Final Review #1
1. _____What is the most important geographic feature to the civilizations of Egypt, Mesopotamia, Shang China, and the Indus Valley? a) high mountains c) deep rivers b) large deserts d) open plains
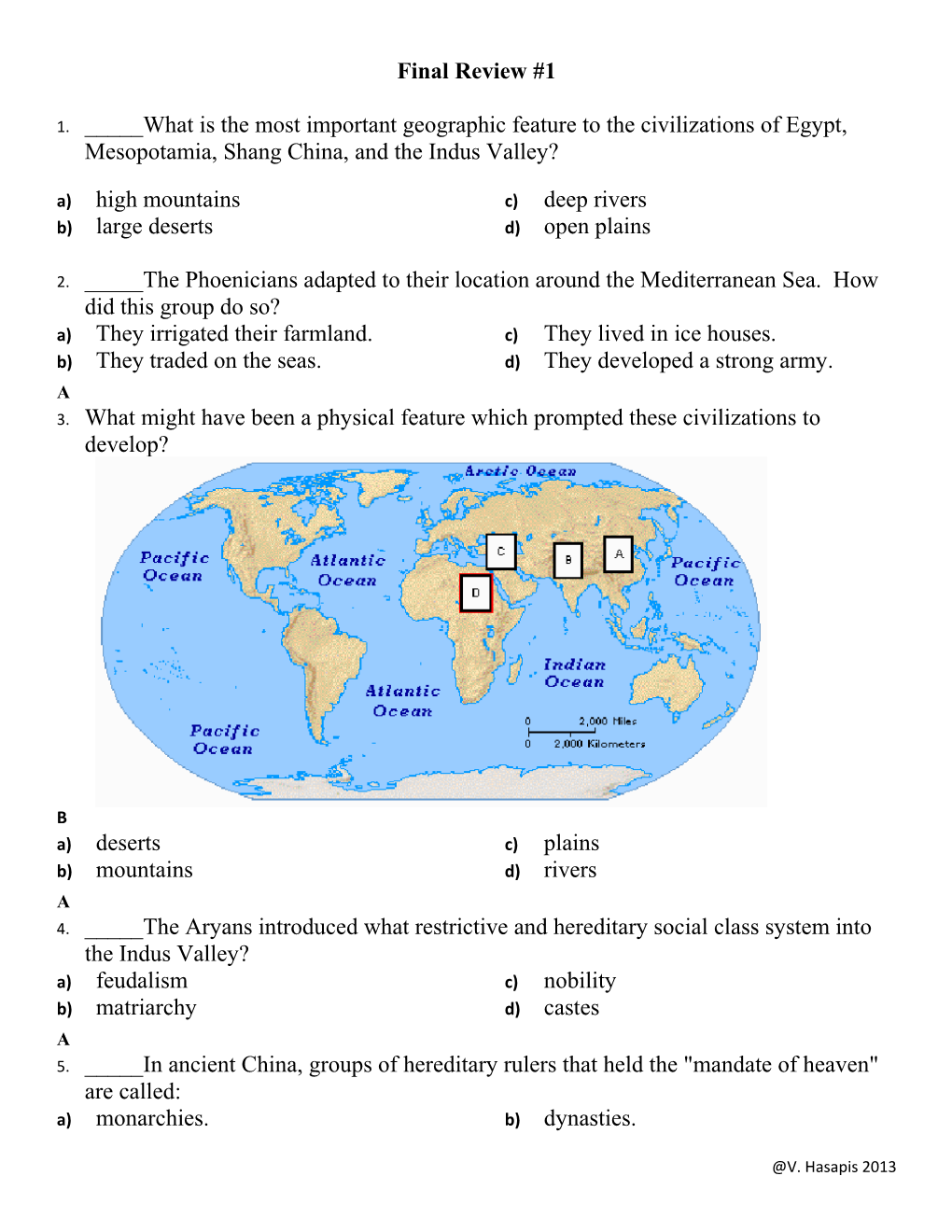
2. _____The Phoenicians adapted to their location around the Mediterranean Sea. How did this group do so? a) They irrigated their farmland. c) They lived in ice houses. b) They traded on the seas. d) They developed a strong army. A 3. What might have been a physical feature which prompted these civilizations to develop?
B a) deserts c) plains b) mountains d) rivers A 4. _____The Aryans introduced what restrictive and hereditary social class system into the Indus Valley? a) feudalism c) nobility b) matriarchy d) castes A 5. _____In ancient China, groups of hereditary rulers that held the "mandate of heaven" are called: a) monarchies. b) dynasties.
@V. Hasapis 2013 c) kingdoms. d) empire. A B C Final Review #2 D 1. _____Which of the following civilizations was located along the Nile River? a) India c) Egypt b) China d) Mesopotamia a) 2. _____The primary reason that civilization first developed in the Nile Valley and in Mesopotamia was that: a) important centers of learning were in the valley b) farmers could use tractors and other machinery easily c) the soil was fertile for farming d) good architects lived there b) c) Use this map to answer the next three questions. d)
e) 3. _____Mesopotamia is located at - a) A c) C b) B d) D a) 4. _____The letter 'D' on the map represents which river valley? a) Nile c) Indus b) Mesopotamia d) Huang He a) @V. Hasapis 2013 5. _____The Indus River is located at - a) A c) C b) B d) D a) Dgs b) Final Review # 3
1. ______The first permanent agricultural community was located on the:
a. Nile and Jericho Rivers.
b. Amazon River.
c. Tigris and Euphrates Rivers.
d. Rhine River.
c)
2. ______Which of the early civilizations are inappropriately matched with its famous river(s)?
a. Mesopotamia- Tigris and Euphrates
b. China- Huang He
c. Egypt- Rhine
d. India- Indus d)
3. ______Early civilizations were primarily built near rivers because:
a. the soil was fertile and supported good crop yield
b. transportation was readily available
c. fishing supported the local economy
d. more lumber to build with was found along rivers
e)
4. ______The Assyrians conquered many peoples and ruled over them. What kind of government is this?
@V. Hasapis 2013 a. constitutional monarchy
b. democracy
c. empire
d. republic
f)
5. ______Hammurabi is known for:
a. conquering the Indian subcontinent.
b. writing the Epic of Gilgamesh.
c. establishing a harsh set of laws.
d. developing the first cuneiform writing.
g) h) i) Final Review #4 j) 1. _____What did the Emperor do to protect China from foreign invaders from the north? k) A construct a large army B invade and take them over C ignore them D build a large wall l) m) 2. _____The Mandate of Heaven - A gave the Zhou kings authority to command. B declared the king a divine being. C put an end to the dynastic cycles. D forbids an overthrow of the ruling king. A B 3. _____The caste system was introduced by what group of invaders? A Muslims B Persians C Romans D Aryans
@V. Hasapis 2013 A B 4. _____What empire stretched from the Mediterranean Sea to India and allowed conquered peoples to remain relatively independent from the empire? A Egypt B China C Persia D Greece A B 5. _____What was true of the Persian Empire? A It frequently relocated conquered peoples to prevent revolts. B It developed a large bureaucracy to manage its vast territory. C It never developed a system of roads and cities. D It was never conquered by a foreign power. C D
@V. Hasapis 2013 E Final Review #5 F 1. _____While creating an empire, the Persians established a system that: A allowed conquered peoples to retain some independence. B forced all eligible men to enlist in the Persian army. C collected additional yearly taxes from non-citizens. D sold all political leaders living in conquered areas into slavery. G 2. _____Hieroglyphic and cuneiform systems provided the basis for the development of: A recorded history B painting and sculpture C oral traditions D subsistence farming 3. 4. _____Which civilization is credited with developing an early alphabet? A Kush B Hebrews C Phoenicians D Chinese A 5. _____Shang China established a series of rulers from the same family. What is the rule of each family called? A dynasty B tyranny C dictatorship D empire A B 6. _____All of the following were effects of the Code of Hammurabi EXCEPT - A uniform law code B mercy C applied to all groups D longevity A B
@V. Hasapis 2013 C Final Review #6
1. _____The Romans exiled the Jews after a series of uprisings in Israel and Judea leading to: D A the Diaspora. B theRed Sea Exodus. C the Nebuchadnezzar Revolts. D their return to Egypt. E
2. _____Geography affected Greece in all of the following ways EXCEPT: A the rugged mountains limited land travel and communication. B excellent harbors encouraged fishing and sea trade. C the mild climate encouraged outdoor activities like theatre and sports D the harsh deserts made agriculture difficult. F
3. _____What two things did each Greek city-state have in common? A currency and government B social structure and topography C economic base and attitude toward slaves D religion and language A
B Use this picture to answer the next question.
C
4. _____The structure pictured above is the Parthenon in Athens. What was its purpose? A It was a fortress for the defense of the city. B It was a market and public meeting place. C It was a temple to the goddess Athena. D It was a monument to Olympic athletes 5. _____Which statement best describes Athenian democracy? A Every male citizen can vote. B Only the strongest rule. C Those of noble birth rule. @V. Hasapis 2013 D Women and men have an equal vote. A
B C Final Review #7 1. _____Which city-state was characterized by strong military discipline, more freedoms for women, and severe treatment of slaves? A. Athens B. Corinth C. Sparta D. Persia 2.
3. _____What did the Persian and Peloponnesian wars indicate about the relationship between Sparta and Athens? A. They always fought on same side in war. B. They were not very successful in war. C. They sometimes fought with and sometimes against each other. D. They usually fought each other and had a long, bitter relationship. 4. 3. _____How did the geography of Greece affect its development? A The cold weather prevented any agriculture from succeeding. B The many mountains and seas caused many rival city-states to develop. C The few natural barriers allowed one strong clan to unite the entire country. D The intense heat generally forced most outdoor activities inside. 5.
4. _____What group was allowed citizenship in Athens? 6. A free men C women B young children D slaves 7. Use this information to answer the next question.
All adult men serve in the military. More freedom for women than other city-states. Ruled by an oligarchy of generals. Possess a permanent slave class. 8.
5. _____The statements above best describe which Greek city-state? A Thebes C Sparta B Athens D Delphi
@V. Hasapis 2013 A B C D Final Review #8 E 1. _____Which type of government was NOT practiced in classical Greece? A democracy – rule by citizens B republic – rule by representatives C monarchy – rule by a king D oligarchy – rule by a small elite F
2. _____What war saw a united Athens and Sparta against an Asian foe? A Persian War C Peloponnesian War B Hellespontine War D Trojan War 3. _____Which of the following statements is NOT true of the geography of Rome? A Rome is located on the Italian peninsula. B Rome was protected by the AlpsMountains to the north. C Rome had easy access to the Mediterranean and AdriaticSeas. D Rome suffered from a lack of good farmland. A
4. _____There were two major social classes in ancient Rome. The ______were wealthy and well born and the ______, who were the poorer members of society. A Patricians, Plebeians B Hittites, Mennonites C Phoenicians, Christians D Romans, Gauls A 5. _____Democracy originated in which ancient culture? B A Egyptian B Roman C Mesopotamian D Greek C
@V. Hasapis 2013 D Final Review #9 E 1. _____Which best describes the Golden Age of Athens? A A period of peace and prosperity when arts and science flourished. B A period when Pericles took power and ruled as a tyrant. C A period when Persia ruled Athens and expanded the rights of citizens. D A period when all the Greek city-states where united under one democratic government. F
2. _____What form of government developed in Athens during the Golden Age of Pericles? A aristocracy B oligarchy C democracy D monarchy A
3. _____Which term describes the blending of Greek culture with Persian, Indian, and Egyptian influences? A classical B arabesque C Hellenism D Gothic A
4. _____Who was assassinated by the Roman Senate to prevent him from becoming a B Dictator?
A Marc Antony B Augustus Caesar C Julius Caesar D Constantine 5. _____What is the 200-year period of Roman peace and prosperity initiated by Augustus Caesar known as? A the Pax Sinica B the Golden Age C the Pax Romana D the Dark Age A
@V. Hasapis 2013 B Final Review #10 C 1. _____All of the following contributed to the end of the Roman empire EXCEPT: A inflation and economic instability. B a weak government and civil unrest. C the rise of the Christian Church and the growing influence of the pope. D the use of foreign mercenaries. D 2. _____What group was allowed citizenship in Athens? E A. free men B. young children C. women D. slaves 2. _____What was one significant contribution of the Greeks? A. They built the first cities. B. They invented the wheel. C. They created the democratic system. D. They invented paper. A
3. _____Which of these accurately describes a type of government used in ancient Greece? A. democracy - rule by adult males B. tyranny - rule by a military general C. aristocracy - rule by wealthy citizens D. monarchy - rule by an elected king A
4. _____What philosopher taught that the way to seek truth is through a series of questions and answers? A. Socrates B. Plato C. Aristotle D. Herodotus
@V. Hasapis 2013 A Final Review #11 B 1. _____Early Rome was governed by a Republic. What is a republic? A. government by all citizens B. government by religious figures C. government by representatives D. government by a king A
2. _____Roman law was codified and displayed in the Forum. What was this set of laws called? A. Code of Hammurabi B. the Roman Constitution C. Laws of Solon D. Twelve Tables A
3. _____Winning the Punic Wars gave Rome control of what sea? A. the Adriatic Sea B. the Aegean Sea C. the Mediterranean Sea D. the Black Sea A
4. _____How were the PaxRomana and the Age of Pericles in Athens similar? A. Both were times of poverty. B. Both had little trade with the outside world. C. Both were times of warfare. D. Both were times of peace and artistic advancement. A
5. _____Which of the following were not related to the 'fall' of Rome? A. Germanic invasions B. corrupt officials C. the assassination of Julius Caesar D. heavy taxes A
@V. Hasapis 2013 B Final Review #12 C 1. _____What group(s) invaded Rome, finally putting an end to the Empire? A. Carthage C. Barbarians B. Egypt D. Greek rebels A B 2. _____What is the most accurate description of the basic relationships under feudalism? A Monarchs granted land to serfs, who farmed it and protected the lords who administered the food supply. B Lords granted land to serfs, who farmed it and protected the monarch, who supplied food to the lords. C Monarchs granted land to local lords, who administered it and protected serfs, who farmed it.
D Serfs protected the monarch, who granted them land in return for feeding the lords. C
3. _____A period of lawlessness and disunity followed the fall of the Roman Empire. What served as the only unifying force in Europe? A Emperor of Rome C Christian Church B Roman legions D localized kings A 4. _____What ultimately strengthened the feudal system? A invasions C rise of trade B rise of towns D increased independence A 5. _____What was a result of the Black Death of the fourteenth century? A African populations destroyed from disease B African culture destroyed from forced slave captures C war in western Europe D dramatic shortages of laborers and people throughout Europe B 6. _____How did the bubonic plague spread in the 14th century? A infected food C rodents with infected fleas B people traveling from Asia D weather systems C 7. _____The Crusades resulted in all of the following EXCEPT - A a significant increase in trade between Asia and Europe. B Christians gaining permanent control of the Holy Lands. C the exchange of ideas between the East and the West. D a legacy of distrust between Muslims and Christians. D 8. _____The signing of the Magna Carta in 1215, gave written recognition to the idea that - A the system of vassalage should be abolished. B the Catholic Church had no authority in England. C the power of the English monarch was not absolute.
@V. Hasapis 2013 D there should be a system of common law throughout England E F
@V. Hasapis 2013