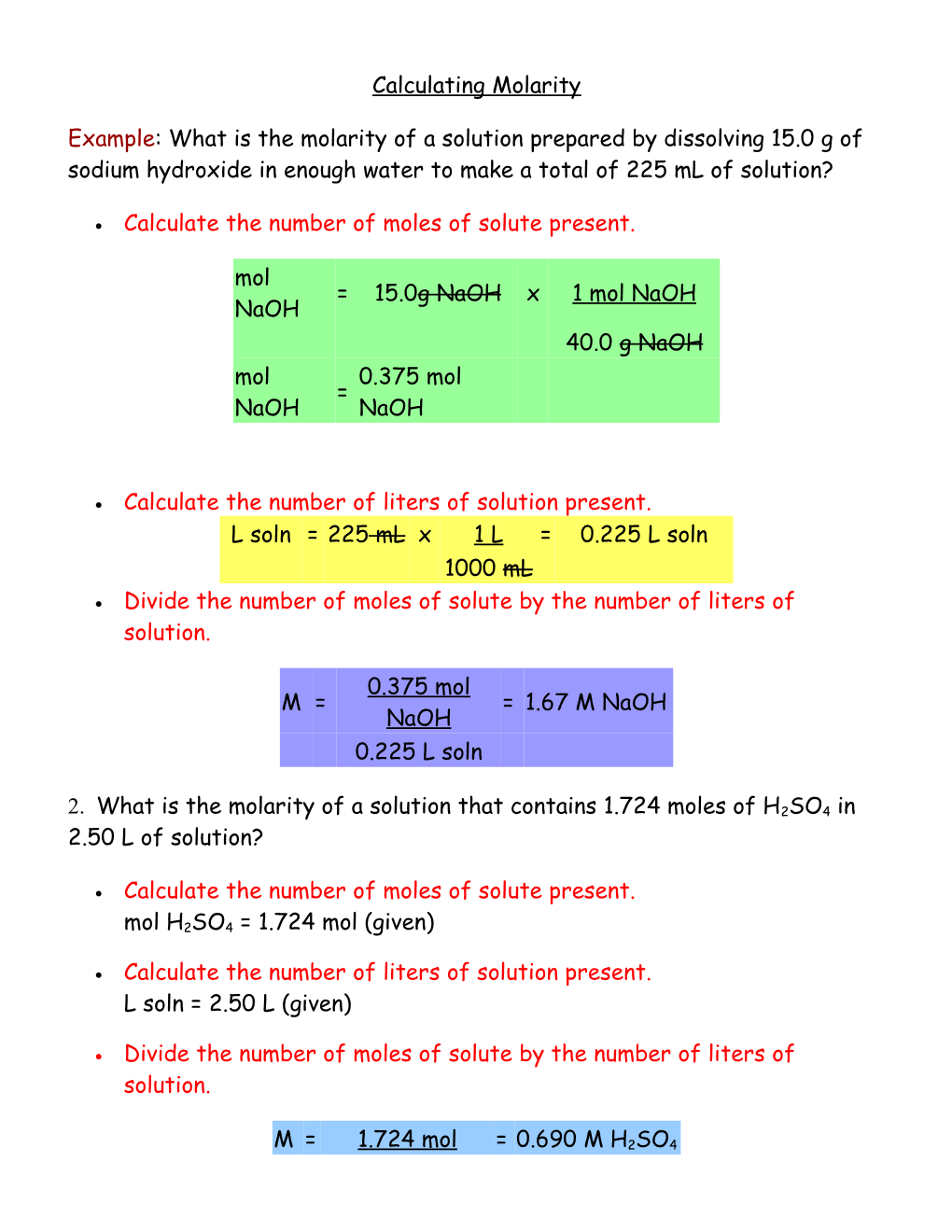
Calculating Molarity
Example: What is the molarity of a solution prepared by dissolving 15.0 g of sodium hydroxide in enough water to make a total of 225 mL of solution?
Calculate the number of moles of solute present.
mol = 15.0g NaOH x 1 mol NaOH NaOH 40.0 g NaOH mol 0.375 mol = NaOH NaOH
Calculate the number of liters of solution present. L soln = 225 mL x 1 L = 0.225 L soln 1000 mL Divide the number of moles of solute by the number of liters of solution.
0.375 mol M = = 1.67 M NaOH NaOH 0.225 L soln
2. What is the molarity of a solution that contains 1.724 moles of H2SO4 in 2.50 L of solution?
Calculate the number of moles of solute present.
mol H2SO4 = 1.724 mol (given)
Calculate the number of liters of solution present. L soln = 2.50 L (given)
Divide the number of moles of solute by the number of liters of solution.
M = 1.724 mol = 0.690 M H2SO4 H2SO4 2.50 L soln
3. What is the molarity of a solution prepared by dissolving 25.0 g of HCl (g) in enough water to make 150.0 mL of solution?
M = 25.0 g HCl x 1 mol HCl x 1000 mL soln 150.0 mL 36.5 g 1 L soln soln HCl M = 4.57 M HCl