Biology 3201 memory tricks
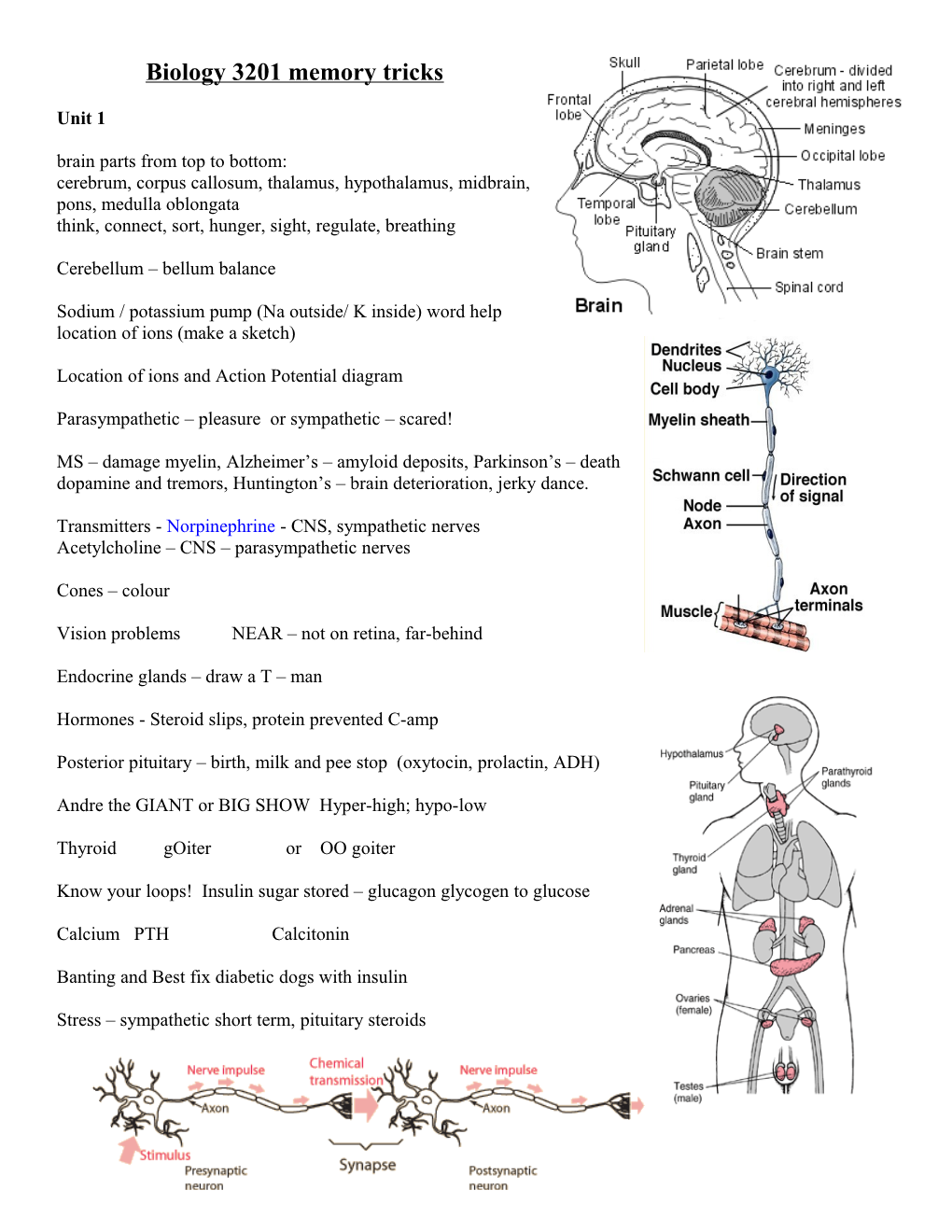
Unit 1 brain parts from top to bottom: cerebrum, corpus callosum, thalamus, hypothalamus, midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata think, connect, sort, hunger, sight, regulate, breathing
Cerebellum – bellum balance
Sodium / potassium pump (Na outside/ K inside) word help location of ions (make a sketch)
Location of ions and Action Potential diagram
Parasympathetic – pleasure or sympathetic – scared!
MS – damage myelin, Alzheimer’s – amyloid deposits, Parkinson’s – death dopamine and tremors, Huntington’s – brain deterioration, jerky dance.
Transmitters - Norpinephrine - CNS, sympathetic nerves Acetylcholine – CNS – parasympathetic nerves
Cones – colour
Vision problems NEAR – not on retina, far-behind
Endocrine glands – draw a T – man
Hormones - Steroid slips, protein prevented C-amp
Posterior pituitary – birth, milk and pee stop (oxytocin, prolactin, ADH)
Andre the GIANT or BIG SHOW Hyper-high; hypo-low
Thyroid gOiter or OO goiter
Know your loops! Insulin sugar stored – glucagon glycogen to glucose
Calcium PTH Calcitonin
Banting and Best fix diabetic dogs with insulin
Stress – sympathetic short term, pituitary steroids Unit 2
Progesterone – Pregnancy
Stages of mitosis and meiosis - Pro-meta-ana, coil up, line up split up.
46 – s – 92 – mitosis – 2 cells (46)
Cytokinesis – fingers for animals and chop for cell plate of plant cells.
Meiosis – 46 – s - 92 – M1 – 2 cells - M2 – 4 cells (23)
Meiosis – crossing over and tetrad separation
Pituitary – LH (ovulation) FSH (duh!) Ovarian – progesterone (preganancy and pee test) estrogen (early) (drawing of cycle)
Path of sperm – testes – epididymis – vas deferens – 3 glands – urethra Path of egg – ovary - oviduct – uterus – cervix – vagina
Fertilization, cleavage, morula, blastulation, gastrula, neurulation, organogenesis, ……fetus
Fertilization high in oviduct
Inner cell mass – embryo. Trophoblast – membranes and placenta
Meso-middle-muscle Ecto-outer-skin endo-inner-gut
Birth – positive oxytocin (oxy – out!)
Asexual : ( budding, binary fission, spores, fragmentation, parthenogenesis.
Hormones development FSH, LH birth control pill prevents, barriers stop, spermicides and morning after pill kill, surgery is like a barrier technologies for babies – invitro, …….. amniocentesis >12 weeks, ultrasound, fetoscopy, and chorionic villus sampling <10 weeks mother – baby connection
Stop here for Midyear exam Unit 3 Practice your crosses using this site - http://mail.esdnl.ca/~patrick_wells/biology/genetics/genetics.html
Flower reproduction (double fertilization)
Mendel pea plants
Homo-same hetero- different
Genotype – Rr, RR, rr (2 alleles per gene)
Phenotype – tall or short – what you see! vocab - know it! allele, gene, hybrid, pure, trait, P1, F1, F2
4 step cross GASR working backwards - showing WORK!
Dominance (RR, Rr – round, rr - wrinkled) Try to use letters that have different cases, Tt, Qq, etc. co-dominance and multiple alleles – blood types (LO, LA, LB) recessive LO, co dominant - LA, LB incomplete – snap dragons (RR, WW, RW) monohybrid – 3:1 and segregation of alleles, dihybrid – 9:3:3:1 and independent assortment sex linkage XX girl, XY boy Anything on X will always be expressed in males (Morgan)
Linkage and crossing over – play dough!
Chromosome theory (Sutton – fly spit!)
Molecular People – Mendel, Sutton and Boveri, Levene, Griffith, Mcleod,McCarty and Avery, Chargaff, Franklin and Wilkins Hershey and Chase, Watson and Crick, McClintock
Model of replication – see text for summary (quite good!) DNA – A to T, G to C
Protein Synthesis and the translation table and use the guide below DNA triplets TAC Transcription to mRNA codons AUG (in nucleus) Translation to tRNA Anticodon UAC (on ribosome) Amino Acid comes from the codon table – Start or methionine
Mutations – frameshift vs point for gene, somatic(body) vs germ (seed)
Chromosome mutations – they are what they say and they are bad! Autosomal recessive inheritance (Tay-Sachs and PKU), Co-dominant inheritance (Sickle-cell Disease), Autosomal dominant inheritance (progeria and huntington’s), Incomplete dominant inheritance (FH), x-linked recessive inheritance (color-blindness, muscular dystrophy, and hemophilia) Pedigree diagrams – key on the recessives or look for males to see if the trait is sex linked.
Define genetic engineering (bacteria, viruses and blenders).
Genetic counseling – using ratios to inform
Diseases - screening and prevention, surgery, environmental control, and gene therapy.
Genetic engineering - restriction enzymes, recombinant DNA, DNA amplification (PCR) and bacterial vectors), gel electrophoresis, and DNA sequencing.
Human genome project – find human genes to help set up gene therapy (virus infection therapy)
Risks of genetics research – privacy, financial, ethical. Benefits – knowledge of predisposition to disease, analysis, prevention, and treatment of disease.
GMF/GMO killer corn, transgenic salmon, insulin producing bacteria, oil eating bacteria - - - - Risks?
Cloners – twinning! Dolly – egg injection and treatment Clones are not diverse………
Unit 4 Evolution
Terms evolution – change over time – simple to complex , adaptation – a trick to survive, variation is diversity in a population
Peppered moth story - population evolution and adaptation.
Natural selection (God) and artificial selection (us)
Charles Lyell (geological theory), Thomas Malthus (human population growth), Alfred Wallace and Charles Darwin (Natural Selection), Georges Cuvier - - Fossils
Lamarck – theory of acquired characteristics and use and disuse
Lamarckian (wrong) and Darwinian (right!) Darwin didn’t know Mendel’s work but knew artificial selection.
Genetics and Evolution come together for the modern synthesis – leading to gene pool concept.
Evidence for Evolution - fossil record, biogeography, comparative anatomy (vestigial structures, homologous structures, analogous structures), comparative embryology, heredity (DNA), and molecular biology (molecules).
Relative age - position of fossils in rock layers. Absolute dating - half-life of radio isotopes
Selection (directional, disruptive and stabilizing) Rate evolution – GRADUAL ISM and Punctuated______equilibrium Origin of Life – Heterotroph then Autotroph (No Oxygen, then oxygen)