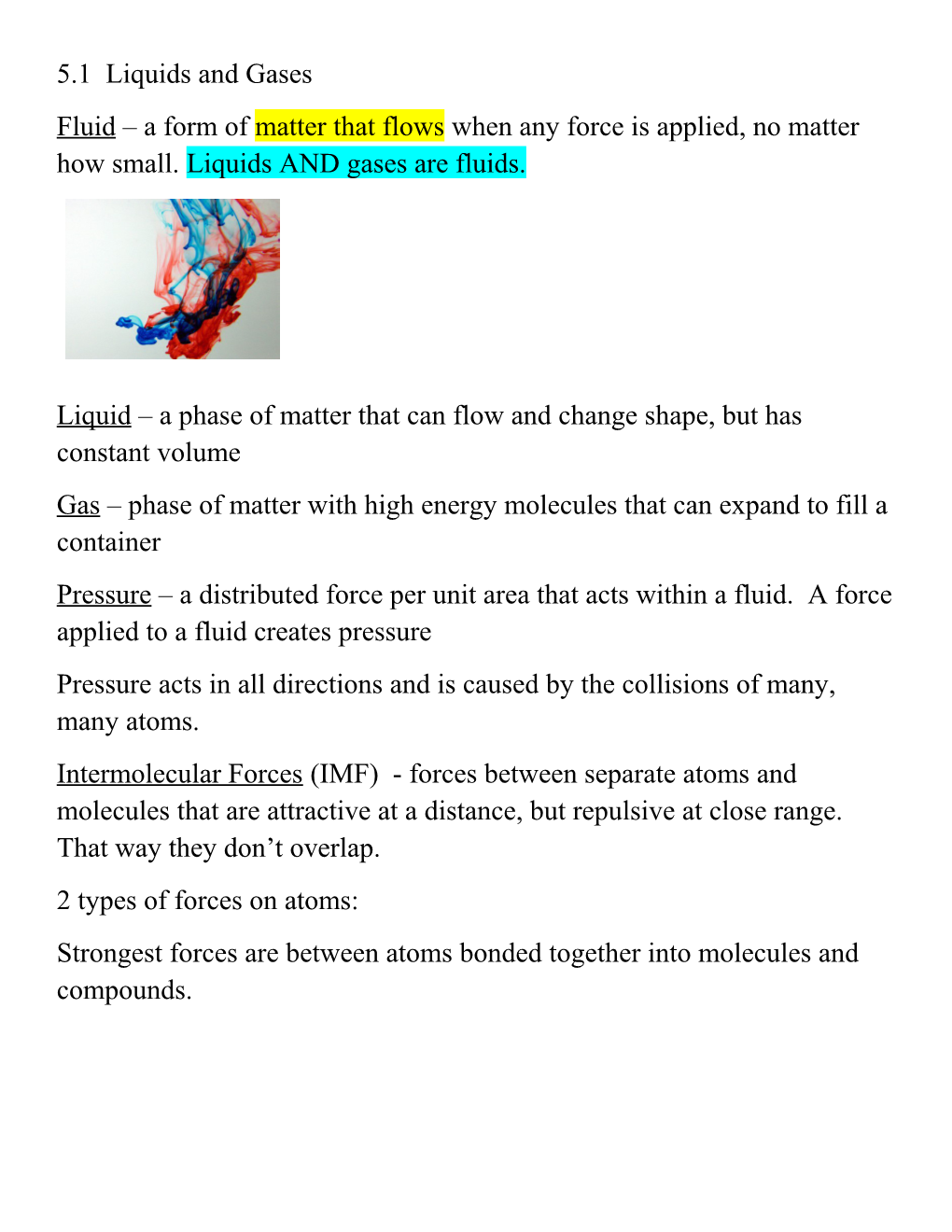
5.1 Liquids and Gases Fluid – a form of matter that flows when any force is applied, no matter how small. Liquids AND gases are fluids.
Liquid – a phase of matter that can flow and change shape, but has constant volume Gas – phase of matter with high energy molecules that can expand to fill a container Pressure – a distributed force per unit area that acts within a fluid. A force applied to a fluid creates pressure Pressure acts in all directions and is caused by the collisions of many, many atoms. Intermolecular Forces (IMF) - forces between separate atoms and molecules that are attractive at a distance, but repulsive at close range. That way they don’t overlap. 2 types of forces on atoms: Strongest forces are between atoms bonded together into molecules and compounds.
The Role of Thermal Energy: The phases of matter (solid, liquid, and gas) exist because of competition between thermal energy and molecular forces. Intermolecular forces try to bring molecules close. Thermal energy causes molecules to vibrate and spread apart. High Thermal Energy (High Temperature) IMF is broken and molecules spread apart in a gas. Medium Thermal Energy – in a liquid, molecules partially break apart IMF and move around, but not enough to escape.
Low Thermal Energy – fixed in a solid
Food coloring in hot and cold water: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YbhwXSv9rk4 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bN7E6FCuMbY
Melting and Boiling Melting point – the temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid Melting point of water is 0*C Different substances have different melting points because IMF have different strengths. Iron melts at 1,500*C IMF in iron are STRONGER than IMF in water Material Melting Boiling Point *C Point *C Tungsten 3,422 5,555 Iron 1,538 2,861 Copper 1,085 2,562 Aluminum 660 2,519 Lead 327 1,749 Hard Plastic 240 300 Candle Wax 50 400 Water 0 100 Alcohol -108 78 Nitrogen -210 -196 Oxygen -219 -183 Helium none -269
Fire Ant Colony with liquid aluminum: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IGJ2jMZ-gaI
Boiling – when enough Thermal Energy is added, IMF are completely broken and liquid becomes gas. The temp at which liquid becomes gas is called the boiling point. Changes in phase require energy Heat is added to ice, temp increases until it reaches 0*C Then temp stops increasing! When all ice is melted, temp starts to increase again We need some materials to be solid at room temp, others to be liquid, and others to be a gas. Most materials have a higher density as a solid than as a liquid EXCEPT WATER! Solid water is a 6-sided crystal structure (snowflake) and molecules spread out! Water expands! ICE floats because it is less dense than water. Density of ice = 0.92 g/cm3 Density of water 1.0 g/cm3 Ice is less dense than liquid water, so it floats on the surface of lakes and ponds when they freeze in winter, which prevents the water below from reaching freezing temperatures. Oxygen and Nitrogen are gases at room temp. If the temp gets low enough, they will become liquid and even solid. Liquid Nitrogen -196*C can rapidly freeze materials Liquid Oxygen is used in rockets, because in outer space, there is no oxygen to burn fuel Making ice cream with liquid nitrogen: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=utjdLDojbCw Liquid oxygen: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7NXfyCezUFk Evaporation and Condensation: Evaporation – change from a liquid to a gas at a temperature below the boiling point. Evaporation of sweat from your skin on a hot day cools your body by carrying away energy Condensation – change from gas to a liquid at a temp below the boiling point. Water vapor molecules stick to a cool surface and form drops of liquid water Relative humidity – ordinary air contains water vapor. Evaporation adds water; condensation removes water. You feel hot and sticky on a humid day Convection – transfer of heat through the motion of fluids such as air and water
Natural convection – fluids expand when they heat up. Hot water or air rises up, cooler air or water sinks to the bottom. Forced convection uses a pump or fan to blow air or water around Atmosphere – air feels light because it is 1000 times less dense than water Air: 76.6% Nitrogen 20.6 % Oxygen 1% Water Vapor 1.8 % Argon, Carbon Dioxide, and other gases Weather: Earth’s weather is created by gigantic convection currents. Energy from the Sun warms the ground. Air near the ground warms up and rises.
Rain – at high altitudes, temperature of air drops and water vapor condenses
Two gas laws: Boyle’s Law: For a fixed amount of a gas at a fixed temperature, pressure and volume are inversely proportional
Charles Law: Gases expand when heated: When pressure on a gas is held constant, temperature and volume are directly related