physical properties Find out how the shapes of solid objects made from some materials can be changed by squashing, bending, twisting and stretching.
RE We will identify places that are special to us and different religions and examining why this is; we will visit a church in the locality to Why Are Some identify and research special objects and areas of the church; we will design our own special place and explain why this is special to Places Special us.
Creative Curriculum Earth and Beyond As scientists we will investigate the concept of light and dark, investigate a range of natural and manmade light sources. We will use a light box to explore how much light various different materials let through. We will explore shadows and reflections. As historians we will look at the lives of significant people particularly Neil Armstrong and space events on a timeline and As geographer’s we research the schools locality on maps and plans, creating our own map of the school, and decide a suitable launch pad for astronauts. We will look at the solar system; learn about the Earth and our place in the universe. As designers we will use the technique of paper Mache to make planets and use clay to make a miniature alien and create our own star constellation torches. As musicians we will listen to space sound effects and select and use instruments to create own space sounds. We will use sounds to accompany space images to compose space music. As linguists we will create poems based on the space theme and describe fantasy space settings. We will use a range of information texts to identify facts about space and present oral and written pieces on what was researched. As performers we will share with our research about planets in our solar system. We will listen, read and recite a range of space themed poems including poems that rhyme. As people we discuss going for goals, personal targets and aspirations linked with those of Neil Armstrong. Perseverance: Children will independently and with a partner research space through books and the internet to present their findings to a wider audience. Knowledge of the World: Children to learn about the significant contributions made by explorers and scientists to help us understand space. Countries which have added to space events. Technology ICT: Use Expresso videos and websites to research space and use google earth and telescopes to further explore our World. As scientists we will name and describe materials used to build homes. We will investigate sorting materials depending on their properties. We will identify materials which are waterproof and non-waterproof to decide whether they are fit for purpose for buildings. As historians we will look at similarities and differences between homes today and homes in the past. We will observe and discuss old household objects and make comparisons with modern day objects, reflecting upon life as it was lived long ago. As geographers we will observe different types of homes in the local area and record in a chart. We will view house plans and draw floor plans of our bedrooms. We will look at similarities and differences in homes around the world. Homes: Appreciate the As artists we will draw from first hand observations, a range of homes. diversity of homes that As designers we will develop a plan of a home we would like to construct and create a list of materials we wish to use as part of our people live in today & design. We will develop ideas by shaping materials and putting components together. making comparisons As mathematicians we will give and follow instructions using roamers moving around a simple road grid. with the past. As linguists we will describe features of our homes and discuss homes from traditional stories. We will build up a bank of words to describe homes and use them when developing ideas to create our own story settings. As performers we will present our descriptions of story settings to Reception Class. We will communicate, through role play what we have learnt about home life. As people we will learn people live in different types of homes which can be dependent on locality and lifestyle. Enterprise: Produce a class display of Victorian household artefacts for other classes to view Knowledge of the World: learn about houses long ago, comparing them with their own homes. Technology: Use cameras to capture different types of homes, expresso to view videos and activities on materials