ACCOUNTACY
ACCOUNTANCY CLASS XII
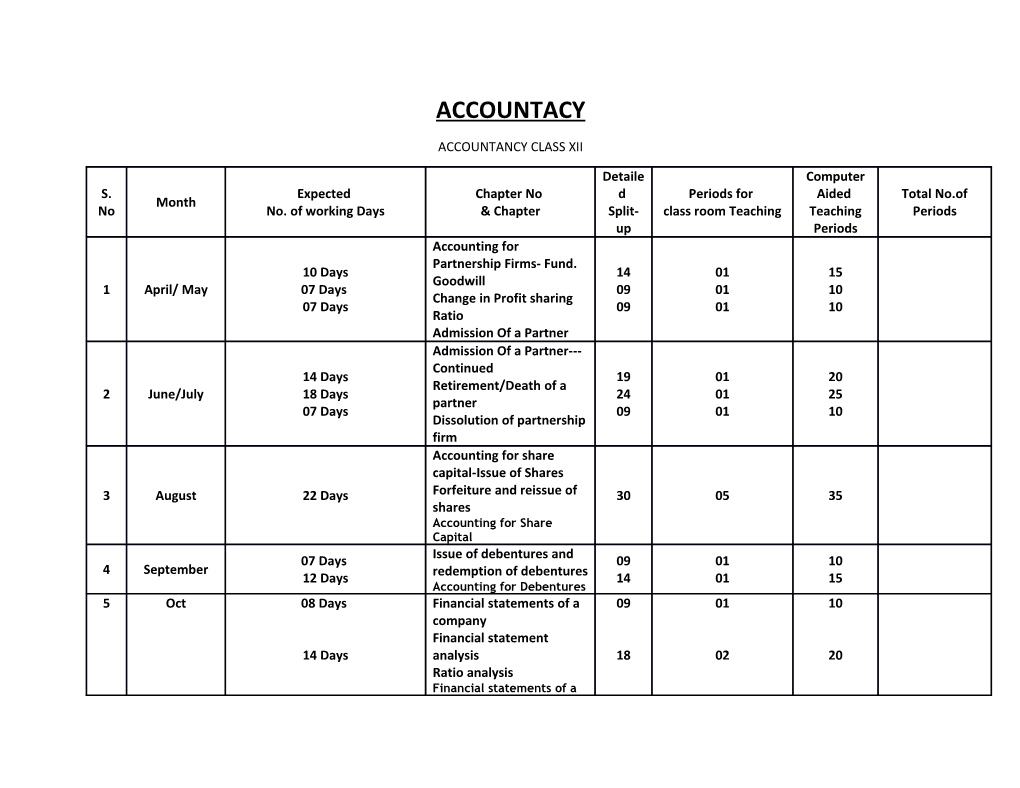
Detaile Computer S. Expected Chapter No d Periods for Aided Total No.of Month No No. of working Days & Chapter Split- class room Teaching Teaching Periods up Periods Accounting for Partnership Firms- Fund. 10 Days 14 01 15 Goodwill 1 April/ May 07 Days 09 01 10 Change in Profit sharing 07 Days 09 01 10 Ratio Admission Of a Partner Admission Of a Partner--- Continued 14 Days 19 01 20 Retirement/Death of a 2 June/July 18 Days 24 01 25 partner 07 Days 09 01 10 Dissolution of partnership firm Accounting for share capital-Issue of Shares 3 August 22 Days Forfeiture and reissue of 30 05 35 shares Accounting for Share Capital 07 Days Issue of debentures and 09 01 10 4 September 12 Days redemption of debentures 14 01 15 Accounting for Debentures 5 Oct 08 Days Financial statements of a 09 01 10 company Financial statement 14 Days analysis 18 02 20 Ratio analysis Financial statements of a company Ratio analysis ---Cont. 6 NOv 14 Days Cash Flow Statement 18 02 20 Solvency Ratios 7 Dec/Jan/Feb Project work and revision
BIOLOGY Detailed Expected Split-up Computer Total No. S. Branch Chapter No Periods for Aided Month No.of of No of Subject & Chapter class room Teaching Teaching working Periods Periods Days 1 April 22+8 UNIT-6 Chap- Chapter-1: 27 03 30 And (Reproduct 1 to 4 Reproduction in Organisms May ion Chapter-2: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Chapter-3: Human Reproduction Chapter-4: Reproductive Health Practical-Study of pollen germination on a slide Isolation of DNA from available plant material Study and identify stages of gametic development i.e T.S. of Testis and T.S. of ovary from permanent slides. Study of flowers adapted to pollination by different agencies
2 June & 8+25 Genetics Chap-5,6,7 Chapter-5: 30 3 33 July and Principles of Inheritance Evolution and Variation (Unit-VII) Heredity and variation: Chapter-6: Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chapter-7: Evolution Practical- Study of T.S. of Blastula through permanent slide Study of meiosis from prepared slides
Study of pedigree from prepared charts Chapter-8: Human Health and Diseases Chapter-9: Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Practical- Exercise on controlled pollination- Biology emasculation, and tagging etc. 3 August 22 Human Chap-7 contd,8,9 To identify 20 02 22 welfare common diseases (Unit-VIII) Study the effect of different temperatures and three different pH on the activity of salivary amylase on starch
4 Septemb 16 Unit-VIII Chap-10-12 Chapter-10: 20 03 23 er and Microbes in Human Unit-IX Welfare (Biotechno Chapter-11: logy) Biotechnology - Principles and processes Chapter-12: Biotechnology and its Application
Practical-Study and comment on Xerophytic and aquatic plants and animals Study of pH , clarity and presence of any living organism in water sample Prepare a temporary mount of onion root tip to study mitosis.
5 October 22 Ecology Chap Chapter-13: 14 02 16 And (Unit-X) 13-16 Organisms and Populations Novemb Chapter-14: er Ecosystem Chapter-15: Biodiversity and its Conservation Chapter-16: Environmental Issues Practical- Collect and study soil, texture, moisture etc Study pH and water holding capacity of different soil samples Study presence of suspended particulate matter in air Population density and population frequency by quadrate method.
BUSINESS STUDIES
Expected Periods for S. No.of Chapter No Detailed Computer Aided Total No.of Month class room No working & Chapter Split-up Teaching Periods Periods Teaching Days Nature and significance of 11 Days management 13 01 1 April 14 11 Days Principles of management 13 01 14 08 Days Business environment 01 12 2 May 11
Planning 3 June 08 Days 01 14 13
Planning ----Continued 03 Days Organizing 01 18 4 July 14 Days 17 Staffing 01 16 08 Days 15 Staffing---Cont. 04 Days Directing 17 01 18 5 August 14 Days Controlling 13 01 14 04 Days Controlling---Cont. 07 Days 6 Sept Financial management 16 Days 20 02 22
Financial market 20 12 Days 18 02 7 Oct Marketing management 04 Days 30 02 32 Marketing management---Cont. Consumer Protection
Project work 8 Product- Concept, branding, labelling and 16 Packaging Price- Concept, Factors determining price Physical Distribution - concept and components, channels of distribution: types, choice of channels. Promotion – Concept and elements; advertising concept, role, objections against advertising, Nov personal selling-concept and qualities of a 15 good 01 salesman, sales promotion- concept and techniques, public relations- concept and role Concept and importance of consumer protection Consumer protection Act 1986: Meaning of consumer and consumer protection. Rights and responsibilities of consumers 30 9 Who can file a complaint against whom? Redressal machinery Remedies available Consumer awareness- Role of consumer organizations and Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs). CHEMISTRY
Total S. Expected Chapter No Detailed Computer Aided Month No.of No No.of working Days & Chapter Split-up Teaching Periods Periods
1 April 22 Unit I: Solid State 9 10
Unit II: Solutions 9 10 Unit III : Electrochemistry 11 12 2 May 16 Unit IV: Chemical Kinetic 9 10 &June
3 July 25 Unit V: Surface Chemistry 7 8
Unit VI: General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements 7 8
4 August 22 Unit VII: "p"-Block Elements 11 12
Unit VIII: "d" and "f" Block Elements 11 12 Unit IX: Coordination Compounds 11 12 5 Septemb 23 Unit X: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes. 9 10 er Unit XI: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers 9 10
Unit XII: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids 9 10 6 OCTOBER 17 Unit XIII: Organic compounds containing Nitrogen 9 10
Unit XIV: Biomolecules 11 12
Unit XV: Polymers 7 8 Unit XVI: Chemistry in Everyday life
5 6 Novemb 7 18 Revision Remedial Step to be taken by teacher er according to student’s requirements Decemb Revision and First 8 20 Remedial Step to be taken by teacher er Pre-board according to student’s requirements Revision and 9 January 15 Remedial Step to be taken by teacher Second Pre-board according to student’s requirements 10 February 22 Revision Remedial Step to be taken by teacher according to student’s requirements ANNUAL BOARD 11 March EXAMINATION COMPUTER SCIENCE (THEORY)
S. Mont Expected No. of Working Days Detailed Split Up Syllabus Periods for class room Teaching C Total No. of N h A Periods o. D
T e a c h i n g
P e r i o d 1. April 22 REVIEW: C++ covered In Class – 18+09 0 31 XI, 4
Object Oriented Programming: OOPs Concepts, Advantages of Object Oriented Programming over earlier programming methodologies, Implementation of Object Oriented Programming concepts in C++: Definition of a class, Member of a class – Data Members and Member Functions (methods), Using Private and Public visibility modes, default visibility mode (private); Member function definition: inside class definition and outside class definition using scope resolution operator (::); Declaration of objects as instances of a class; accessing members from object (s), Objects as function arguments–pass by value and pass by reference; 2. May, 08 + 08 + 25 = 41 Constructor and Destructor 36+16 0 57 June Inheritance: Concept, Base Class, 5 & July Derived classes, protected visibility mode; Single level inheritance, Multilevel inheritance and Multiple inheritance, Privately derived, publicly derived and Protectedly derived class, accessibility of members from objects and within derived class (es); Data File Handling: Need for a data file, Types of data files – Text file and Binary file; Text File: Basic file operations on text file, Binary File: Creation of file, Writing data/Searching required data/Appending data/Insertion of data/ Deletion of data/Modification of data in a file; Components of C++ to be used with file handling: Header file: fstream.h; ifstream, ofstream, classes; Open(), get (), read () put (), write(), getline() and close() functions; Detecting end-of-file (with or without using eof() function), tellg(), tellp(), seekg().seekp(); Introduction to Pointer, Declaration and Initialization of Pointer; Dynamic memory allocation/de-allocation operators: new, delete; Pointers and Arrays: Array of Pointers, Pointer to an array (1 dimensional array), Function returning a pointer, Reference variables and use of alias; Function call by reference. Pointer to structure: De-reference/Deference operator: *, ->; self referential structure; 3. Aug. 22 Array: Searching, Sorting, 18 + 10 0 32 Merging 4 Stack (Array and Linked implementation of Stack):Stack, PUSH and POP Operations and its Implementation, Converting expressions from INFIX to POSTFIX notation and evaluation of Postfix expression; Queue: (Array and Linked Implementation):Introduction to Queue, Operations on Queue, circular queue using array. 4. Sep. 23 Data base Concepts, Relational 20+ 14 0 37 data model, Relational algebra, 3 Structured Query Language, Advantages of using SQL, DDL & DML, Data Types, SQL Commands, SQL functions, SELECT query, equi-join, Cartesian product and Union Role of Logical Operations in Computing. Binary-valued Quantities, Boolean Variable, Boolean Constant and Boolean Operators, Truth Tables; DeMorgan‟s Law and their applications; Obtaining SOP and POS form the Truth Table, Reducing Boolean Expression (SOP and POS) to its minimal form, Use of Karnaugh Map for minimization of Boolean expressions (up to 4 variables);circuit design using basic Logic Gates 5. Oct. 16 Evolution of Networking, Data 14 + 03 0 19 Communication terminologies, 2 Transmission media, Network Topologies and types, Network Protocol, Mobile Telecommunication Technologies, Network Security Concepts, Introduction To Web services (Syllabus Completion upto 31 st October) Revision Work& Pre-Boards Economics Comput Periods er Aided for S. Expected Chapter No Detailed Total No. of Month class No No. of working Days & Chapter Split-up Teachin Periods room g Teaching Periods 1 April 22 Economics 36 2 38 Introduction: Meaning of micro and macroeconomics what is an economy . central problem of an economy. What, how and for whom to produce : concept of PPC and opportunity cost Consumers equilibrium meaning of utility, marginal utility law of diminishing marginal utility conditions of consumers equilibrium using marginal utility analysis. Indifference curve analysis of consumer’s equilibrium the consumers budget (budget set and budget line), preferences of the consumers (indifference curve, indifference map )and conditions of consumers equilibrium. Demand market demand determinants of demand, demand schedule, demand curve and its slope, movement along and shifts in the demand curve: price elasticity of demand – a- %age change method and b- geometric method (linear demand curve ; relationship between price elasticity of demand and total expenditure.
Producer Behaviour and Supply Production function – Short- Run and Long-Run Total 2 May/June 16 Product, Average Product and 18 2 20 Marginal Product. Returns to a Factor 3 July 25 Producer Behaviour and Supply 34 4 38 Forms of Market and Price Determination under Perfect Competition with simple applications Cost: Short run costs - total cost, total fixed cost, total variable cost; Average cost; Average fixed cost, average variable cost and marginal cost-meaning and their relationships. Revenue - total, average and marginal revenue - meaning and their relationships. Producer's equilibrium- meaning and its conditions in terms of marginal revenue- marginal cost. Supply, market supply, determinants of supply, supply schedule, supply curve and its slope, movements along and shifts in supply curve, price elasticity of supply; measurement of price elasticity of supply - (a) percentage-change method and (b) geometric method. Forms of Market and Price Determination under Perfect Competition with simple applications. Perfect competition - Features; Determination of market equilibrium and effects of shifts in demand and supply. Other Market Forms - monopoly, monopolistic competition, oligopoly - their meaning and features. Simple Applications of Demand and Supply: Price ceiling, price floor. Forms of Market and Price Determination under Perfect Competition with simple applications.
4 August 22 National Income and Related 36 2 38 Aggregates ,Some basic concepts: consumption goods, capital goods, final goods, intermediate goods; stocks and flows; gross investment and depreciation. Circular flow of income; Methods of calculating National Income - Value Added or Product method, Expenditure method, Income method. Aggregates related to National Income: Gross National Product (GNP), Net National Product (NNP), Gross and Net Domestic Product (GDP and NDP) - at market price, at factor cost; National Disposable Income (gross and net), Private Income, Personal Income and Personal Disposable Income; Real and Nominal GDP. GDP and Welfare. 5 September 23 Money and Banking, Money - 36 2 38 its meaning and functions Supply of money - Currency held by the public and net demand deposits held by commercial banks. Money creation by the commercial banking system. Central bank and its functions (example of the Reserve Bank of India): Bank of issue, Govt. Bank, Banker's Bank, Controller of Credit through Bank Rate, CRR, SLR, Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate, Open Market Operations, Margin requirement Aggregate demand & its components. Propensity to consume and propensity to save (average and marginal ). Short run equilibrium output; investment multiplier and its mechanism. Meaning of full employment and involuntary unemployment. Problems of excess demand and deficient; measures to correct them. Changes government spending taxes and money supply. 6 October 16 Government Budget and the 20 2 22 economy, Balance of Payments Government budget - meaning, objectives and components. Classification of receipts - revenue receipts and capital receipts; classification of expenditure –revenue expenditure and capital expenditure. Measures of government deficit - revenue deficit, fiscal deficit, primary deficit their meaning. Balance of payments account - meaning and components; balance of payments deficit-meaning. Foreign exchange rate - meaning of fixed and flexible rates and managed floating. Determination of exchange rate in a free market.
7 November 18 Revision
Revision and First Pre-board 8 December 20
Revision and Second Pre-board 9 January 15
Revision 10 February 22
English Core (301) S.No. Flamingo (Text BOOK) Vistas – (Supplementary Book) Reading and Periods of No. of Working Prose/Poem The Invisible Man – HG Wells Writing Skills Classroom Days / Period (Novel) Teaching (Discussion & Questions on Theme , Plot , Characters and Incidents) 1 L-1.The Last Lesson (Prose) L-1. The Tiger King (vistas) Poster Designing 16 22 (pds-4) (pds -4) (Social issues , general awareness P-1.My Mother at Sixty- Six Introduction to the novel & ,commercial (Poem)(pds2) novelist (The Invisible Man –HG issues) (pds 2) Wells)(pds-2) Letter to P-2. An Elementary School Editor(pds-2) Classroom In A Slum (Poem) Article writing (pds3) (pds- 3)
2. L-2. Lost Spring(Prose)(pds4) Thorough Discussion (The Recapitulation of 06 08 Invisible Man –HG Wells Note- Making and ,chapters 1-4)(pds-2) summarizing (pds- 2) 3. L-3. Deep Water(Prose)(pds3) Thorough Discussion (The Advertisements 06 08 invisible Man –HG Wells, chapters (classified and 5,6)(pds-2) display- To-Let ,for sale, Matrimonial, Obituary, Situation Vacant, etc)(pds -3)
4. P-3. Keeping Quiet – (Poem) L-2. The Enemy.(pds6) Speech Writing 19 25 (pds-3) L-3. Should Wizard Hit Mommy? (pds2 ) P-4. A Thing of Beauty (Poem) (pds3) Debate Writing (pds3) Discussion of chapters 7to 12 of (pds3) *I Unit Test the novel(pds3) Notice Writing (pds2)
5. L-4. The Rattrap (Prose) L-4. On The Face Of It.(pds5) Invitation Writing 17 22 (pds 5) Discussion Of Chapters 13 to 18 - Formal & (Novel) (pds4) Informal & Replies (acceptance & Decline) (pds 5) Reading comprehension (pds 3) 6. L-5. Indigo(Prose)(pds4) Discussion Of Chapters 19 to 24 Letter Of 12 16 + 7 days for P-5. Aunt Jennifer's Tigers (Novel)(pds3) Complaint Selection Test = (Poem (pds 4) (pds 2) 23 *Selection/ Achievement Test Letter of Placing Orders & Cancellation (pds3) 7. L-6.Going Places. (Prose) L-5.Evans Tries An 0-Level.(pds4) Letter of Enquiry 11 16 (pds 3) L-6.Memories of Childhood(pds 2) (pds2) Discussion of Chapters 25 to 28 Job Application (Novel)(pds 2) (pds 3) 8. *Half Yearly Revision(Chapters 1 to 6 ) Revision from 13 18 Question Bank Question Bank Theme, Plot, Characters and (Short and long incidents from Novel Compositions)
S.No. Flamingo (Text BOOK) Vistas – (Supplementary Book) Reading and Periods of No. of Working Prose/Poem The Invisible Man – HG Wells Writing Skills Classroom Days / Period (Novel) Teaching (Discussion & Questions on Theme , Plot , Characters and Incidents) 9. REVISION Revision , Revision 15 20 Value based Questions, HOTS Value based Questions, Reading & MLL HOTS & MLL Section and * I Pre-Board Letters 10. REVISION from Study Revision Revision 10 15 Material and Sample Papers Study Material and Sample Study Material and Discussion and solving I PB Papers Sample Papers QP Discussion and solving I PB QP Discussion and * II Pre-Board solving I PB QP 11. Revision Revision Revision 10 15 Study Material and Sample Study Material and Sample Study Material and Papers Papers Sample Papers SPLIT-UP SYLLABUS XII CLASS GEOGRAPHY 2016-17 MONTHS BOOK-1: PDS BOOK-1: PDS PRACTICALS PDS FUNDAMENTALS OF FUNDAMENTALS HUMAN GEOGRAPHY OF HUMAN GEOGRAPHY APRIL/ 1. Human Geography: 1. Population: 15 1.Data: Its Sources 7 MAY Nature and Scope Distribution, and Compilation 2. The World Population: Density, Growth 2. Data Processing Distribution, Density and 17 and Composition Growth 2. Migration: 3. Population Types, Causes and Composition Consequences JUNE/ 4. Human Development 3. Human 14 Part-1: Graphical JULY 5. Primary Activities Development Representation of 6. Secondary Activities 22 4. Human Data 14 7. Tertiary and Settlements Part II: Graphical Quaternary Activities Representation of Data AUGUST 8. Transport and 5. Land Resources 16 Use of Computer in Communication 16 and Agriculture Data Processing 12 9. International Trade 6. Water Resources and Mapping
SEPT. 9. International Trade 7. Mineral and 15 10. Human Settlements 15 Energy Resources 8. Manufacturing Industries OCT. REVISION 9. Planning and 22 Field Survey Sustainable Development in 6 Indian Context 10. Transport and Communication NOV. REVISION 11. International 20 Spatial Trade Information 8 12. Geographical Technology Perspective on Selected Issues and Problems DEC, REVISION & PB-1 REVISION JAN. REVISION & PB REVISION FEB. REVISION REVISION &PRACTICALS
हहहदद कम ससखखख मखह अननमखननत कखखर ददवस ववषख अधखखख ससखखख ववसतत� - कखलखसश कसपखपटर शशकण कखलखसश कन ल कखलखसश पखठखकम
1 अपपल 22 दहसदद कक 5 1.आतम पररचख, एक ग�त- २२ एक 4 हररवसश रखख बचचन 5 2.भक– �तन महखदकव� वमखर 4 3.ववशभनन ससचखर मखधखम� 4 कख पररचख 4 4.शसलवर वपड�सग- मन�हर शखखम ज�श� 5.ननबसध-लकखन (सखमकजक ववषख� पर) 2 मई-जपन 16 दहसदद कक 5 1.पत– सग आल�क धनवख १६ एक 3 2.कववतख कक बहखus, बखत 4 स– �ध� थ� पर कनस वर 4 नखरखखण 3 3.ब– खजखर दशरन जपनकन� 1 कन मखर 4.ससचखर– मखधखम पररचख वपसट म�ड�खख 5.ननबसध– लकखन सखदहकतखक ननबसध(दहसदद सखदहतख कख इनतहखस,रखष�भखषख दहसदद) 3 जनलखई 25 दहसदद कक 6 1.कपमरक– म� बसद अपखदहज २५ एक 4 रघनव�र सहखख 5 2.कखलक– मकघख पखन� दक 5 धमरव�र भखरत� 4 3.ज– पझ आनसद खखदव 4 4.समखचखर, पत लकखन– 2 (औपचखररकपत ) 5.न– नबसध समसखमखनखक ववषख� पर- नखरद- सशक�तकरण,२१व�स सदद कख भखरत) 6.समपखदक�ख पररचख 4 अगसत 22 दहसदद कक 6 1.सहषर– सव�कखरख हप २२ एक 5 मनक�तcks/k xtkuu 5 ek/ko 6 2 2.पहलवखन– क� ढ�लक Q.kh’ojukFk 2 रकणन 2 js.kq 3.अत�त– म� दबक पख�व ओम थखनव� 4.कखखखरलख� पत (पखचखखर ,समपखदक,सवखस�ख अधधकखरद कक नखम पत) 5.न– नबसध ववववध ववषख� पर(ववजखन: वरदखन खख अशभशखप, इनटरनकट) 6.समपखदक�ख - पखरप
5 शसतमबर 23 दहसदद कक 8 1.उषख– jk मकशवर बहखदरन २३ एक 2 शससह 3 2.बखदल रखग-ननर!लख 3 3-चखल�चपकपलन खखन� हम 3 सब-ववषणन खरक 8 4-नमक-रकजखख सजजखद 1 जहदर 1 5-�खखरद कक पननक-ऐन फ�क 1 6.ररप�टर एवस आलकख 7.र�जगखर समबनध� पत 8.सववसत� लकखन 6 अ�टपबर 17 दहसदद कक 7 1.कववतखवलद ,लकमण-मपच�खर १७ एक 4 और रखम– कख ववलखप 3 तनलस�दखस 3 3.रबखइखखस x जल-फ़�रखक 1 ग�रखपनरद 1 1 4.श�रद”k कक फप ल- हजखरद f} पसखद वकदद 2 5.फ�चर-लकखन 6. अपद�त- गदखखसश,पदखखसश 7.ननबनध-सखससक�नतक ववषख� ( ) पर ववशभननतख म� एकतख 2 8.��टख मकरख खकत-उमखशसकर ज�श� बगनल� कक पख-उमखशसकर ज�श� 9. शम- ववभखजन और जखनत- पथख-��. आसबक�कर मकरद कलपनख कख आदशर समखज- ��. आसबक�कर 7 नवमबर 18 दहसदद कक 4 3. ववशभनन समसखखओस पर १८ एक 4 ववभखग�ख अधधकखfj ख� क� 3 शलखक जखनक वखलक पत 4 2 4. पननर!व fRr पशन-पत- 6 अभखखस कखखर HISTORY
Chapter Detailed Total S. Expected No Split-up Computer Aided No. of Month P No No. of working Days & THEORY-80 MARKS Teaching Periods Period Chapter PROJECT-20 MARKS(start in April ) s
Ch. 1. Bricks, Beads and Bones April/M 01 30 Days Ch. 2. Kings, Farmers and Towns 36 43 ay Ch. 3. Kingship, Caste and class 02 June 08 Ch. 4.Thinkers, Beliefs and Buildings 10 12
Ch. 8. Peasants, Zamindars and the state 03 July 25 Ch.9. Kings and chronicles 23 26 Sr. No. of lesson in second part changed by C.B.S.E Ch. 7. An Imperial capital- Vijaya Nagar 04 August 22 Ch.6. The Bhakti-Sufi traditions 34 39 Ch.5. Through the eyes of the travellers Ch.10. Colonialism and the countryside 05 Sept 23 Ch.11. Rebels and the Raj 33 39 Ch. 12. Colonial cities
Ch. 13. Mahatma Gandhi 06 Oct 16 25 27 Ch.14 Understanding Partition
07 Nov 18 Ch. 15. Framing the constitution 12 14 08 Dec to Map work and revision Feb 1st Preboard-2015-16(Nov-Dec 2016) 2nd Preboard-2015-16(Jan 2017) Informatics Practices (065) S. No. Exp Chapter Detailed Split Up Syllabus Computer Aided Total ecte Teaching Period No. of d Period No. s of Wor king Day s 1. 22 Computer Networking: Overview, Communication Media, Wireless 02 24 Networkin Technologies, Network Devices, Types of network: LAN, g MAN, WAN, PAN,Network Topologies, Network Protocols; Domain name, MAC&IP Address, DNS, Network security, Internet Applications, Wireless/Mobile Communication, Network Security Concepts Open Source Concepts:OSS, FOSS/FLOSS examples, Open standards (WWW, HTML, XML, ODF, TCP,IP) Open Indian Language Computing: character encoding, Source UNICODE, different types of fonts (open type vs true type, Concepts static vs dynamic), entering Indian Language Text – phonetic and key map based, Inscript. 2. 08 + Revision All the programming concepts studied in class XI for 04 62 08 + Tour of Review. 25 = Class XI; Basic concept of Access-specifier for class members (data 41 Class & members and methods) Object; Basic concept of Inheritance Inheritanc Commonly used libraries: e; String class and methods: toString(), concat(), length(), Standard toLowerCase(), toUpperCase(),trim(), substring() Functions Math class methods: pow(), round() 3. 22 Database Accessing My SQL database using ODBC/JDBC to 02 28 Connectiv connect with database. ity Web application development: URL, Web server, Web Communicating with the web server, concept of Client and Applicatio Server Side n HTML based web pages covering basic tags Developm Creating and accessing static pages using HTML and ent. introduction to XML
HTML-I,II XML 4. 23 Review of RDBMS from Class XI 02 43 Database Database Fundamentals Concepts Concept of Database transaction, Committing and revoking a transaction using COMMIT and ROLLBACK. MYSQL Grouping Records: GROUP BY, Group functions - MAX(), Functions MIN(), AVG(), SUM(), COUNT(); using COUNT(*), DISTINCT clause with COUNT; Group Functions and Null Values. 5. 16 Constraint Displaying Data From Multiple Tables: Cartesian product, 04 30 s and Data Union, Intersection concept of Foreign Key, Equi-Join Manipulati Creating a Table with PRIMARY KEY and NOT NULL on constraints, Viewing Constraints, Viewing the Columns Command Associated with Constraints using DESC command. s ALTER TABLE for deleting column(s), modifying data type(s) of column(s),adding a constraint, enabling constraints, dropping constraints. DROP Table for deleting a table Front-end Interface: Introduction; content and features; identifying and using appropriate component (Text Box, Radio Button, Check Box, List etc. as learnt in Unit 2 (Programming)) for data entry, validation and display. IT- Back-end Database: Introduction and its purpose, Applicatio exploring the requirement of tables and its essential ns attributes. Front-End and Database Connectivity: Introduction, requirement and benefits Demonstration and development of appropriate Front-end interface and Back-end Database for e-Governance, e-Business and e-Learning applications Impact of ICT on society: Social, environmental and Economic benefits. In each of the above domains, identify at least two real-life problems, list the expected outputs and the input(s) required for the output, and describe the problem solving approach and develop relevant front-end interface and back-end database.(Syllabus Completion Up to 31st October) Revision Work& Pre-Boards) MATHS
S.NO. M Expect Subject Chapter No& Detailed Split-up Periods for Computer Aided Total No. o ed No. Chapter class room Teaching Periods of n of Teaching Periods t workin h g Days 1 A 22 MATHEM 1. Relations and 1.Types of relations: reflexive, 13 Pds 2 Pds 15 P ATICS Functions symmetric, transitive and R 2. Inverse equivalence relations. I Trigonometric One to one and onto L Functions functions, composite 3 Matrices functions, inverse of a function. Binary operations. 13 Pds 2 Pds 15 2.Definition, range, domain, principal value branch. Graphs of inverse trigonometric functions. Elementary properties of inverse trigonometric 23 Pds 2 Pds 25 functions. 3.Concept, notation, order, equality, types of matrices, zero and identity matrix, transpose of a matrix, symmetric and skew symmetric matrices. Operation on matrices: Addition and multiplication and multiplication with a scalar. Simple properties of addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication. Noncommutativity of multiplication of matrices and existence of non-zero matrices whose product is the zero matrix (restrict to square matrices of order 2).Concept of elementary row and column operations. Invertible matrices and proof of the uniqueness of inverse, if it exists; (Here all matrices will have real entries). 2 M 16 MATHEM 4. Determinants 4. Determinant of a square 23 Pds 2 Pds 25 A ATICS 5. Continuity and matrix (up to 3 x 3 matrices), Y Differentiability properties of determinants, minors, co-factors and & applications of determinants in finding the area of a
triangle. Adjoint and inverse J of a square matrix. U Consistency, inconsistency N and number of solutions of E system of linear equations by examples ,solving system of 18 Pds 2 Pds 20 linear equations in two or three variables (having unique solution) using inverse of a matrix. 5.. Continuity and differentiability, derivative of composite functions, chain rule, derivatives of inverse trigonometric functions, derivative of implicit functions. Concept of exponential and logarithmic functions. Derivatives of logarithmic and exponential functions. Logarithmic differentiation, derivative of functions expressed in parametric forms. Second order derivatives. Rolle's and Lagrange's Mean Value Theorems (without proof) and their geometric interpretation
3 J 25 MATHEM 6. Applications of rate of change of bodies, 8 Pds 2 Pds 10 U ATICS Derivatives increasing/decreasing L 7. Integrals functions, tangents and Y normals, use of derivatives in approximation, maxima and minima (first derivative test motivated geometrically and second derivative test given as 20 a provable tool)Simple --- 20 problems (that illustrate basic principles and understanding of the subject as well as real- life situations). 7. Integration as inverse process of differentiation. Integration of a variety of functions by substitution, by partial fractions and by parts, Evaluation of simple integrals of the following types and problems based on them.
A u g u Definite integrals as a limit of s a sum, Fundamental Theorem t of Calculus (without proof).Basic Properties of definite integrals and evaluation of definite integral 4 22 MATHEM 8. Applications of the 8. Applications in finding the 13 Pds 2 Pds 15 ATICS Integrals area under simple curves, 9. Differential especially lines, Equations. circles/parabolas/ellipses (in standard form only), Area between any of the two above said curves (the region should 15 Pds -- 15 be clearly identifiable). 9. Definition, order and degree, general and particular solutions of a differential equation. Formation of differential equation whose general solution is given. Solution of differential equations by method of separation of variables solutions of homogeneous differential equations of first order and first degree Solutions of linear differential equation of the type: 5 S 23 MATHEM 10. Vectors 10. Vectors and scalars, 13 Pds 2Pds 15 E ATICS 11. Three - magnitude and direction of a P T dimensional vector. Direction cosines and E Geometr1y direction ratios of a M *SELECTION TEST vector. Types of vectors B (equal, unit, zero, parallel and E collinear vectors), position R vector of a point, negative of a vector, components of a vector, addition of vectors, multiplication of a vector by a scalar, 13 Pds 2Pds 15 position vector of a point dividing a line segment in a given ratio.
Definition, Geometrical Interpretation, properties and application of scalar (dot) product of vectors, vector (cross) product of vectors, scalar triple product of vectors 11. Direction cosines and direction ratios of a line joining two points. Cartesian equation and vector equation of a line, coplanar and skew lines, shortest distance between two lines. Cartesian and vector equation of a plane. Angle between (i) two lines, (ii) two planes, (iii) a line and a plane. Distance of a point from a plane.
6 O 16 MATHEM 12. Linear 12. Introduction, C ATICS Programming related terminology such as T 13. Probability constraints objective function, O optimization different types of B linear programming (L.P.) 8 Pds 2 Pds 10 E problems, mathematical formulation of L.P. problems, R graphical method of solution for problems in two variables, feasible and infeasible regions(bounded and unbounded), feasible and 20 Pds 2 Pds 22 infeasible solutions, optimal feasible solutions (up to three non-trivial constraints). 13.-Conditional probability, multiplication theorem on probability, independent events, total probability Bayes’ theorem, Random variable and its probability distribution mean and variance of random variable. Repeated independent (Bernoulli) trials and Binomial distribution
PHYSICS
UNIT PERFORMANCE TEST S Expect TEST ed Branch Computer Total Chapter No Detailed Periods for Aided Month No.of of Concerned No.of N & Chapter Split-up class room Teaching Teaching workin Subject Periods Periods o g Days
First Term 1 April 22 Electrostatics Chapter–1: Electric Electric 8 2 10 Charges and Fields Charges; Conservatio n of charge, Coulomb's 15 law-force between two point charges, forces 25 between multiple charges; superpositio n principle and continuous charge distribution. Electric field, electric field due to a point charge, electric field lines, electric dipole, electric field due to a dipole, torque on a dipole in uniform electric field. Electric flux, statement of Gauss's theorem and its applications to find field due to infinitely long straight wire, uniformly charged infinite plane sheet and uniformly charged thin spherical shell (field inside and outside). Chapter–2: Electrostatic Electric 9 1 10 Potential and Capacitance potential, potential difference, electric potential due to a point charge, a dipole and system of charges; equipotenti al surfaces, electrical potential energy of a system of two point charges and of electric dipole in an electrostati c field. Conductors and insulators, free charges and bound charges inside a conductor. Dielectrics and electric polarization , capacitors and capacitance , combination of capacitors in series and in parallel, capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with and without dielectric medium between the plates, energy stored in a capacitor Electric current, flow of electric charges in a metallic conductor, Current Chapter–3: Current drift Electricity Electricity velocity, 2 0 2 mobility and their relation with electric current; Ohm's law, 2 May & 8+8 Current Chapter–3: Current electrical 7 1 8 June Electricity Electricity resistance, V-I characteristi cs (linear and non- linear), electrical energy and power, electrical resistivity and conductivity , Carbon resistors, colour code for carbon resistors; series and parallel combination s of resistors; temperature dependence of resistance. Internal resistance of a cell, potential difference and emf of a cell, combination of cells in series and in parallel, Kirchhoff's laws and simple applications , Wheatstone bridge, meter bridge. Potentiomet er - principle and its applications to measure potential difference and for comparing EMF of two cells; measureme nt of internal resistance of a cell. Magnetic Effects of Chapter–4: Moving Concept of 7 1 8 Current and Charges and Magnetism magnetic Magnetism field, Oersted's experiment. Biot - Savart law and its application to current carrying circular loop. Ampere's 15 law and its applications to infinitely long straight wire. Straight and toroidal 25 solenoids (only qualitative treatment), force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields, Cyclotron.
July 25 Magnetic Chapter–4: Moving Force on a 4 1 5 3 Effects of Charges and Magnetism current- Current and carrying conductor in Magnetism a uniform magnetic field, force between two parallel current- carrying conductors- definition of ampere, torque experienced by a current loop in uniform magnetic field; moving coil galvanomet er-its current sensitivity and conversion to ammeter and voltmeter.
Chapter–5: Magnetism and Current loop 6 1 7 Matter as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic dipole moment, magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron, magnetic field intensity due to a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) along its axis and perpendicul ar to its axis, torque on a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) in a uniform magnetic field; bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid, magnetic field lines; earth's magnetic field and magnetic elements. Para-, dia- and ferro - magnetic substances, with examples. Electromagn ets and factors affecting their strengths, permanent magnets. UNIT TEST - Ist Electromagn etic induction; Faraday's laws, induced EMF Electromagnetic Chapter–6: and current; Induction and Electromagnetic Induction Alternating Lenz's Law, 8 2 10 Currents Eddy currents. Self and mutual induction. Alternating currents, Chapter–7: Alternating peak and Current RMS value of 3 0 3 alternating current/volt age; 4 August 22 reactance and impedance; LC oscillations (qualitative treatment only), LCR series circuit, Electromagnetic resonance; Induction and Chapter–7: Alternating power in AC 6 1 7 Alternating Current circuits, Currents power factor wattless current. AC generator and transformer .
4 Electromagne Chapter–8: Basic idea 3 1 4 30 tic waves Electromagnetic Waves of displacemen t current, Electromagn etic waves, their characteristi cs, their Transverse nature (qualitative ideas only). Electromagn etic spectrum (radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-rays, gamma rays) including elementary facts about their uses.
Optics Chapter–9: Ray Optics and Ray Optics: 9 2 11 Optical Instruments Reflection Chapter–9: Ray Optics and of light, Optical Instruments spherical mirrors, mirror formula, refraction of light, total internal reflection and its applications , optical fibres, refraction at spherical surfaces, lenses, thin lens formula, lensmaker's formula, magnificatio n, power of a lens, combination of thin lenses in contact, refraction and dispersion of light through a prism. Scattering of light - blue colour of sky and reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset. Optical instruments: Microscopes and astronomica l telescopes (reflecting and refracting) and their magnifying powers. 5 Septem 23 Optics Chapter–10: Wave Optics 8 2 10 ber Perfor
mance test Wave optics: Wave front and Huygen's principle, reflection and refraction of plane wave at a plane surface using wave fronts. Proof of laws of reflection and refraction using Huygen's principle. Interference , Young's double slit experiment and expression for fringe width, coherent sources and sustained interference of light, diffraction due to a single slit, width of central maximum, resolving power of microscope and astronomica l telescope, polarization , plane polarized light, Brewster's law, uses of plane polarized light and Polaroids. Dual Nature of Chapter–11: Dual Nature Dual nature 5 1 6 Radiation and of Radiation and Matter of radiation, Matter Photoelectri c effect, Hertz and Lenard's observations ; Einstein's photoelectri c equation- particle nature of light. Matter waves-wave nature of particles, de-Broglie relation, Davisson- Germer experiment (experiment al details should be omitted; only conclusion should be explained).
Alpha- particle scattering experiment; Rutherford's Chapter–12: Atoms model of Atoms and Nuclei atom; Bohr 3 0 3 model, energy levels, hydrogen spectrum. Chapter–13: Nuclei Composition 3 1 4 and size of nucleus, Radioactivit y, alpha, beta and gamma particles/ra ys and their properties; radioactive decay law. Mass-energy relation, mass defect; binding energy per nucleon and its variation with mass number; nuclear fission, nuclear fusion.
6 October 16 Electronic Chapter–14: Energy 9 2 11 Devices Semiconduc bands in tor conductors, Electronics: semiconduct Materials, ors and Devices and insulators Simple (qualitative Circuits ideas only) Semiconduc tor diode - I-V characteristi cs in forward and reverse bias, diode as a rectifier; Special purpose p-n junction diodes: LED, photodiode, solar cell and Zener diode and their characteristi cs, zener diode as a voltage regulator. Junction transistor, transistor action, characteristi cs of a transistor and transistor as an amplifier (common emitter configuratio n), basic idea of analog and digital signals, Logic gates (OR, AND, NOT, NAND and NOR). Communic Chapter–15: Elements of 4 1 5 ation Communica a Systems tion communicat Systems ion system (block diagram only); bandwidth of signals (speech, TV and digital data); bandwidth of transmission medium. Propagation of electromagn etic waves in the atmosphere, sky and space wave propagation , satellite communicat ion. Need for modulation, amplitude modulation