Physics 30: Module 2: Lesson 3 1
MODULE 2: LESSON 3 PERPENDICULAR COLLISION WORKSHEET
Inelastic Perpendicular Collision 40 marks Complete Question 1 and 3 other questions
Example Problem
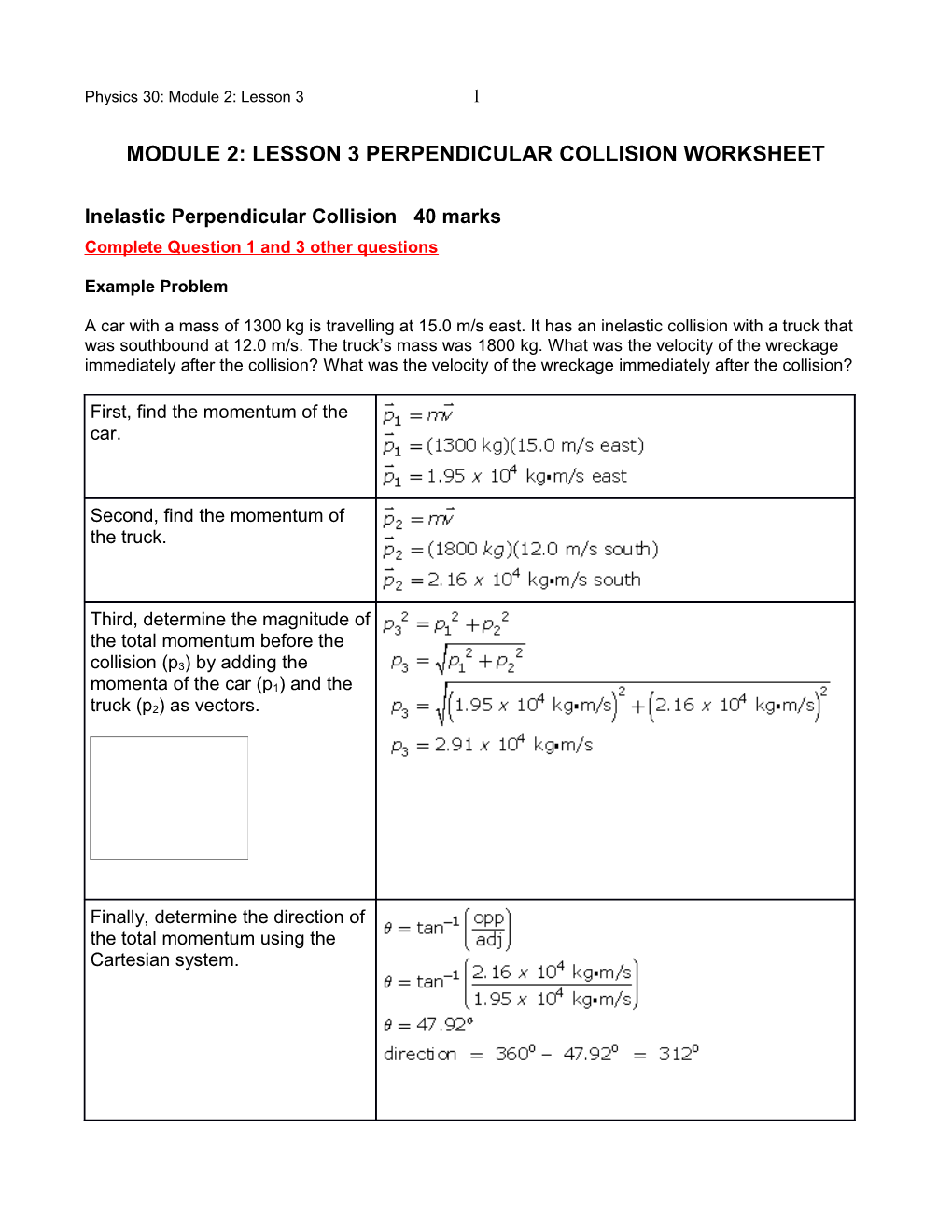
A car with a mass of 1300 kg is travelling at 15.0 m/s east. It has an inelastic collision with a truck that was southbound at 12.0 m/s. The truck’s mass was 1800 kg. What was the velocity of the wreckage immediately after the collision? What was the velocity of the wreckage immediately after the collision?
First, find the momentum of the car.
Second, find the momentum of the truck.
Third, determine the magnitude of the total momentum before the collision (p3) by adding the momenta of the car (p1) and the truck (p2) as vectors.
Finally, determine the direction of the total momentum using the Cartesian system. Physics 30: Module 2: Lesson 3 2
The total momentum before the collision is identical to the total momentum after the collision:
(polar positive direction)
To determine the final velocity, simply divide the total momentum by the total mass.
Perpendicular Collision Analysis Worksheet
As part of your Module 2: Lesson 3 Assignment, you are must complete the odd numbered questions and submit the solutions to your teacher for marks. Show all your work. Demonstrate that you have used the GRASP form. Of course, these questions provide you with the practice that you need to successfully complete this course. You should respond to all of the questions and place the answers in your course folder.
The answer(s) for each question follows in brackets. All directions are in the polar positive specification.
1. Add the following momenta to determine the resultant momentum for the following collisions:
5 marks a. 100 kg•m/s at 0° and 50.0 kgm/s at 90°
Answer:
5 marks b. 75 kg•m/s at 90° and 43 kgm/s at 180°
Answer: Physics 30: Module 2: Lesson 3 3
5 marks c. 166 kg•m/s at 180° and 53 kgm/s at 90°
Answer:
5 marks d. 347 kg•m/s at 0° and 347 kgm/s at 270o
Answer:
5 marks e. 1.87 kg•m/s at 360° and 3.25 kgm/s at 270o
Answer:
5 marks 2. A car with a mass of 1400 kg is westbound at 50 km/h. It collides at an intersection with a northbound truck travelling 40 km/h that has a mass of 2000 kg. What is the initial common velocity of the car and truck immediately after the collision if they have an inelastic collision?
Answer:
5 marks 3. A westbound truck with a mass of 1300 kg had a speed of 62 km/h, as recorded by a police radar unit it had just passed. The truck ran a red light and collided with a car heading south at an unknown speed and a mass of 1200 kg. The wreckage of the car and truck (it was an inelastic collision) ended up at a heading of 225°.
Answer:
a. If the posted speed limit was 80 km/h, was the driver of the car guilty of speeding?
Answer:
b. What was the speed of the car?
Answer: Physics 30: Module 2: Lesson 3 4
5 marks 4. A police car with a mass of 1460 kg is headed west at 60 km/h when it has an inelastic collision with a southbound 2000-kg ambulance. The wreckage ended up travelling at 45 km/h at 236°. What was the initial speed of the ambulance?
Answer:
5 marks 5. A car with a mass of 1000 kg is headed west at 75 km/h when it collides with a southbound 2000-kg truck. The initial velocity of the wreckage is 85 km/h at 253°. What was the speed of the truck before the collision?
Answer:
5 marks 6. A car with a mass of 1500 kg is northbound at 70 km/h when it is struck by an eastbound van with a mass of 2200 kg and a speed of 30 km/h. If the vehicles lock on contact, what is their initial common velocity?
Answer:
5 marks 7. A car with a mass of 1350 kg is westbound at 80 km/h when a 2450-kg truck enters the intersection from the south at 20 km/h. The vehicles have an inelastic collision. What is the velocity of the wreckage immediately after the impact?
Answer:
Once you have completed all of the questions, submit your work to your teacher.