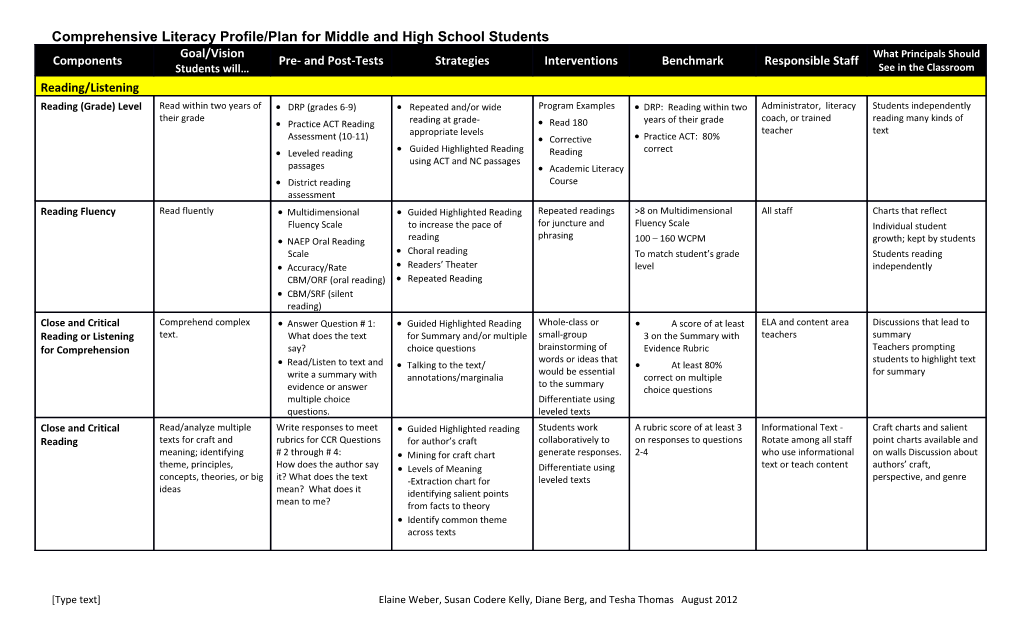
Comprehensive Literacy Profile/Plan for Middle and High School Students Goal/Vision What Principals Should Components Pre- and Post-Tests Strategies Interventions Benchmark Responsible Staff Students will… See in the Classroom Reading/Listening Reading (Grade) Level Read within two years of DRP (grades 6-9) Repeated and/or wide Program Examples DRP: Reading within two Administrator, literacy Students independently their grade coach, or trained reading many kinds of Practice ACT Reading reading at grade- Read 180 years of their grade appropriate levels teacher text Assessment (10-11) Corrective Practice ACT: 80% Leveled reading Guided Highlighted Reading Reading correct using ACT and NC passages passages Academic Literacy District reading Course assessment Reading Fluency Read fluently Multidimensional Guided Highlighted Reading Repeated readings >8 on Multidimensional All staff Charts that reflect Fluency Scale to increase the pace of for juncture and Fluency Scale Individual student phrasing NAEP Oral Reading reading 100 – 160 WCPM growth; kept by students Scale Choral reading To match student’s grade Students reading Accuracy/Rate Readers’ Theater level independently CBM/ORF (oral reading) Repeated Reading CBM/SRF (silent reading) Close and Critical Comprehend complex Answer Question # 1: Guided Highlighted Reading Whole-class or A score of at least ELA and content area Discussions that lead to Reading or Listening text. What does the text for Summary and/or multiple small-group 3 on the Summary with teachers summary for Comprehension say? choice questions brainstorming of Evidence Rubric Teachers prompting words or ideas that students to highlight text Read/Listen to text and Talking to the text/ At least 80% would be essential for summary write a summary with annotations/marginalia correct on multiple to the summary evidence or answer choice questions multiple choice Differentiate using questions. leveled texts Close and Critical Read/analyze multiple Write responses to meet Guided Highlighted reading Students work A rubric score of at least 3 Informational Text - Craft charts and salient Reading texts for craft and rubrics for CCR Questions for author’s craft collaboratively to on responses to questions Rotate among all staff point charts available and meaning; identifying # 2 through # 4: Mining for craft chart generate responses. 2-4 who use informational on walls Discussion about theme, principles, How does the author say Levels of Meaning Differentiate using text or teach content authors’ craft, concepts, theories, or big it? What does the text -Extraction chart for leveled texts perspective, and genre ideas mean? What does it identifying salient points mean to me? from facts to theory Identify common theme across texts
[Type text] Elaine Weber, Susan Codere Kelly, Diane Berg, and Tesha Thomas August 2012 Comprehensive Literacy Profile/Plan for Middle and High School Students Goal/Vision What Principals Should Components Pre- and Post-Tests Strategies Interventions Benchmark Responsible Staff Students will… See in the Classroom Profundity for Reading Read fiction and Respond to the scales of Written or oral response to Students work Internalized profundity ELA teachers Literature discussion Fiction determine the profundity with a piece of each plane of the profundity collaboratively to applied seamlessly focusing on character that themes/principles/big fiction scored using the scale. generate responses leads to theme and life ideas. profundity scales. to each plane of the lessons scale Read Informational Recognize argument in Analyze text written as Inquiry and/or GHR to identify Differentiate using MS: Correctly identify claim All teachers using Students using the Text for Argument text argument to identify the and compare Toulmin’s leveled argument and evidence. informational text and Stephen Toulmin's parts of an argument: elements of argument: claim, texts HS: Correctly identify claim, literary non-fiction elements of argument in claim, evidence, evidence, counterclaim, and evidence, counterclaim, discussion counterclaim, and rebuttal rebuttal and rebuttal. Graphic organizers
Writing/ Speaking Modes of Discourse Compose written and All-school writing to Shift focus from narrative; “They Say, I Say” Students score at least a 3 ELA and content- area Students’ access to spoken narrative, prompts or performance increase informative/ templates on the Smarter Balanced teachers rubrics for each mode of informative/explanatory, tasks. Score with SBAC explanatory, and argument. Graphic organizer rubrics for argument and discourse, informative/explanatory exemplary writing pieces, and argumentative text. and MEAP/MME rubrics Mini lessons on Smarter for structure Balanced rubric traits, text Text structure writing and Toulmin’s elements structure, and formal style card game of an argument (CCSS Appendix C Student writing samples) Text structure charts Text structure card game Use mentor texts as models for student writing Analyze and discuss traits of mentor texts Go Edit Card Game Revision Rummy
Writing Fluency Write continuously for Choice or prompted Writing Tracker Brainstorm verbs MS: 100–125 words per 5 Rotate among Writing tracker folders five minutes. writing for five minutes. Quick writes and nouns minutes mathematics, science, with pieces of writing and Students count and record Prompted writes Mnemonics (ex: HS: 125-150 words social studies tracker chart the number of words per 5 minutes Turn and talk in preparation parts on your Students writing during written. Students score at least a 3 for writing. fingers) content-area class time on the Smarter Balanced Text structure card game
[Type text] Elaine Weber, Susan Codere Kelly, Diane Berg, and Tesha Thomas August 2012 Comprehensive Literacy Profile/Plan for Middle and High School Students Goal/Vision What Principals Should Components Pre- and Post-Tests Strategies Interventions Benchmark Responsible Staff Students will… See in the Classroom Brainstorm domain-specific rubric for brief writing words
Persuasive Writing Create a persuasive essay ACT prompt/rubric Pro-Con research, discussion, Provide students ACT Standards ELA high school The ACT rubrics and on demand. Practice ACT Assessment and debates with research on rubric scored, revised to a 5 teachers sample persuasive essays Electronic version on Analyze and discuss methods opposing or 6 Essays from the previous MeL.org th used in effective persuasive viewpoints. year’s 11 grade students Student ACT writing texts. Graphic organizers Students writing/revising exemplars Mini-lessons on ACT rubric for structure traits, text structure, and formal style Persuasive writing prompts Steps for revising ACT writing to score of 5 or 6
Handwriting Write legibly and fluently Students copy a passage Training on Letters per minute: All teachers Legible student writing for 1.5 minutes. Score ---- proper holding of Students score at level with grade level/gender pencil (ex: hold consistent with grade chart and legibility rubric. cotton ball with level and gender ring finger and Score at least 4 on rubric pinky) for legibility Practice copying text
Oral Language Speak in complete Middle School: Recite the Students select 2-3 sentences More practice with Recite with complete, All teachers Students speak in an sentences with proper Pledge of Allegiance from text and read out loud to Readers’ Theater, coherent sentences articulate manner pronunciation and High School: Gettysburg small groups to enhance choral reading, prosody. Address listeners’ understanding of the repeated readings, content. and recitation of Score with rubric Readers’ Theater poetry. Choral reading Repeated readings Poetry Recitation
[Type text] Elaine Weber, Susan Codere Kelly, Diane Berg, and Tesha Thomas August 2012 Comprehensive Literacy Profile/Plan for Middle and High School Students Goal/Vision What Principals Should Components Pre- and Post-Tests Strategies Interventions Benchmark Responsible Staff Students will… See in the Classroom
Word Study Vocabulary Acquire general Pre and post with a cloze GHR for Vocabulary Struggling students 100% of Grade and All teachers Self-awareness chart, should be given academic vocabulary procedure on selected Marzano’s 6 Steps content- appropriate data chart, word walls, more opportunities knowledge, particularly words Vocabulary Squares academic vocabulary words evidence of vocabulary words found on the Pre-Assessment : for speaking, from Smarter Balanced activities Frayer Concept Attainment Smarter Balanced grade Vocabulary self-awareness writing, and using grade level vocabulary list Model level vocabulary list chart the words through Post assessment : Jim Linear Arrays activities listed Burke Vocabulary Squares Vocabulary Trees under strategies. Vocabulary Notebook Word sorts Word Lists (SBAC, academic and domain-specific)
Spelling Understand how words Words their Way Upper Word study activities Activities to support Spelling skills up through ELA Teachers Appropriate word study students’ stage are constructed level spelling inventory Syllables, affixes and derivational relations stage activities through derivational Feature guides derivational relations relations stage (ex: Students analyze their word sorts, spelling assessment using the separating root feature analysis chart. They words, prefixes, document areas of need. suffixes, etc.)
Grammar and Word Usage Grammar of the ACT and Use correct grammar and Identify and correct 15 Guided Highlighted Use diagnostic tests Students score at least 80% English teachers and/or Guided Highlighted ELA Common Core word usage in the errors of grammar and Reading for grammar errors for continued on assessment literacy coaches Reading activities for Standards context of text at the word usage (ACT English and word usage progress monitoring grammar errors and word appropriate grade level Test Preparation from usage Mini-Lessons (10 min.) Correction and Dakota State University) based on student need explanations of Students collaborating to or Peer editing practice grammar and word identify grammar errors ACT mock assessment for usage – limit to 2-3 and make corrections Mock assessments grammar and word usage. daily with explanations of choice Short grammar mini- Grammar assessments Use diagnostic tests One-to-one teacher lessons from MISD HS Literature for continued progress student conferences Units monitoring Additional mini- lessons based on
[Type text] Elaine Weber, Susan Codere Kelly, Diane Berg, and Tesha Thomas August 2012 Comprehensive Literacy Profile/Plan for Middle and High School Students Goal/Vision What Principals Should Components Pre- and Post-Tests Strategies Interventions Benchmark Responsible Staff Students will… See in the Classroom student need
[Type text] Elaine Weber, Susan Codere Kelly, Diane Berg, and Tesha Thomas August 2012