Career and Technical Education
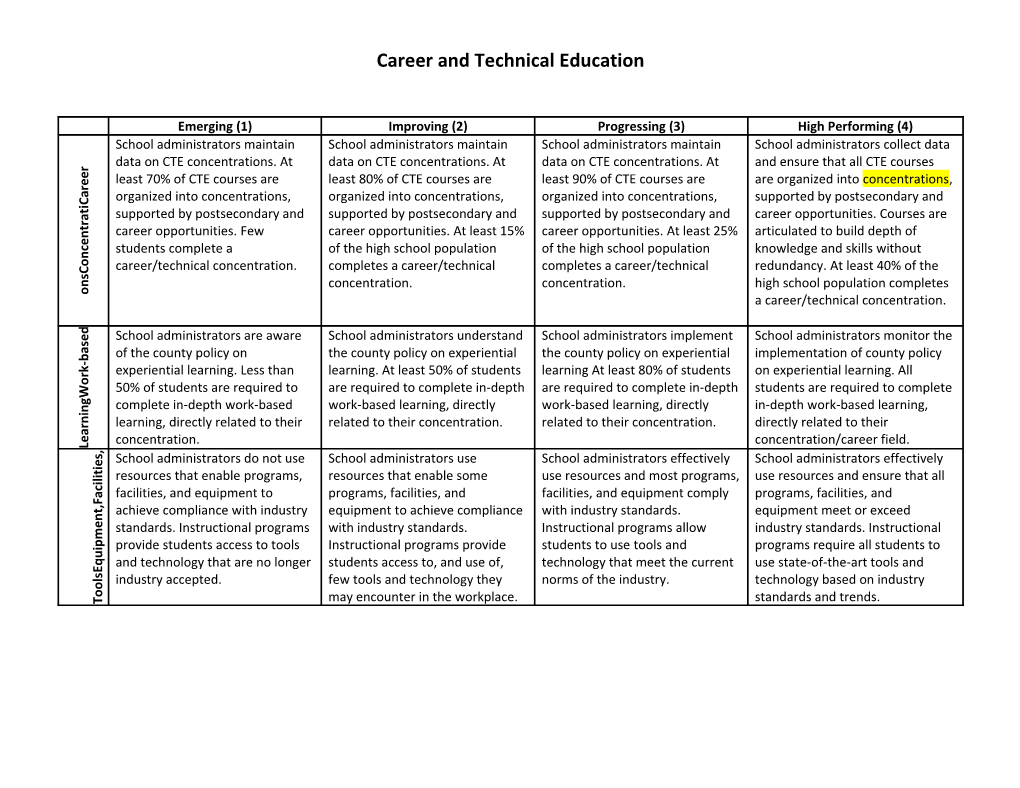
Emerging (1) Improving (2) Progressing (3) High Performing (4) School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators collect data data on CTE concentrations. At data on CTE concentrations. At data on CTE concentrations. At and ensure that all CTE courses r e
e least 70% of CTE courses are least 80% of CTE courses are least 90% of CTE courses are are organized into concentrations, r a organized into concentrations, organized into concentrations, organized into concentrations, supported by postsecondary and C i t
a supported by postsecondary and supported by postsecondary and supported by postsecondary and career opportunities. Courses are r t
n career opportunities. Few career opportunities. At least 15% career opportunities. At least 25% articulated to build depth of e c students complete a of the high school population of the high school population knowledge and skills without n o career/technical concentration. completes a career/technical completes a career/technical redundancy. At least 40% of the C s n concentration. concentration. high school population completes o a career/technical concentration. d e School administrators are aware School administrators understand School administrators implement School administrators monitor the s a of the county policy on the county policy on experiential the county policy on experiential implementation of county policy b - k
r experiential learning. Less than learning. At least 50% of students learning At least 80% of students on experiential learning. All o 50% of students are required to are required to complete in-depth are required to complete in-depth students are required to complete W g
n complete in-depth work-based work-based learning, directly work-based learning, directly in-depth work-based learning, i n r learning, directly related to their related to their concentration. related to their concentration. directly related to their a e concentration. concentration/career field. L , s
e School administrators do not use School administrators use School administrators effectively School administrators effectively i t i
l resources that enable programs, resources that enable some use resources and most programs, use resources and ensure that all i c
a facilities, and equipment to programs, facilities, and facilities, and equipment comply programs, facilities, and F , t achieve compliance with industry equipment to achieve compliance with industry standards. equipment meet or exceed n e standards. Instructional programs with industry standards. Instructional programs allow industry standards. Instructional m p
i provide students access to tools Instructional programs provide students to use tools and programs require all students to u
q and technology that are no longer students access to, and use of, technology that meet the current use state-of-the-art tools and E s l industry accepted. few tools and technology they norms of the industry. technology based on industry o o
T may encounter in the workplace. standards and trends. Career and Technical Education
Emerging (1) Improving (2) Progressing (3) High Performing (4) s p
i School administrators and School administrators and School administrators and School administrators and h s teachers have no formal teachers develop limited teachers implement partnerships teachers implement strong r e
n partnership agreements that partnerships that have little that include at least one external multiple partnerships with t r a address program goals or impact impact on the program and organization. The partnership business, industry, post-secondary P student achievement. student achievement. enhances the program and and community collaborators. impacts student achievement. Measurable results document partnerships’ impact on program and student achievement. Career and Technical Education
Emerging (1) Improving (2) Progressing (3) High Performing (4) School administrators and School administrators and School administrators and School administrators and teachers make few curriculum teachers occasionally make teachers frequently make most teachers consistently make and instructional decisions based curriculum and instructional curriculum and instructional curriculum and instructional on industry standards and decisions based on industry decisions based on industry decisions based on industry workforce projections. The standards and workforce standards and workforce standards and workforce schoolwide advisory committee projections. Program and projections. Program and projections. Program and hears reports but does not make schoolwide advisory committees schoolwide advisory committees schoolwide advisory committees recommendations for future provide limited input and have meet at least once a year and are actively engaged in continuous program changes. Meetings may limited effect on program represent most stakeholders, program improvement. Advisory have an agenda. improvement. Meetings have an including business/industry, committees are composed of
y agenda developed by school secondary and post secondary stakeholders and persons who can r o
s personnel. leaders, teachers, parents, and influence policy decisions and i v
d students. Meetings have an meet at least once a semester to A s established agenda, attendance is consider actions requiring input e e t taken, and minutes are recorded. from stakeholders and employers. t i Program and schoolwide advisory The committees hear progress m m committees hear progress reports, make recommendations, o C reports, provide input, and make and receive feedback on actions limited recommendations. taken. Agendas are developed by the advisory committees and minutes are published. Committees take ownership of the CTE program, work with school and district leadership to ensure program quality, and raise funds/in-kind contributions to support the program. Career and Technical Education
Emerging (1) Improving (2) Progressing (3) High Performing (4)
d Teachers have not organized Teachers have organized CTSOs Teachers have chartered CTSOs Teachers operate CTSOs as a co- n a
r Career and Technical Student and conduct some local activities. with state and national curricular component in all e e Organizations (CTSOs). CTSOs are used as a co-curricular organizations, and most programs programs and provide leadership r a
C resource in a few programs. Less use CTSOs as a co-curricular opportunities for all students. l a than 50% of students participate resource. At least 50% of students Service learning develops c i n in leadership opportunities. participate in leadership occupational, employability, and h c e opportunities. leadership skills for all students. T
t Students take part annually in n e regional, state, and national d u t competitive events. S o i t a z i n a g r O s n E
T School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators maintain, C c data on CTE performance data on CTE performance and use data on CTE performance monitor, and use data on CTE n a assessments; 25% or less of assessments. At least 50% of assessments. At least 66% of performance assessments. At least m r o career/technical completers have career/technical completers have career/technical completers have 90% of career/technical f r e met the minimal standard scores met the minimal standard scores met the minimal standard scores completers have met the minimal P e
t on WVDE CTE Performance on WVDE CTE Performance on WVDE CTE Performance standard scores on WVDE CTE n e Assessment. Assessment. Assessment. Performance Assessment. m s s e s s A Career and Technical Education
Emerging (1) Improving (2) Progressing (3) High Performing (4) School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators maintain, data on ACT WorkKeys data on ACT WorkKeys and use data on ACT WorkKeys monitor, and use data on ACT Assessments; 25% or less of the Assessments. At least 50% of Assessments. At least 75% of WorkKeys® Assessments. At least T C
A career/technical completers have career/technical completers have career/technical completers have 90% of career/technical s y met the WorkKeys® standard met the WorkKeys® standard met the WorkKeys® standard completers have met the e K
k scores in Reading for Information, scores in Reading for Information, scores in Reading for Information, WorkKeys® standard scores in r o Applied Mathematics, and Applied Mathematics, and Applied Mathematics, and Reading for Information, Applied W Locating Information for their Locating Information for their Locating Information for their Mathematics, and Locating program area. program area. program area. Information for their program area. 2
T School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators maintain, S
E data on WESTEST 2; 25% or less of data on WESTEST 2. At least 50% and use data on WESTEST 2. At monitor, and use data on T S
E career/technical completers have of career/technical completers least 75% of career/technical WESTEST 2. At least 90% of
W met the Mastery or above have met the Mastery or above completers have met the Mastery career/technical completers have benchmark on the West Virginia benchmark on the West Virginia or above benchmark on the West met the Mastery or above State Assessment. State Assessment. Virginia State Assessment. benchmark on the West Virginia State Assessment. Career and Technical Education
Emerging (1) Improving (2) Progressing (3) High Performing (4) d
n School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators maintain, a
k data on Work and College data on Work and College and use data on Work and College monitor, and use data on Work r o Readiness Credentials; 25% or less Readiness Credentials. At least Readiness Credentials. At least and College Readiness Credentials. W e of career/technical completers 50% of career/technical 75% of career/technical At least 90% of career/technical g e l
l have earned the WVDE- completers have earned the completers have earned the completers have earned the o
C established college readiness and WVDE-established college WVDE-established college WVDE-established college s s
e work readiness credentials. readiness and work readiness readiness and work readiness readiness and work readiness n i
d credentials. credentials. credentials. a e R s l a i t n e d e r C School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators maintain, d data on postsecondary credits; data on postsecondary credits. At and use data on postsecondary monitor, and use data on n o
c 25% percent or less of least 50% of CTE completers have credits. At least 75% of CTE postsecondary credits. At least e s
t career/technical completers have earned EDGE, dual credit, or completers have earned EDGE, 90% of CTE completers have s o earned EDGE (Earn a Degree, Advanced Placement credit in dual credit, or Advanced earned EDGE, dual credit, or P s t i Graduate Early), dual credit, or career/technical and/or academic Placement credit in Advanced Placement credit in d e Advanced Placement (AP) credit in courses. career/technical and/or academic career/technical and/or academic r C career/technical and/or academic courses. courses. y r a courses. Career and Technical Education
Emerging (1) Improving (2) Progressing (3) High Performing (4) r
e School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators maintain, t e l data on completer status. The data on completer status. The and use data on completer status. monitor, and use data on p
m percentage of completers who required improvement—based on The percentage of completers completer status. At least 90% of o
C enter full- or part-time the Improvement Plan—in the who enter full- or part-time CTE completers enter full- or part- s u t employment or continue their percentage of completers who employment in the field or time employment in the field or a t
S education does not meet enter full- or part-time continue with postsecondary continue with postsecondary established WVDE standards. employment in the field, or education/training meets education/training. continue with postsecondary established WVDE standards. education/training, has been achieved. The percentage does not yet meet established WVDE standards.
School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators maintain School administrators maintain, - n data on nontraditional data on nontraditional and use data on nontraditional monitor, and use data on o N l enrollment. The percentages of enrollment. The required enrollment. The percentage of nontraditional enrollment. The a n nontraditional enrollment and percentage of improvement— nontraditional enrollment and percentage of nontraditional o i t i completion rates do not meet based on the Improvement Plan— completion rates meets enrollment and completion rates d a
r established WVDE standards. for nontraditional enrollment and established WVDE standards. exceeds established WVDE t t
n completion rates has been standards. e achieved. The percentage does m l l
o not yet meet established WVDE r n standards. E Career and Technical Education
Emerging (1) Improving (2) Progressing (3) High Performing (4) A few teachers do not hold Teachers who do not hold the Most teachers hold appropriate All teachers hold appropriate o i t appropriate certification, appropriate certification are certifications, licensures, and certifications, licensures, and a c i
f licensures, or credentials. Few actively seeking required credentials. Most programs are credentials. All programs are i t r programs have applied for licensures and/or credentials. recognized by agencies issuing certified and/or recognized by e C ,
s recognition by agencies issuing Some programs are recognized by licenses, certifications, or postsecondary, industry, n ,
s licenses, credentials, or a few agencies issuing licenses, postsecondary credentials. Based professional, and/or trade l a i postsecondary certifications. Few credentials, or postsecondary on available industry certifications associations and state or national t n
e CTE completers earn an industry- certifications. Based on available or licenses, at least 40% of licensing and/or credentialing d
e recognized credential or license. industry certifications or licenses, completers earn an industry- agencies. Based on available r C
s at least 10% of completers earn recognized credential or license. industry certifications or licenses, e s
n an industry-recognized credential at least 60% of completers earn an e c
i or license. industry-recognized credential or L license. y t School administrators do not School administrators have School administrators have School administrators have e i c charter a Career/Technical Honor chartered a Career/Technical established a Career/Technical established a Career/Technical o S
r Society. Honor Society, but activities are Honor Society that has inducted Honor Society that annually o
n disorganized and are not several groups of students. CTE inducts students. Students, o H
conducted on a regular basis. Honor Society sponsors school parents, and community members E
T and community activities. participate in the ceremony. The C activities of the CTE Honor Society receive media coverage.
m School administrators do not School administrators conduct School administrators actively School administrators aggressively a r g market CTE programs. limited activities to market the market CTE programs to inform market CTE programs to recruit o r
P CTE programs to parents and students, parents, and the students. Marketing activities link
E
T students. community about future study postsecondary and employment C
f and workforce needs. opportunities to CTE programs o
g and monitor workforce needs to n i t adjust programming. e k r a M Career and Technical Education
Glossary
Concentrations – series of at least four career/technical courses directly related to the student’s career cluster and pathway
CTE completer – student who completes the four career/technical courses that have been identified by the WV Department of Education for a specific concentration
Acceptable Evidence
Career Concentrations – programs of study; articulation agreements; administrator, teacher, and student interviews
Work-based learning – student portfolios; county experiential learning policy; administrator, teacher, and student interviews
Facilities, Equipment, Tools – inventories of equipment and tools; hardware; software; program-specific technology; vision and mission; technology plan; e-learning classes for both faculty and students; management of technology use; shared file servers; use of Listservs, digital lesson plans, Web site, and Web pages; technical support personnel; active technology integration specialists; classroom observation form; administrator, teacher, and student interviews
Partnerships – partnership membership, agendas, and minutes; administrator, teacher, and student interviews
Advisory Committees – advisory committee membership, agendas, and minutes; administrator, teacher, and student interviews
Career and Technical Student Organizations – CTSO(s) charter and membership, agendas, and minutes; administrator, teacher, and student interviews; artifacts from student involvement in regional, state, and national competitive events; examples of service learning projects and community connections
CTE Performance Assessment – performance assessment data; administrator, teacher, and student interviews
ACT WorkKeys® – ACT WorkKeys® data; administrator, teacher, and student interviews Career and Technical Education
WESTEST 2 – WESTEST 2 data; administrator, teacher, and student interviews
Work and college readiness credentials – ACT WorkKeys® data, ACT College Readiness Scores
Postsecondary credits – student transcripts; EDGE, dual credit, and Advanced Placement data; administrator, teacher, and student interviews
Completer status – postgraduate follow-up data, administrator interview
Non-traditional enrollment – course enrollment data, administrator interview
Certifications, credentials, licenses – county personnel records; evidence of program certifications, licenses, and/or credentials; administrator interview
CTE Honor Society – CTE Honor Society charter and membership, agendas, and minutes; administrator, teacher, and student interviews; artifacts of ceremonies and school/community activities; evidence of media coverage
Marketing of CTE program – brochures, videos, CD’s, DVD’s, teacher exchange programs, summer professional development sponsored by business and industry organizations, orientations, open house meetings, memberships of administration and staff in community service organizations, participation in postsecondary fairs