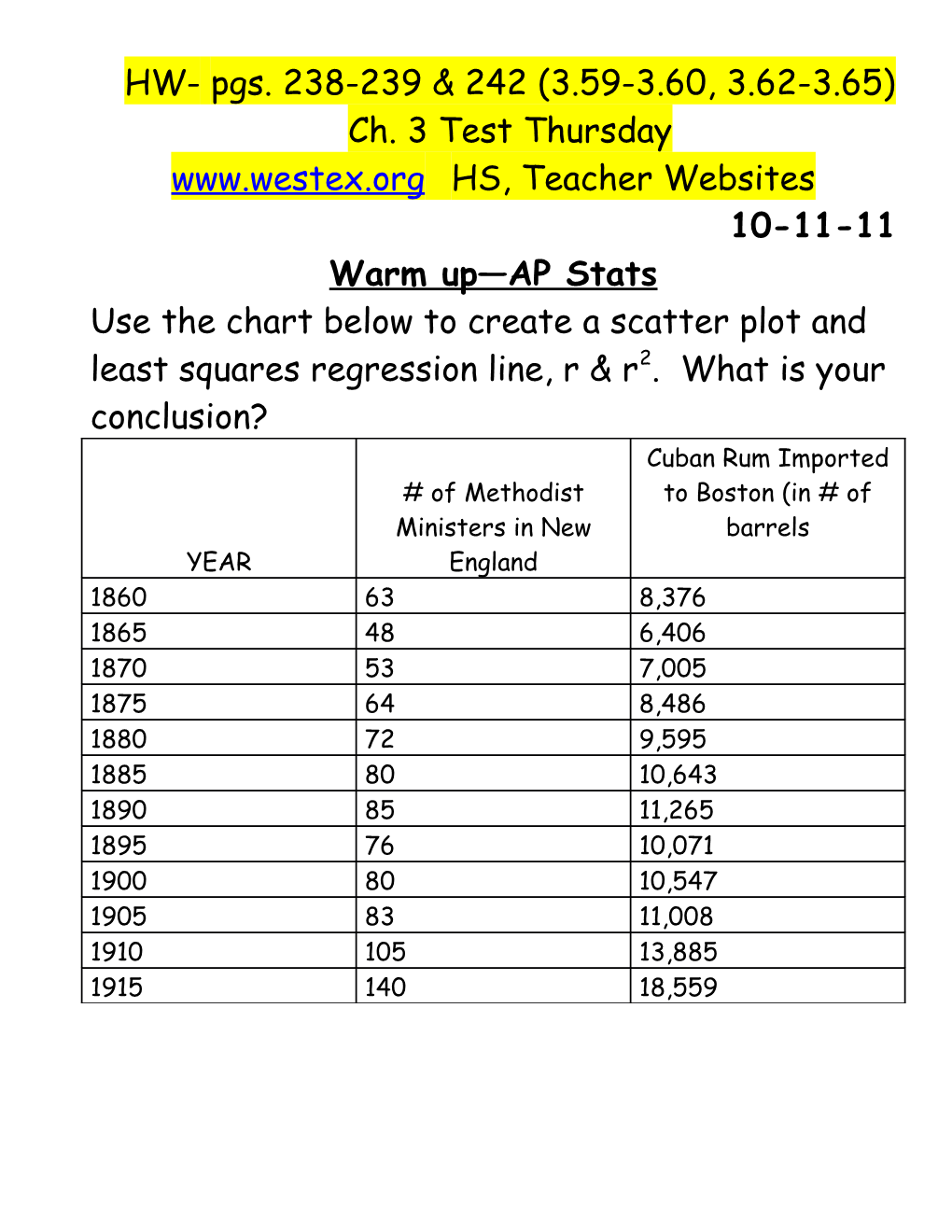
HW- pgs. 238-239 & 242 (3.59-3.60, 3.62-3.65) Ch. 3 Test Thursday www.westex.org HS, Teacher Websites 10-11-11 Warm up—AP Stats Use the chart below to create a scatter plot and least squares regression line, r & r2. What is your conclusion? Cuban Rum Imported # of Methodist to Boston (in # of Ministers in New barrels YEAR England 1860 63 8,376 1865 48 6,406 1870 53 7,005 1875 64 8,486 1880 72 9,595 1885 80 10,643 1890 85 11,265 1895 76 10,071 1900 80 10,547 1905 83 11,008 1910 105 13,885 1915 140 18,559 Name ______Date ______AP Stats
Ch. 1 Ch. 2 Test Test 0.7778 0.7632 0.9583 0.8816 0.4722 0.6053 0.9167 1 0.9861 0.9342 0.9861 0.8816 0.7361 0.9737 0.8333 0.8289 0.5278 0.7895 0.9167 1 0.7778 0.8553 0.9444 0.8421 0.6111 0.7105 0.4583 0.8816 0.7778 0.8421 0.8333 0.7895 0.75 0.8816 To the right are the paired scores for the two test we have taken so far for 17 of you. Compute the correlation Calculate the LSRL Graph the scatterplot and the LSRL on the graph below Predict what score the 4th person would get on the second test based on their first test score of 0.9167 Calculate the residual for this prediction What does r2 tell us in the context of the problem? Is the first test score a good predictor of an individual’s second test score? Name ______Date ______AP Stats 3 Examining Relationships 3.3 Correlation and Regression Wisdom
Objectives Recall the 3 limitations on the use of correlation and regression. Explain what is meant by an outlier in bivariate data Explain what is meant by an influential observation and how it relates to regression. Given a scatterplot in a regression setting, identify outliers and influential observations. Define a lurking variable. Give an example of what it means to say “association does not imply causation”. Explain how correlations based on averages differ from correlations based on individuals.
Correlation and regression are powerful tools for describing the relationship between 2 variables. But there are ______.
LIMITATIONS: Correlation & regression describe only linear relationships
Extrapolation often produces unreliable predictions
Correlation is not resistant
Distinction between outliers and influential observations Influential points are almost always outliers, but all outliers are not influential.
Influential point o Test is what happens to ______when point is removed. If a major change, then it’s an influential point.
Outlier o Far away from data set in y or x direction (no rule like with univariate data) . Outliers in y direction affect:
. Outliers in x direction affect: Lurking variable (Think about today’s warm up!!!) Variable that is not the explanatory or the response, yet may influence the ______of the relationship between those two!
Can make a correlation or regression misleading. Always think about possible lurking variables!!!
***For this reason, ASSOCIATION doesn’t IMPLY CAUSATION!***
Beware of correlations based on average data. (see pg. 241-242) When not using individuals for a scatter plot the correlations calculated tend to be too high when applied to an individual. HW- pgs. 238-239 & 242 (3.59-3.60, 3.62-3.65) Ch. 3 Test Thursday www.westex.org HS, Teacher Websites