2HS301: Discrete Mathematics & Probability [4 0 0 4 0]
Learning Outcomes: After successful completion of this course, student will be able to Understand discrete mathematical preliminaries Apply discrete mathematics in formal representation of various computing constructs Recognize the importance of analytical problem solving approach in engineering problems
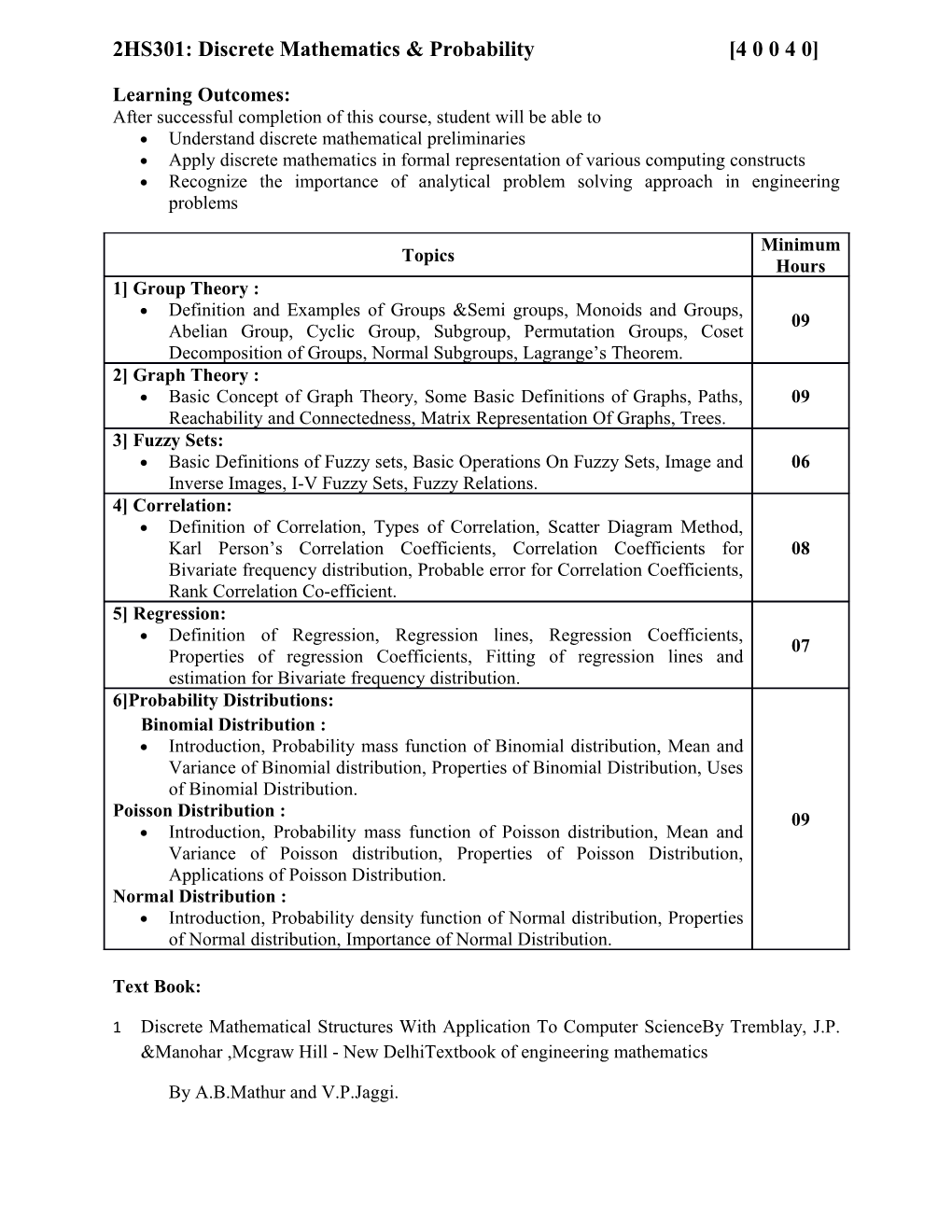
Minimum Topics Hours 1] Group Theory : Definition and Examples of Groups &Semi groups, Monoids and Groups, 09 Abelian Group, Cyclic Group, Subgroup, Permutation Groups, Coset Decomposition of Groups, Normal Subgroups, Lagrange’s Theorem. 2] Graph Theory : Basic Concept of Graph Theory, Some Basic Definitions of Graphs, Paths, 09 Reachability and Connectedness, Matrix Representation Of Graphs, Trees. 3] Fuzzy Sets: Basic Definitions of Fuzzy sets, Basic Operations On Fuzzy Sets, Image and 06 Inverse Images, I-V Fuzzy Sets, Fuzzy Relations. 4] Correlation: Definition of Correlation, Types of Correlation, Scatter Diagram Method, Karl Person’s Correlation Coefficients, Correlation Coefficients for 08 Bivariate frequency distribution, Probable error for Correlation Coefficients, Rank Correlation Co-efficient. 5] Regression: Definition of Regression, Regression lines, Regression Coefficients, 07 Properties of regression Coefficients, Fitting of regression lines and estimation for Bivariate frequency distribution. 6]Probability Distributions: Binomial Distribution : Introduction, Probability mass function of Binomial distribution, Mean and Variance of Binomial distribution, Properties of Binomial Distribution, Uses of Binomial Distribution. Poisson Distribution : 09 Introduction, Probability mass function of Poisson distribution, Mean and Variance of Poisson distribution, Properties of Poisson Distribution, Applications of Poisson Distribution. Normal Distribution : Introduction, Probability density function of Normal distribution, Properties of Normal distribution, Importance of Normal Distribution.
Text Book:
1 Discrete Mathematical Structures With Application To Computer ScienceBy Tremblay, J.P. &Manohar ,Mcgraw Hill - New DelhiTextbook of engineering mathematics
By A.B.Mathur and V.P.Jaggi. Reference Books:
2 Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications
By Rosen,KennethL.Mcgraw Hill - New Delhi
3 Discrete Mathematical Structures For Computer Science
By Kolman, B& Busby R.C,Prentice Hall Of India PvtLtd.,New Delhi
4 Applied Discrete Structures For Computer Science
By Alan Doerr&Kenneth ,GalgotiaPub.Pvt.Ltd. New Delhi
5 Fuzzy Sets and Fuzzy Logic. Theory and Applications
By Georgr J. Klir/Bo Yuan
6 Fundamental of Applied Statistics
By S.C. Gupta & V.K. Kapoor , Sultan Chand Publication
7 Probability, Statistics and Random Process
By T Veerarajan, TMH 2IT302: Computer System Organization [3 0 2 3 1]
Learning Outcomes: To learn various number systems and their conversion used in digital components To design basic electronics circuit for various applications and their analysis To introduce the main concepts and components of basic computer To introduce internal operations of computer and various instructions to perform operations in computer
Minimum Topics Hours 1] Digital Electronics: 5 Binary Systems:
Digital Computer & Systems, binary numbers, number base conversions, different number systems & their relations, complements, binary codes, addition and subtraction of binarynumbers. 4 Boolean Algebra & Logic Gates:
Basic definitions, axiomatic definition of Boolean algebra, basic theorems & properties, Boolean functions, canonical & standard forms, Logic 5 operations, Digital Logic gates. Simplification of Boolean Functions: 4
Map method, Two, Three, Four, Five & Six variable maps, products of sum & sum of products simplification, don't care conditions, tabulation method. 5 Combinational Logic: 6 Design procedure, adder, subtractors, code conversion, analysis procedure, exclusive- OR & equivalence functions. Combinational Logic with MSI & LSI: 3
Binary parallel adder, magnitude comparator, decoders, multiplexers, de- multiplexers Sequential Logic:
Flip-Flop, state reduction and assignment, flip-flop excitation table, design procedure, design of counters Registers
Registers, shift registers
2] Introduction to microprocessor Introduction 8085, high level languages, assembly/machine language, 8085 5 Programmable model, Instruction set, basic assembly programming 3] Computer Organization 7 Basic Computer Organization and Design
Von Neumann Model Of Computer, IEEE Floating point representation, CPU, Arithmetic micro operations, Logical micro operations, Instruction cycles, addressing modes.
Text Book:
1 Digital Logic and Computer Design
By Morris Mano
Reference Books:
2 Digital Electronics Circuits & Systems
By V. K. Puri
3 Microprocessor Architecture, Programming & application with 8085/8080A
By Ramesh S. Gaonkar
4 Computer Organization & Architecture
By William Stallings
5 Computer Organization and Design
By P.PalChaudhuri 2IT303: Internet Programming [3 0 4 3 2]
Learning Outcomes: After successful completion of this course, student will be able to Understand basics of internet and to develop different web applications. Understand java script and its usage Be able to create simple web pages using HTML and CSS Be able to write simple programs using JavaScript To have hands on experience for HTML using CSS, PHP this will help them to prepare website and web base application.
Minimum Topics Hours 1] Introduction to Internet & Internet Programming: Basics of Internet, Internet programming and its applications 02 Website & its Types with Example Main Objectives and study purpose of HTML,CSS & JavaScript 2] Hypertext Markup Language -- HTML Basic: Introduction of HTML Elements of HTML HTML Basic Tags HTML Formatting HTML Entities HTML Links, 05 HTML Images HTML Frames HTML Tables HTML Lists HTML Forms Meta-tags and search engine 3] Cascaded Style Sheet – CSS: Introduction to CSS CSS Syntax & How to Insert a Style Sheet CSS Background CSS Text CSS Font CSS Border 06 CSS Margin & Padding CSS List CSS Tables CSS Dimension CSS Pseudo Class CSS Image Opacity 4] Basics of Java Script and Advance JavaScript: 18 Introduction to JavaScript How to Insert a JavaScript JavaScript Variable JavaScript Operator JavaScript Conditional Statement JavaScript Popup Boxes JavaScript Function JavaScript Loop Statement JavaScript Break and continue Statement JavaScript Events JavaScript try, catch & throw Statement JavaScript Object JavaScript Form Validation JavaScript Cookies JavaScript Browser JSON 5] Introduction to HTML5 & CSS3 (In Lecture): Introduction to HTML 5.0 and its tags. 02 Introduction to CSS 3.0 and its properties. 6] Introduction to Web Design and Development Tool: 02 Design and Deployment of Website. (on Local and real IP) 7] Introduction to PHP: PHP Introduction, advantages, drawbacks, comparison with other language, Installation, PHP Syntax, PHP Variables, String, Printing statements, 05 Operators, If...Else, Switch, Looping, Arrays, Functions, Forms, ways to passing information : $_GET, $_POST etc, Date, Include, File, File Upload, Cookies, Sessions
Text Book:
1. Introduction to Internet and HTML scripting By Bhaumik Shroff Reference Books:
2. Teach yourself HTML in 24 hours By Techmedia 3. HTML4 BIBLE By BraynOmdex 4. ABC of JavaScript By Purcell lee BPB publication 5. Pure java Script By Gilliam Johnson Techmedia 6. Introduction to web Technology By Uttam K. Roy 7. Programming PHP By RasmusLerdorf, Kevin Tatroe& Peter MacIntyre
Web References:
www.w3school.com www.tutorialspoint.com
2IT304: Object Oriented Programming [3 0 4 3 2] Learning Outcomes: After successful completion of this course, student will be able to Understand and describe the basic principles and constructs of object-oriented programming Understand the significance of object oriented tools and technologies for modular development Design, develop, execute, debug and validate programs in object oriented programming environment Minimum Topics Hours 1] Introduction: Object Oriented Programming Concepts (Encapsulation, Inheritance & Polymorphism), 4 Features Of JAVA Language, Types Of JAVA Programs, JAVA Architecture 2] Literals, Data Types And Variables: Literals (Integer Literals, Floating Point Literals, Character Literals, String Literals, Boolean Literals), 1 Data Types (Integer Types, Floating Point Types, Character Type, Boolean Type), Variables. 3] The Structure Of a Java Program: Structure Of a Java Program, Comments, Expressions and Statements, 3 Type Conversion, Block Statements and Scope. 4] Operators: Arithmetic Operators, Bitwise Operators, Relational Operators, Boolean 1 Logical Operators, Ternary Operator, Operator Precedence 5] Control Statements: The if...else Statement, The switch Statement, The while Statement, The do...while Statement, The for...Statement, 2 The break Statement, The continue Statement, The comma Statement 6] Arrays: 3 One-Dimensional Array, Multi-Dimensional Array 7] Classes: Defining a Class, The new Operator and Objects, The dot operator, Method Declaration and Calling, 6 Constructors, Instance Variable Hiding, this in Constructor, Method Overloading, Passing Objects as Parameters to Methods 8] Inheritance: Creating Subclasses, Method Overriding, Final Class, Final Variables, Object Destruction and Garbage Collection, 5 Recursion, Static Methods, Block and Variables (Static Class, Static Variables, Static Block), Abstract Classes. 9] Packages and Interfaces: Package, The import Statement, Access Modifier, Interfaces (Defining 4 Interfaces, Implementing an Interface) 10] Exceptions: Type Of Exceptions, Catching Exceptions (Nested try Blocks, Hierarchy Of Multiple Catch Blocks), 4 Rethrowing Exceptions, Creating Your Own Exceptions, Broadcasting that a Method Throws Exception, The finally Block, Checked and Unchecked Exceptions 11] Input And Output Classes: I/O Streams, The File Class, Byte Stream (InputStream, OutputStream), Disk File Handling (FileInputStream, FileOutputStream), Memory Handling (ByteArrayInputStream, ByteArrayOutputStream), Filtered Byte Streams (BufferedInputStream, BufferedOutputStream, 2 DataInputStream, DataOutputStream), SequenceInputStream, ObjectOutputStream, ObjectInputStream, Random Access File, Character Stream(CharArrayReader, CharArrayWriter, InputStreamReader, Output StreamWriter, FileWriter, FileReader, BufferedReader, BufferedWriter) 12] Strings: The String Class( Equality Operator and equals Method, String 3 Concatenation with +), The StringBuffer Class 13] Applets: Applet Basics, Methods of Building an Applet, Some General Methods of Applet, Displaying Text in Status Bar, Embedding Applet Information, The HTML Applet Tag, Reading Parameters into Applets, Colors in Applet, 3 Getting Documentbase and Codebase, Interfaces in Applet, Multimedia in Applet (Playing Audio Clips, Images in Applet, Applet Showing Other HTML Pages) 14] Event Handling: Delegation Event Model, Events (The ActionEvent Class, The AdjustmentEvent Class, The ComponentEvent Class, The ItemEvent Class, The KeyEvent Class, The MouseEvent Class, The TextEvent Class, The 1 WindowEvent Class), Event Listeners, Registering Listners with Source, Adapter Classes
Text Book:
1. Java - The Complete Reference By Herbet Shield, Tata Mc-Graw Hill Publication
Reference Books:
2. Programming with Java – A primer By E. Balagurasamy, Tata Mc-Graw Hill Publication. 3. Programming in Java2 By Dr. K. Somasundaram, Jaico Books
2IT305: Database Management System-I [3 0 2 3 1]
Learning Outcomes: After successful completion of this course, student will be able to Distinguish between data and information and Knowledge. Distinguish between Traditional file processing system and DBMS. Understand the needs for and uses of database management systems in business Study the physical and logical database designs, database modeling, relational, hierarchical, and network models. Understand the components of a computerized database information system (application) like, database languages, users etc Describe data models, schemas and instances. To design a correct, new database information system for a business functional area and implement the design To understand and use of data manipulation language to query, update, and manage a database. Describe basic storage, data and file organizations. Minimum Topics Hours 1] Introduction: Database system applications Database Systems versus File Systems View of Data 5 Database Languages Database Users and Administrators Database System Structure 2] Relational Data Model: Structure of Relational Databases The Relational Algebra Extended Relational Algebra Operations 6 Modifications of the Database Views The Tuple Relational Calculus The Domain Relational Calculus 3] SQL: Background , Basic Structure Set Operations Aggregate Functions Null Values Nested Subqueries , Views, Complex Queries , Modification of Database, Joined Relations 8 Data-Definition Language Other SQL Features Domain Constraint Referential Integrity Authorization 4] Database Design & E-R Model : 7 Basic Concepts Constraints, Keys Design Issues Entity Relationship Diagram, Weak Entity Sets, Extended E-R Features Design of an E-R Database Schema Reduction of an E-R Schema to Tables 5] Relational Database Design: Data redundancy and inconsistency 8 Normalization Normal Forms: 1NF, 2NF, 3NF, Functional Dependency Functional Dependencies Decomposition Desirable Properties of Decomposition More Normal Forms: BCNF, 4 NF 6] Storage and File Structure : Overview of Physical Storage Media Magnetic Disks, RAID , Tertiary Storage 6 Storage Access , File Organization Organization of Records in Files Data-Dictionary Storage
Text Book:
1. Database System Concepts 5th Edition, By Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan
Reference Books:
2. An Introduction to Database Systems:7th Edition By C. J. Date. 3. Practical Book: - SQI, PL/SQL 3rd Edition, By Ivan Bayross 2HS401: Mathematics for Computer Engineering & Information Technology [4 0 0 4 0]
Learning Outcomes: After successful completion of the course, student will be able to Express physical phenomenon in mathematical formulation Understand and solve differential equations Basic knowledge of widely used Fourier transform techniques and their applications in computer and IT Engineering Minimum Topics Hours 1] Laplace Transforms: Definition, Laplace transform of elementary functions. Formulas of Laplace transform, Inverse Laplace transforms. Laplace transform of derivatives, Laplace transform of integration. Multiplication by tn, Division by t, 10 Convolution theorem, Unit step and Heaviside’s unit function, Dirac-delta function. Periodic functions, Solution of ordinary linear differential equations, simultaneous equation with constant co-efficient applied to electrical circuits 2] Fourier Series: Definition of periodic function, Euler’s formula, Functions having points of discontinuity, Change of intervals, Odd and Even functions, Expansion of 10 odd or even periodic functions, Half range sine and cosine series, Elements of harmonic analysis. 3] Fourier Transforms: Definition, Fourier integral, Fourier sine and cosine integration, complex 04 form of Fourier integral, Fourier sine transform, Fourier cosine transform, Inverse Fourier transforms. 4] Theory Of Complex Variables: Analytic functions, Cauchy-Riemann equation, Line integral, Cauchy’s theorem and Cauchy’s integral formula, Simple form of conformal 08 transformation with application of the solution of two-dimensional problems. 5] Finite Differences And Difference Equations: Finite differences interpolation, Newton’s and LaGrange’s formula, Difference equation with constants co-efficient, Solution of ordinary and 07 partial differential equations with boundary conditions by finite difference method. 6] Numerical Methods: Roots of algebraic equations, Solution of linear simultaneous equations, Numerical differentiation and Numerical integration, Numerical methods to 09 solve first order, first degree ordinary differential equations.
Text Book:
1. Higher engineering mathematics By B.S.Grewal. Reference Books:
2. Engineering mathematics By Srivastava. 3. Textbook of engineering mathematics By A.B.Mathur and V.P.Jaggi. 4. Theory of functions of complex variables By Shanti Narayan. 5. Introductory Methods of Numerical Analysis By S.S.Sastry. 6. Advanced engineering mathematics By Erwin Kreyzing. 2IT402: Operating System [3 0 2 3 1]
Learning Outcomes: To give the fundamental knowledge of how operating system works, manages the applications that are running. To give fundamental principles of operating system design and its components To understand process management, memory management including virtual memory, protection and security management. Minimum Topics Hours 1] Introduction: What is an OS? Evolution Of OS, services, Types of OS, Different view of 04 OS, Basics of memory and architecture 2] Process Management: Process, Process Control Block, Process States 04 Threads, Types of Threads, Multithreading 3] Inter process Communication: Race Conditions, Critical Section, Mutual Exclusion Hardware Solution, Strict Alternation, Peterson’s Solution 06 The Producer Consumer Problem, Semaphores, Event Counters, Monitors Message Passing and Classical IPC Problems: Reader’s & Writer Problem, Dinning Philosopher Problem etc., Scheduling, Scheduling Algorithms. 4] Deadlock: Deadlock Problem, Deadlock Characterization Deadlock Detection, Deadlockrecovery 06 Deadlock avoidance: Banker’s algorithm for single & multiple resources Deadlock Prevention. 5] Memory Management: Paging: Principle Of Operation, Page Allocation, H/W Support For Paging Multiprogramming With Fixed partitions Segmentation 11 Swapping Virtual Memory: Concept, Performance Of Demand Paging, Page Replacement Algorithms, Thrashing, Locality 6] Input Output Management: I/O Devices, Device Controllers, Direct Memory Access Principles Of Input/outputs, Interrupt Handler, Device Driver, Device 04 Independent I/O Software Disks: RAID levels, Disks Arm Scheduling Algorithm Error Handling 7] File Systems: 04 File Naming, File Structure, File Types, File Access, File Attributes, File Operations, Memory Mapped Files Directories: Hierarchical Directory System, Pathnames, Directory Operations File System Implementation, Contiguous Allocation, Linked List Allocation, Linked List Using Index, Inodes, Implementing Directories In C, MS-DOS, and UNIX. Shared Files Disk Space Management File System Reliability File System Performance 8] Case Study: File System of Unix Operating System and Linux, Role Of Kernel & Function Of Kernel, Design Structure of Unix Operating System, System 04 Calls, Elementary Shell Programming, Directory Structure, System Administration.
Text Book:
1. Operating System Concepts ByAviSilberschatz, Peter Baer Galvin, Greg Gagne, Ninth Edition, Wiley Reference Books:
2. Modern Operating Systems By Andrew S. Tanenbaum, Third Edition PHI 3. Operating Systems, D.M.Dhamdhare, TMH 4. Operating Systems Internals and Design Principles , William Stallings , Seventh Edition, Prentice Hall 5. Unix System Concepts & Applications, Sumitabha Das, TMH 6. Unix Shell Programming, YashwantKanitkar By BPB Publications 2IT403: Database Management System- II [3 0 2 3 1]
Learning Outcomes: Enhance the previous knowledge of database systems by deepening the understanding of the theoretical and practical aspects of the database technologies. Apply the principles of query optimization to a database schema. Understand basic principles of database transaction processing and managing concurrent execution environment. Explain the various types of locking mechanisms utilized within database management systems. Explain the different types of database failures as well as the methods used to recover from these failures Describe various database architectures and distributed database management system. Get familiar with the currently available database processing environment (client –server model)and query language to build business applications and services Develope practical skills in the use of this model and approach to be able to select and apply the appropriate methods for a particular. Be able to apply learned skills to solving practical database related tasks This course introduces students to PL/SQL and helps them to understand the benefits of this powerful programming Language. Students learns to create PL/SQL blocks of application code and are introduced various database objects. They learn about declaring variables, trapping exceptions and they also learn to declare and control cursors. Students learn to develop, execute and manage PL\SQL stored program units like procedures, functions, packages and database triggers.
Minimum Topics Hours 1] Query Processing & Query Optimization: Overview Query Evaluation 03 Measure of Query Cost Query Optimization Overview 2] Transaction: Transaction concepts Transaction state ACID Property Implementation of Atomicity & Durability Concurrent executions 07 Serializibility Conflict serializability View serializability Recoverability Recoverable schedules Cascade less schedules 3] Concurrency control: 08 Lock based protocols Locks Granting of locks Two phase locking protocol Implementation of locking Graph based protocols Timestamp based protocols Timestamps Timestamp ordering protocol Thomas’ write rules Multiple granularity Deadlock handling Deadlock prevention 4] Recovery system: Failure classification Storage structure Storage type Stable storage implementation Data access 05 Recovery & atomicity Log based recovery Deferred database modification Immediate database modification Checkpoints Shadow paging. 5] Database system architecture: Centralized & client server architectures Centralized systems Client server system Server system architecture Transaction server process structure Data servers Parallel systems Speedup & scale up 06 Interconnection networks Parallel database architectures . Shared memory . Shared Disk . Shared nothing . Hierarchical Distributed systems An example of a distributed database 6] Distributed databases: Homogeneous & heterogeneous databases. Distributed data storage Data replication Data fragmentation Transparency Distributed transactions 06 System architecture System failure modes Commit protocols Two phase commit protocol. . Commit protocol . Handling of failures Three phase commit protocol 7] PL/SQL: 05 Theoretical Fundamentals Text Book:
1. Database System Concepts5th Edition By, Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan Reference Books:
2. An Introduction to Database Systems: 7th Edition By C. J. Date. 3. Practical Book : - SQI, PL/SQL 2nd Edition By Ivan Bayross
2IT404: Data Structures [4 0 4 4 2] Learning Outcomes: To explain concepts of Data structure such as stack, link list, tree, queue, searching and sorting. To explain importance and applications of data structures.
Minimum Topics Hours 1] Overview of C: Arrays, Functions
Strings 4 Structures
Pointers
2] Introduction to Data Structures: Importance 2 Applications Algorithm & Algorithmic Notation 3] Stack: Definition & Concept Operations on Stacks (Push, Pop, Peep, Change -Algorithm & Implementation). 8 Applications of Stack. Polish expression and Conversions 4] Queue: The queue and its sequential representation. 5 Simple Queue, Circular Queue, Double ended Queue, Priority Queue 5] Sorting: Elementary sorts: Bubble sort, Quick sort, Selection sort, Insertion sort, 7 Merge sort, Radix sort Worst case and average behavior 6] Searching: Basic search techniques-Sequential searching, 2 Binary Search 7] Linked List: Concept. Sequential Allocation method Vs linked Allocation method. Dynamic Data structure Vs Static Data structure. Pointer and Linked Allocation. 12 Singly Linked List Storage Structures & Basic Operations. Circular Linked List Storage Structures & Basic Operations. Doubly Linked List Storage Structures & Basic Operations. Application of Linked List Storage Structures. 8] Graph Theory: Definition Graph Representation. 3 Graph Terms Graph Traversal 9] Tree: 5 Tree & Graph Binary trees Binary tree representation Binary tree traversals Threaded binary tree Different binary tree Tree applications
Text Book:
1. An Introduction to Data Structures with Application
By Jean-Paul Tremblay ,Paul G. Sorenson (second Edition)
Reference Books:
2. Data Structures using C and C++
By Aaron M. Tenenbaum, Moshe J. Augenstein, YedidyahLangsam (Second Edition)
3. Classic Data Structure
By D. Samanta 2IT405: Application Development Tools [2 0 4 2 2]
Learning Outcomes: Explain the architecture of .NET Framework. Explain features of C# using Console Application. Develop Windows based applicationusing MicrosoftVisual Studio. Develop ADO.net based database driven .NET application Develop simple web application. Minimum Topics Hours 1] Introduction To .Net Framework: The Common Language Runtime Compilation in .NET (MSIL and JIT), CTS, CLS Cross language Integration 5 Garbage Collection Assemblies, Name spaces Versioning and deployment Framework class Library 2] C# Basics using Console Application: Variables and Constants Data Types, Scope of variables Formatting Data Handling Exceptions 7 Conditions Input Validation Loops,Arrays Functions 3] Windows Forms and Controls: Creating Windows Forms, Windows Forms Properties and Events Controls (Properties and Events of Controls):Button, Label, TextBox, NumericUpDown, CheckBox, RadioButton, DateTimePicker, GroupBox 7 ListBox, ListView, ComboBox, TabControl, PictureBox, ProgressBar ToolTips, RichTextbox, Timer DatagridView 4] Working With ADO.NET: Introduction to ADO.NET, ADO.NET Architecture 5 Understanding SqlConnection, SqlCommands, SqlDataReaders DataSet and DataAdapter 5] Introduction to ASP.NET: 5 Introduction to ASP.NET, Working with Web and HTMLControls Text Book:
1. Beginning Visual C# Programming By Wrox publication References Books:
2. Professional C# and .NET By Wrox Publication