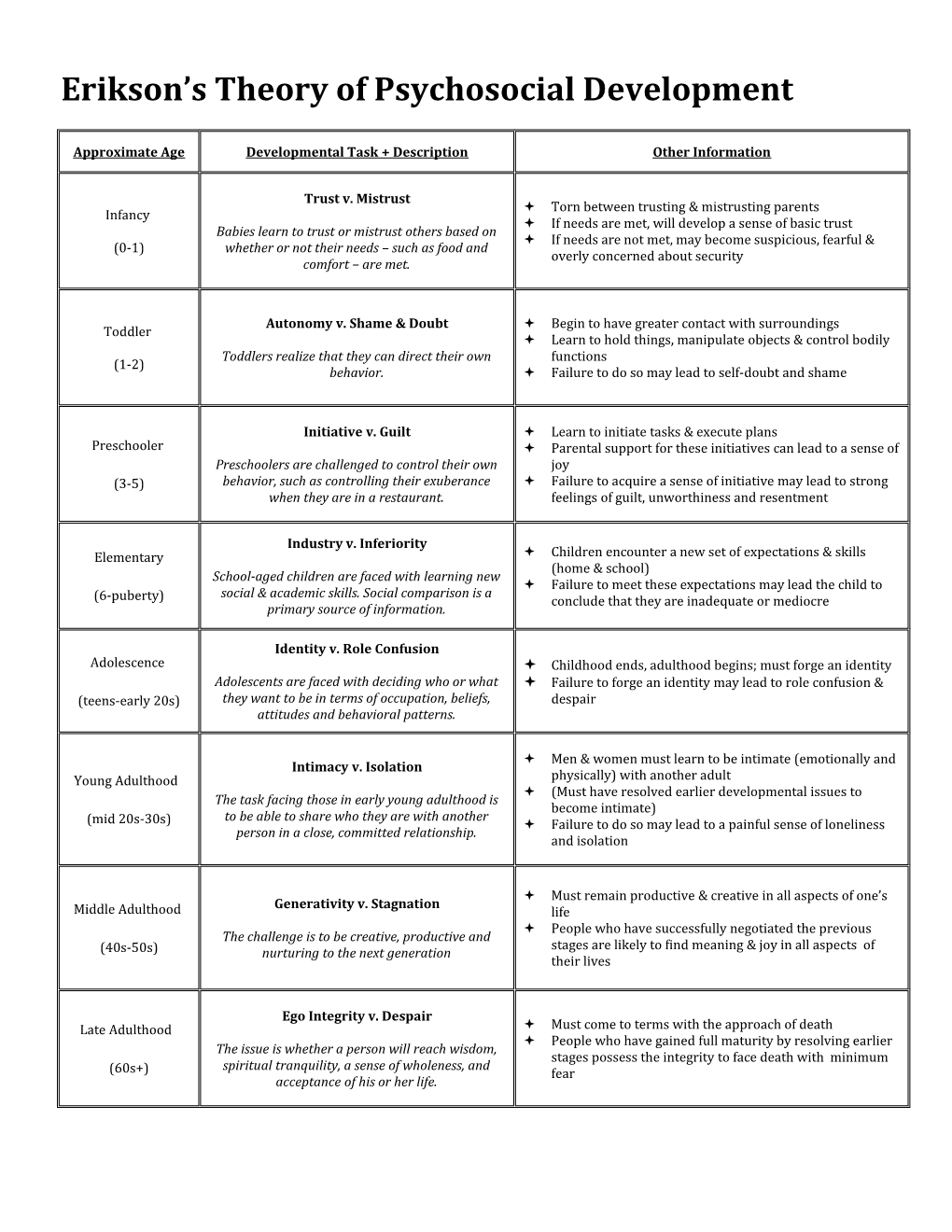
Erikson’s Theory of Psychosocial Development
Approximate Age Developmental Task + Description Other Information
Trust v. Mistrust Torn between trusting & mistrusting parents Infancy If needs are met, will develop a sense of basic trust Babies learn to trust or mistrust others based on If needs are not met, may become suspicious, fearful & (0-1) whether or not their needs – such as food and overly concerned about security comfort – are met.
Autonomy v. Shame & Doubt Begin to have greater contact with surroundings Toddler Learn to hold things, manipulate objects & control bodily Toddlers realize that they can direct their own functions (1-2) behavior. Failure to do so may lead to self-doubt and shame
Initiative v. Guilt Learn to initiate tasks & execute plans Preschooler Parental support for these initiatives can lead to a sense of Preschoolers are challenged to control their own joy (3-5) behavior, such as controlling their exuberance Failure to acquire a sense of initiative may lead to strong when they are in a restaurant. feelings of guilt, unworthiness and resentment
Industry v. Inferiority Elementary Children encounter a new set of expectations & skills (home & school) School-aged children are faced with learning new Failure to meet these expectations may lead the child to social & academic skills. Social comparison is a (6-puberty) conclude that they are inadequate or mediocre primary source of information.
Identity v. Role Confusion Adolescence Childhood ends, adulthood begins; must forge an identity Adolescents are faced with deciding who or what Failure to forge an identity may lead to role confusion & (teens-early 20s) they want to be in terms of occupation, beliefs, despair attitudes and behavioral patterns.
Men & women must learn to be intimate (emotionally and Intimacy v. Isolation Young Adulthood physically) with another adult (Must have resolved earlier developmental issues to The task facing those in early young adulthood is become intimate) to be able to share who they are with another (mid 20s-30s) Failure to do so may lead to a painful sense of loneliness person in a close, committed relationship. and isolation
Must remain productive & creative in all aspects of one’s Generativity v. Stagnation Middle Adulthood life People who have successfully negotiated the previous The challenge is to be creative, productive and stages are likely to find meaning & joy in all aspects of (40s-50s) nurturing to the next generation their lives
Ego Integrity v. Despair Late Adulthood Must come to terms with the approach of death People who have gained full maturity by resolving earlier The issue is whether a person will reach wisdom, stages possess the integrity to face death with minimum spiritual tranquility, a sense of wholeness, and (60s+) fear acceptance of his or her life.