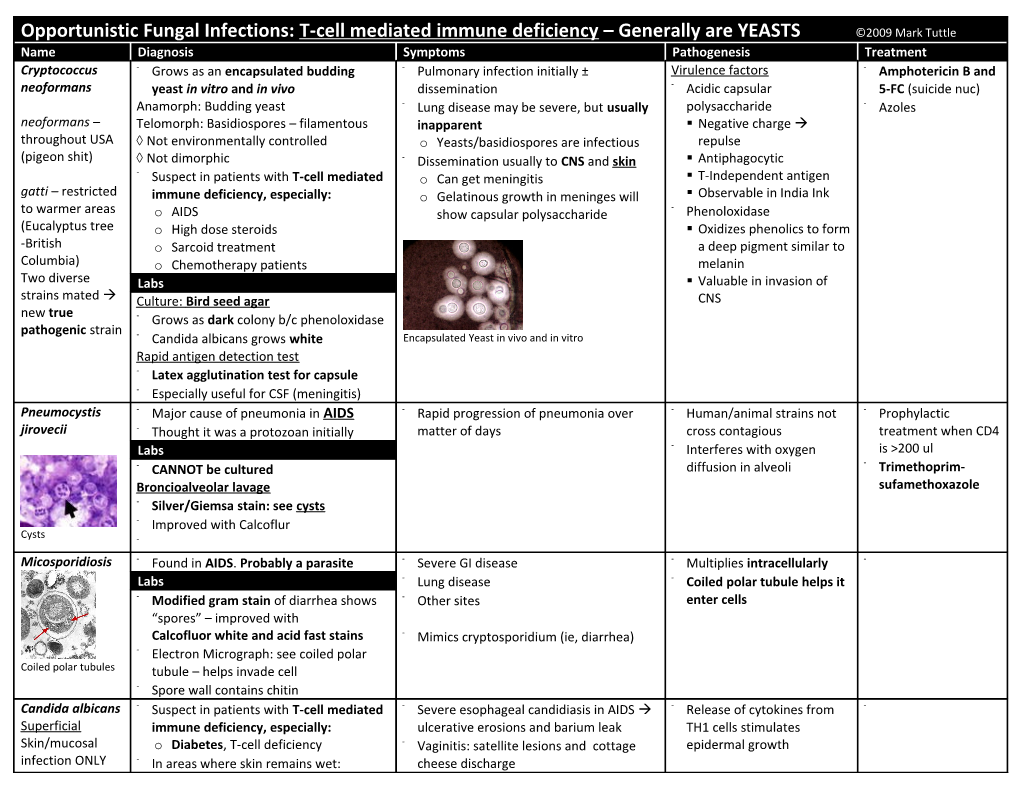
Opportunistic Fungal Infections: T-cell mediated immune deficiency – Generally are YEASTS ©2009 Mark Tuttle Name Diagnosis Symptoms Pathogenesis Treatment Cryptococcus - Grows as an encapsulated budding - Pulmonary infection initially ± Virulence factors - Amphotericin B and neoformans yeast in vitro and in vivo dissemination - Acidic capsular 5-FC (suicide nuc) Anamorph: Budding yeast - Lung disease may be severe, but usually polysaccharide - Azoles neoformans – Telomorph: Basidiospores – filamentous inapparent . Negative charge throughout USA Not environmentally controlled o Yeasts/basidiospores are infectious repulse (pigeon shit) Not dimorphic - Dissemination usually to CNS and skin . Antiphagocytic - Suspect in patients with T-cell mediated o Can get meningitis . T-Independent antigen gatti – restricted immune deficiency, especially: o Gelatinous growth in meninges will . Observable in India Ink - to warmer areas o AIDS show capsular polysaccharide Phenoloxidase (Eucalyptus tree o High dose steroids . Oxidizes phenolics to form -British o Sarcoid treatment a deep pigment similar to Columbia) o Chemotherapy patients melanin Two diverse Labs . Valuable in invasion of strains mated Culture: Bird seed agar CNS new true - Grows as dark colony b/c phenoloxidase pathogenic strain - Candida albicans grows white Encapsulated Yeast in vivo and in vitro Rapid antigen detection test - Latex agglutination test for capsule - Especially useful for CSF (meningitis) Pneumocystis - Major cause of pneumonia in AIDS - Rapid progression of pneumonia over - Human/animal strains not - Prophylactic jirovecii - Thought it was a protozoan initially matter of days cross contagious treatment when CD4 Labs - Interferes with oxygen is >200 ul - - CANNOT be cultured diffusion in alveoli Trimethoprim- Broncioalveolar lavage sufamethoxazole - Silver/Giemsa stain: see cysts - Improved with Calcoflur Cysts - Micosporidiosis - Found in AIDS. Probably a parasite - Severe GI disease - Multiplies intracellularly - Labs - Lung disease - Coiled polar tubule helps it - Modified gram stain of diarrhea shows - Other sites enter cells “spores” – improved with Calcofluor white and acid fast stains - Mimics cryptosporidium (ie, diarrhea) - Electron Micrograph: see coiled polar Coiled polar tubules tubule – helps invade cell - Spore wall contains chitin Candida albicans - Suspect in patients with T-cell mediated - Severe esophageal candidiasis in AIDS - Release of cytokines from - Superficial immune deficiency, especially: ulcerative erosions and barium leak TH1 cells stimulates Skin/mucosal o Diabetes, T-cell deficiency - Vaginitis: satellite lesions and cottage epidermal growth infection ONLY - In areas where skin remains wet: cheese discharge o Mouth corners (Dentures), fingers - ↑inflammation/erosion vs. Malassezia Opportunistic Fungal Infections: Neutrophil immune deficiency – Generally are MOLDS ©2009 Mark Tuttle Name Diagnosis Symptoms Pathogenesis Treatment Aspergillus - Mold producing abundant - Infects via lungs unless injected somehow . See air crescent - Newer azoles fumigates, blastoconidia on conidiophores - Pulmonary phagocytes fail to kill spores in with high dose steroid treatment (Voriconazole/ flavus, - On composts and rotting plant - Hyphae branch (usually at 45°), expands and penetrates blood vessel walls Poscaonazole) niger materials . Infarcts follow BV penetration replacing - Septate branching hyphae; angiotrophic - Hyphae in lung present problem of size but normal neutrophils are effective amphotericin B - - - Fusarium mimics growth pattern but is at killing them with Reactive Oxygen, H2O2, Myeloperoxidase, and Cl Treat on suspicion rare (Contact lenses) Non-neutropenic complications because of rapid - More and more seen post bone marrow - Aspergilloma: Grows in a ball in a pre-existing scarred cavity (TB/Sarcoid) progression Septate hyphae, transplant . Corrodes edge – danger of hemoptysis (coughing blood) branching at 45° - Sporegerm tubehyphae/mycelium . Grows saprophytically outside the reach of the immune system Labs . Treatment: Need surgery . See air crescent Culture: Grows very well at 45°C - Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis CT scan: Air crescent in lungs (except in . Spores germinate in bronchioles and begin to grow people with absolutely no neutrophils) . Allergic mucus response leads to plugging of bronchioles. ABs ↑↑ Biopsy . Significantly reduced lung capacity Won’t see in blood sample usually! Zygomycetes - Anamorphs: sporangiospores Rhinocerebral zygomycosis - Usually via lung with - Resistant to azoles, - Germinate to form hyphae/mycelium - Infection via nasal turbinates and dissemination, but can occur via including resistance . Wide, aseptate, irregular hyphae sinuses into CNS (lethal in brain) GI and wounds to newer azoles: - Much rarer than Aspergillus - ONLY diabetics with ketoacidosis - Hyphae are angiotrophic Voriconazole/ Sporangiospores - Can get coinfection with Aspergillus Bone marrow transplant recipients - Iron stimulates growth Posconazole - Get zygomacosis when given - MUST USE voriconazole/posaconazole amphotericin B prophylactically for Aspergillus Aseptate hyphae Candida albicans - See BOTH yeasts and hyphae in tissues - Serious skin and mucosal infections - NOT respiratory route of infection - Some species Invasive also in Tinea Versicolor (Malassezia) but do not cause disseminated disease - Infect via GI and indwelling resistant to Deep-seated, these are noninflammatory/localized unless neutropenia develops catheters fluconazole thus systemic Culture (Sarabound agar) - Normal Flora of mucosal surfaces important to identify - - On low Glucose and pCO2↑ Chronic Muscocutaneous Candidiasis Dissemination to eye, vitreous species; based on - yeast converts to filamentous form Rare fluid, heart patterns of sugar - Yeast: Pseudohyphae - Candida on dry skin and nails Phenotype switching (10-5) assimilation (Elongated budding yeast) - Masses of antibodies - Not a product of mutation Pseudohyphae - Filamentous: Chlamydospore** - Susceptibility is multifactorial - Switches morphology and Diagnostic for Candida albicans o T-cell anergy for Candida metabolism (and Candida dubliniensis) o Zinc deficiency (Treat w/Zinc!!) - Enhances ability to thrive in Germ Tube test (Mix Candida w/serum) o Endocrinopathy different environments - C. albicans (and C. dubliniensis) will - Chlamydospore Can develop resistance to drugs form germ tubes - Can develop antiphagocitosis
Algae!! Diarrhea (profuse bleeding, malodorous, 90% H2O, steatorrhea, similar to anthraxebolaids)