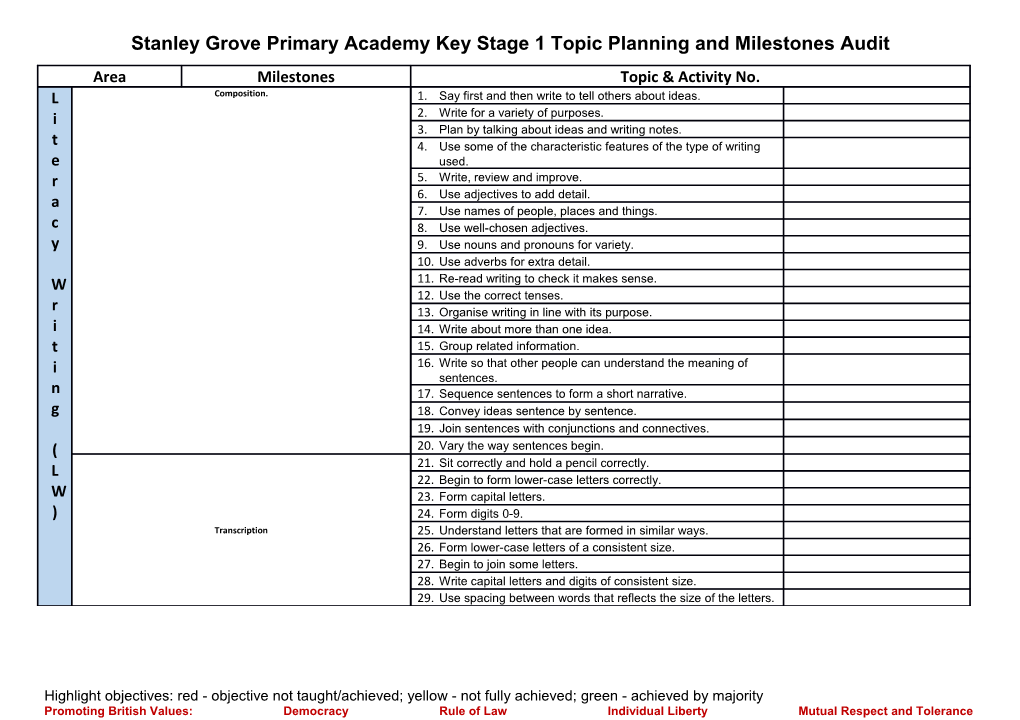
Stanley Grove Primary Academy Key Stage 1 Topic Planning and Milestones Audit Area Milestones Topic & Activity No. L Composition. 1. Say first and then write to tell others about ideas. i 2. Write for a variety of purposes. 3. Plan by talking about ideas and writing notes. t 4. Use some of the characteristic features of the type of writing e used. r 5. Write, review and improve. a 6. Use adjectives to add detail. 7. Use names of people, places and things. c 8. Use well-chosen adjectives. y 9. Use nouns and pronouns for variety. 10. Use adverbs for extra detail. W 11. Re-read writing to check it makes sense. 12. Use the correct tenses. r 13. Organise writing in line with its purpose. i 14. Write about more than one idea. t 15. Group related information. i 16. Write so that other people can understand the meaning of sentences. n 17. Sequence sentences to form a short narrative. g 18. Convey ideas sentence by sentence. 19. Join sentences with conjunctions and connectives. ( 20. Vary the way sentences begin. L 21. Sit correctly and hold a pencil correctly. 22. Begin to form lower-case letters correctly. W 23. Form capital letters. ) 24. Form digits 0-9. Transcription 25. Understand letters that are formed in similar ways. 26. Form lower-case letters of a consistent size. 27. Begin to join some letters. 28. Write capital letters and digits of consistent size. 29. Use spacing between words that reflects the size of the letters.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance L Transcription 1. Spell words containing 40+ learned phonemes. 2. Spell common exception words (the, said, one, two and the i days of the week). t 3. Name letters of the alphabet in order. e 4. Use letter names to describe spellings of words. r 5. Add prefixes and suffixes, learning the rule for adding s and es as a plural marker for nouns, and the third person singular a marker for verbs (I drink - he drinks). c 6. Use the prefix un. y 7. Use suffixes where no change to the spelling of the root word is needed: helping, helped, helper, eating, quicker, quickest. 8. Use spellings rules. W 9. Write simple sentences dictated by the teacher. r 10. Spell by segmenting words into phonemes and represent them with the correct graphemes. i 11. Learn some new ways to represent phonemes. t 12. Spell common exception words correctly. i 13. Spell contraction words correctly (can’t, don’t). n 14. Add suffixes to spell longer words (-ment, -ness, -ful and -less). g 15. Use the possessive apostrophe. (singular) (for example, the girl's book) ( 16. Distinguish between homophones and near-homophones. L 17. Leave spaces between words. 18. Use the word ‘and’ to join words and sentences. W 19. Begin to punctuate using a capital letter for the name of ) people, places, the days of the week and I. 20. Use both familiar and new punctuation correctly, including full stops, capital letters, exclamation marks, question marks, commas for lists and apostrophes for contracted forms. 21. Use sentences with different forms: statement, question, exclamation and command. 22. Use extended noun phrases to describe and specify (e.g. the blue butterfly). 23. Use subordination (when, if, that or because). 24. Use coordination (or, and, but). 25. Use some features of standard written English. 26. Use the present and past tenses correctly, including the progressive form. Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Analysis and presentation 27. Discuss writing with the teacher and other pupils. 28. Use and understand grammatical terminology in discussing writing: word, sentence, letter, capital letter, full stop, punctuation, singular, plural, question mark, exclamation mark. 29. Use and understand grammatical terminology in discussing writing: verb, tense (past, present), adjective, noun, suffix, apostrophe, comma. 30. Read aloud writing clearly enough to be heard by peers and the teacher. 31. Read aloud writing with some intonation.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Area Milestones Topic & Activity No. To read 1. Apply phonic knowledge and Literacy Reading (LR) words accurately skills as the route to decode words. 2. Respond speedily with the correct sound to graphemes (letters or groups of letters) for all 40+ phonemes, including, where applicable, alternative sounds for graphemes. 3. Read accurately by blending sounds in unfamiliar words containing GPCs that have been taught. 4. Read common exception words, noting unusual correspondences between spelling and sound and where these occur in the word. 5. Read words containing taught GPCs and –s, –es, –ing, –ed, – er and –est endings. 6. Read other words of more than one syllable that contain taught GPCs. 7. Read words with contractions (for example, I’m, I’ll, we’ll) and understand that the apostrophe represents the omitted letter(s). 8. Read aloud accurately books that are consistent with phonic knowledge and that do not require other strategies to work out words. 9. Re-read these books to build up fluency and confidence in word reading. 10. Read accurately by blending the sounds in words that contain the graphemes taught so far, especially recognising alternative sounds for Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance graphemes. 11. Read accurately words of two or more syllables that contain the same graphemes as above. 12. Read words containing common suffixes. 13. Read common exception words, noting unusual correspondences between spelling and sound and where these occur in the word. 14. Read most words quickly and accurately, without overt sounding and blending, when they have been frequently encountered. 15. Read aloud books closely matched to their improving phonic knowledge, sounding out unfamiliar words accurately, automatically and without undue hesitation. 16. Re-read books to build up fluency and confidence in word reading. To 17. Discuss events. understand texts 18. Predict events. 19. Link reading to own experience. 20. Join in with stories or poems. 21. Check that reading makes sense and self-correct. 22. Infer what characters are like from actions. 23. Ask and answer questions about texts. 24. Discuss favourite words and phrases. 25. Listen to and discuss a wide range of texts. 26. Recognise and join in with (including role-play) recurring Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance language. 27. Explain and discuss understanding of texts. 28. Discuss the significance of the title and events. 29. Make inferences on the basis of what is being said and done.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Area Milestones Topic & Activity No. Literacy Communication (LC) 1. Sift information and focus on the important points. Seek clarification when a To listen carefully and understand 2. message is not clear. 3. Understand instructions with more than one point. 4. Use subject specific vocabulary to explain and describe. Suggest words or phrases To develop a wide and interesting vocabulary 5. appropriate to the topic being discussed. 6. Identify homophones. 7. Speak in a way that is clear and easy to understand. 8. Demonstrate good phonic To speak with clarity knowledge by clearly pronouncing the sounds within words. 9. Identify syllables within words. 10. Ensure stories have a setting, plot and a sequence of events. 11. Recount experiences with To tell stories with structure interesting detail. 12. Predict events in a story. 13. Give just enough detail to keep the audience engaged. 14. Take turns to talk, listening carefully to the contributions of others. Vary language between formal To hold conversations and debates 15. and informal according to the situation. 16. Add humour to a discussion or debate where appropriate.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Area Milestones Topic & Activity No. N To know and use numbers 1. Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number. u 2. Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals; count in m multiples of twos, fives and tens. e 3. Given a number, identify one more and one less. 4. Count in steps of 2, 3, 5 and 10 from 0 or 1 and in tens from r any number, forward and backward. a 5. Identify, represent and estimate numbers using different representations, including the number line. c 6. Read and write numbers initially from 1 to 20 and then to at y least 100 in numerals and in words. 7. Use the language of: equal to, more than, less than (fewer), most and least. ( 8. Compare and order numbers from 0 up to 100; use <, > and = N signs. 9. Recognise the place value of each digit in a two-digit ) number (tens, ones). 10. Use place value and number facts to solve problems. To add and subtract 11. Solve one-step problems with addition and subtraction: Using concrete objects and pictorial representations including those involving numbers, quantities and measures. Using the addition (+), subtraction (-) and equals (=) signs. Applying their increasing knowledge of mental and written methods. 12. • Add and subtract numbers using concrete objects, pictorial representations, and mentally, including: One-digit and two-digit numbers to 20, including zero. A two-digit number and ones. A two-digit number and tens. Two two-digit numbers. Adding three one-digit numbers. 13. Show that addition of two numbers can be done in any order (commutative) and subtraction of one number from another cannot. 14. Recognise and use the inverse relationship between addition and subtraction and use this to check calculations and solve missing number problems. 15. Represent and use number bonds and related subtraction Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance facts within 20. 16. Recall and use addition and subtraction facts to 20 fluently, and derive and use related facts up to 100.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance N To multiply and divide 17. Solve one-step problems involving multiplication and division by calculating the answer using concrete objects, pictorial u representations and arrays with the support of the teacher. m 18. Represent and use number bonds and related subtraction facts within 20. e 19. Recall and use addition and subtraction facts to 20 fluently, r and derive and use related facts up to 100. a 20. Calculate mathematical statements for multiplication and division within the multiplication tables and write them using c the multiplication (.), division (÷) and equals (=) signs. y 21. Show that multiplication of two numbers can be done in any order (commutative) and division of one number by another cannot. ( 22. Solve problems involving multiplication and division using mental methods. N 23. Use known multiplication facts to check the accuracy of ) calculations. 24. Recall and use multiplication and division facts for the 2, 5 and 10 multiplication tables. 25. Recognise odd and even numbers. 26. Use multiplication and division facts to solve problems. Fractions (including decimals, %, ratio & proportion) 27. Recognise, find and name a half as one of two equal parts of an object, shape or quantity. 28. Recognise, find and name a quarter as one of four equal parts of an object, shape or quantity. 29. Recognise, find, name and write fractions 1/2, 1/4, 2/4 and 3/4 of a length, shape, set of objects or quantity. 30. Recognise the equivalence of 2/4 and 1/2. 31. Write simple fractions for example, 1/2 of 6 = 3. To understand the properties of shapes 32. Recognise and name common 2D and 3D shapes. 33. Identify and describe the properties of 2-D shapes, including the number of sides and line symmetry in a vertical line. 34. Identify and describe the properties of 3-D shapes, including the number of edges, vertices and faces. 35. Identify 2-D shapes on the surface of 3-D shapes. 36. Compare and sort common 2-D and 3-D shapes and everyday objects.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance 37. Describe position, direction and movement, including whole, half, quarter and three-quarter turns. 38. Order and arrange combinations of mathematical objects in patterns and sequences. To describe position, direction and movement 39. Use mathematical vocabulary to describe position, direction and movement, including movement in a straight line and distinguishing between rotation as a turn and in terms of right angles for quarter, half and three-quarter turns (clockwise and anti-clockwise).
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Numeracy (N) To use measures 40. • Compare, describe and solve practical problems for: lengths and heights. mass/weight. capacity and volume. time. Measure and begin to record: lengths and heights. mass/weight. capacity and volume. time. (hours, minutes, seconds). 41. Recognise and know the value of different denominations of coins and notes. 42. Sequence events in chronological order using language. 43. Recognise and use language relating to dates, including days of the week, weeks, months and years. 44. Tell the time to the hour and half past the hour and draw the hands on a clock face to show these times. 45. Choose and use appropriate standard units to estimate and measure length/height (m/cm); mass (kg/g); temperature (°C); capacity (litres/ml) to the nearest appropriate unit, using rulers, scales, thermometers and measuring vessels. 46. Compare and order lengths, mass, volume/capacity and record the results using >, < and =.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance 47. Recognise and use symbols for pounds (£) and pence (p); combine amounts to make a particular value. 48. Find different combinations of coins that equal the same amounts of money. 49. Solve simple problems in a practical context involving addition and subtraction of money of the same unit, including giving change. 50. Compare and sequence intervals of time. 51. Tell and write the time to five minutes, including quarter past/to the hour and draw the hands on a clock face to show these times. 52. Know the number of minutes in an hour and the number of hours in a day. 53. Interpret and construct simple pictograms, tally charts, block diagrams and simple tables. 54. Ask and answer simple questions by counting the To use statistics number of objects in each category and sorting the categories by quantity. 55. Ask and answer questions about totalling and comparing categorical data. 56. Solve addition and subtraction To use algebra problems involving missing numbers.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Area Milestones Topic & Activity No. S 1. Ask simple questions. c 2. Observe closely, using simple equipment. 3. Perform simple tests. i To work scientifically 4. Identify and classify. e 5. Use observations and ideas to suggest answers to n questions. 6. Gather and record data to help in answering c questions. e Biology 7. Identify and name a variety of common plants, including garden plants, wild plants and trees and those classified as deciduous and evergreen. ( 8. Identify and describe the basic structure of a variety of S common flowering plants, including roots, stem/trunk, leaves and flowers. c 9. Observe and describe how seeds and bulbs grow into mature ) plants. 10. Find out and describe how plants need water, light and a suitable temperature to grow and stay healthy 11. Identify and name a variety of common animals that are birds, fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and invertebrates. 12. Identify and name a variety of common animals that are carnivores, herbivores and omnivores. 13. Describe and compare the structure of a variety of common animals (birds, fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and invertebrates, including pets). 14. Identify name, draw and label the basic parts of the human body and say which part of the body is associated with each sense. 15. Notice that animals, including humans, have offspring which grow into adults. 16. Investigate and describe the basic needs of animals, including humans, for survival (water, food and air). 17. Describe the importance for humans of exercise, eating the right amounts of different types of food and hygiene. 18. Explore and compare the differences between things that are living, that are dead and that have never been alive. 19. Identify that most living things live in habitats to which they are suited and describe how different habitats provide for the basic needs of different kinds of animals and plants and how they depend on each other. Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance 20. Identify and name a variety of plants and animals in their habitats, including micro-habitats. 21. Describe how animals obtain their food from plants and other animals, using the idea of a simple food chain, and identify and name different sources of food.
22. Identify how humans resemble their parents in many features.
Statements in italics are not statutory in the English National Curriculum.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance S 23. Distinguish between an object and the material from which it is made. c 24. Identify and name a variety of everyday materials, including i wood, plastic, glass, metal, water and rock. 25. Describe the simple physical properties of a variety of e everyday materials. n Chemistry 26. Compare and group together a variety of everyday materials c on the basis of their simple physical properties. 27. Find out how the shapes of solid objects made from some e materials can be changed by squashing, bending, twisting and stretching. 28. Identify and compare the suitability of a variety of everyday ( materials, including wood, metal, plastic, glass, brick/rock, and S paper/cardboard for particular uses. 29. Notice and describe how things move, using simple c comparisons such as faster and slower. ) 30. Compare how different things move. 31. Observe and name a variety of sources of light, including electric lights, flames and the Sun, explaining that we see things because light travels from them to our eyes. 32. Observe and name a variety of sources of sound, noticing that Physics we hear with our ears. 34. Identify common appliances that run on electricity. 35. Construct a simple series electrical circuit. 36. Observe the apparent movement of the Sun during the day. 37. Observe changes across the four seasons. 38. Observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies. Statements in italics are not statutory in the English National Curriculum.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Opportunit Biology Chemistry Physics ies: Across all Plants Materials Light year • Identify, classify and describe their basic structure. • Identify, name, describe, classify, compare properties and • Look at sources and reflections. groups • Observe and describe growth and conditions for growth. changes. Sound scientific Habitats • Look at the practical uses of everyday materials. • Look at sources. knowledge • Look at the suitability of environments and at food chains. Electricity and skills Animals and humans • Look at appliances and circuits. should be • Identify, classify and observe. Forces learned by • Look at growth, basic needs, exercise, food and hygiene. • Describe basic movements. working All living things Earth and space scientificall • Investigate differences. • Observe seasonal changes. y.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Area Milestones Topic & Activity No. A 1. Respond to ideas and starting points. 2. Explore ideas and collect visual information. r To develop ideas 3. Explore different methods and materials as ideas t develop. a 4. Use thick and thin brushes. n 5. Mix primary colours to make secondary. 6. Add white to colours to make tints and black to colours to d make tones. 7. Create colour wheels. D 8. Use a combination of materials that are cut, torn and glued. e 9. Sort and arrange materials. 10. Mix materials to create texture. s 11. Use a combination of shapes. i 12. Include lines and texture. g 13. Use rolled up paper, straws, paper, card and clay as materials. n 14. Use techniques such as rolling, cutting, moulding and carving. 15. Draw lines of different sizes and thickness. To master techniques 16. Colour (own work) neatly following the lines. ( 17. Show pattern and texture by adding dots and lines. A 18. Show different tones by using coloured pencils. D 19. Use repeating or overlapping shapes. T 20. Mimic print from the environment (e.g. wallpapers). 21. Use objects to create prints (e.g. fruit, vegetables or sponges). ) 22. Press, roll, rub and stamp to make prints. 23. Use weaving to create a pattern. 24. Join materials using glue and/or a stitch. 25. Use plaiting. 26. Use dip dye techniques. 27. Use a wide range of tools to create different textures, lines, tones, colours and shapes. 28. Describe the work of notable artists, artisans and designers. To take inspiration from the greats (classic and modern) 29. Use some of the ideas of artists studied to create pieces.
Opportunities • Explore a variety of techniques. Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance • Use experiences and ideas as the inspiration for artwork. • Learn about the work of a range of artists, artisans and designers. • Share ideas using drawing, painting and sculpture.
Design and To master practical skills 30. Cut, peel or grate ingredients safely and Technology (ADT) hygienically. 31. Measure or weigh using measuring cups or electronic scales. 32. Assemble or cook ingredients. 33. Cut materials safely using tools provided. 34. Measure and mark out to Food the nearest centimetre. 35. Demonstrate a range of cutting and shaping techniques (such as tearing, cutting, folding and curling). 36. Demonstrate a range of Materials joining techniques (such as gluing, hinges or combining materials to strengthen). 37. Shape textiles using templates. 38. Join textiles using running stitch. 39. Colour and decorate textiles using a number of techniques (such as dyeing, adding sequins or printing). Textiles 40. Diagnose faults in battery operated devices (such as Electricals and electronics low battery, water damage or battery terminal damage). Computing 41. Model designs using software.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance 42. Use materials to practise drilling, screwing, gluing Construction and nailing materials to make and strengthen products. 43. Create products using Mechanics levers, wheels and winding mechanisms. 44. Design products that have a clear purpose and an intended user. 45. Make products, refining the To design, make, evaluate and improve design as work progresses. 46. Use software to design. 47. Explore objects and designs to identify likes and dislikes of the designs. To take inspiration from design throughout history 48. Suggest improvements to existing designs. 49. Explore how products have been created.
Opportunities Make • select from and use a range of tools and equipment to perform practical tasks such as cutting, shaping, Through a variety of creative and practical activities, pupils should be taught the knowledge, understanding joining and finishing. and skills needed to engage in an iterative process of designing and making. They should work in a range • select from and use a wide range of materials and components, including construction materials, textiles of relevant contexts, such as the home and school, gardens and playgrounds, the local community, and ingredients, according to their characteristics. industry and the wider environment. Evaluate When designing and making, pupils should be taught to: • explore and evaluate a range of existing products. Design • evaluate their ideas and products against design criteria. • design purposeful, functional, appealing products for themselves and other users based on design Technical knowledge criteria. • build structures, exploring how they can be made stronger, stiffer and more stable. generate develop, model and communicate their ideas through talking, drawing, templates, mock-ups • • explore and use mechanisms, such as levers, sliders, wheels and axles, in their products. and, where appropriate, information and communication technology. Cooking and nutrition • use the basic principles of a healthy and varied diet to prepare dishes. • understand where food comes from.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Area Milestones Topic & Activity No. H Geography 1. Ask and answer geographical questions (such as: What is this place like? What or who will I see in this place? What do people i do in this place?). s 2. Identify the key features of a location in order to say whether it is a t city, town, village, coastal or rural area. 3. Use world maps, atlases and globes to identify the United o Kingdom and its countries, as well as the countries, continents r and oceans studied. 4. Use simple fieldwork and observational skills to study the i geography of the school and the key human and physical features c of its surrounding environment. 5. Use aerial images and plan perspectives to recognise landmarks a and basic physical features. l 6. Name, locate and identify characteristics of the four countries and , capital cities of the United Kingdom and its surrounding seas. 7. Name and locate the world’s continents and oceans. a 8. Understand geographical similarities and differences through n studying the human and physical geography of a small area of the d United Kingdom and of a contrasting non-European country. 9. Identify seasonal and daily weather patterns in the United Kingdom and the location of hot and cold areas of the world in G relation to the Equator and the North and South Poles. 10. Identify land use around the school. e 11. Use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to: o key physical features, including: beach, coast, forest, hill, g mountain, ocean, river, soil, valley, vegetation and weather. key human features, including: city, town, village, factory, farm, r house, office and shop. a 12. Use compass directions (north, south, east and west) and locational language (e.g. near and far) to describe the location of p features and routes on a map. h 13. Devise a simple map; and use and construct basic symbols in a i key. Use simple grid references (A1, B1). History 14. Observe or handle evidence to ask questions and find answers to c questions about the past. a 15. Ask questions such as: What was it like for people? What l happened? How long ago? 16. Use artefacts, pictures, stories, online sources and databases to ( find out about the past. 17. Identify some of the different ways the past has been represented. Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance H 18. Describe historical events. G 19. Describe significant people from the past. 20. Recognise that there are reasons why people in the past acted as ) they did. 21. Place events and artefacts in order on a time line. 22. Label time lines with words or phrases such as: past, present, older and newer. 23. Recount changes that have occurred in their own lives. 24. Use dates where appropriate. 25. Use words and phrases such as: a long time ago, recently, when my parents/carers were children, years, decades and centuries to describe the passing of time. 26. Show an understanding of the concept of nation and a nation’s history. 27. Show an understanding of concepts such as civilisation, monarchy, parliament, democracy, and war and peace.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Geography History Investigate the world’s continents • The lives of significant individuals in Britain’s past who have contributed to our nation’s achievements - and oceans. scientists such as Isaac Newton or Michael Faraday, reformers such as Elizabeth Fry or William • Investigate the countries and Wilberforce, medical pioneers such as William Harvey or Florence Nightingale, or creative geniuses capitals of the United Kingdom. such as Isambard Kingdom Brunel or Christina Rossetti. • Compare and contrast a small • Key events in the past that are significant nationally and globally, particularly those that coincide with area of the United Kingdom with festivals or other events that are commemorated throughout the year. that of a non-European country. • Significant historical events, people and places in their own locality. • Explore weather and climate in the United Kingdom and around Opportunities the world. • Use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to and describe key physical and human features of locations. • Use world maps, atlases and globes. • Use simple compass directions. • Use aerial photographs. • Use fieldwork and observational skills.
Area Milestones Topic & Activity No. Music (M) 1. Take part in singing, accurately following the melody. 2. Follow instructions on how and when to sing or play an To perform instrument. 3. Make and control long and short sounds, using voice and instruments. Imitate changes in pitch. To compose 4. Create a sequence of long and short sounds. 5. Clap rhythms. 6. Create a mixture of different sounds (long and short, loud and quiet, high and low). 7. Choose sounds to create an effect. 8. Sequence sounds to create an overall effect. 9. Create short, musical patterns. 10. Create short, rhythmic phrases Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance 11. Use symbols to represent a To transcribe composition and use them to help with a performance. 12. Identify the beat of a tune. To describe music 13. Recognise changes in timbre, dynamics and pitch.FL
Opportunities • Use their voices expressively by singing songs and speaking chants and rhymes. • Play tuned and untuned instruments musically. • Listen with concentration and understanding to a range of high-quality live and recorded music. • Make and combine sounds using the inter-related dimensions of music.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Area Milestones Topic & Activity No. P To develop practical skills in order to participate, 1. Use the terms ‘opponent’ and ‘team-mate’. compete and lead a healthy lifestyle 2. Use rolling, hitting, running, jumping, catching and kicking skills in h combination. y 3. Develop tactics. 4. Lead others when appropriate. s 5. Copy and remember moves and positions. i 6. Move with careful control and coordination. c 7. Link two or more actions to perform a sequence. 8. Choose movements to communicate a mood, feeling or idea. a 9. Copy and remember actions. l 10. Move with some control and awareness of space. E 11. Link two or more actions to make a sequence. 12. Show contrasts (such as small/tall, straight/curved and wide/narrow). d 13. Travel by rolling forwards, backwards and sideways. u 14. Hold a position whilst balancing on different points of the body. c 15. Climb safely on equipment. 16. Stretch and curl to develop flexibility. a 17. Jump in a variety of ways and land with increasing control and t balance. 18. Swim unaided up to 25 metres. i 19. Use one basic stroke, breathing correctly. o 20. Control leg movements. n 21. Athletic activities are combined with games in Years 1 and 2.
( P E )
Opportunities • Participate in team games, developing simple tactics for attacking and defending. • Perform dances using simple movement patterns. • Swimming and water safety: take swimming instruction either in Key Stage 1 or Key Stage 2.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Area Milestones Topic & Activity No. T Motion 1. Control motion by specifying the number of steps to travel, direction and turn. C o o Looks 2. Add text strings, show and hide objects and change the features of an object. c Sound 3. Select sounds and control when they are heard, their duration and volume. o m d Draw 4. Control when drawings appear and set the pen colour, size and shape. p e Events 5. Specify user inputs (such as clicks) to control events.
u ( Control 6. Specify the nature of events (such as a single event or a loop). u 7. Create conditions for actions by waiting for a user input (such as responses to questions like: t s i What is your name?). i n g n S Sensing g c r a ( t c C h ) ) 8. Participate in class social media accounts. To connect 9. Understand online risks and the age rules for sites. To communicate 10. Use a range of applications and devices in order to communicate ideas, work and messages. To collect 11. Use simple databases to record information in areas across the curriculum.
Opportunities
• Understand what algorithms are, how they are implemented as programs on digital devices, and that programs execute by following a sequence of instructions. • Write and test simple programs. • Use logical reasoning to predict the behaviour of simple programs. • Organise, store, manipulate and retrieve data in a range of digital formats. • Communicate safely and respectfully online, keeping personal information private and recognise common uses of information technology beyond school.
Area Milestones Topic & Activity No. To 1. Describe some of the teachings of a religion. R understand beliefs and 2. Describe some of the main festivals or celebrations of a religion. e teachings l To understand 3. Recognise, name and describe some religious artefacts, places and practices. i practices and lifestyles g To 4. Name some religious symbols.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance understand i how beliefs 5. Explain the meaning of some religious symbols. o are conveyed 6. Identify the things that are important in their own lives and compare these to religious beliefs. u To reflect 7. Relate emotions to some of the experiences of religious figures studied. s 8. Ask questions about puzzling aspects of life. E 9. Identify how they have to make their own choices in life. d 10. Explain how actions affect others. u c a t i To understand values o 11. Show an understanding of the term ‘morals’. n
( R E )
Opportunities Study the main stories of Christianity. • Study at least one other religion. Choose from Buddhism, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism or Sikhism. • Study other religions of interest to pupils.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Area Milestones Topic & Activity No. Modern Foreign Languages 1. Read out loud everyday words and phrases. (MFL) 2. Use phonic (or logographic in Mandarin) knowledge to read words. To read fluently 3. Read and understand short written phrases. 4. Read out loud familiar words and phrases. 5. Use books or glossaries to find out the meanings of new words 6. Write or copy everyday words correctly. 7. Label items and choose appropriate words to complete To write imaginatively short sentences. 8. Write one or two short sentences. 9. Write short phrases used in everyday conversations correctly. 10. Understand a range of spoken phrases. 11. Understand standard language (sometimes asking for words or phrases to be repeated). To speak confidently 12. Answer simple questions and give basic information. 13. Give responses to questions about everyday events. 14. Pronounce words showing a knowledge of sound (or pitch in Mandarin) patterns To understand the culture of the countries in which 15. Identify countries and the language is spoken communities where the language is spoken. 16. Demonstrate some knowledge and understanding of the customs and features of the countries or communities where the language is spoken.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance 17. Show awareness of the social conventions when speaking to someone. MFL is optional at KS1
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Area Topic & Activity No. SMSC and Personal 1. to recognise what they like and dislike, what is fair and unfair, and Development (SMSCPD) what is right and wrong 2. to share their opinions on things that matter to them and explain Developing confidence and responsibility and their views making the most of their abilities. 3. to recognise, name and deal with their feelings in a positive way 4. to think about themselves, learn from their experiences and recognise what they are good at 5. how to set simple goals. Preparing to play an active role as citizens. 6. to take part in discussions with one other person and the whole class 7. to take part in a simple debate about topical issues 8. to recognise choices they can make, and recognise the difference between right and wrong 9. to agree and follow rules for their group and classroom, and understand how rules help them 10. to realise that people and other living things have needs, and that they have responsibilities to meet them 11. that they belong to various groups and communities, such as family and school 12. what improves and harms their local, natural and built environments and about some of the ways people look after them 13. to contribute to the life of the class and school 14. to realise that money comes from Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance different sources and can be used for different purposes. 15. how to make simple choices that improve their health and well- being 16. to maintain personal hygiene 17. how some diseases spread and can be controlled 18. about the process of growing from young to old and how people's Developing a healthy, safer lifestyle. needs change 19. the names of the main parts of the body 20. that all household products, including medicines, can be harmful if not used properly 21. rules for, and ways of, keeping safe, including basic road safety, and about people who can help them to stay safe. 22. to recognise how their behaviour affects other people 23. to listen to other people, and play and work cooperatively 24. to identify and respect the Developing good relationships and respecting the differences and similarities differences between people. between people 25. that family and friends should care for each other 26. that there are different types of teasing and bullying, that bullying is wrong, and how to get help to deal with bullying.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Promoting British Values: Democracy: Making decisions together. Individual Liberty: Freedom for all. Rule of Law: Understanding rules matter. Mutual Respect and Tolerance: Treat others as you want to be treated.
Personal Development:
The eight areas of success:
Try new things Work hard Concentrate Push themselves To imagine Improve Understand other Not give up Opportunities
• Discuss and learn techniques to improve in the eight areas of success. • Study role models who have achieved success.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance Areas of success Bronze Silver Gold
To try new things • Try new things with the help • Try new things when encouraged. • Enjoy new things and take opportunities wherever possible. of others. • Enjoy new experiences. • Find things to do that give energy. • Talk about some things of • Join clubs or groups. • Become fully involved in clubs or groups. personal interest. • Talk about new experiences with others. • Meet up with others who share interests in a safe environment. • Join in with familiar activities. • Concentrate on things of interest.
To work hard • Work hard with the help of • Enjoy working hard in a range of activities. • Have fun working hard. others. • Reflect on how effort leads to success. • Understand the benefits of effort and commitment. • Enjoy the results of effort in • Begin to encourage others to work hard. • Continue to practise even when accomplished. areas of interest. • Encourage others by pointing out how their efforts gain results. • Take encouragement from others in areas of interest.
To concentrate • Give attention to areas of • Focus on activities. • Give full concentration. interest. • ‘Tune out’ some distractions. • ‘Tune out’ most distractions. • Begin to ‘tune out’ • Search for methods to help with concentration. • Understand techniques and methods that aid concentration. distractions. • Develop areas of deep interest. • Develop expertise and deep interest in some things. • Begin to show signs of concentration. • Begin to seek help when needed.
To push themselves • Express doubts and fears. • Begin to understand why some activities • Find ways to push past doubts, fears, or a drop in motivation even • Explain feelings in feel uncomfortable. in challenging circumstances. uncomfortable situations. • Show a willingness to overcome fears. • Push oneself in areas that are not so enjoyable. • Begin to push past fears • Push past fears and reflect upon the emotions • Listen to others who encourage and help, thanking them for their (with encouragement). felt afterwards. advice. • Listen to people who try to • Begin to take encouragement and advice from others. • Reflect upon how pushing past doubts, fears or a drop in help. • Keep trying after a first attempt. motivation leads to a different outlook. • Begin to try to do something more than once.
To imagine • With help, develop ideas. • Begin to enjoy having new ideas. • Generate lots of ideas. • Respond to the ideas of • Show some enthusiasm for the ideas of others. • Show a willingness to be wrong. others’. • Ask some questions in order to develop ideas. • Know which ideas are useful and have value. • Respond to questions about • Show enjoyment in trying out some ideas. • Act on ideas. ideas. • Ask lots of questions. • Act on some ideas.
To improve • Share with others likes about • Share with others a number of positive features of own • Clearly identify own strengths. own efforts. efforts. • Identify areas for improvement. • Choose one thing to improve • Identify a few areas for improvement. • Seek the opinion of others to help identify improvements. (with help). • Attempt to make improvements. • Show effort and commitment in refining and adjusting work. • Make a small improvement (with help).
To understand others • Show an awareness of • Listen to others, showing attention. • Listen first to others before trying to be understood. someone who is talking. • Think of the effect of behaviour on others • Change behaviours to suit different situations. • Show an understanding that before acting. • Describe and understand others’ points of view. ones own behaviour affects • Describe the points of view of others.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance other people. • Listen to other people’s point of view.
To not give up • Try again with the help of • Find alternative ways if the first attempt does not work. • Show a determination to keep going, despite failures or set backs. others. • Bounce back after a disappointment or failure. • Reflect upon the reasons for failures and find ways to bounce • Try to carry on even if a • Show the ability to stick at an activity (or a club back. failure causes upset. or interest). • Stick at an activity even in the most challenging of circumstances. • Keep going in activities of • See oneself as lucky. • See possibilities and opportunities even after a disappointment. interest. • Consider oneself to be lucky and understand the need to look for • Try to think of oneself as luck. lucky.
Highlight objectives: red - objective not taught/achieved; yellow - not fully achieved; green - achieved by majority Promoting British Values: Democracy Rule of Law Individual Liberty Mutual Respect and Tolerance