R9
HOW SOON WILL I HAVE TO WAIT, BEFORE MY HOUSE STARTS TO FLOOD?
TASK. Complete the river data log below A to F . When you have completed all of the six sections you will be able to see if your house will get flooded, and if it does, by how much.
RIVER SEVERN DATA FOR IRONBRIDGE
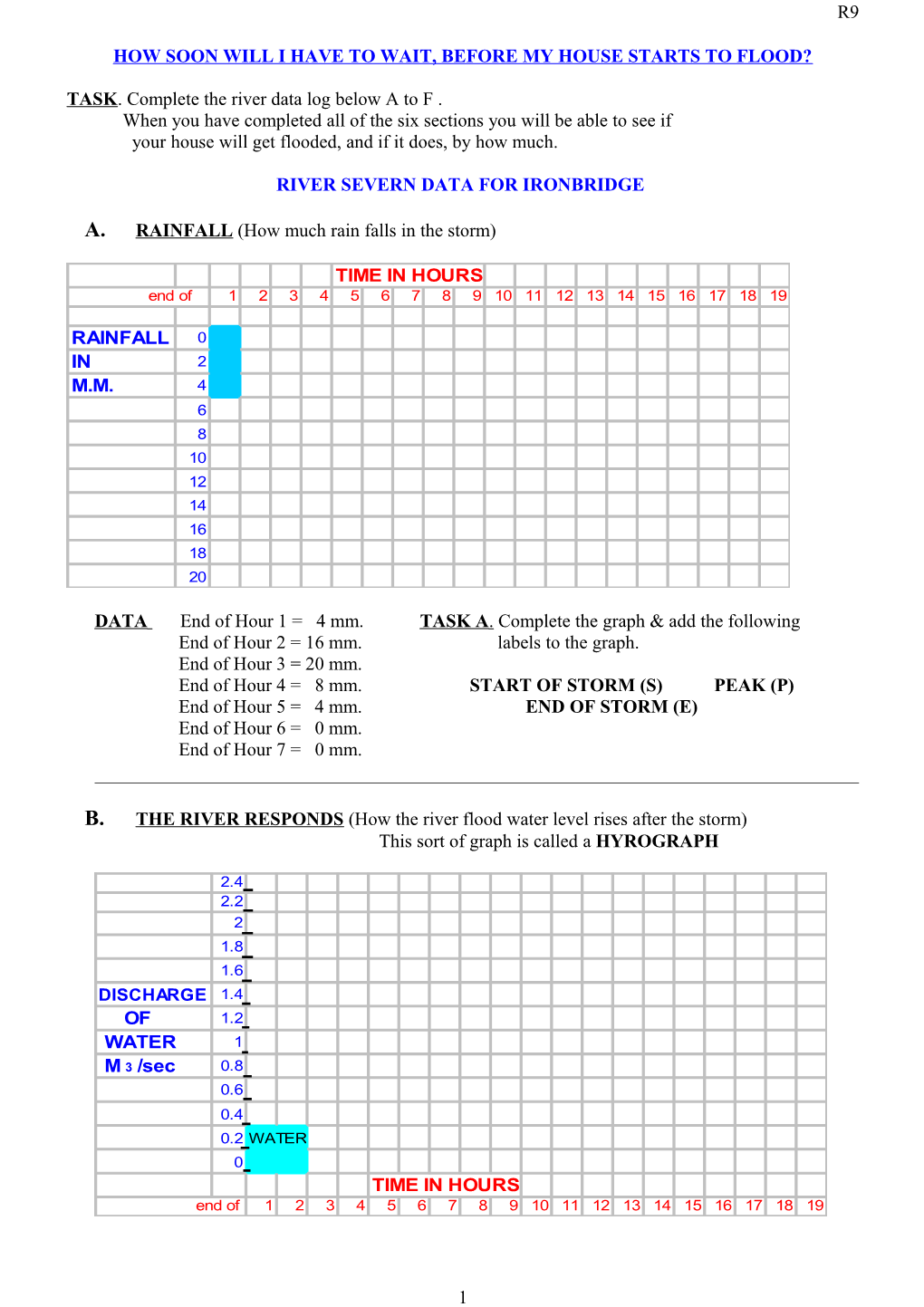
A. RAINFALL (How much rain falls in the storm)
TIME IN HOURS end of 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
RAINFALL 0 IN 2 M.M. 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
DATA End of Hour 1 = 4 mm. TASK A . Complete the graph & add the following End of Hour 2 = 16 mm. labels to the graph. End of Hour 3 = 20 mm. End of Hour 4 = 8 mm. START OF STORM (S) PEAK (P) End of Hour 5 = 4 mm. END OF STORM (E) End of Hour 6 = 0 mm. End of Hour 7 = 0 mm.
B. THE RIVER RESPONDS (How the river flood water level rises after the storm) This sort of graph is called a HYROGRAPH
2.4 2.2 2 1.8 1.6 DISCHARGE 1.4 OF 1.2 WATER 1 M 3 /sec 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 WATER 0 TIME IN HOURS end of 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
1 R9
DATA End of Hour 1 = 0.4 cubic meters per second TASK B. Complete the graph End of Hour 2 = 0.4 “ “ “ “ using the data provided & add End of Hour 3 = 0.4 “ “ “ “ the following labels. End of Hour 4 = 0.4 “ “ “ “ End of Hour 5 = 0.6 “ “ “ “ PEAK (P) End of Hour 6 = 0.8 “ “ “ “ RISING WATER LEVEL (R) End of Hour 7 = 1.2 “ “ “ “ FALLING WATER LEVEL (F) End of Hour 8 = 1.8 “ “ “ “ BASE FLOW (B) End of Hour 9 = 2.0 “ “ “ “ TIME LAG (L) End of Hour 10 = 2.4 “ “ “ “ End of Hour 11 = 2.2 “ “ “ “ End of Hour 12 = 1.8 “ “ “ “ End of Hour 13 = 1.8 “ “ “ “ End of Hour 14 = 1.6 “ “ “ “ End of Hour 15 = 1.4 “ “ “ “ End of Hour 16 = 1.4 “ “ “ “ End of Hour 17 = 1.0 “ “ “ “ End of Hour 18 = 1.0 “ “ “ “ End of Hour 19 = 0.8 “ “ “ “
NOTE: The normal winter level of the river (Base Flow) is on average flowing at 0.4 Cubic metres of water per second. At the end of the storm it took 36 hours to get back to it’s average level at 0.4 M3 /sec
TASK B. SUMMARY Explain what has happened to the river discharge & reasons for any pattern you notice.
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
C. CROSS SECTION SURVEY DATA ( The shape of the flooded river at the peak of the storm)
TASK C. Study the completed cross section.
Calculate (a) The CROSS SECTIONAL AREA = ………….. Square meters.
(b) The distance along the Wetted Perimeter. This is were the water comes in contact with the bank & stream bed. Marked on the diagram in red and two arrows. The distance along the WETTED PERIMETER = ……………. Meters. HINT: It is simply a mater of counting squares in (a) & measuring a distance in (b) Notice that 1 square on the grid below equals 4 sq. Metre
2 R9
CROSS SECTIONAL DIAGRAM OF THE RIVER IN FULL FLOOD
16 14 DEPTH 12 IN 10 METRES 8 6 4 normal level of water wetted perimeter 2 0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 52 54 58 60 62 64 DISTANCE ACROSS THE RIVER IN METRES
D. THE FRICTION IN A STREAM (the turbulence of the rapids /white water & the drag effect on the river bank and bed in flood.)
TASK D. Calculate the efficiency of the river channel above. Use this formula.
EFFICIENCY RATIO = Cross sectional area (a) = (a) ………………… = Ans. ………. Wetted perimeter (b) (b) …………………
Note. The higher the value in your answer the more efficient the river is & the less friction is occurring. At normal level the efficiency ratio is 1.33 ______
E. THE SPEED OF THE RIVER IN FULL FLOOD. (Five readings were taken over a distance of 50 metres)
RUN 1 = 32 seconds RUN 2 = 25 seconds RUN 3 = 18 seconds RUN 4 = 29 seconds RUN 5 = 21 seconds
TASK E. Calculate the average speed of the river. (remember your computer probably has a calculator program)
Total speeds ______5 = …… (average speed for 50 metres)
THE AVERAGE SPEED FOR 1 METRE PER SECOND is therefore = …………..M./ sec. ______
F. THE RIVER FLOOD DISCHARGE (the volume of water in the flooding river)
This is calculated by: DISCHARGE = CROSS SECTION AREA X AVERAGE SPEED = Cubic metres per second (cumecs)
TASK F (a) Calculate the discharge for the river in flood . ANSWER = …………….cumecs.
(b) If ONE cubic meter of water equals 1,000 litres of water, how many litres of water will flow down the river in ONE SECOND? ANSWER = …………….litres per sec.
3 R9
G. WHAT WILL HAPPEN TO MY HOUSE IN IRONBRIDGE?
I really need to know three things.
(a) WILL THE FLOOD WATER REACH UP TO MY FRONT DOOR ?
(b) IF THE FLOOD WATER DOES REACH MY HOUSE, HOW HIGH WILL THE WATER LEVEL BE INSIDE MY HOUSE ?
(c) HOW MANY HOURS DO I HAVE FROM, WHEN IT STARTS TO RAIN, TO WHEN THE RIVER LEVEL STARTS TO FALL?
TASK G. Calculate the three answers above by using the data in A to F. The diagram below can be used to see how high the water rises and how it may endanger your house in Ironbridge.
300 290 280 270 260 250 240 230 220 FLOOD 210 DATA 200 IN 190 CUMECS 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 NORMAL 10
LEVEL 0 not to scale horizontally ANSWERS. (a) YES or NO ? …………. (b) (mark and LABEL your answer on the sketch above) The DISCHARGE in FLOOD is …………….. Cumecs (Cubic metres per second) (c) …………………….. hours.
4