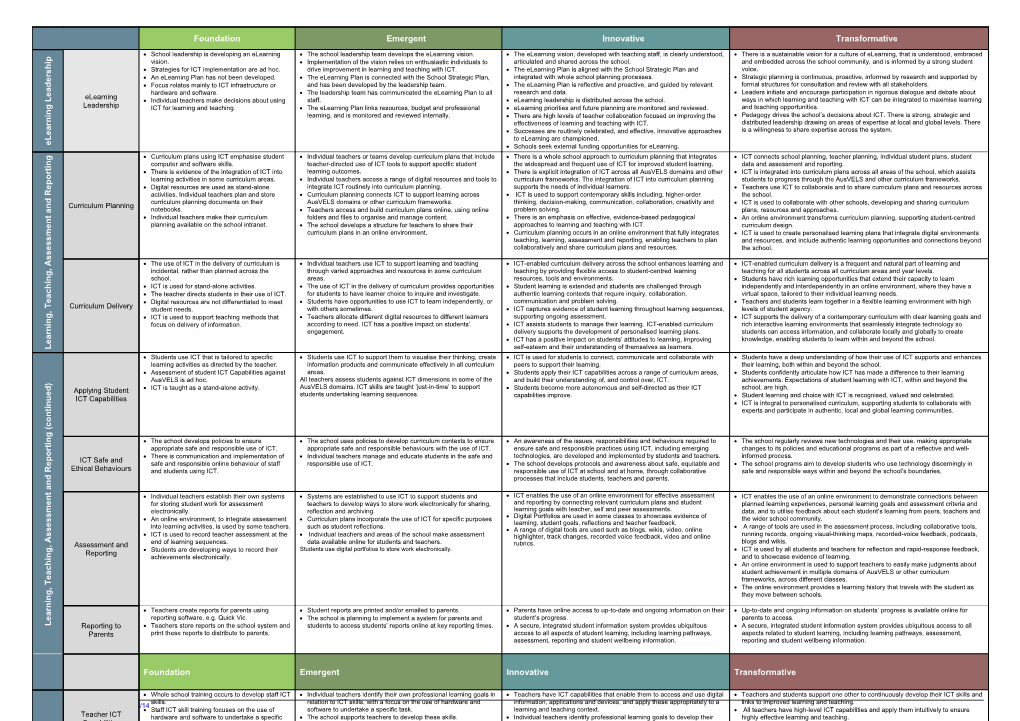
Foundation Emergent Innovative Transformative
School leadership is developing an eLearning The school leadership team develops the eLearning vision. The eLearning vision, developed with teaching staff, is clearly understood, There is a sustainable vision for a culture of eLearning, that is understood, embraced p
i vision. Implementation of the vision relies on enthusiastic individuals to articulated and shared across the school. and embedded across the school community, and is informed by a strong student h Strategies for ICT implementation are ad hoc. drive improvement in learning and teaching with ICT. The eLearning Plan is aligned with the School Strategic Plan and voice. s r An eLearning Plan has not been developed. The eLearning Plan is connected with the School Strategic Plan, integrated with whole school planning processes. Strategic planning is continuous, proactive, informed by research and supported by e
d Focus relates mainly to ICT infrastructure or and has been developed by the leadership team. The eLearning Plan is reflective and proactive, and guided by relevant formal structures for consultation and review with all stakeholders. a hardware and software. The leadership team has communicated the eLearning Plan to all research and data. Leaders initiate and encourage participation in rigorous dialogue and debate about e eLearning L Individual teachers make decisions about using staff. eLearning leadership is distributed across the school. ways in which learning and teaching with ICT can be integrated to maximise learning Leadership g ICT for learning and teaching. The eLearning Plan links resources, budget and professional eLearning priorities and future planning are monitored and reviewed. and teaching opportunities. n
i learning, and is monitored and reviewed internally. There are high levels of teacher collaboration focused on improving the Pedagogy drives the school’s decisions about ICT. There is strong, strategic and n
r effectiveness of learning and teaching with ICT. distributed leadership drawing on areas of expertise at local and global levels. There a Successes are routinely celebrated, and effective, innovative approaches is a willingness to share expertise across the system. e
L to eLearning are championed. e Schools seek external funding opportunities for eLearning. Curriculum plans using ICT emphasise student Individual teachers or teams develop curriculum plans that include There is a whole school approach to curriculum planning that integrates ICT connects school planning, teacher planning, individual student plans, student g
n computer and software skills. teacher-directed use of ICT tools to support specific student the widespread and frequent use of ICT for improved student learning. data and assessment and reporting. i t
r There is evidence of the integration of ICT into learning outcomes. There is explicit integration of ICT across all AusVELS domains and other ICT is integrated into curriculum plans across all areas of the school, which assists
o learning activities in some curriculum areas. Individual teachers access a range of digital resources and tools to curriculum frameworks. The integration of ICT into curriculum planning students to progress through the AusVELS and other curriculum frameworks. p
e Digital resources are used as stand-alone integrate ICT routinely into curriculum planning. supports the needs of individual learners. Teachers use ICT to collaborate and to share curriculum plans and resources across
R Curriculum planning connects ICT to support learning across ICT is used to support contemporary skills including, higher-order activities. Individual teachers plan and store the school.
d curriculum planning documents on their AusVELS domains or other curriculum frameworks. thinking, decision-making, communication, collaboration, creativity and ICT is used to collaborate with other schools, developing and sharing curriculum
n Curriculum Planning notebooks. problem solving.
a Teachers access and build curriculum plans online, using online plans, resources and approaches.
t Individual teachers make their curriculum folders and files to organise and manage content. There is an emphasis on effective, evidence-based pedagogical An online environment transforms curriculum planning, supporting student-centred n planning available on the school intranet. approaches to learning and teaching with ICT.
e The school develops a structure for teachers to share their curriculum design. curriculum plans in an online environment. Curriculum planning occurs in an online environment that fully integrates m ICT is used to create personalised learning plans that integrate digital environments
s teaching, learning, assessment and reporting, enabling teachers to plan and resources, and include authentic learning opportunities and connections beyond s
e collaboratively and share curriculum plans and resources. the school. s s
A The use of ICT in the delivery of curriculum is Individual teachers use ICT to support learning and teaching ICT-enabled curriculum delivery across the school enhances learning and ICT-enabled curriculum delivery is a frequent and natural part of learning and
, incidental, rather than planned across the through varied approaches and resources in some curriculum teaching by providing flexible access to student-centred learning teaching for all students across all curriculum areas and year levels. g
n school. areas. resources, tools and environments. Students have rich learning opportunities that extend their capacity to learn i
h ICT is used for stand-alone activities. The use of ICT in the delivery of curriculum provides opportunities Student learning is extended and students are challenged through independently and interdependently in an online environment, where they have a c The teacher directs students in their use of ICT. for students to have learner choice to inquire and investigate. authentic learning contexts that require inquiry, collaboration, virtual space, tailored to their individual learning needs. a
e Digital resources are not differentiated to meet Students have opportunities to use ICT to learn independently, or communication and problem solving. Teachers and students learn together in a flexible learning environment with high
T Curriculum Delivery student needs. with others sometimes. ICT captures evidence of student learning throughout learning sequences, levels of student agency. ,
g ICT is used to support teaching methods that Teachers allocate different digital resources to different learners supporting ongoing assessment. ICT supports the delivery of a contemporary curriculum with clear learning goals and n
i focus on delivery of information. according to need. ICT has a positive impact on students’ ICT assists students to manage their learning. ICT-enabled curriculum rich interactive learning environments that seamlessly integrate technology so n
r engagement. delivery supports the development of personalised learning plans. students can access information, and collaborate locally and globally to create
a ICT has a positive impact on students’ attitudes to learning, improving knowledge, enabling students to learn within and beyond the school. e
L self-esteem and their understanding of themselves as learners. Students use ICT that is tailored to specific Students use ICT to support them to visualise their thinking, create ICT is used for students to connect, communicate and collaborate with Students have a deep understanding of how their use of ICT supports and enhances learning activities as directed by the teacher. information products and communicate effectively in all curriculum peers to support their learning. their learning, both within and beyond the school. Assessment of student ICT Capabilities against areas. Students apply their ICT capabilities across a range of curriculum areas, Students confidently articulate how ICT has made a difference to their learning AusVELS is ad hoc. All teachers assess students against ICT dimensions in some of the and build their understanding of, and control over, ICT. achievements. Expectations of student learning with ICT, within and beyond the ) AusVELS domains. ICT skills are taught ‘just-in-time’ to support school, are high. d Applying Student ICT is taught as a stand-alone activity. Students become more autonomous and self-directed as their ICT e students undertaking learning sequences. capabilities improve. Student learning and choice with ICT is recognised, valued and celebrated.
u ICT Capabilities
n ICT is integral to personalised curriculum, supporting students to collaborate with i
t experts and participate in authentic, local and global learning communities. n o c (
g
n The school develops policies to ensure The school uses policies to develop curriculum contexts to ensure An awareness of the issues, responsibilities and behaviours required to The school regularly reviews new technologies and their use, making appropriate i t
r appropriate safe and responsible use of ICT. appropriate safe and responsible behaviours with the use of ICT. ensure safe and responsible practices using ICT, including emerging changes to its policies and educational programs as part of a reflective and well-
o There is communication and implementation of Individual teachers manage and educate students in the safe and technologies, are developed and implemented by students and teachers. informed process. p ICT Safe and
e safe and responsible online behaviour of staff responsible use of ICT. The school develops protocols and awareness about safe, equitable and The school programs aim to develop students who use technology discerningly in
R Ethical Behaviours and students using ICT. responsible use of ICT at school and at home, through collaborative safe and responsible ways within and beyond the school’s boundaries.
d processes that include students, teachers and parents. n a
t Individual teachers establish their own systems Systems are established to use ICT to support students and ICT enables the use of an online environment for effective assessment ICT enables the use of an online environment to demonstrate connections between n
e for storing student work for assessment teachers to develop ways to store work electronically for sharing, and reporting by connecting relevant curriculum plans and student planned learning experiences, personal learning goals and assessment criteria and learning goals with teacher, self and peer assessments. m electronically. reflection and archiving. data, and to utilise feedback about each student’s learning from peers, teachers and s Digital Portfolios are used in some classes to showcase evidence of the wider school community. s An online environment, to integrate assessment Curriculum plans incorporate the use of ICT for specific purposes learning, student goals, reflections and teacher feedback. e into learning activities, is used by some teachers. such as student reflections. A range of tools are used in the assessment process, including collaborative tools,
s A range of digital tools are used such as blogs, wikis, video, online s ICT is used to record teacher assessment at the Individual teachers and areas of the school make assessment highlighter, track changes, recorded voice feedback, video and online running records, ongoing visual-thinking maps, recorded-voice feedback, podcasts,
A blogs and wikis. end of learning sequences. data available online for students and teachers. rubrics. , Assessment and Students use digital portfolios to store work electronically. ICT is used by all students and teachers for reflection and rapid-response feedback, g Reporting Students are developing ways to record their n and to showcase evidence of learning. i achievements electronically.
h An online environment is used to support teachers to easily make judgments about c
a student achievement in multiple domains of AusVELS or other curriculum
e frameworks, across different classes. T
, The online environment provides a learning history that travels with the student as
g they move between schools. n i n
r Teachers create reports for parents using Student reports are printed and/or emailed to parents. Parents have online access to up-to-date and ongoing information on their Up-to-date and ongoing information on students’ progress is available online for a
e reporting software, e.g. Quick Vic. The school is planning to implement a system for parents and student’s progress. parents to access.
L Reporting to Teachers store reports on the school system and students to access students’ reports online at key reporting times. A secure, integrated student information system provides ubiquitous A secure, integrated student information system provides ubiquitous access to all Parents print these reports to distribute to parents. access to all aspects of student learning, including learning pathways, aspects related to student learning, including learning pathways, assessment, assessment, reporting and student wellbeing information. reporting and student wellbeing information.
Foundation Emergent Innovative Transformative
Whole school training occurs to develop staff ICT Individual teachers identify their own professional learning goals in Teachers have ICT capabilities that enable them to access and use digital Teachers and students support one other to continuously develop their ICT skills and skills. relation to ICT skills, with a focus on the use of hardware and information, applications and devices, and apply these appropriately to a links to improved learning and teaching. eLearning Planning Matrix - 29/08/14 Staff ICT skill training focuses on the use of software to undertake a specific task. learning and teaching context. All teachers have high-level ICT capabilities and apply them intuitively to ensure Teacher ICT hardware and software to undertake a specific The school supports teachers to develop these skills. Individual teachers identify professional learning goals to develop their highly effective learning and teaching. Capabilities task. Teachers’ ICT capabilities enable them to access and use digital skills in using current and/or emerging technologies. They are supported