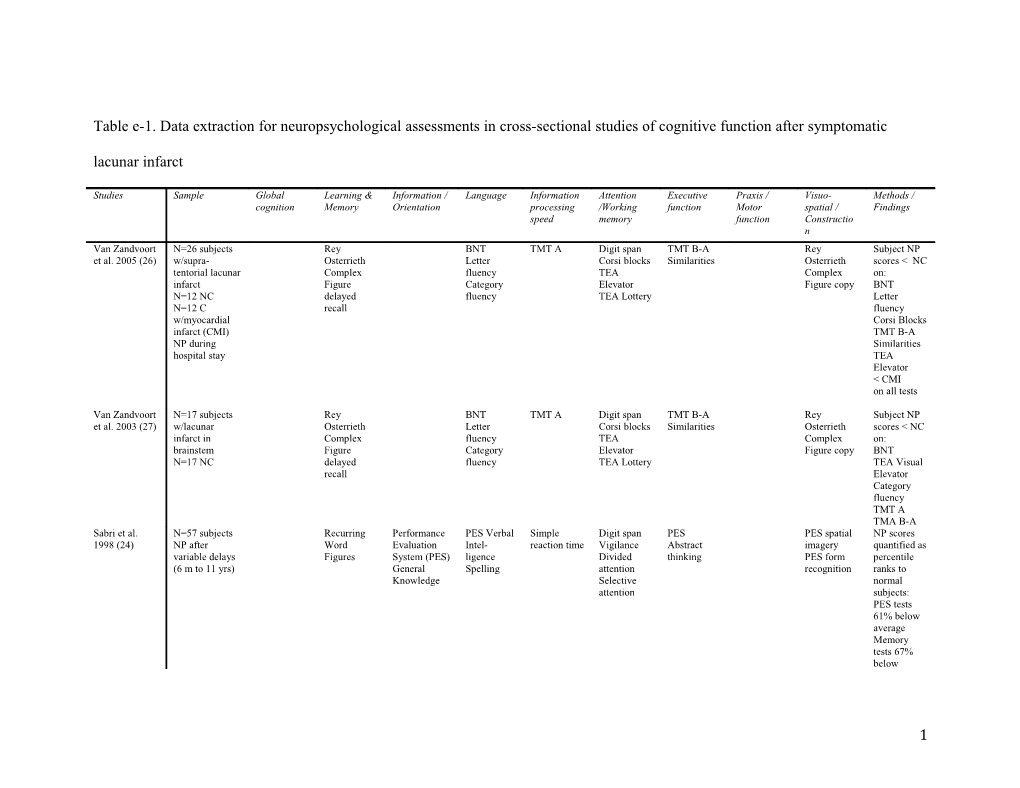
Table e-1. Data extraction for neuropsychological assessments in cross-sectional studies of cognitive function after symptomatic lacunar infarct
Studies Sample Global Learning & Information / Language Information Attention Executive Praxis / Visuo- Methods / cognition Memory Orientation processing /Working function Motor spatial / Findings speed memory function Constructio n Van Zandvoort N=26 subjects Rey BNT TMT A Digit span TMT B-A Rey Subject NP et al. 2005 (26) w/supra- Osterrieth Letter Corsi blocks Similarities Osterrieth scores < NC tentorial lacunar Complex fluency TEA Complex on: infarct Figure Category Elevator Figure copy BNT N=12 NC delayed fluency TEA Lottery Letter N=12 C recall fluency w/myocardial Corsi Blocks infarct (CMI) TMT B-A NP during Similarities hospital stay TEA Elevator < CMI on all tests
Van Zandvoort N=17 subjects Rey BNT TMT A Digit span TMT B-A Rey Subject NP et al. 2003 (27) w/lacunar Osterrieth Letter Corsi blocks Similarities Osterrieth scores < NC infarct in Complex fluency TEA Complex on: brainstem Figure Category Elevator Figure copy BNT N=17 NC delayed fluency TEA Lottery TEA Visual recall Elevator Category fluency TMT A TMA B-A Sabri et al. N=57 subjects Recurring Performance PES Verbal Simple Digit span PES PES spatial NP scores 1998 (24) NP after Word Evaluation Intel- reaction time Vigilance Abstract imagery quantified as variable delays Figures System (PES) ligence Divided thinking PES form percentile (6 m to 11 yrs) General Spelling attention recognition ranks to Knowledge Selective normal attention subjects: PES tests 61% below average Memory tests 67% below
1 average Attentional tests 54% below average O’Sullivan et N=36 MMSE WMS Letter WAIS Digit Digit span Wisconsin Finger Facial NP raw al. 2004 w/ischaemic WAIS-R Logical Fluency Symbol* Card Sorting Tapping Recognition scores (28, 29) leukoaraiosis FSIQ* memory Test* converted to (hx of LI) WMS Paired TMT B-A* z scores N=19 NC associates based on NC learning M and SD: Mean scores z>=-1 on tests of global cognition, information processing, attention, executive functioning* Memory relatively preserved O’Sullivan et N=36 MMSE WMS WAIS-R WAIS Digit Digit span WAIS-R Finger WAIS-R Subject NP al. 2005 w/ischaemic WAIS-R Logical Vocab.* Symbol* backwards* Similarities* Tapping* Blocks* scores < NC (28, 29) leukoaraiosis VIQ* memory* Letter TMT A* WAIS-R WAIS-R on all tests (hx of LI) PIQ* WMS Paired Fluency* Comprehen- Object Brief N=17 NC associates sion* assembly* battery learning Wisconsin (TMT B-A, Card Sorting Letter Test* fluency, TMT B-A* Digits backwards, Digit Symbol) sensitivity/ specificity to leukoaraiosis 88/88 Fure et al. 2006 N=71 subjects MMSE Object Letter TMT A Assessment Pre- (30) with lacunar Learning fluency of stroke and determined infarct Test Ullevaal other brain cutoffs to aphasia damage compute screening percent impaired:
2 40% on TMT A, 10-20% on all other tests 58% any impaired score Babikian et al. N=23 w/mixed Sum of all CVLT BNT WAIS-R TMT B Luria Hooper NP scores 1990 (31) (12) or lacunar scaled scores immediate Letter Digit span Stroop reciprocal visual scaled to (11) infarct and delayed fluency Symbol Interference motor organization ordinal scale recall Category cancellation Visual- programmin Block (0-5) and Biber Figure fluency Continuous verbal test g Design averaged by immediate BDAE performance Luria Drawing to domain and delayed Cookie test graphmotor command LI group recall theft alternation and copy showed impairment in all domains except in attention Anderson et al. N=17 subjects WAIS-R Dual task RT slowing 2008 (32) with lacunar FSIQ paradigms under ant. circul. (DTP): increased Infarct 1) Increasing attentional WAIS-R 3 m, distracters demands: RT paradigms paradigm highest 3-5 y from 2)Simult- distractor index event aneous level in DTP N=13 NC processing 1, shortest paradigm ISI in DTP 2 Interaction group x complexity Van der Werf N=22 subjects Groeniger Verbal Category Brown- Concept NP scores et al. 2003 (33) w/thalamic Intelligence Learning fluency Petersen shifting scaled to lacunar infarct Test Test paradigm Trails B ordinal: NP 3 m – 24 yrs Cognitive immediate Digit span Stroop normal, after index Screening and delayed Concentratio Tower of mildly event Test recall, recog n endurance London impaired, Portable Rey Paper/pencil Wisconsin strongly Mental Osterrieth scanning Card Sorting impaired. Status Complex test Episodic Question- Figure memory naire delayed impaired in recall n=3 subjects,
3 Warrington frontal Recog functions Memory and/or Test for attentional Faces processes Visual impaired in Association n=8 subjects test Recall of word triplets Van N=16 subjects Rey BNT TMT A Digit span TMT B-A Rey NP scores Zandervoort et with Osterrieth Letter Corsi blocks Similarities Osterrieth impaired al. 1998 (34) symptomatic Complex fluency TEA Complex compared to supratentorial Figure Category Elevator Figure copy NC on: lacunar stroke delayed fluency TEA Lottery Rey-O N=16 NC recall delayed NP 6 to 45 m recall after stroke BNT TEA visual elevator TEA lottery Similarities McMurtray et N=8 subjects MMSE AVLT Letter Digit span Proverbs CERAD NP raw al. 2008 (35) with caudate fluency Serial threes Category construction scores stroke stroke Comprehen Arithmetic assignment subjects < N=8 Controls sion Luria Hand controls on: with subjective Repetition sequence MMSE memory Mini-BNT Go-no-go Episodic complaints Luria memory alternating tests, all programs executive functioning tests Grau-Olivares N=40 subjects RAVLT Letter TMT A Digit span TMT B Luria Block 57.5% et al. 2007 (36) with first-ever WMS Visual fluency Digit Stroop manual Design classified as lacunar stroke Reproductio Category Symbol interference sequences Benton MCI-V: NP 1 m. After n fluency Luria Judgement Syndrome index event BNT manual of Line associated Token test sequences orientation with greatest impairment atypical lacunar symdrome Gainotti et al. N=39 >= two MMSE RAVLT Letter Digit span Raven’s Construct- NP scores 2004 (37) subcortical imm/del/ fluency Line matrices ional praxis used for ischemic lesions recognition cancellation Ideomotor classification
4 Immediate Multiple praxis into visual features dementia memory cancellation and no task dementia: MMSE<24, >=2 RAVLT scores impaired >= 1 other NP score impaired 64% dementia
5 Table e-2. Data extraction for neuropsychological assessments in longitudinal studies of cognitive function after symptomatic lacunar infarct
Studies Global Learning & Information Language Information Attention / Executive functioning Praxis / Visuo-spatial Methods / cognition Memory / processing Working Motor /Constructio Findings Orientation speed memory function n
Anderson IQCODE Rivermead WAIS Letter WAIS WAIS Digit Clock drawing Clock NP raw and et al. SMMSE behavioural Information fluency Arithmetic Span WAIS Similarities drawing domain scores 2008 (32) memory test KSNAP WAIS KSNAP Four Letter Rey compared to RAVLT Mental Arithmetic Words Complex controls; Immediate Status WAIS Digit Figure Copy domain scores & delayed Symbol WAIS for MCI recall KSNAP Picture classification: Rey Mental Completion No group Complex Status WAIS Block impairment at Figure KSNAP Design BL and FU on Immediate Number KSNAP any domain / & Delayed Recall Gestalt test; 7% multi- recall Closure domain MCI Mok et al. MMSE Mattis Dementia NP raw scores 2008 (18) ADAS-cog Rating Scale compared to Initiation/Perseveration controls: Large, comparable group impairments at BL and FU Nitkunan North WMS WAIS D-KEFS WMS Digit WAIS Matrix D-KEFS WAIS NP age- et al. American Logical Vocabulary Trails motor span reasoning Trails motor Matrix corrected 2008 (19) Reading Memory D-KEFS speed forwards & D-KEFS Trails speed reasoning individual and Test Immediate Letter backwards switching composite MMSE & Delayed fluency scores: no recall longitudinal change on single tests or on global and executive function
6 composite scores Rasquin AVLT CAMCOG CAMCOG Stroop Groniger Stroop Colour Word CAMCOG Groniger NP scores used et al. Immediate orientation language Naming Intelligence Concept shifting praxis Intelligence for VMCI 2007 (20) & Delayed subtest subtest scale CAMCOG abstract subtest scale subtest classification Calculation reasoning (<10th CAMCOG percentile on attention any test): 75% subtest at BL, 60% at FU, no amnestic MCI Van RAVLT Boston Trails A WAIS Digit Trails B Benton NP raw scores Zandvoort Immediate Naming span WAIS Similarities* Judgement of compared to et al. & Delayed Test* Corsi TEA Visual Elevator& Line controls: 2001 (21) Rey Token Test Blocks Test Orientation Moderate, Complex Letter Rey comparable figure fluency Complex group immediate Category figure Copy impairments at & delayed fluency* WAIS Block BL and FU on recall* Chapman Design memory, reading task language, and executive functioning tests marked*
7 Table e-3. Neuropsychological measures used in the calculation of the effect-size estimates
Global Cognition N Studies Scales/ Sub-composite Composite 1 Anderson et al 2008a S-MMSE - 2 Babikian et al 1990 MMSE - 3 McMurtray et al 2008 MMSE - 4 Mok et al 2008 MMSE - 5 O'Sullivan et al 2005 Composite WAIS-R performance IQ/ WAIS-R verbal IQ Processing speed 1 Anderson et al 2008a WAIS-R digit - symbol 2 O'Sullivan et al 2005 Digit symbol - 3 Van Zandvoort et al 2003 TMT-A - 4 Van Zandvoort et al 2005 Trailmaking - Visuospatial/construction 1 Anderson et al 2008a Composite Clock drawing test/KSNAP-gestalt closure/RCFT-copy/WAIS-R block design/ WAIS-R picture completion 2 Babikian et al 1990 Composite Visuospatial- author defined 3 O'Sullivan et al 2005 Composite WAIS-R block design/ WAIS-R object assembly 4 Van Zandvoort et al 2001 Benton - judgment of line orientation (ms) 5 Van Zandvoort et al 2003 Rey-O copy - 6 Van Zandvoort et al 2005 Rey-O complex - figure copy Executive functioning
8 1 Anderson et al 2008a Composite KSNAP-four letter word/ WAIS-R similarities 2 Mok et al 2008 MDRS-I/P - 3 O'Sullivan et al 2005 Composite Trail making B-A/WAIS-R comprehension/WAIS-R similarities/WCST-total errors 4 Van Zandvoort et al 2001 Composite Task of everyday attention-visual elevator/WAIS- similarities 5 Van Zandvoort et al 2003 Composite TMT interference/WAIS-similarities 6 Van Zandvoort et al 2005 Composite Trailmaking interference/ WAIS-similarities Memory 1 Anderson et al 2008a Composite RAVLT-total/RBMT 2 Babikian et al 1990 Composite Memory- author defined 3 McMurtray et al 2008 Composite Non-verbal (delayed recall and recognition)/verbal (delayed recall and recognition) 4 O'Sullivan et al 2005 Composite PAL/WMS-total 5 Van Zandvoort et al 2001 Rey-Osterrieth - delayed recall 6 Van Zandvoort et al 2003 Composite Rey-O delayed recall/Rey-O immediate recall Language 1 Anderson et al 2008a COWAT-FAS - 2 Babikian et al 1990 Composite Language-author defined 3 McMurtray et al 2008 Composite Mini BNT/verbal fluency 4 O'Sullivan et al 2005 Composite Verbal fluency/WAIS-R vocabulary 5 Van Zandvoort et al 2001 Composite BNT/Category fluency 6 Van Zandvoort et al 2003 Composite BNT/Category fluency/Letter fluency 7 Van Zandvoort et al 2005 Composite BNT/Category fluency/Verbal fluency Attention 1 Anderson et al 2008a Composite WAIS-R arithmetic/WAIS-R digit span 2 Babikian et al 1990 Composite Attention- author defined 3 McMurtray et al 2008 Composite Digit span reverse/digit span forward
9 4 O'Sullivan et al 2005 Digit span - backward 5 Van Zandvoort et al 2003 Composite Corsi block span/Digit span total/ TEA lottery/ TEA visual elevators time 6 Van Zandvoort et al 2005 Composite Corsi block tapping task/ Digit span/ TEA lottery/ TEA visual elevator accuracy. Abbreviations: BNT=Boston Naming test/task; TEA=Task of Everyday Attention; RAVLT=Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test; WAIS- R=Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale- revised; COWAT-FAS=Controlled oral word association test; Rey-O=Rey-Osterrieth; PAL=Paired Associated Learning; WMS=Wechsler Memory Scale; RBMT=Rivermead Behavioral Memory Test; WCST=Wisconsin Card Sorting Test; KSNAP=Kaufman Short Neuropsychological Assessment Procedure; MDRS-I/P=Mattis Dementia Rating Scale-Initiation/perseveration subset; TMT=Trail Making Test; RCFT=Rey-Osterrieth complex figure test; S-MMSE=Standardized Mini Mental State Examination; nc=number correct; rs=raw score; ms=millisecond
10 Table e-4. Heterogeneity in cognitive domains, adjusted for moderating factors significant for at least one cognitive domain
(neuropsychological protocol, time since stroke, study design and sampling frame)
Statistics Domains Moderating Description N Q- P- I2 (Studies) Factors value value MMSE 3 6.58 0.04 69.61 NP Protocol Composite 1 - - - Single-other 1 - - - Short (≤ 3m) 3 10.02 0.01 80.03 Global Time Since Stroke Long (> 12m) - - - - Cognition NR 2 1.15 0.28 12.72 (N=5) CS 3 2.36 0.31 15.14 Design L 2 3.70 0.06 72.94 Hospital 4 6.64 0.08 54.81 Sampling Frame Population 1 - - - Composite 5 5.83 0.21 31.40 NP Protocol Single-other 1 - - - Short (≤ 3m) 2 11.50 0.00 91.31 Executive Time Since Stroke Long (> 12m) 2 0.01 0.93 0.00 Function Unclear 2 1.60 0.21 37.41 (N=6) CS 3 1.86 0.40 0.00 Design L 3 11.55 0.00 82.68 Hospital 5 6.20 0.19 35.48 Sampling Frame Population 1 - - - Visuospatial Composite 3 9.23 0.01 78.33 NP Protocol Processing Single-other 1 - - - (N=6) Time Since Stroke Short (≤ 3m) 1 - - - Long (> 12m) 2 2.18 0.14 54.09
11 NR 3 1.46 0.48 0.00 CS 4 2.85 0.42 0.00 Design L 2 7.06 0.01 85.84 Hospital 5 3.79 0.44 0.00 Sampling Frame Population 1 - - - NP Protocol Single-other 1 - - - Short (≤ 3m) 1 - - - Time Since Stroke Long (> 12m) 1 - - - Information Processing NR 2 3.31 0.07 69.81 Speed CS 3 4.23 0.12 52.74 (N=4) Design L 1 - - - Hospital 3 4.23 0.12 52.74 Sampling Frame Population 1 - - - N=number of studies; NP=neuropsychological; NR=Not reported; CS=cross-sectional design; L=longitudinal design; m=months
12