Chapter 11 Handout: Teen Physical/Social Development *Note: homosexuality, sex and pregnancy in CH12 notes (ch 11 in book)
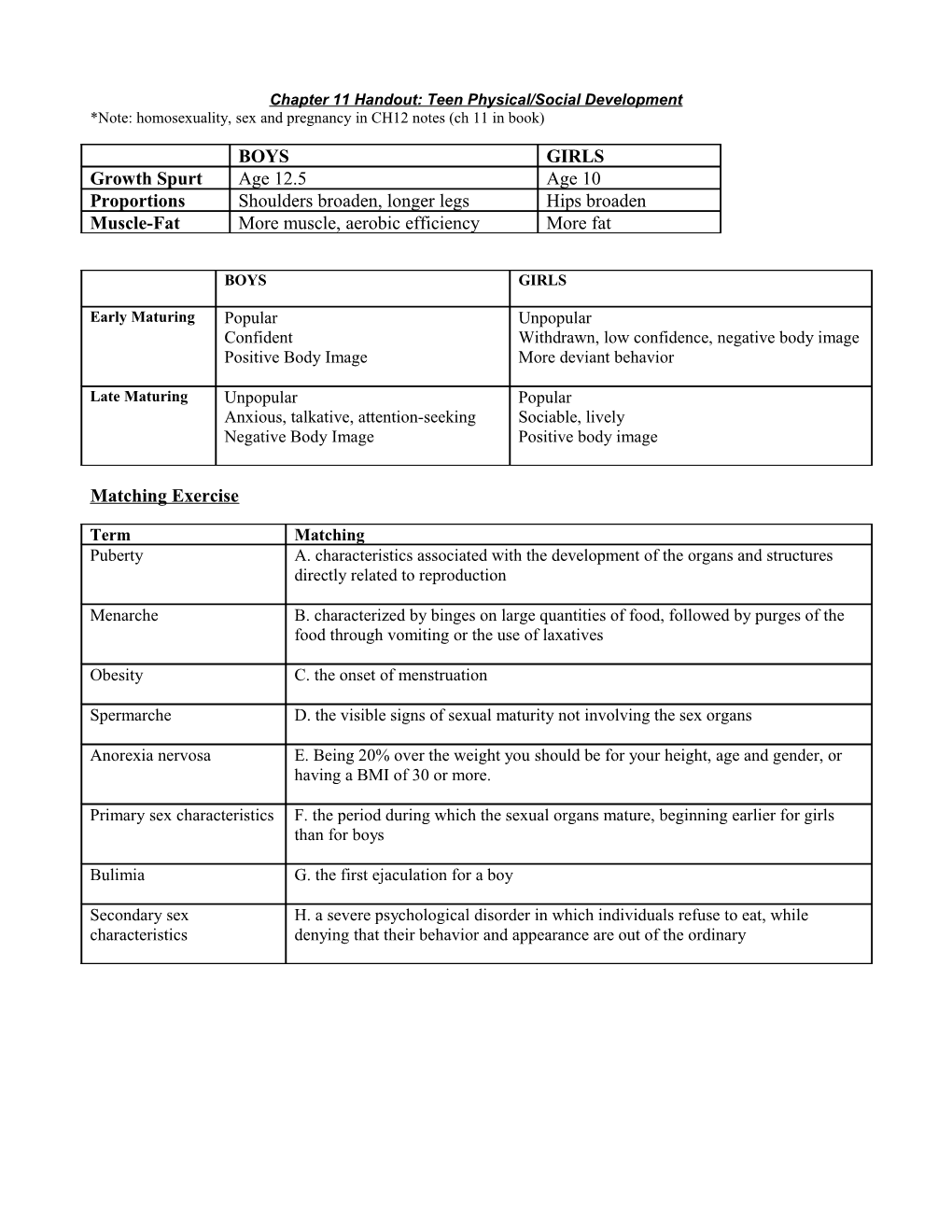
BOYS GIRLS Growth Spurt Age 12.5 Age 10 Proportions Shoulders broaden, longer legs Hips broaden Muscle-Fat More muscle, aerobic efficiency More fat
BOYS GIRLS
Early Maturing Popular Unpopular Confident Withdrawn, low confidence, negative body image Positive Body Image More deviant behavior
Late Maturing Unpopular Popular Anxious, talkative, attention-seeking Sociable, lively Negative Body Image Positive body image
Matching Exercise
Term Matching Puberty A. characteristics associated with the development of the organs and structures directly related to reproduction
Menarche B. characterized by binges on large quantities of food, followed by purges of the food through vomiting or the use of laxatives
Obesity C. the onset of menstruation
Spermarche D. the visible signs of sexual maturity not involving the sex organs
Anorexia nervosa E. Being 20% over the weight you should be for your height, age and gender, or having a BMI of 30 or more.
Primary sex characteristics F. the period during which the sexual organs mature, beginning earlier for girls than for boys
Bulimia G. the first ejaculation for a boy
Secondary sex H. a severe psychological disorder in which individuals refuse to eat, while characteristics denying that their behavior and appearance are out of the ordinary Matching Exercise
Term Definition Formal operational A. a state of self-absorption in which the world is viewed from one's own point of thinking view
Information-processing B. the knowledge that people have regarding their own thinking process, and their ability to monitor their own cognition
Metacognition C. The tendency of teens to assume that although bad things might happen to other people, their own actions will not result in negative consequences
Adolescent egocentrism D. adolescent's belief that his or her own behavior is a primary focus of others' attention and concerns
Imaginary audience E. characterized by the ability to think abstractly
Personal fable F. the model that seeks to identify the way that individuals take in, use, and store information
Invincibility fable G. the view held by some adolescents that what happens to them is unique, exceptional, and shared by no one else, which can lead to risk-taking