Supplemental Table S1: 147 SNPs reported to be associated with T2D as of May 2005
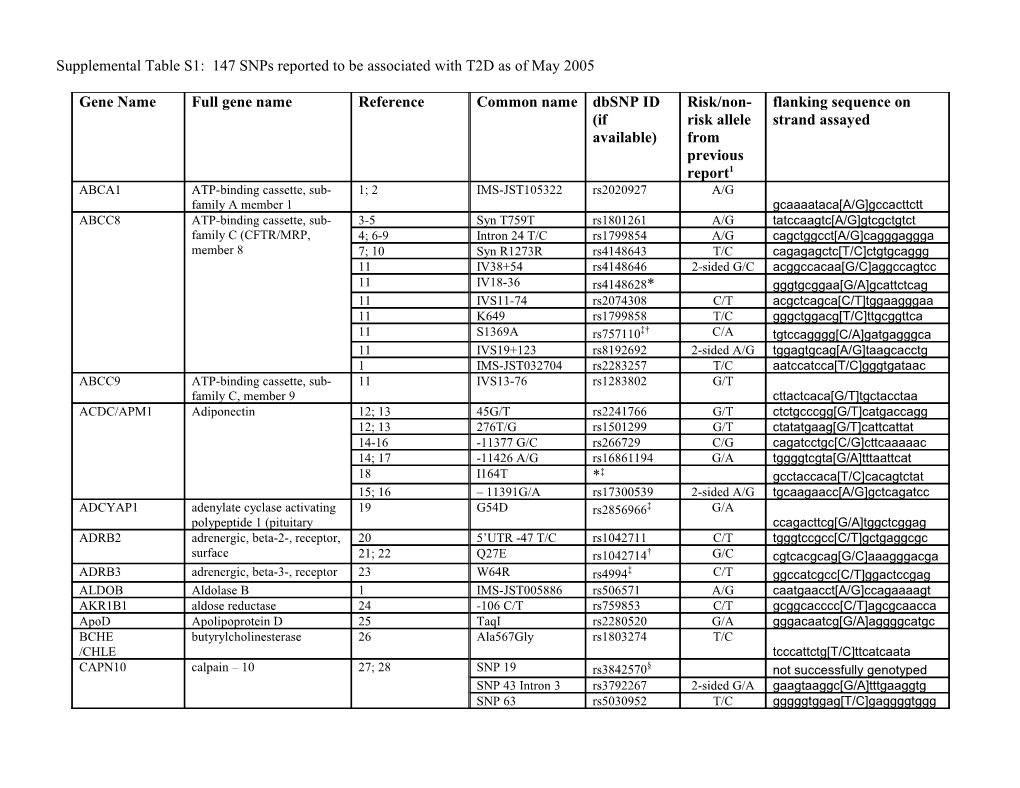
Gene Name Full gene name Reference Common name dbSNP ID Risk/non- flanking sequence on (if risk allele strand assayed available) from previous report1 ABCA1 ATP-binding cassette, sub- 1; 2 IMS-JST105322 rs2020927 A/G family A member 1 gcaaaataca[A/G]gccacttctt ABCC8 ATP-binding cassette, sub- 3-5 Syn T759T rs1801261 A/G tatccaagtc[A/G]gtcgctgtct family C (CFTR/MRP, 4; 6-9 Intron 24 T/C rs1799854 A/G cagctggcct[A/G]cagggaggga member 8 7; 10 Syn R1273R rs4148643 T/C cagagagctc[T/C]ctgtgcaggg 11 IV38+54 rs4148646 2-sided G/C acggccacaa[G/C]aggccagtcc 11 IV18-36 rs4148628* gggtgcggaa[G/A]gcattctcag 11 IVS11-74 rs2074308 C/T acgctcagca[C/T]tggaagggaa 11 K649 rs1799858 T/C gggctggacg[T/C]ttgcggttca 11 S1369A rs757110‡† C/A tgtccagggg[C/A]gatgagggca 11 IVS19+123 rs8192692 2-sided A/G tggagtgcag[A/G]taagcacctg 1 IMS-JST032704 rs2283257 T/C aatccatcca[T/C]gggtgataac ABCC9 ATP-binding cassette, sub- 11 IVS13-76 rs1283802 G/T family C, member 9 cttactcaca[G/T]tgctacctaa ACDC/APM1 Adiponectin 12; 13 45G/T rs2241766 G/T ctctgcccgg[G/T]catgaccagg 12; 13 276T/G rs1501299 G/T ctatatgaag[G/T]cattcattat 14-16 -11377 G/C rs266729 C/G cagatcctgc[C/G]cttcaaaaac 14; 17 -11426 A/G rs16861194 G/A tggggtcgta[G/A]tttaattcat 18 I164T *‡ gcctaccaca[T/C]cacagtctat 15; 16 – 11391G/A rs17300539 2-sided A/G tgcaagaacc[A/G]gctcagatcc ADCYAP1 adenylate cyclase activating 19 G54D rs2856966‡ G/A polypeptide 1 (pituitary ccagacttcg[G/A]tggctcggag ADRB2 adrenergic, beta-2-, receptor, 20 5’UTR -47 T/C rs1042711 C/T tgggtccgcc[C/T]gctgaggcgc surface 21; 22 Q27E rs1042714† G/C cgtcacgcag[G/C]aaagggacga ADRB3 adrenergic, beta-3-, receptor 23 W64R rs4994‡ C/T ggccatcgcc[C/T]ggactccgag ALDOB Aldolase B 1 IMS-JST005886 rs506571 A/G caatgaacct[A/G]ccagaaaagt AKR1B1 aldose reductase 24 -106 C/T rs759853 C/T gcggcacccc[C/T]agcgcaacca ApoD Apolipoprotein D 25 TaqI rs2280520 G/A gggacaatcg[G/A]aggggcatgc BCHE butyrylcholinesterase 26 Ala567Gly rs1803274 T/C /CHLE tcccattctg[T/C]ttcatcaata CAPN10 calpain – 10 27; 28 SNP 19 rs3842570§ not successfully genotyped SNP 43 Intron 3 rs3792267 2-sided G/A gaagtaaggc[G/A]tttgaaggtg SNP 63 rs5030952 T/C gggggtggag[T/C]gaggggtggg 29; 30 SNP 44 C/T and C/T T504A rs2975760 acgcttgctg[C/T]gaagtaaggc CASQ1 calsequestrin 1 31; 32 CASQ2312 rs617698 2-sided G/A tctattcctt[G/A]tgaagttcca 31 CASQ2399 rs617599† G/A tggagggaag[G/A]ggagtcgggg 32 rs2275703 rs2275703 C/A ccagacaagc[C/A]cctccagtat CD38 CD38 antigen 33 R140W rs1800561*‡ acaggtccag[C/T]gggacatgtt COG2/LDLC Low density lipoprotein 1 2312A/G rs1051038 G/A receptor defect C- IMS-JST051114 complementing protein agcagcctta[G/A]gcatcttgga CRP C-reactive protein, pentraxin- 34 SNP 133552 rs2794521 C/T related agtgagaaca[C/T]gcggtgtttg ENPP1/PCSK1/P proprotein convertase 35; 36 K121Q rs1044498‡ C/A C1 subtilisin/kexin type 1 ctgcaaggac[C/A]agggcgactg FABP2 intestinal fatty acid binding 1 IMS-JST031915 rs1397613 T/G protein 2 agttaaagag[T/G]gaaggaaaca FRDA Friedreich ataxia 37 rs2498429 rs2498429 A/T ctaagtaaaa[A/T]gtatatacat GCGR Glucagon receptor 38; 39 G40S rs1801483*‡ gaagctctac[G/A]gtgaccagtg GFPT2 glutamine-fructose-6- 40 I471V rs2303007‡ C/T phosphate transaminase 2 gccacgccga[C/T]ctccggccct GNB3 guanine nucleotide binding 41 825T rs5443 T/C protein (G protein, beta polypeptide 3 gcatcacgtc[T/C]gtggccttct GYS1 glycogen synthase 1 42 XbaI A2 rs8103451 A/G gttactctag[A/G]atggagtgca HFE hemochromatosis 43 H63D rs1799945‡ G/C gttctatgat[G/C]atgagagtcg 44 C282Y rs1800562‡ A/G agatatacgt[A/G]ccaggtggag HNF1A/TCF1 hepatic nuclear factor 1 45 G391S rs1169305§ not successfully genotyped 46 GE117881_360 G/A aaaattagcc[G/A]ggtgtagtgg 46 GE117884_349 G/A catagaatta[G/A]cgtgtccttt 46 rs1169289† 2-sided C/G cggccctgct[C/G]gagtcagggc 47 Ala98Val rs1800574‡ T/C gaggaggcgg[T/C]ccaccagaaa 46 rs1920792 T/C agatcctacc[T/C]cattgggttg 46 rs2178463† A/G ccactgcgcc[A/G]tgcctgtcct 46 rs2393792† G/A caagtgatcc[G/A]cctgcctcag 46 rs2701175 C/A ttttttgtag[C/A]gatgaggtct HSD11B1 hydroxysteroid (11-beta 48 SNP1 rs846910§ not successfully genotyped dehydrogenase 1 SNP5 rs12086634 T/G caaccccaga[T/G]gatttcttaa HSP70-2/HSPA2 heat shock 70kDa protein 1B 49 P2 rs1061581§ C/G not successfully genotyped HTR2C 5-hydroxytryptamine 50 -995 G/A rs3813928§ not successfully genotyped (serotonin receptor 2C -759 C/T rs3813929 T/C cccctcatcc[T/C]gcttttggcc IDE insulin-degrading enzyme 51; 52 -179 T/C rs4646953 A/G aggacggtga[A/G]gaccgcggac IL-6 53; 54 -174 G/C rs1800795 C/G tgtgtcttgc[C/G]atgctaaagg interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 54 -598A/G rs1800797† G/A 2 aaatttgagg[G/A]tggccaggca IL-6R interleukin 6 receptor 55 Asp358Ala rs8192284‡ A/C ctagtgcaag[A/C]ttcttcttca 56 V385I (SNP12 rs2228146‡§ not successfully genotyped INS proinsulin precursor 11 3p+9 rs3842752 A/G ggctgcctgc[A/G]ggctgcgtct INSR insulin receptor 57 V985M rs1799816*‡ T/C tcgtccggca[T/C]gtacacagag 11 IVS6+43 (SNP131 rs2860177 2-sided T/G cctcgcctcc[T/G]cagcgtctct 11 IVS6+31 (SNP132 rs2860178 2-sided A/G ccggtccctc[A/G]tgccaaaaag 11 IVS7+28 (SNP130 rs7252268 A/C tcttccacta[A/C]accggtccct IPF1 insulin promoter factor 1, 58 Asp76Asn *‡ homeodomain cctcgccgac[A/G]accccgcggt IRS1 insulin receptor substrate 1 41; 59; 60 G972R rs1801278‡ A/G tgcacctccc[A/G]gggctgctag 61 -7120 G/A rs12053536 T/C attgctaggt[T/C]accatgtccc 61 -446 G/A rs13306465 T/C cctctggaag[T/C]agcgattccc 61 Ala 804 rs1801123 C/T aagaatcatc[C/T]gctgttgcag IRS2 Insulin receptor substrate-2 62 G1057D rs1805097‡ 2-sided T/C tgaggcggcg[T/C]ccgggccctg ITGB3/PIA1/GPII integrin, beta 3 (platelet 63; 64 A2 rs5918 T/C Ia glycoprotein IIIa, antigen CD61 gccctgcctc[T/C]gggctcacct KCNJ9 potassium inwardly- 65 SNP3 A/G rs2180752 A/G aaactagacc[A/G]tgatggtcag rectifying channel, subfamily SNP11 T/C rs2737705 C/T cagtagacaa[C/T]tggtccactc J, member 9 SNP13 A/G rs2753268 G/A ggatgaaggc[G/A]tgcaaggggc KCNJ11 potassium inwardly- 11; 66-70 E23K (I337V rs5219‡ A/G ggaccctgcc[A/G]agcccaggta rectifying channel, subfamily † 11 A190 rs5218 G/A cgtggcgcag[G/A]gcgatcaccg J, member 11 11 3p+215 rs5210 G/A agccagtcct[G/A]aattgggttg Lep Leptin 1 IMS-JST026278 rs2278815 G/A aatgagaggg[G/A]ctgtgtaagg LIPC lipase, hepatic 11 IVS1+49 rs8192701 C/T ctttttaaaa[C/T]gtgtgtcaca 71 -250 G/A rs2070895§ not successfully genotyped LPL lipoprotein lipase 72 Intron 6 PvuII rs285 T/C catcttttag[T/C]agctgtgggg LTA lymphotoxin alpha (TNF 73 T60N rs1041981‡ A/C superfamily gcccacagca[A/C]cctcaaacct MCP1/CCL2 chemokine (C-C motif ligand 74 -2518 G/A rs3760399 A/G 2 tgaaatggcc[A/G]ctccatagag MET Hepatocyte growth factor 1 IMS-JST054758 rs38848 T/C tagatatgtt[T/C]tcaaatgcaa receptor T3912C, IMS- rs41736 T/C JST000713 cttatcctga[T/C]gtaaacacct MGEA5 Meningioma-expressed 75 LLY-MGEA5-14 § antigen 5 not successfully genotyped NEUROD1 neurogenic differentiation 1 76; 77 Ala45Thr rs1801262‡ T/C gcgttcatgg[T/C]ttcgaggtcg NOS3 Endothelial nitric oxide 78 E298D rs1799983 T/G ccccagatga[T/G]cccccagaac /eNOS synthase IVS18 + 27A/C rs1799984§ not successfully genotyped PAX4 paired box gene 4 79-81 R121W rs2233578*‡ gacctgagcc[G/A]tgtgcacggt PCK1 phosphoenolpyruvate 82 -232 C/G rs2071023 C/G carboxykinase 1 tgtgtcaaaa[C/G]tcactatggt PIK3R1 phosphoinositide-3-kinase, 11 IVS4+82 rs8192680§ regulatory subunit not successfully genotyped PKLR pyruvate kinase, liver and 83 PKLR1 rs3020781 G/A aatttttgtt[G/A]aatgaatgac RBC PKLR2 rs2071053† G/A ccaaccctac[G/A]ggcgccgcct PKLR4 R569R rs1052176† T/G cttagcaccc[T/G]catgatgttg PKLR5 rs1052177† G/A gggccagagg[G/A]gggaggggc g PPARG peroxisome proliferative 84-91 P12A rs1801282‡ C/G tcctattgac[C/G]cagaaagcga activated receptor, gamma 92 1431 C/T rs3856806 T/C tcacggaaca[T/C]gtgcagctac PPARGC1A/PGC peroxisome proliferative 11; 93; 94 G482S rs8192678‡ G/A 1 activated receptor, gamma, see coactivator 1 95 agacaagacc[G/A]gtgaactgag 11 T528T rs3755863† C/T aataggattg[C/T]gtgccatccc PPP1R3 Protein phosphatase type-1 96; 97 D905Y rs1799999‡ C/A glycogen targeting subunit ctattagtgt[C/A]tgagttaaaa PRKCZ protein kinase C, zeta 98 rs436045 rs436045 G/A tgcctgtcag[G/A]tttggtccaa PTGS2 prostaglandin-endoperoxide 99 rs20417 rs20417 C/G gaaagagagg[C/G]gggaaaggt synthase 2 precursor a rs2066826 rs2066826 C/T tgggtataag[C/T]ggtaataact PTPN1/PTP1B protein tyrosine phosphatase, 100-102 Nons P387L rs16995309*‡ T/C gctgcctccc[T/C]agccaaaggg non-receptor type 1 Syn exon8 C/T rs2282146 C/T agcccccacc[C/T]gagcatatcc rs718630 rs718630 G/T ctgttgcaca[G/T]gtaaagtgcc rs2206656 rs2206656 G/C tgcaataata[G/C]cttgtgacat rs3787345 rs3787345† C/T gctacctctg[C/T]ggagctgtgg rs4811078 rs4811078 C/T gaaactccgt[C/T]taaaaaaaaa rs718049 rs718049† G/A tggtccacgc[G/A]ccctgttccc rs941798 rs941798 A/G gcaccaaagt[A/G]tcatcctagt rs3787348 rs3787348† not genotyped rs718050 rs718050† A/G ttgagtacct[A/G]ttgatatgtg rs754118 rs754118† not genotyped rs2282147 rs2282147† not genotyped PYY peptide YY 11 IVS3+68 rs162430 A/G acgtcgttaa[A/G]tgatgttgcc RETN resistin 103; 104 -420 rs1862513 C/G gacatgaaga[C/G]ggaggccctg SLC2A1/GLUT1 solute carrier family 2 105-108 XbaI rs841853 A/C (facilitated glucose transporter, member 1 gaagagcttt[A/C]tagacttcag SLC2A2 109 TaqI rs6785803† 2-sided C/G gtataggctc[C/G]attattgtcg 11 IVS5-15 rs5406† 2-sided A/G ccaagaaaat[A/G]atcaggttga solute carrier family 2 11 T198 rs5404 2-sided T/C taagaatgcc[T/C]gtgacgatgg (facilitated glucose 11 T110I rs5400‡ 2-sided A/G gaatgatgca[A/G]tcattccacc transporter, member 2 110 Phe497 rs5398 2-sided A/G taaaaaatgt[A/G]aacagggtaa SORBS1 sorbin and SH3 domain 111 T228A rs2281939‡ T/C containing 1 gatggtggcg[T/C]ctggctaatg SOS1 son of sevenless homolog 1 11 IVS17+53 rs7577088 A/G ttaatgaaat[A/G]agtgttttgt SPINK1 serine protease inhibitor, 112 N34S rs17107315‡ C/T Kazal type 1 attaagttca[C/T]tgtaacattt SREBF1 Sterol regulatory element- 113 SNP17, +54G/C, rs2297508 G/C binding protein -1 exon 18c ggaagccttt[G/C]cctaggtgct TNF Tumor necrosis factor alpha 1 IMS-JST005889 rs1800610 A/G agaaaaaaac[A/G]tggagaaaga 49; 114 -308 G/A rs1800629 A/G gaggggcatg[A/G]ggacggggtt 115 -857 C/T rs1799724† T/C ccccccttaa[T/C]gaagacaggg UCP1 uncoupling protein 1 116 5’ UTR A/C rs10011540 G/T ccgatttctg[G/T]tttttgaacc M229L rs2270565† A/T ggggaggaca[A/T]agctgttgcg UCP2 uncoupling protein 2 117; 118 -866G/A rs659366 2-sided C/T gggtaactga[C/T]gcgtgaacag 119 Ala55Val rs660339‡ T/C cgcgctacag[T/C]cagcgcccag UCP3 uncoupling protein 3 120 5’ -55 C/T rs1800849 G/A ttatacacac[G/A]ggctgacctg UTS2 urotensin 2 121 S89N rs2890565‡ T/C aatgttggta[T/C]ttgagtctga VLDLR very low density lipoprotein 1 IMS-JST014197 rs2242103 A/T receptor agacttaatc[A/T]ggttagtttg WFS1 Wolfram syndrome 1 122; 123 R456H rs1801208‡ G/A ccctacacgc[G/A]cagggccctg H611R rs734312‡ A/G ctgctgttgc[A/G]ctggtggacc WNT5b wingless-type MMTV 124 Intron 4+438 rs2270031 C/G integration site family, IMS-JST024404 tcttccactt[C/G]aacctttgac member 5B Intron 4 + 6763 rs2270036 C/T IMS-JST024409 cttaccgccc[C/T]ggcctcattc 1 Alleles are designated according to the strand typed in our study 2-sided indicates SNPs tested with a 2-sided test because the previous risk allele was difficult to determine for ambiguous SNPs (such as C/G) or the SNP shows evidence for association with both alleles in different studies * SNPs that were monomorphic or MAF < .005 in our sample ‡ nonsynonymous SNPs † SNPs in r2 > .8 with another genotyped SNP (r2 values are given in Table S3) § SNP could not be successfully genotyped in our sample References for Table S1
1. Daimon M, Ji G, Saitoh T, Oizumi T, Tominaga M, Nakamura T, Ishii K, Matsuura T, Inageda K, Matsumine H, Kido T, Htay L, Kamatani N, Muramatsu M, Kato T: Large-scale search of SNPs for type 2 DM susceptibility genes in a Japanese population. In Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2003, p. 751-758 2. Daimon M, Kido T, Baba M, Oizumi T, Jimbu Y, Kameda W, Yamaguchi H, Ohnuma H, Tominaga M, Muramatsu M, Kato T: Association of the ABCA1 gene polymorphisms with type 2 DM in a Japanese population. In Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2005, p. 205-210 3. Hani EH, Clement K, Velho G, Vionnet N, Hager J, Philippi A, Dina C, Inoue H, Permutt MA, Basdevant A, North M, Demenais F, Guy- Grand B, Froguel P: Genetic studies of the sulfonylurea receptor gene locus in NIDDM and in morbid obesity among French Caucasians. In Diabetes, 1997, p. 688-694 4. Inoue H, Ferrer J, Welling CM, Elbein SC, Hoffman M, Mayorga R, Warren-Perry M, Zhang Y, Millns H, Turner R, Province M, Bryan J, Permutt MA, Aguilar-Bryan L: Sequence variants in the sulfonylurea receptor (SUR) gene are associated with NIDDM in Caucasians. In Diabetes, 1996, p. 825-831 5. Hansen T, Echwald SM, Hansen L, Moller AM, Almind K, Clausen JO, Urhammer SA, Inoue H, Ferrer J, Bryan J, Aguilar-Bryan L, Permutt MA, Pedersen O: Decreased tolbutamide-stimulated insulin secretion in healthy subjects with sequence variants in the high-affinity sulfonylurea receptor gene. In Diabetes, 1998, p. 598-605 6. Hart LM, de Knijff P, Dekker JM, Stolk RP, Nijpels G, van der Does FE, Ruige JB, Grobbee DE, Heine RJ, Maassen JA: Variants in the sulphonylurea receptor gene: association of the exon 16-3t variant with Type II diabetes mellitus in Dutch Caucasians. In Diabetologia, 1999, p. 617-620 7. Rissanen J, Markkanen A, Karkkainen P, Pihlajamaki J, Kekalainen P, Mykkanen L, Kuusisto J, Karhapaa P, Niskanen L, Laakso M: Sulfonylurea receptor 1 gene variants are associated with gestational diabetes and type 2 diabetes but not with altered secretion of insulin. In Diabetes Care, 2000, p. 70-73 8. Meirhaeghe A, Helbecque N, Cottel D, Arveiler D, Ruidavets JB, Haas B, Ferrieres J, Tauber JP, Bingham A, Amouyel P: Impact of sulfonylurea receptor 1 genetic variability on non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus prevalence and treatment: a population study. In Am J Med Genet, 2001, p. 4-8 9. Ji L, Han X, Wang H: [Sulfonylurea receptor gene polymorphism is associated with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in Chinese population]. In Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi, 1998, p. 774-775 10. Reis AF, Ye WZ, Dubois-Laforgue D, Bellanne-Chantelot C, Timsit J, Velho G: Association of a variant in exon 31 of the sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) gene with type 2 diabetes mellitus in French Caucasians. In Hum Genet, 2000, p. 138-144 11. Barroso I, Luan J, Middelberg RP, Harding AH, Franks PW, Jakes RW, Clayton D, Schafer AJ, O'Rahilly S, Wareham NJ: Candidate Gene Association Study in Type 2 Diabetes Indicates a Role for Genes Involved in beta-Cell Function as Well as Insulin Action. In PLoS Biol, 2003, p. E20 12. Hara K, Boutin P, Mori Y, Tobe K, Dina C, Yasuda K, Yamauchi T, Otabe S, Okada T, Eto K, Kadowaki H, Hagura R, Akanuma Y, Yazaki Y, Nagai R, Taniyama M, Matsubara K, Yoda M, Nakano Y, Tomita M, Kimura S, Ito C, Froguel P, Kadowaki T: Genetic variation in the gene encoding adiponectin is associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. In Diabetes, 2002, p. 536-540 13. Zacharova J, Chiasson JL, Laakso M: The common polymorphisms (single nucleotide polymorphism [SNP] +45 and SNP +276) of the adiponectin gene predict the conversion from impaired glucose tolerance to type 2 diabetes: the STOP-NIDDM trial. In Diabetes, 2005, p. 893- 899 14. Gu HF, Abulaiti A, Ostenson CG, Humphreys K, Wahlestedt C, Brookes AJ, Efendic S: Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the Proximal Promoter Region of the Adiponectin (APM1) Gene Are Associated With Type 2 Diabetes in Swedish Caucasians. In Diabetes, 2004, p. S31-S35 15. Vasseur F, Helbecque N, Dina C, Lobbens S, Delannoy V, Gaget S, Boutin P, Vaxillaire M, Lepretre F, Dupont S, Hara K, Clement K, Bihain B, Kadowaki T, Froguel P: Single-nucleotide polymorphism haplotypes in the both proximal promoter and exon 3 of the APM1 gene modulate adipocyte-secreted adiponectin hormone levels and contribute to the genetic risk for type 2 diabetes in French Caucasians. In Hum Mol Genet, 2002, p. 2607-2614 16. Vasseur F, Helbecque N, Lobbens S, Vasseur-Delannoy V, Dina C, Clement K, Boutin P, Kadowaki T, Scherer PE, Froguel P: Hypoadiponectinaemia and high risk of type 2 diabetes are associated with adiponectin-encoding (ACDC) gene promoter variants in morbid obesity: evidence for a role of ACDC in diabesity. In Diabetologia, 2005 17. Gibson F, Froguel P: Genetics of the APM1 locus and its contribution to type 2 diabetes susceptibility in French Caucasians. In Diabetes, 2004, p. 2977-2983 18. Kondo H, Shimomura I, Matsukawa Y, Kumada M, Takahashi M, Matsuda M, Ouchi N, Kihara S, Kawamoto T, Sumitsuji S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y: Association of adiponectin mutation with type 2 diabetes: a candidate gene for the insulin resistance syndrome. In Diabetes, 2002, p. 2325-2328 19. Gu HF: Genetic variation screening and association studies of the adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide 1 (ADCYAP1) gene in patients with type 2 diabetes. In Hum Mutat, 2002, p. 572-573 20. Yamada K, Ishiyama-Shigemoto S, Ichikawa F, Yuan X, Koyanagi A, Koyama W, Nonaka K: Polymorphism in the 5'-leader cistron of the beta2-adrenergic receptor gene associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes. In J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 1999, p. 1754-1757 21. Ishiyama-Shigemoto S, Yamada K, Yuan X, Ichikawa F, Nonaka K: Association of polymorphisms in the beta2-adrenergic receptor gene with obesity, hypertriglyceridaemia, and diabetes mellitus. In Diabetologia, 1999, p. 98-101 22. Carlsson M, Orho-Melander M, Hedenbro J, Groop LC: Common variants in the beta2-(Gln27Glu) and beta3-(Trp64Arg)--adrenoceptor genes are associated with elevated serum NEFA concentrations and type II diabetes. In Diabetologia, 2001, p. 629-636 23. Oizumi T, Daimon M, Saitoh T, Kameda W, Yamaguchi H, Ohnuma H, Igarashi M, Eguchi H, Manaka H, Tominaga M, Kato T: Genotype Arg/Arg, but not Trp/Arg, of the Trp64Arg polymorphism of the beta(3)-adrenergic receptor is associated with type 2 diabetes and obesity in a large Japanese sample. In Diabetes Care, 2001, p. 1579-1583 24. Sivenius K, Niskanen L, Voutilainen-Kaunisto R, Laakso M, Uusitupa M: Aldose reductase gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to microvascular complications in Type 2 diabetes. In Diabet Med, 2004, p. 1325-1333 25. Baker WA, Hitman GA, Hawrami K, McCarthy MI, Riikonen A, Tuomilehto-Wolf E, Nissinen A, Tuomilehto J, Mohan V, Viswanathan M, et al.: Apolipoprotein D gene polymorphism: a new genetic marker for type 2 diabetic subjects in Nauru and south India. In Diabet Med, 1994, p. 947-952 26. Hashim Y, Shepherd D, Wiltshire S, Holman RR, Levy JC, Clark A, Cull CA: Butyrylcholinesterase K variant on chromosome 3 q is associated with Type II diabetes in white Caucasian subjects. In Diabetologia, 2001, p. 2227-2230 27. Malecki MT, Moczulski DK, Klupa T, Wanic K, Cyganek K, Frey J, Sieradzki J: Homozygous combination of calpain 10 gene haplotypes is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Polish population. In Eur J Endocrinol, 2002, p. 695-699 28. Iwasaki N, Horikawa Y, Tsuchiya T, Kitamura Y, Nakamura T, Tanizawa Y, Oka Y, Hara K, Kadowaki T, Awata T, Honda M, Yamashita K, Oda N, Yu L, Yamada N, Ogata M, Kamatani N, Iwamoto Y, Del Bosque-Plata L, Hayes MG, Cox NJ, Bell GI: Genetic variants in the calpain-10 gene and the development of type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. In J Hum Genet, 2005, p. 92-98 29. Evans JC, Frayling TM, Cassell PG, Saker PJ, Hitman GA, Walker M, Levy JC, O'Rahilly S, Rao PV, Bennett AJ, Jones EC, Menzel S, Prestwich P, Simecek N, Wishart M, Dhillon R, Fletcher C, Millward A, Demaine A, Wilkin T, Horikawa Y, Cox NJ, Bell GI, Ellard S, McCarthy MI, Hattersley AT: Studies of association between the gene for calpain-10 and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the United Kingdom. In Am J Hum Genet, 2001, p. 544-552 30. del Bosque-Plata L, Aguilar-Salinas CA, Tusie-Luna MT, Ramirez-Jimenez S, Rodriguez-Torres M, Auron-Gomez M, Ramirez E, Velasco- Perez ML, Ramirez-Silva A, Gomez-Perez F, Hanis CL, Tsuchiya T, Yoshiuchi I, Cox NJ, Bell GI: Association of the calpain-10 gene with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Mexican population. In Mol Genet Metab, 2004, p. 122-126 31. Das SK, Chu W, Zhang Z, Hasstedt SJ, Elbein SC: Calsquestrin 1 (CASQ1) gene polymorphisms under chromosome 1q21 linkage peak are associated with type 2 diabetes in Northern European Caucasians. In Diabetes, 2004, p. 3300-3306 32. Fu M, Damcott CM, Sabra M, Pollin TI, Ott SH, Wang J, Garant MJ, O'Connell JR, Mitchell BD, Shuldiner AR: Polymorphism in the calsequestrin 1 (CASQ1) gene on chromosome 1q21 is associated with type 2 diabetes in the old order Amish. In Diabetes, 2004, p. 3292-3299 33. Yagui K, Shimada F, Mimura M, Hashimoto N, Suzuki Y, Tokuyama Y, Nata K, Tohgo A, Ikehata F, Takasawa S, Okamoto H, Makino H, Saito Y, Kanatsuka A: A missense mutation in the CD38 gene, a novel factor for insulin secretion: association with Type II diabetes mellitus in Japanese subjects and evidence of abnormal function when expressed in vitro. In Diabetologia, 1998, p. 1024-1028 34. Wolford JK, Gruber JD, Ossowski VM, Vozarova B, Antonio Tataranni P, Bogardus C, Hanson RL: A C-reactive protein promoter polymorphism is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Pima Indians. In Mol Genet Metab, 2003, p. 136-144 35. Hamaguchi K, Terao H, Kusuda Y, Yamashita T, Hazoury Bahles JA, Cruz LM, Brugal VL, Jongchong WB, Yoshimatsu H, Sakata T: The PC-1 Q121 allele is exceptionally prevalent in the Dominican Republic and is associated with type 2 diabetes. In J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2004, p. 1359-1364 36. Meyre D, Bouatia-Naji N, Tounian A, Samson C, Lecoeur C, Vatin V, Ghoussaini M, Wachter C, Hercberg S, Charpentier G, Patsch W, Pattou F, Charles MA, Tounian P, Clement K, Jouret B, Weill J, Maddux BA, Goldfine ID, Walley A, Boutin P, Dina C, Froguel P: Variants of ENPP1 are associated with childhood and adult obesity and increase the risk of glucose intolerance and type 2 diabetes. In Nat Genet, 2005, p. 863-867 37. Holmkvist J, Almgren P, Parikh H, Zucchelli M, Kere J, Groop L, Lindgren CM: Haplotype construction of the FRDA gene and evaluation of its role in type II diabetes. In Eur J Hum Genet, 2005 38. Hager J, Hansen L, Vaisse C, Vionnet N, Philippi A, Poller W, Velho G, Carcassi C, Contu L, Julier C, et al.: A missense mutation in the glucagon receptor gene is associated with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. In Nat Genet, 1995, p. 299-304 39. Gough SC, Saker PJ, Pritchard LE, Merriman TR, Merriman ME, Rowe BR, Kumar S, Aitman T, Barnett AH, Turner RC, et al.: Mutation of the glucagon receptor gene and diabetes mellitus in the UK: association or founder effect? In Hum Mol Genet, 1995, p. 1609-1612 40. Zhang H, Jia Y, Cooper JJ, Hale T, Zhang Z, Elbein SC: Common variants in glutamine:fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase 2 (GFPT2) gene are associated with type 2 diabetes, diabetic nephropathy, and increased GFPT2 mRNA levels. In J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2004, p. 748-755 41. Rosskopf D, Frey U, Eckhardt S, Schmidt S, Ritz E, Hofmann S, Jaksch M, Muller N, Husing J, Siffert W, Jocke KH: Interaction of the G protein beta 3 subunit T825 allele and the IRS-1 Arg972 variant in type 2 diabetes. In Eur J Med Res, 2000, p. 484-490 42. Groop LC, Kankuri M, Schalin-Jantti C, Ekstrand A, Nikula-Ijas P, Widen E, Kuismanen E, Eriksson J, Franssila-Kallunki A, Saloranta C, et al.: Association between polymorphism of the glycogen synthase gene and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. In N Engl J Med, 1993, p. 10- 14 43. Fernandez-Real JM, Vendrell J, Baiget M, Gimferrer E, Ricart W: C282Y and H63D mutations of the hemochromatosis candidate gene in type 2 diabetes. In Diabetes Care, 1999, p. 525-526 44. Moczulski DK, Grzeszczak W, Gawlik B: Role of hemochromatosis C282Y and H63D mutations in HFE gene in development of type 2 diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. In Diabetes Care, 2001, p. 1187-1191 45. Hegele RA, Cao H, Harris SB, Hanley AJ, Zinman B: The hepatic nuclear factor-1alpha G319S variant is associated with early-onset type 2 diabetes in Canadian Oji-Cree. In J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 1999, p. 1077-1082 46. Winckler W, Burtt NP, Holmkvist J, Cervin C, de Bakker PI, Sun M, Almgren P, Tuomi T, Gaudet D, Hudson TJ, Ardlie KG, Daly MJ, Hirschhorn JN, Altshuler D, Groop L: Association of common variation in the HNF1alpha gene region with risk of type 2 diabetes. In Diabetes, 2005, p. 2336-2342 47. Weedon MN, Owen KR, Shields B, Hitman G, Walker M, McCarthy MI, Hattersley AT, Frayling TM: A large-scale association analysis of common variation of the HNF1alpha gene with type 2 diabetes in the U.K. Caucasian population. In Diabetes, 2005, p. 2487-2491 48. Nair S, Lee YH, Lindsay RS, Walker BR, Tataranni PA, Bogardus C, Baier LJ, Permana PA: 11beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase Type 1: genetic polymorphisms are associated with Type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians independently of obesity and expression in adipocyte and muscle. In Diabetologia, 2004, p. 1088-1095 49. Zouari Bouassida K, Chouchane L, Jellouli K, Cherif S, Haddad S, Gabbouj S, Danguir J: Polymorphism of stress protein HSP70-2 gene in Tunisians: susceptibility implications in type 2 diabetes and obesity. In Diabetes Metab, 2004, p. 175-180 50. Yuan X, Yamada K, Ishiyama-Shigemoto S, Koyama W, Nonaka K: Identification of polymorphic loci in the promoter region of the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor gene and their association with obesity and type II diabetes. In Diabetologia, 2000, p. 373-376 51. Groves CJ, Wiltshire S, Smedley D, Owen KR, Frayling TM, Walker M, Hitman GA, Levy JC, O'Rahilly S, Menzel S, Hattersley AT, McCarthy MI: Association and haplotype analysis of the insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) gene, a strong positional and biological candidate for type 2 diabetes susceptibility. In Diabetes, 2003, p. 1300-1305 52. Karamohamed S, Demissie S, Volcjak J, Liu C, Heard-Costa N, Liu J, Shoemaker CM, Panhuysen CI, Meigs JB, Wilson P, Atwood LD, Cupples LA, Herbert A: Polymorphisms in the insulin-degrading enzyme gene are associated with type 2 diabetes in men from the NHLBI Framingham Heart Study. In Diabetes, 2003, p. 1562-1567 53. Vozarova B, Fernandez-Real JM, Knowler WC, Gallart L, Hanson RL, Gruber JD, Ricart W, Vendrell J, Richart C, Tataranni PA, Wolford JK: The interleukin-6 (-174) G/C promoter polymorphism is associated with type-2 diabetes mellitus in Native Americans and Caucasians. In Hum Genet, 2003, p. 409-413 54. Illig T, Bongardt F, Schopfer A, Muller-Scholze S, Rathmann W, Koenig W, Thorand B, Vollmert C, Holle R, Kolb H, Herder C: Significant association of the interleukin-6 gene polymorphisms C-174G and A-598G with type 2 diabetes. In J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2004, p. 5053-5058 55. Hamid YH, Urhammer SA, Jensen DP, Glumer C, Borch-Johnsen K, Jorgensen T, Hansen T, Pedersen O: Variation in the interleukin-6 receptor gene associates with type 2 diabetes in Danish whites. In Diabetes, 2004, p. 3342-3345 56. Wang H, Zhang Z, Chu W, Hale T, Cooper JJ, Elbein SC: Molecular screening and association analyses of the interleukin 6 receptor gene variants with type 2 diabetes, diabetic nephropathy, and insulin sensitivity. In J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2005, p. 1123-1129 57. Hart LM, Stolk RP, Heine RJ, Grobbee DE, van der Does FE, Maassen JA: Association of the insulin-receptor variant Met-985 with hyperglycemia and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in the Netherlands: a population-based study. In Am J Hum Genet, 1996, p. 1119-1125 58. Hani EH, Stoffers DA, Chevre JC, Durand E, Stanojevic V, Dina C, Habener JF, Froguel P: Defective mutations in the insulin promoter factor-1 (IPF-1) gene in late-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus. In J Clin Invest, 1999, p. R41-48 59. Sigal RJ, Doria A, Warram JH, Krolewski AS: Codon 972 polymorphism in the insulin receptor substrate-1 gene, obesity, and risk of noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. In J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 1996, p. 1657-1659 60. Sesti G, Marini MA, Cardellini M, Sciacqua A, Frontoni S, Andreozzi F, Irace C, Lauro D, Gnasso A, Federici M, Perticone F, Lauro R: The Arg972 variant in insulin receptor substrate-1 is associated with an increased risk of secondary failure to sulfonylurea in patients with type 2 diabetes. In Diabetes Care, 2004, p. 1394-1398 61. Kovacs P, Hanson RL, Lee YH, Yang X, Kobes S, Permana PA, Bogardus C, Baier LJ: The role of insulin receptor substrate-1 gene (IRS1) in type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians. In Diabetes, 2003, p. 3005-3009 62. Mammarella S, Romano F, Di Valerio A, Creati B, Esposito DL, Palmirotta R, Capani F, Vitullo P, Volpe G, Battista P, Della Loggia F, Mariani-Costantini R, Cama A: Interaction between the G1057D variant of IRS-2 and overweight in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. In Hum Mol Genet, 2000, p. 2517-2521 63. Tschoepe D, Menart B, Ferber P, Altmann C, Haude M, Haastert B, Roesen P: Genetic variation of the platelet- surface integrin GPIIb-IIIa (PIA1/A2-SNP) shows a high association with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. In Diabetologia, 2003, p. 984-989 64. Lopes C, Dina C, Durand E, Froguel P: PAI-1 polymorphisms modulate phenotypes associated with the metabolic syndrome in obese and diabetic Caucasian population. In Diabetologia, 2003, p. 1284-1290 65. Wolford JK, Hanson RL, Kobes S, Bogardus C, Prochazka M: Analysis of linkage disequilibrium between polymorphisms in the KCNJ9 gene with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Pima Indians. In Mol Genet Metab, 2001, p. 97-103 66. Hani EH, Boutin P, Durand E, Inoue H, Permutt MA, Velho G, Froguel P: Missense mutations in the pancreatic islet beta cell inwardly rectifying K+ channel gene (KIR6.2/BIR): a meta-analysis suggests a role in the polygenic basis of Type II diabetes mellitus in Caucasians. In Diabetologia, 1998, p. 1511-1515 67. Gloyn AL, Hashim Y, Ashcroft SJ, Ashfield R, Wiltshire S, Turner RC: Association studies of variants in promoter and coding regions of beta-cell ATP-sensitive K-channel genes SUR1 and Kir6.2 with Type 2 diabetes mellitus (UKPDS 53). In Diabet Med, 2001, p. 206-212 68. Gloyn AL, Weedon MN, Owen KR, Turner MJ, Knight BA, Hitman G, Walker M, Levy JC, Sampson M, Halford S, McCarthy MI, Hattersley AT, Frayling TM: Large-scale association studies of variants in genes encoding the pancreatic beta-cell KATP channel subunits Kir6.2 (KCNJ11) and SUR1 (ABCC8) confirm that the KCNJ11 E23K variant is associated with type 2 diabetes. In Diabetes, 2003, p. 568-572 69. Sakura H, Wat N, Horton V, Millns H, Turner RC, Ashcroft FM: Sequence variations in the human Kir6.2 gene, a subunit of the beta-cell ATP-sensitive K-channel: no association with NIDDM in while Caucasian subjects or evidence of abnormal function when expressed in vitro. In Diabetologia, 1996, p. 1233-1236 70. Riedel MJ, Steckley DC, Light PE: Current status of the E23K Kir6.2 polymorphism: implications for type-2 diabetes. In Hum Genet, 2005, p. 133-145 71. Zacharova J, Todorova BR, Chiasson JL, Laakso M: The G-250A substitution in the promoter region of the hepatic lipase gene is associated with the conversion from impaired glucose tolerance to type 2 diabetes: the STOP-NIDDM trial. In J Intern Med, 2005, p. 185-193 72. Wang XL, McCredie RM, Wilcken DE: Common DNA polymorphisms at the lipoprotein lipase gene. Association with severity of coronary artery disease and diabetes. In Circulation, 1996, p. 1339-1345 73. Hamid YH, Urhammer SA, Glumer C, Borch-Johnsen K, Jorgensen T, Hansen T, Pedersen O: The common T60N polymorphism of the lymphotoxin-alpha gene is associated with type 2 diabetes and other phenotypes of the metabolic syndrome. In Diabetologia, 2005, p. 445-451 74. Simeoni E, Hoffmann MM, Winkelmann BR, Ruiz J, Fleury S, Boehm BO, Marz W, Vassalli G: Association between the A-2518G polymorphism in the monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene and insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes mellitus. In Diabetologia, 2004, p. 1574-1580 75. Lehman DM, Fu DJ, Freeman AB, Hunt KJ, Leach RJ, Johnson-Pais T, Hamlington J, Dyer TD, Arya R, Abboud H, Goring HH, Duggirala R, Blangero J, Konrad RJ, Stern MP: A Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in MGEA5 Encoding O-GlcNAc-selective N-Acetyl-{beta}-D Glucosaminidase Is Associated With Type 2 Diabetes in Mexican Americans. In Diabetes, 2005, p. 1214-1221 76. Ye L, Xu Y, Zhu Y, Fan Y, Deng H, Zhang J: [Association of polymorphism in neurogenic differentiation factor 1 gene with type 2 diabetes]. In Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi, 2002, p. 484-487 77. Kavvoura FK, Ioannidis JP: Ala45Thr polymorphism of the NEUROD1 gene and diabetes susceptibility: a meta-analysis. In Hum Genet, 2005, p. 192-199 78. Monti LD, Barlassina C, Citterio L, Galluccio E, Berzuini C, Setola E, Valsecchi G, Lucotti P, Pozza G, Bernardinelli L, Casari G, Piatti P: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase polymorphisms are associated with type 2 diabetes and the insulin resistance syndrome. In Diabetes, 2003, p. 1270-1275 79. Shimajiri Y, Shimabukuro M, Tomoyose T, Yogi H, Komiya I, Takasu N: PAX4 mutation (R121W) as a prodiabetic variant in Okinawans. In Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2003, p. 342-344 80. Shimajiri Y, Sanke T, Furuta H, Hanabusa T, Nakagawa T, Fujitani Y, Kajimoto Y, Takasu N, Nanjo K: A missense mutation of Pax4 gene (R121W) is associated with type 2 diabetes in Japanese. In Diabetes, 2001, p. 2864-2869 81. Holm P, Rydlander B, Luthman H, Kockum I: Interaction and association analysis of a type 1 diabetes susceptibility locus on chromosome 5q11-q13 and the 7q32 chromosomal region in Scandinavian families. In Diabetes, 2004, p. 1584-1591 82. Cao H, van der Veer E, Ban MR, Hanley AJ, Zinman B, Harris SB, Young TK, Pickering JG, Hegele RA: Promoter polymorphism in PCK1 (phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene) associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2004, p. 898-903 83. Wang H, Chu W, Das SK, Ren Q, Hasstedt SJ, Elbein SC: Liver pyruvate kinase polymorphisms are associated with type 2 diabetes in northern European Caucasians. In Diabetes, 2002, p. 2861-2865 84. Deeb SS, Fajas L, Nemoto M, Pihlajamaki J, Mykkanen L, Kuusisto J, Laakso M, Fujimoto W, Auwerx J: A Pro12Ala substitution in PPARgamma2 associated with decreased receptor activity, lower body mass index and improved insulin sensitivity. In Nat Genet, 1998, p. 284- 287 85. Hara K, Okada T, Tobe K, Yasuda K, Mori Y, Kadowaki H, Hagura R, Akanuma Y, Kimura S, Ito C, Kadowaki T: The Pro12Ala polymorphism in PPAR gamma2 may confer resistance to type 2 diabetes. In Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2000, p. 212-216 86. Mori H, Ikegami H, Kawaguchi Y, Seino S, Yokoi N, Takeda J, Inoue I, Seino Y, Yasuda K, Hanafusa T, Yamagata K, Awata T, Kadowaki T, Hara K, Yamada N, Gotoda T, Iwasaki N, Iwamoto Y, Sanke T, Nanjo K, Oka Y, Matsutani A, Maeda E, Kasuga M: The Pro12 -->Ala substitution in PPAR-gamma is associated with resistance to development of diabetes in the general population: possible involvement in impairment of insulin secretion in individuals with type 2 diabetes. In Diabetes, 2001, p. 891-894 87. Altshuler D, Hirschhorn JN, Klannemark M, Lindgren CM, Vohl MC, Nemesh J, Lane CR, Schaffner SF, Bolk S, Brewer C, Tuomi T, Gaudet D, Hudson TJ, Daly M, Groop L, Lander ES: The common PPARgamma Pro12Ala polymorphism is associated with decreased risk of type 2 diabetes. In Nat Genet, 2000, p. 76-80 88. Doney AS, Fischer B, Cecil JE, Boylan K, McGuigan FE, Ralston SH, Morris AD, Palmer CN: Association of the Pro12Ala and C1431T variants of PPARG and their haplotypes with susceptibility to Type 2 diabetes. In Diabetologia, 2004 89. Ghoussaini M, Meyre D, Lobbens S, Charpentier G, Clement K, Charles MA, Tauber M, Weill J, Froguel P: Implication of the Pro12Ala polymorphism of the PPAR-gamma 2 gene in type 2 diabetes and obesity in the French population. In BMC Med Genet, 2005, p. 11 90. Pinterova D, Cerna M, Kolostova K, Novota P, Cimburova M, Romzova M, Kubena A, Andel M: The frequency of alleles of the Pro12Ala polymorphism in PPARgamma2 is different between healthy controls and patients with type 2 diabetes. In Folia Biol (Praha), 2004, p. 153-156 91. Horiki M, Ikegami H, Fujisawa T, Kawabata Y, Ono M, Nishino M, Shimamoto K, Ogihara T: Association of Pro12Ala polymorphism of PPARgamma gene with insulin resistance and related diseases. In Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2004, p. S63-67 92. Evans D, de Heer J, Hagemann C, Wendt D, Wolf A, Beisiegel U, Mann WA: Association between the P12A and c1431t polymorphisms in the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma) gene and type 2 diabetes. In Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes, 2001, p. 151- 154 93. Ek J, Andersen G, Urhammer SA, Gaede PH, Drivsholm T, Borch-Johnsen K, Hansen T, Pedersen O: Mutation analysis of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 (PGC-1) and relationships of identified amino acid polymorphisms to Type II diabetes mellitus. In Diabetologia, 2001, p. 2220-2226 94. Hara K, Tobe K, Okada T, Kadowaki H, Akanuma Y, Ito C, Kimura S, Kadowaki T: A genetic variation in the PGC-1 gene could confer insulin resistance and susceptibility to Type II diabetes. In Diabetologia, 2002, p. 740-743 95. Kubaszek A, Markkanen A, Eriksson JG, Forsen T, Osmond C, Barker DJ, Laakso M: The association of the K121Q polymorphism of the plasma cell glycoprotein-1 gene with type 2 diabetes and hypertension depends on size at birth. In J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2004, p. 2044-2047 96. Xia J, Scherer SW, Cohen PT, Majer M, Xi T, Norman RA, Knowler WC, Bogardus C, Prochazka M: A common variant in PPP1R3 associated with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. In Diabetes, 1998, p. 1519-1524 97. Wang G, Qian R, Li Q, Niu T, Chen C, Xu X: The association between PPP1R3 gene polymorphisms and type 2 diabetes mellitus. In Chin Med J (Engl), 2001, p. 1258-1262 98. Li YF, Sun HX, Wu GD, Du WN, Zuo J, Shen Y, Qiang BQ, Yao ZJ, Wang H, Huang W, Chen Z, Xiong MM, Meng Y, Fang FD: Protein kinase C/zeta (PRKCZ) gene is associated with type 2 diabetes in Han population of North China and analysis of its haplotypes. In World J Gastroenterol, 2003, p. 2078-2082 99. Konheim YL, Wolford JK: Association of a promoter variant in the inducible cyclooxygenase-2 gene (PTGS2) with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Pima Indians. In Hum Genet, 2003, p. 377-381 100. Echwald SM, Bach H, Vestergaard H, Richelsen B, Kristensen K, Drivsholm T, Borch-Johnsen K, Hansen T, Pedersen O: A P387L variant in protein tyrosine phosphatase-1B (PTP-1B) is associated with type 2 diabetes and impaired serine phosphorylation of PTP-1B in vitro. In Diabetes, 2002, p. 1-6 101. Mok A, Cao H, Zinman B, Hanley AJ, Harris SB, Kennedy BP, Hegele RA: A single nucleotide polymorphism in protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP-1B is associated with protection from diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance in Oji-Cree. In J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2002, p. 724-727 102. Bento JL, Palmer ND, Mychaleckyj JC, Lange LA, Langefeld CD, Rich SS, Freedman BI, Bowden DW: Association of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B gene polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes. In Diabetes, 2004, p. 3007-3012 103. Ma X, Warram JH, Trischitta V, Doria A: Genetic variants at the resistin locus and risk of type 2 diabetes in Caucasians. In J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2002, p. 4407-4410 104. Osawa H, Yamada K, Onuma H, Murakami A, Ochi M, Kawata H, Nishimiya T, Niiya T, Shimizu I, Nishida W, Hashiramoto M, Kanatsuka A, Fujii Y, Ohashi J, Makino H: The G/G genotype of a resistin single-nucleotide polymorphism at -420 increases type 2 diabetes mellitus susceptibility by inducing promoter activity through specific binding of Sp1/3. In Am J Hum Genet, 2004, p. 678-686 105. Li SR, Baroni MG, Oelbaum RS, Stock J, Galton DJ: Association of genetic variant of the glucose transporter with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. In Lancet, 1988, p. 368-370 106. Baroni MG, Oelbaum RS, Pozzilli P, Stocks J, Li SR, Fiore V, Galton DJ: Polymorphisms at the GLUT1 (HepG2) and GLUT4 (muscle/adipocyte) glucose transporter genes and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). In Hum Genet, 1992, p. 557-561 107. Tao T, Tanizawa Y, Matsutani A, Matsubara A, Kaneko T, Kaku K: HepG2/erythrocyte glucose transporter (GLUT1) gene in NIDDM: a population association study and molecular scanning in Japanese subjects. In Diabetologia, 1995, p. 942-947 108. Pontiroli AE, Capra F, Veglia F, Ferrari M, Xiang KS, Bell GI, Baroni MG, Galton DJ, Weaver JU, Hitman GA, Kopelman PG, Mohan V, Viswanathan M: Genetic contribution of polymorphism of the GLUT1 and GLUT4 genes to the susceptibility to type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in different populations. In Acta Diabetol, 1996, p. 193-197 109. Alcolado JC, Baroni MG, Li SR: Association between a restriction fragment length polymorphism at the liver/islet cell (GluT 2) glucose transporter and familial type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. In Diabetologia, 1991, p. 734-736 110. Yasuda K, Seino Y: [Candidate gene approach in Japanese NIDDM: liver/pancreatic beta cell type glucose transporter (GLUT2)]. In Nippon Rinsho, 1994, p. 2693-2696 111. Lin WH, Chiu KC, Chang HM, Lee KC, Tai TY, Chuang LM: Molecular scanning of the human sorbin and SH3-domain-containing-1 (SORBS1) gene: positive association of the T228A polymorphism with obesity and type 2 diabetes. In Hum Mol Genet, 2001, p. 1753-1760 112. Schneider A, Suman A, Rossi L, Barmada MM, Beglinger C, Parvin S, Sattar S, Ali L, Khan AK, Gyr N, Whitcomb DC: SPINK1/PSTI mutations are associated with tropical pancreatitis and type II diabetes mellitus in Bangladesh. In Gastroenterology, 2002, p. 1026-1030 113. Eberle D, Clement K, Meyre D, Sahbatou M, Vaxillaire M, Le Gall A, Ferre P, Basdevant A, Froguel P, Foufelle F: SREBF-1 Gene Polymorphisms Are Associated With Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes in French Obese and Diabetic Cohorts. In Diabetes, 2004, p. 2153-2157 114. Heijmans BT, Westendorp RG, Droog S, Kluft C, Knook DL, Slagboom PE: Association of the tumour necrosis factor alpha -308G/A polymorphism with the risk of diabetes in an elderly population-based cohort. In Genes Immun, 2002, p. 225-228 115. Kamizono S, Yamada K, Seki N, Higuchi T, Kimura A, Nonaka K, Itoh K: Susceptible locus for obese type 2 diabetes mellitus in the 5'- flanking region of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene. In Tissue Antigens, 2000, p. 449-452 116. Mori H, Okazawa H, Iwamoto K, Maeda E, Hashiramoto M, Kasuga M: A polymorphism in the 5' untranslated region and a Met229-->Leu variant in exon 5 of the human UCP1 gene are associated with susceptibility to type II diabetes mellitus. In Diabetologia, 2001, p. 373-376 117. Bulotta A, Ludovico O, Coco A, Di Paola R, Quattrone A, Carella M, Pellegrini F, Prudente S, Trischitta V: The common -866G/A polymorphism in the promoter region of the UCP-2 gene is associated with reduced risk of type 2 diabetes in Caucasians from Italy. In J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2005, p. 1176-1180 118. D'Adamo M, Perego L, Cardellini M, Marini MA, Frontoni S, Andreozzi F, Sciacqua A, Lauro D, Sbraccia P, Federici M, Paganelli M, Pontiroli AE, Lauro R, Perticone F, Folli F, Sesti G: The -866A/A genotype in the promoter of the human uncoupling protein 2 gene is associated with insulin resistance and increased risk of type 2 diabetes. In Diabetes, 2004, p. 1905-1910 119. Xiu LL, Weng JP, Sui Y, Wang J, Yan JH, Huang ZM: [Common variants in beta 3-adrenergic-receptor and uncoupling protein-2 genes are associated with type 2 diabetes and obesity]. In Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2004, p. 375-379 120. Meirhaeghe A, Amouyel P, Helbecque N, Cottel D, Otabe S, Froguel P, Vasseur F: An uncoupling protein 3 gene polymorphism associated with a lower risk of developing Type II diabetes and with atherogenic lipid profile in a French cohort. In Diabetologia, 2000, p. 1424-1428 121. Suzuki S, Wenyi Z, Hirai M, Hinokio Y, Suzuki C, Yamada T, Yoshizumi S, Suzuki M, Tanizawa Y, Matsutani A, Oka Y: Genetic variations at urotensin II and urotensin II receptor genes and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japanese. In Peptides, 2004, p. 1803-1808 122. Minton JA, Hattersley AT, Owen K, McCarthy MI, Walker M, Latif F, Barrett T, Frayling TM: Association studies of genetic variation in the WFS1 gene and type 2 diabetes in U.K. populations. In Diabetes, 2002, p. 1287-1290 123. Kawamoto T, Horikawa Y, Tanaka T, Kabe N, Takeda J, Mikuni M: Genetic variations in the WFS1 gene in Japanese with type 2 diabetes and bipolar disorder. In Mol Genet Metab, 2004, p. 238-245 124. Kanazawa A, Tsukada S, Sekine A, Tsunoda T, Takahashi A, Kashiwagi A, Tanaka Y, Babazono T, Matsuda M, Kaku K, Iwamoto Y, Kawamori R, Kikkawa R, Nakamura Y, Maeda S: Association of the gene encoding wingless-type mammary tumor virus integration-site family member 5B (WNT5B) with type 2 diabetes. In Am J Hum Genet, 2004, p. 832-843