Regulations for Online Coursework for International Students
"For F-1 students* enrolled in classes for credit or classroom hours, no more than the equivalent of one class or three credits per session, term, semester, trimester, or quarter may be counted if taken on-line or through distance education in a course that does not require the student's physical attendance for classes, examination or other purposes integral to completion of the class. An on-line or distance education course is a course that is offered principally through the use of television, audio, or computer transmission including open broadcast, closed circuit, cable, microwave, or satellite, audio conferencing, or computer conferencing. If the F-1 student's course of study is in a language study program, no on-line or distance education classes may be considered to count toward classroom hours or credit."
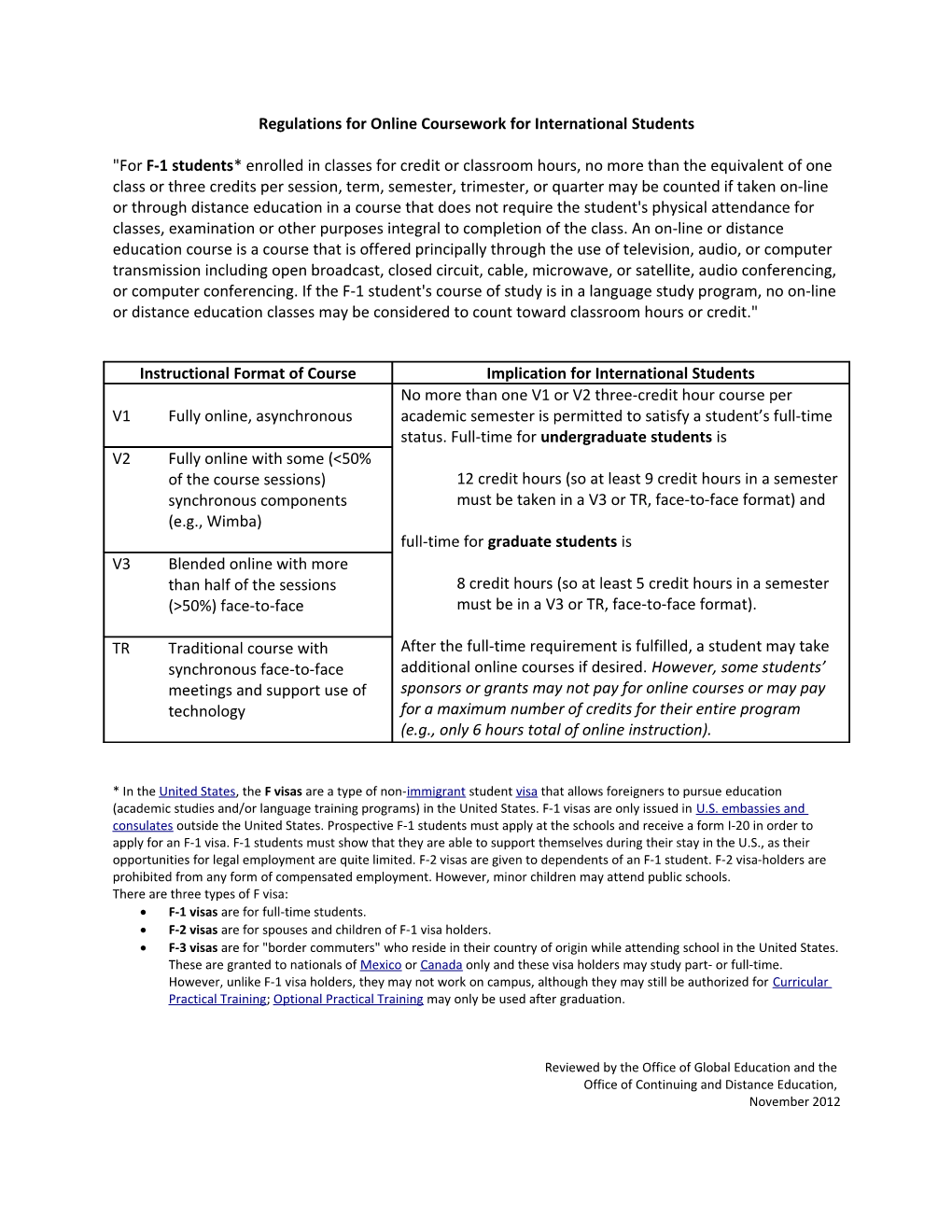
Instructional Format of Course Implication for International Students No more than one V1 or V2 three-credit hour course per V1 Fully online, asynchronous academic semester is permitted to satisfy a student’s full-time status. Full-time for undergraduate students is V2 Fully online with some (<50% of the course sessions) 12 credit hours (so at least 9 credit hours in a semester synchronous components must be taken in a V3 or TR, face-to-face format) and (e.g., Wimba) full-time for graduate students is V3 Blended online with more than half of the sessions 8 credit hours (so at least 5 credit hours in a semester (>50%) face-to-face must be in a V3 or TR, face-to-face format).
TR Traditional course with After the full-time requirement is fulfilled, a student may take synchronous face-to-face additional online courses if desired. However, some students’ meetings and support use of sponsors or grants may not pay for online courses or may pay technology for a maximum number of credits for their entire program (e.g., only 6 hours total of online instruction).
* In the United States, the F visas are a type of non-immigrant student visa that allows foreigners to pursue education (academic studies and/or language training programs) in the United States. F-1 visas are only issued in U.S. embassies and consulates outside the United States. Prospective F-1 students must apply at the schools and receive a form I-20 in order to apply for an F-1 visa. F-1 students must show that they are able to support themselves during their stay in the U.S., as their opportunities for legal employment are quite limited. F-2 visas are given to dependents of an F-1 student. F-2 visa-holders are prohibited from any form of compensated employment. However, minor children may attend public schools. There are three types of F visa: F-1 visas are for full-time students. F-2 visas are for spouses and children of F-1 visa holders. F-3 visas are for "border commuters" who reside in their country of origin while attending school in the United States. These are granted to nationals of Mexico or Canada only and these visa holders may study part- or full-time. However, unlike F-1 visa holders, they may not work on campus, although they may still be authorized for Curricular Practical Training; Optional Practical Training may only be used after graduation.
Reviewed by the Office of Global Education and the Office of Continuing and Distance Education, November 2012