Biology Test: Chapter 3 and 4.2 2010-2011
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
____ 1. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere enters the biotic parts of the biosphere through _____. a. burning of forests c. combustion of fossil fuels b. photosynthesis d. all of these ____ 2. A ______is several species in an area interacting with one another. a. organism c. community b. population d. ecosystem
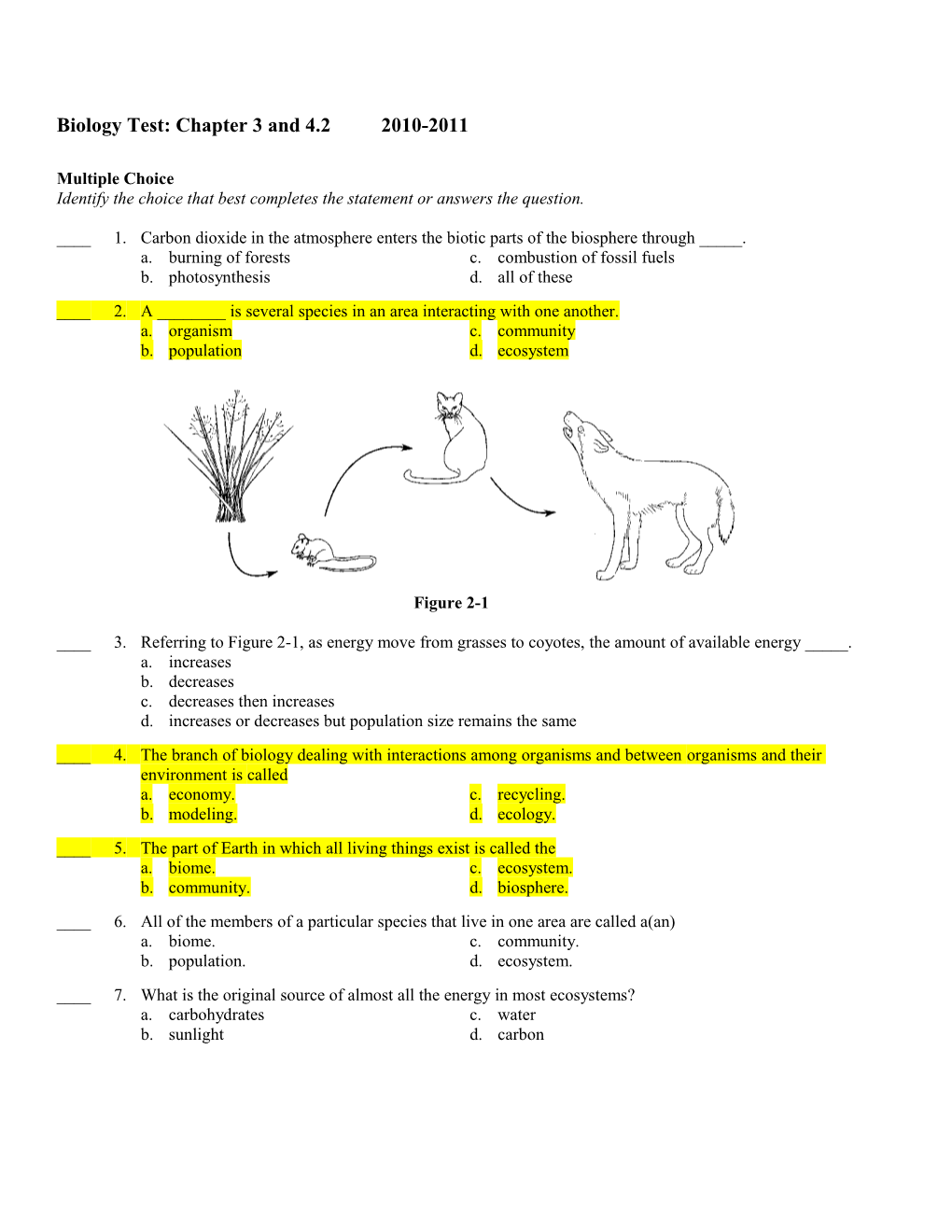
Figure 2-1
____ 3. Referring to Figure 2-1, as energy move from grasses to coyotes, the amount of available energy _____. a. increases b. decreases c. decreases then increases d. increases or decreases but population size remains the same ____ 4. The branch of biology dealing with interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment is called a. economy. c. recycling. b. modeling. d. ecology. ____ 5. The part of Earth in which all living things exist is called the a. biome. c. ecosystem. b. community. d. biosphere. ____ 6. All of the members of a particular species that live in one area are called a(an) a. biome. c. community. b. population. d. ecosystem. ____ 7. What is the original source of almost all the energy in most ecosystems? a. carbohydrates c. water b. sunlight d. carbon Figure 3-1
____ 8. The algae at the beginning of the food chain in Figure 3-1 are a. consumers. c. producers. b. decomposers. d. heterotrophs. ____ 9. An organism that produces its own food supply from inorganic compounds is called a(an) a. heterotroph. c. detritivore. b. consumer. d. autotroph. ____ 10. An organism that cannot make its own food is called a(an) a. heterotroph. c. autotroph. b. chemotroph. d. producer. ____ 11. Organisms that break down and feed on wastes and dead organisms are called a. decomposers. c. autotrophs. b. omnivores. d. producers. ____ 12. What is an organism that feeds only on plants called? a. carnivore c. omnivore b. herbivore d. detritivore ____ 13. What is an ecological model of the relationships that form a network of complex interactions among organisms in a community from producers to decomposers? a. food web c. food chain b. an ecosystem d. a population ____ 14. What animals eat both producers and consumers? a. herbivores c. chemotrophs b. omnivores d. autotrophs ____ 15. What is the term for each step in the transfer of energy and matter within a biological community? a. energy path c. trophic level b. food web d. food pyramid ____ 16. A bird stalks, kills, and then eats an insect. Based on its behavior, which ecological terms describe the bird? a. herbivore, decomposer c. carnivore, consumer b. producer, heterotroph d. autotroph, herbivore ____ 17. Which type of pyramid shows the amount of living tissue at each trophic level in an ecosystem? a. a numbers pyramid c. a biomass pyramid b. an energy pyramid d. a food pyramid ____ 18. The repeated movement of water between Earth’s surface and the atmosphere is called a. the water cycle. c. precipitation. b. the condensation cycle. d. evaporation. ____ 19. What is the process by which organisms convert nitrogen gas in the air to ammonium? a. nitrogen fixation c. decomposition b. excretion d. denitrification ____ 20. Nitrogen fixation is carried out primarily by a. humans. c. bacteria. b. plants. d. ammonia. ____ 21. A food chain generally begins with a. an autotroph c. a decomposer b. an omnivore d. a heterotroph ____ 22. Besides energy, what moves through the organisms at each trophic level of an ecosystem? a. organisms c. sunlight b. nutrients d. cycles ____ 23. An uncut lawn becomes a meadow and eventually a forest. This process is an example of a. evolution c. secondary succession b. primary succession d. niche ____ 24. The stable ecosystem that develops due to succession is called a. a niche c. a climax community b. a forest d. a biome ____ 25. Different species can share the same habitat, but compeition among them is reduced if they a. reproduce at different times c. increase their populations b. eat less d. occupy different niches ____ 26. An interaction in which one organism captures and feeds on another organism is called a. competition c. mutualism b. symbiosis` d. predation ____ 27. Primary succession can begin after a. a forest fire c. farmland is abandoned b. a lava flow d. a severs storm ____ 28. Symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit is called a. symbiosis c. commensalism b. mutualism d. parasitism ____ 29. What type of relationship exists between E.coli inside your intestine a. symbiosis c. parasitism b. mutualism d. commensalism ____ 30. What type of relationship exists between worms on your eyelashes a. symbiosis c. parasitism b. mutualism d. commensalism ____ 31. What type of relationship exists between HIV and monkeys a. symbiosis c. parasitism b. mutualism d. commensalism ____ 32. At which stage in Figure 3-3 are the most pioneer species found?
Figure 3-3 a. A c. C b. B d. D ____ 33. In figure 3-3 which species represents the climax community? a. mosses c. pines b. ferns, shrubs and grasses d. beeches and maples
____ 34. The process by which NH3 is converted into NH4. a. nitrogen fixation c. ammonification b. nitrification d. denitrification
____ 35. The process by which NO3 is converted into N2 a. nitrogen fixation c. ammonification b. nitrification d. denitrification Biology Test: Chapter 3 and 4.2 2010-2011 Answer Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 2-6 2. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 2-2 3. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 2-5 4. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 3.1.1 5. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 3.1.1 6. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 3.1.1 7. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 3.2.1 8. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: A OBJ: 3.2.1 9. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: A OBJ: 3.2.1 10. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 3.2.1 11. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 3.2.2 12. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 3.2.2 13. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: E OBJ: 3.2.2 14. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: A OBJ: 3.2.2 15. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: E OBJ: 3.2.2 16. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: E OBJ: 3.2.2 17. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 3.2.3 18. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 3.3.1 19. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: A OBJ: 3.3.1 20. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: B OBJ: 3.3.1 21. ANS: A PTS: 1 22. ANS: B PTS: 1 23. ANS: C PTS: 1 24. ANS: C PTS: 1 25. ANS: D PTS: 1 26. ANS: D PTS: 1 27. ANS: B PTS: 1 28. ANS: B PTS: 1 29. ANS: B PTS: 1 30. ANS: D PTS: 1 31. ANS: D PTS: 1 32. ANS: A PTS: 1 33. ANS: D PTS: 1 34. ANS: C PTS: 1 35. ANS: D PTS: 1 36. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: III OBJ: 4.2.1 37. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: III OBJ: 4.2.2 38. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: III OBJ: 4.2.2 39. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: III OBJ: 4.2.2