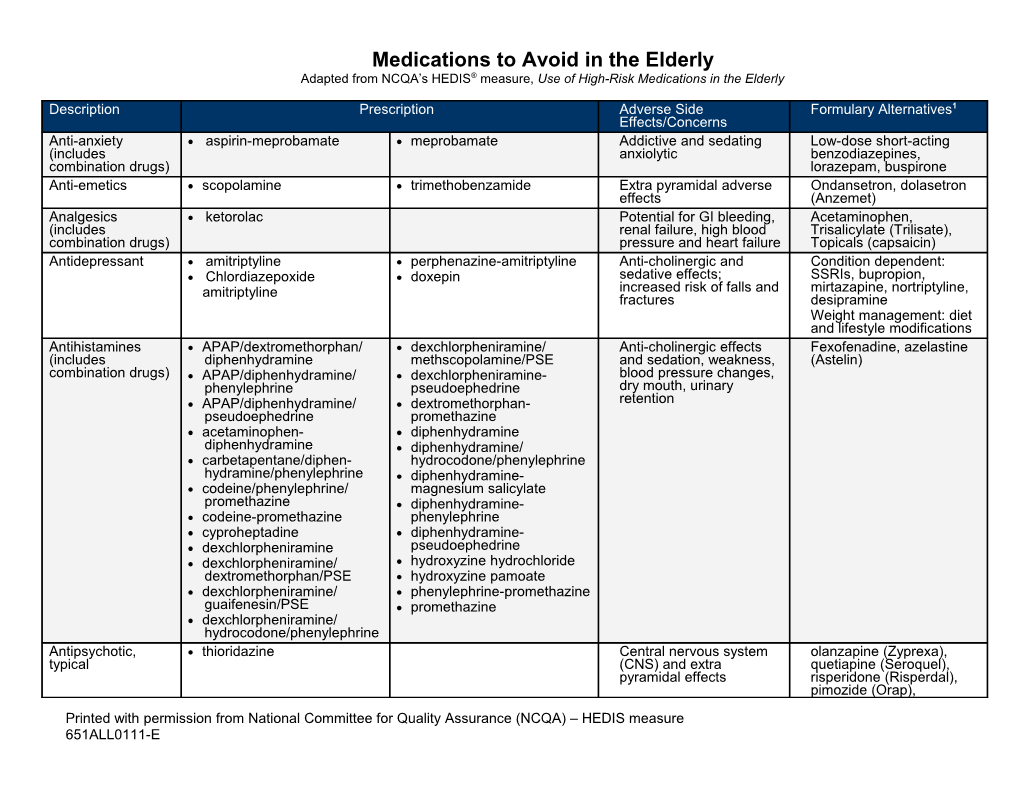
Medications to Avoid in the Elderly Adapted from NCQA’s HEDIS® measure, Use of High-Risk Medications in the Elderly
Description Prescription Adverse Side Formulary Alternatives1 Effects/Concerns Anti-anxiety aspirin-meprobamate meprobamate Addictive and sedating Low-dose short-acting (includes anxiolytic benzodiazepines, combination drugs) lorazepam, buspirone Anti-emetics scopolamine trimethobenzamide Extra pyramidal adverse Ondansetron, dolasetron effects (Anzemet) Analgesics ketorolac Potential for GI bleeding, Acetaminophen, (includes renal failure, high blood Trisalicylate (Trilisate), combination drugs) pressure and heart failure Topicals (capsaicin) Antidepressant amitriptyline perphenazine-amitriptyline Anti-cholinergic and Condition dependent: Chlordiazepoxide doxepin sedative effects; SSRIs, bupropion, amitriptyline increased risk of falls and mirtazapine, nortriptyline, fractures desipramine Weight management: diet and lifestyle modifications Antihistamines APAP/dextromethorphan/ dexchlorpheniramine/ Anti-cholinergic effects Fexofenadine, azelastine (includes diphenhydramine methscopolamine/PSE and sedation, weakness, (Astelin) combination drugs) APAP/diphenhydramine/ dexchlorpheniramine- blood pressure changes, phenylephrine pseudoephedrine dry mouth, urinary APAP/diphenhydramine/ dextromethorphan- retention pseudoephedrine promethazine acetaminophen- diphenhydramine diphenhydramine diphenhydramine/ carbetapentane/diphen- hydrocodone/phenylephrine hydramine/phenylephrine diphenhydramine- codeine/phenylephrine/ magnesium salicylate promethazine diphenhydramine- codeine-promethazine phenylephrine cyproheptadine diphenhydramine- dexchlorpheniramine pseudoephedrine dexchlorpheniramine/ hydroxyzine hydrochloride dextromethorphan/PSE hydroxyzine pamoate dexchlorpheniramine/ phenylephrine-promethazine guaifenesin/PSE promethazine dexchlorpheniramine/ hydrocodone/phenylephrine Antipsychotic, thioridazine Central nervous system olanzapine (Zyprexa), typical (CNS) and extra quetiapine (Seroquel), pyramidal effects risperidone (Risperdal), pimozide (Orap), Printed with permission from National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) – HEDIS measure 651ALL0111-E Medications to Avoid in the Elderly Adapted from NCQA’s HEDIS® measure, Use of High-Risk Medications in the Elderly
trifluoperazine Description Prescription Adverse Side Formulary Alternatives1 Effects/Concerns Amphetamines amphetamine- methamphetamine Addictive properties, angina, Condition dependent: dextroamphetamine methylphenidate hypertension and Depression: SSRIs, benzphetamine phendimetrazine myocardial infarction bupropion, mirtazapine, dexmethylphenidate phentermine nortriptyline, desipramine dextroamphetamine diethylpropion Barbiturates butabarbital phenobarbital Condition-dependent mephobarbital secobarbital Insomnia: zolpidem pentobarbital Long-acting amitriptyline- chlordiazepoxide-clidinium Causes prolonged sedation, Low-dose short–acting benzodiazepines chlordiazepoxide diazepam increased risk of falls and benzodiazepines, if they (includes chlordiazepoxide flurazepam fractures must be used combination drugs) Calcium channel nifedipine short-acting only Potential for hypotension. Felodipine, nifedipine- blockers Use long-acting formulation long-acting (nifedipine to avoid adverse effects. ER) Cardiovascular amiodarone Anti-arrhythmia Metoprolol, Atenolol; (amiodarone) associated Sotalol with prolonged QT intervals; possible torsades de pointes, bradycardia and thyroiditis Gastrointestinal dicyclomine propantheline Anti-cholinergic effects Duodenal ulcer: anti-spasmodics omeprazole Constipation: psyllium, PEG, stool softener, lubiprostone (Amitiza) Diarrhea: loperamide, aluminum hydroxide Belladonna atropine atropine-edrophonium Anti-cholinergic effects Constipation: psyllium, alkaloids (includes atropine/CPM/hyoscyamine/ belladonna PEG, stool softener, combination drugs) PE/scopolamine belladonna/ergotamine/ lubiprostone (Amitiza) atropine/hyoscyamine/PB/ phenobarbital Diarrhea: loperamide, scopolamine butabarbital/hyoscyamine/ aluminum hydroxide atropine-difenoxin phenazopyridine atropine-diphenoxylate digestive enzymes/hyos- cyamine/phenyltoloxamine
Printed with permission from National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) – HEDIS measure 651ALL0111-E Medications to Avoid in the Elderly Adapted from NCQA’s HEDIS® measure, Use of High-Risk Medications in the Elderly
hyoscyamine hyoscyamine/methenam/ m-blue/phenyl salicylate Description Prescription Adverse Side Formulary Alternatives1 Effects/Concerns Skeletal muscle ASA/caffeine/orphenadrine chlorzoxazone Anti-cholinergic effects, Baclofen, tizanidine relaxants (includes ASA/carisoprodol/codeine cyclobenzaprine sedation and weakness. combination drugs) aspirin-carisoprodol metaxalone Poorly tolerated aspirin-methocarbamol methocarbamol carisoprodol orphenadrine Oral estrogens conjugated estrogen esterified estrogen Cardio-protective properties Hot flashes: nondrug (includes conjugated estrogen- esterified estrogen- are absent; high comfort therapy, SSRIs, combination drugs) medroxyprogesterone methyl-testosterone carcinogenic effects (breast venlafaxine estropipate cancer and endometrial Bone density: calcium, cancer) vitamin D, alendronate Oral hypoglycemics Chlorpropamide Prolonged half-life causing Glipizide prolonged hypoglycemia. Causes syndrome of inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) Narcotics (includes ASA/caffeine/propoxyphene meperidine-promethazine Pentazocine produces high Hydrocodone, morphine combination drugs) acetaminophen-pentazocine naloxone-pentazocine CNS adverse effects oxycodone, fentanyl acetaminophen- pentazocine Propoxyphene produces transdermal patch, propoxyphene propoxyphene similar effects as other acetaminophen (not in belladonna-opium hydrochloride narcotic medications combination product) meperidine propoxyphene napsylate Respiratory theophylline Delirium, seizures and status Inhaled corticosteroid (e.g., epilepticus Flovent HFA or QVAR) with or without Serevent. Note: Long-acting beta agonists (LABAs) should be used in combination with ICS, for asthma maintenance therapy. LABAs are NOT indicated as monotherapy for asthma. Vasodilators Dipyridamole short-acting isoxsuprine Orthostatic hypotension Aspirin/Dipyridamole only extended-release ergot mesyloid capsules, low-dose Printed with permission from National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) – HEDIS measure 651ALL0111-E Medications to Avoid in the Elderly Adapted from NCQA’s HEDIS® measure, Use of High-Risk Medications in the Elderly
aspirin
Description Prescription Adverse Side Formulary Alternatives1 Effects/Concerns Others (including methyltestosterone nitrofurantoin Prostatic hypertrophy and Danazol androgens and nitrofurantoin macrocrystals- cardiac concerns; anabolic steroids, nitrofurantoin macrocrystals monohydrate nitrofurantoin causes renal thyroid drugs, thyroid desiccated impairment urinary anti- infectives)
1Source: Potentially Harmful Drugs in the Elderly: Beers List and More. Pharmacist's Letter/Prescriber's Letter 23.9. (2007):230907.
Printed with permission from National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) – HEDIS measure 651ALL0111-E