Chemistry Semester 2 Final Exam Study Guide 2017
Chemical Reactions and Equations
1. Be able to balance chemical equations from formulas or pictures of molecules.
2. Be able to identify different types of reactions.
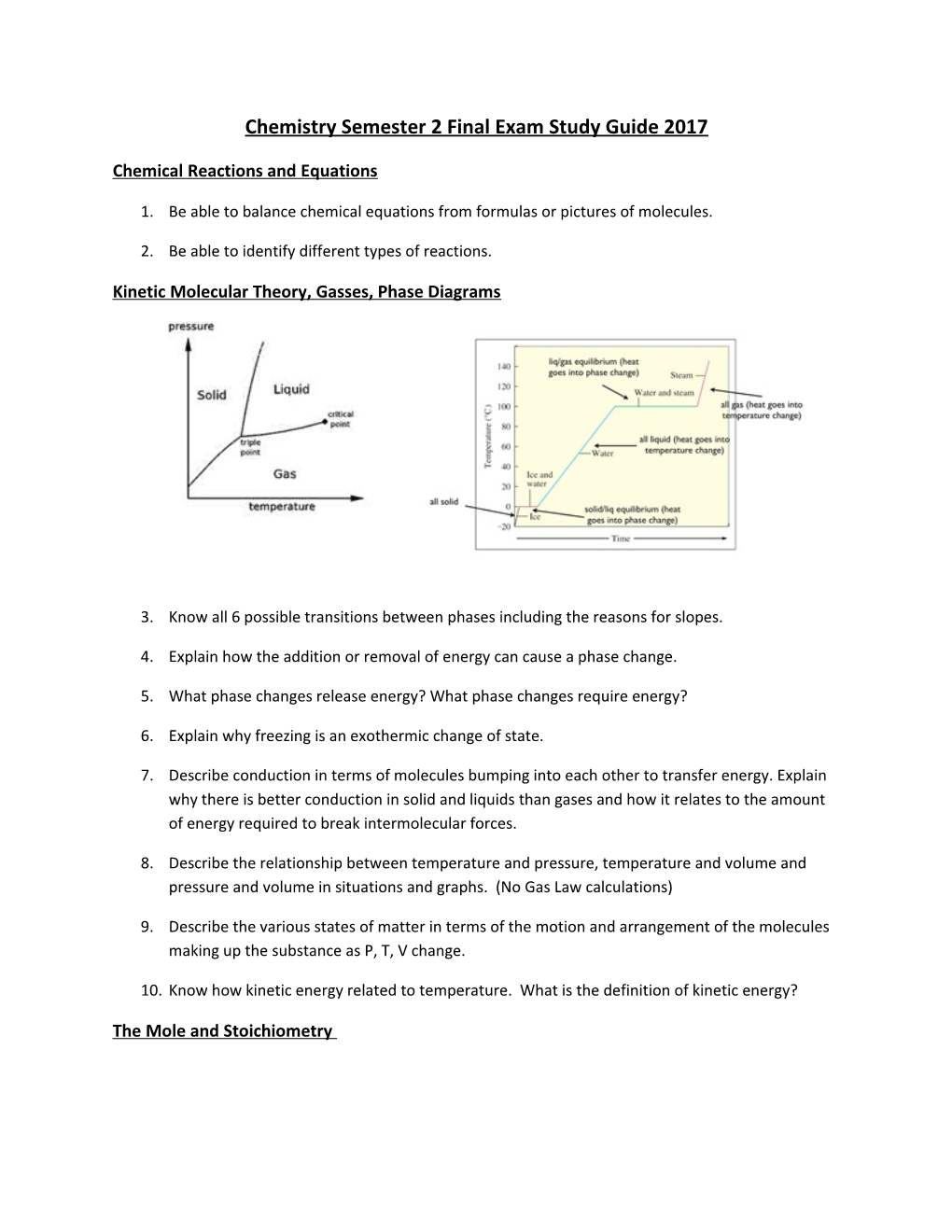
Kinetic Molecular Theory, Gasses, Phase Diagrams
3. Know all 6 possible transitions between phases including the reasons for slopes.
4. Explain how the addition or removal of energy can cause a phase change.
5. What phase changes release energy? What phase changes require energy?
6. Explain why freezing is an exothermic change of state.
7. Describe conduction in terms of molecules bumping into each other to transfer energy. Explain why there is better conduction in solid and liquids than gases and how it relates to the amount of energy required to break intermolecular forces.
8. Describe the relationship between temperature and pressure, temperature and volume and pressure and volume in situations and graphs. (No Gas Law calculations)
9. Describe the various states of matter in terms of the motion and arrangement of the molecules making up the substance as P, T, V change.
10. Know how kinetic energy related to temperature. What is the definition of kinetic energy?
The Mole and Stoichiometry
11. Find the mole ratio when given a molecular view of a chemical equation. 12. Find the molar mass of elements or compounds using a given periodic table.
13. Given the following equations KClO3 KCl + O2 find how many grams of oxygen are made if
3.75 moles of KClO3 decompose?
14. Given the following equation: K + Cl2 → KCl. How many grams of KCl is produced from 2.50 g of K?
15. How many moles are in 2.5 grams of KCN? 16. Know Avogadro’s number and how to use it to find molecules or atoms. 17. How many atoms of NaCl are in a 28.6 g sample?
18. Calculate the percent composition of each element in Na2SO4.
19. Calculate to formula when given a percent composition; benzene is 92.3% C and 7.8% H.
20. Calculate molecular formula when given an empirical formula. Use your to benzene answer given a formula mass of 78.12 g/mol.
21. Recognize compounds that have the same empirical formulas.
Acid, Base Chemistry
22. Use the pH scale, classify how various solutions are acidic or basic given their pH.
23. Explain real world examples including why lakes with limestone or calcium carbonate experience less adverse effects from acid rain than lakes with granite beds.
24. Describe the outcomes of a litmus paper, PHTH and other indicator tests that can be used to distinguish an acid from a base.
25. Explain the concentration of hydronium ions and hydroxide ions as they move across the pH scale.
26. Recognize formulas for common acids and bases formed from families I and II.
27. Predict products and balance neutralization reactions:
a) __ CsOH + __ H2CO3 ______+ ______b) __ HF + __ Mg(OH)2 ______+ ______
Organic Chemistry
28. Define organic compound. What are basic elements in organic compounds?
29. Recognize the name, formula and structure for simple hydrocarbons with 1 to 10 C.
30. Recognize structural isomers possible for a given alkane.
31. Recognize that proteins, starches, and other large biological molecules are polymers.