Supplementary Information
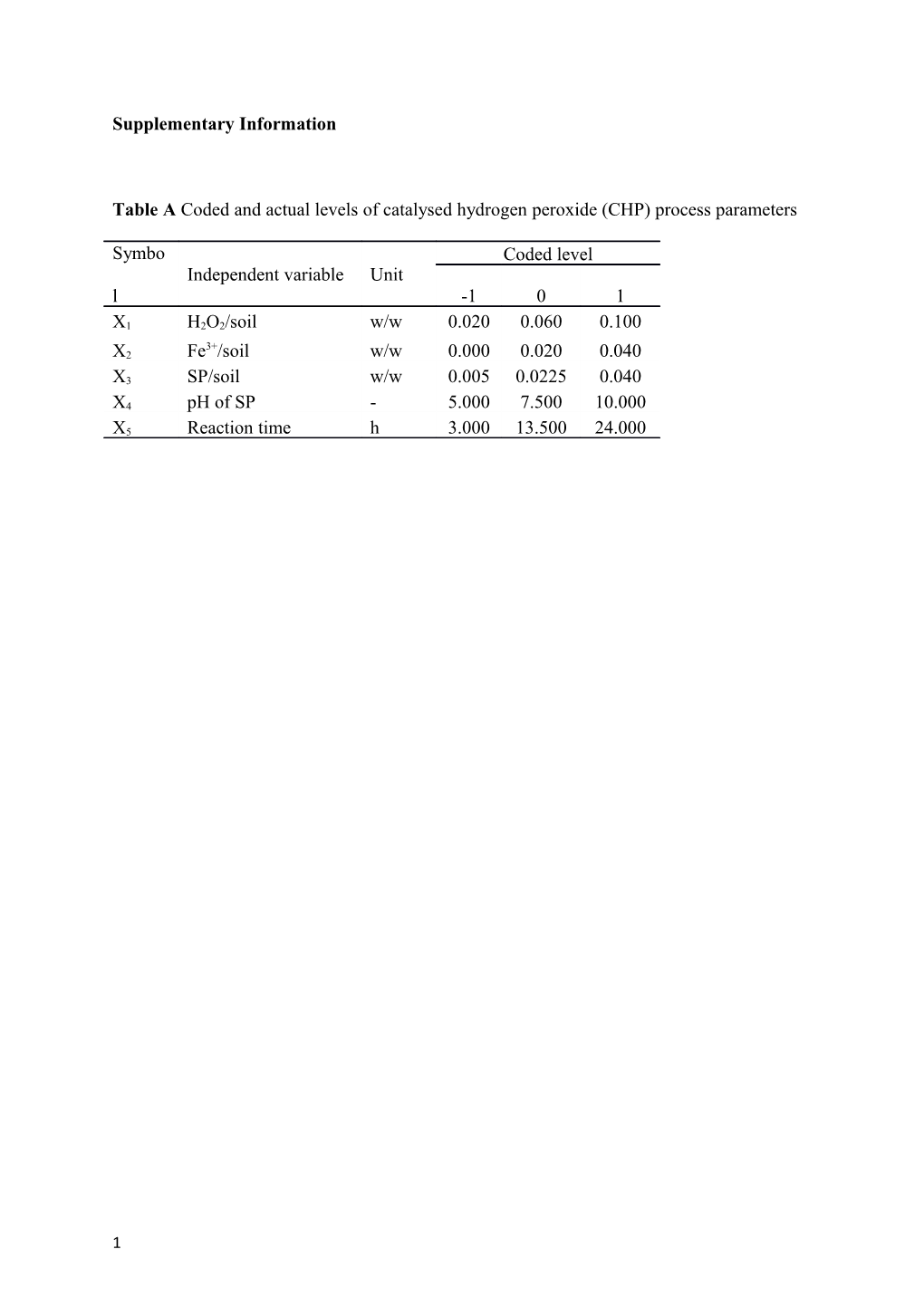
Table A Coded and actual levels of catalysed hydrogen peroxide (CHP) process parameters
Symbo Coded level Independent variable Unit l -1 0 1
X1 H2O2/soil w/w 0.020 0.060 0.100 3+ X2 Fe /soil w/w 0.000 0.020 0.040
X3 SP/soil w/w 0.005 0.0225 0.040
X4 pH of SP - 5.000 7.500 10.000
X5 Reaction time h 3.000 13.500 24.000
1 Table B Experimental design matrix for CHP process
Cod ed Real values Run no. Point type valu es Observed responses
x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 Y1 Y2 Y3 1 Factorial -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 0.02 0 0.005 5 3 8.46 4.53 4.82 2 Factorial 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 0.1 0 0.005 5 3 17.61 14.04 4.55 3 Factorial -1 1 -1 -1 -1 0.02 0.04 0.005 5 3 18.84 16.32 4.28 4 Factorial 1 1 -1 -1 -1 0.1 0.04 0.005 5 3 29.72 26.47 4.09 5 Factorial -1 -1 1 -1 -1 0.02 0 0.04 5 3 5.36 3.86 4.94 6 Factorial 1 -1 1 -1 -1 0.1 0 0.04 5 3 17.03 12.88 4.73 7 Factorial -1 1 1 -1 -1 0.02 0.04 0.04 5 3 23.91 20.46 4.56 8 Factorial 1 1 1 -1 -1 0.1 0.04 0.04 5 3 35.77 31.81 4.29 9 Factorial -1 -1 -1 1 -1 0.02 0 0.005 10 3 6.43 4.25 8.06 10 Factorial 1 -1 -1 1 -1 0.1 0 0.005 10 3 17.82 14.93 6.37 11 Factorial -1 1 -1 1 -1 0.02 0.04 0.005 10 3 23.32 19.67 7.44 12 Factorial 1 1 -1 1 -1 0.1 0.04 0.005 10 3 49.55 45.99 7.21 13 Factorial -1 -1 1 1 -1 0.02 0 0.04 10 3 17.18 15.64 8.69 14 Factorial 1 -1 1 1 -1 0.1 0 0.04 10 3 21.34 18.06 6.94 15 Factorial -1 1 1 1 -1 0.02 0.04 0.04 10 3 26.28 22.83 7.78 16 Factorial 1 1 1 1 -1 0.1 0.04 0.04 10 3 59.75 56.33 7.49 17 Factorial -1 -1 -1 -1 1 0.02 0 0.005 5 24 18.37 15.66 4.76 18 Factorial 1 -1 -1 -1 1 0.1 0 0.005 5 24 26.45 24.48 4.43 19 Factorial -1 1 -1 -1 1 0.02 0.04 0.005 5 24 32.30 28.77 4.19 20 Factorial 1 1 -1 -1 1 0.1 0.04 0.005 5 24 47.15 43.69 4.05 21 Factorial -1 -1 1 -1 1 0.02 0 0.04 5 24 10.22 7.41 4.78 22 Factorial 1 -1 1 -1 1 0.1 0 0.04 5 24 17.59 15.22 4.58 23 Factorial -1 1 1 -1 1 0.02 0.04 0.04 5 24 40.72 37.35 4.35
2 24 Factorial 1 1 1 -1 1 0.1 0.04 0.04 5 24 53.07 49.18 4.03 25 Factorial -1 -1 -1 1 1 0.02 0 0.005 10 24 9.81 7.64 7.93 26 Factorial 1 -1 -1 1 1 0.1 0 0.005 10 24 13.55 10.82 6.28 27 Factorial -1 1 -1 1 1 0.02 0.04 0.005 10 24 41.67 37.55 7.34 28 Factorial 1 1 -1 1 1 0.1 0.04 0.005 10 24 58.84 53.37 7.17 29 Factorial -1 -1 1 1 1 0.02 0 0.04 10 24 8.60 5.04 8.22 30 Factorial 1 -1 1 1 1 0.1 0 0.04 10 24 17.08 13.24 6.31 31 Factorial -1 1 1 1 1 0.02 0.04 0.04 10 24 55.73 53.91 7.45 32 Factorial 1 1 1 1 1 0.1 0.04 0.04 10 24 62.29 58.33 7.27 33 Axial -1 0 0 0 0 0.02 0.02 0.0225 7.5 13.5 58.54 56.70 5.49 34 Axial 1 0 0 0 0 0.1 0.02 0.0225 7.5 13.5 63.62 61.25 5.14 35 Axial 0 -1 0 0 0 0.06 0 0.0225 7.5 13.5 24.58 21.89 5.58 36 Axial 0 1 0 0 0 0.06 0.04 0.0225 7.5 13.5 60.11 56.77 5.04 37 Axial 0 0 -1 0 0 0.06 0.02 0.005 7.5 13.5 39.09 37.08 5.41 38 Axial 0 0 1 0 0 0.06 0.02 0.04 7.5 13.5 59.77 54.60 5.82 39 Axial 0 0 0 -1 0 0.06 0.02 0.0225 5 13.5 77.48 74.29 4.23 40 Axial 0 0 0 1 0 0.06 0.02 0.0225 10 13.5 72.13 68.66 7.92 41 Axial 0 0 0 0 -1 0.06 0.02 0.0225 7.5 3 86.42 81.03 5.26 42 Axial 0 0 0 0 1 0.06 0.02 0.0225 7.5 24 81.27 77.82 5.38 43 Centre 0 0 0 0 0 0.06 0.02 0.0225 7.5 13.5 66.93 64.17 5.85 44 Centre 0 0 0 0 0 0.06 0.02 0.0225 7.5 13.5 79.22 75.30 5.70 45 Centre 0 0 0 0 0 0.06 0.02 0.0225 7.5 13.5 63.25 61.80 4.91 46 Centre 0 0 0 0 0 0.06 0.02 0.0225 7.5 13.5 71.89 67.93 5.36 47 Centre 0 0 0 0 0 0.06 0.02 0.0225 7.5 13.5 71.07 66.28 5.46 48 Centre 0 0 0 0 0 0.06 0.02 0.0225 7.5 13.5 78.66 74.74 5.57 49 Centre 0 0 0 0 0 0.06 0.02 0.0225 7.5 13.5 60.82 58.31 5.72 50 Centre 0 0 0 0 0 0.06 0.02 0.0225 7.5 13.5 74.04 71.65 5.64
X1 (H2O2/soil, w/w) is calculated as: X1=0.06 + x1 (0.04) X4 (pH of SP) is calculated as: X4=7.5 + x4 (2.5) 3+ X2 (Fe /soil, w/w) is calculated as: X2=0.02 + x2 (0.02) X5 (reaction time, h) is calculated as X5=13.5 + x5 (10.5) X3 (SP/soil, w/w) is calculated as: X3=0.0225 + x3 (0.0175)
3 Note: Only run # 1, 9, 17 and 25 (total reagent applied < water holding capacity) were characterised as unsaturated conditions.
4 PAH extractions from solid (soil) and aqueous (leachate) phases
PAH extraction from solid phase was performed using automated Soxhlet extraction
(Gerhardt, Malaysia). Five grams of soil sample was placed in a thimble and mixed with
Na2SO4 at a ratio of 2:1 w/w. The mixture was extracted with 140 ml of n-pentane for 3 h.
The remaining solvent was evaporated to dryness using a rotary evaporator (Heidolph,
Germany) and subsequently solvent-exchanged using 1 ml of ACN.
PAH extraction from aqueous phase (column leachate) was carried out by liquid- liquid extraction using 1:1 (v/v) n-hexane. Similarly, the upper hexane segment (containing
PAHs) was evaporated to dryness and subsequently solvent-exchanged using 1 ml of ACN.
GC analysis for PAH determination
PAH residuals in the extracts from Soxhlet extraction and liquid-liquid extraction were analysed using a GC autosampler (Perkin Elmer Clarus 500, USA) equipped with a flame ionisation detector and fused silica capillary column (DB-5MS, 30 m x 0.25 mm x 0.25 µm) according to the US EPA Method 8100.Helium (16 psi) was used as the carrier gas. The temperatures of the injector and the detector were set at 290°C and 300°C, respectively. The temperature in the oven was set at 100°C for 1 min, ramped at 25°C/min to 310°C and held for 2 min. The concentration of individual PAHs in the solvent was quantified using standard calibration method (all R2 >0.98). Individual PAHs were identified by retention times of approximately 8.50 min and 9.90 min for PHE and FLUT, respectively. The limits of detection (LOD) were found to be 1.24 and 0.9 mg/kg and the limits of quantification (LOQ) were found to be 1.97 and 1.30 mg/kg for PHE and FLUT, respectively.
The collected uncontaminated soil samples were also subjected to detection of possible PAH content in the fresh soil. The GC chromatogram showed concentration values of 0.01 and 0.02 mg/kg at retention time 8.50 min and 9.90 min, respectively. These values
5 are below the LOD and LOQ of the GC analysis. Hence, it is plausible to assume that the fresh soil collected before spiking was never exposed to PAH contamination.
GC analysis for soil respiration
The rates of soil respiration were analysed using a GC (Perkin Elmer Clarus 500, USA) equipped with a thermal conductivity detector and a stainless steel column (Porapak R 80/100 mesh, 6 ft. x 1/8”). Helium served as the carrier gas at a flow rate of 20 ml/min. The operating temperatures for the oven, injector and detector were 60ºC, 100ºC and 200ºC, respectively. The CO2 produced was quantified against 1 ml of CO2 external standard (1%,
Scotty Gases, Bellefonte, PA) at approximately 0.85 min retention time.
6