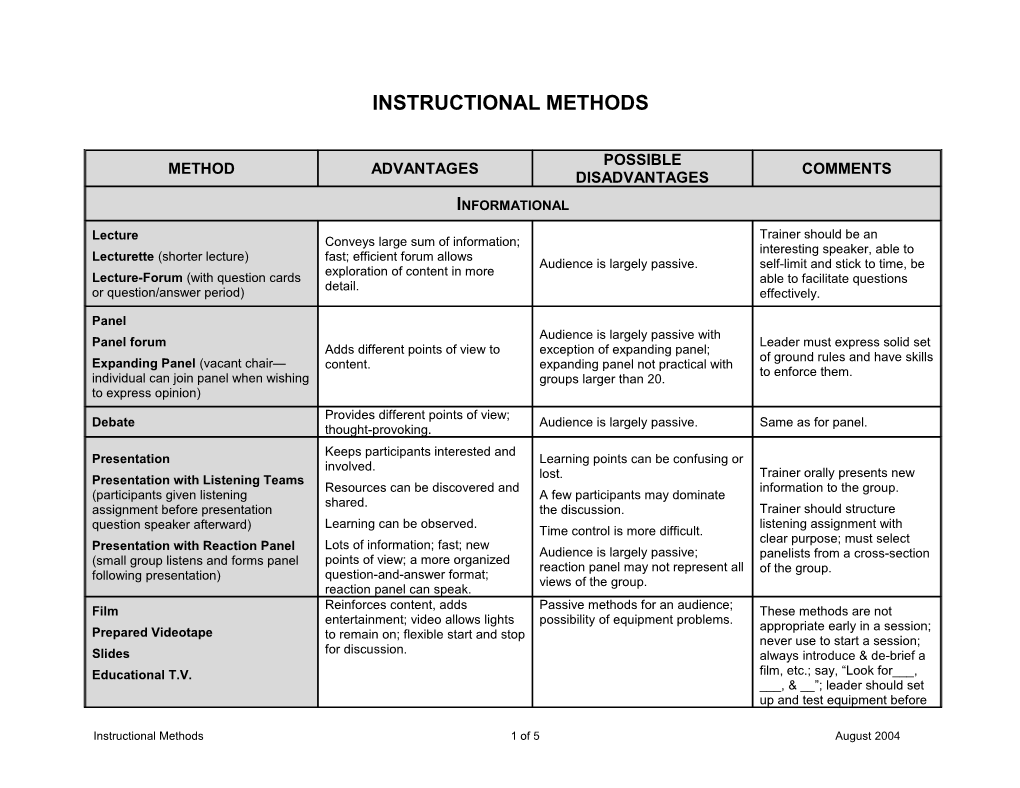
INSTRUCTIONAL METHODS
POSSIBLE METHOD ADVANTAGES COMMENTS DISADVANTAGES INFORMATIONAL
Trainer should be an Lecture Conveys large sum of information; interesting speaker, able to Lecturette (shorter lecture) fast; efficient forum allows Audience is largely passive. self-limit and stick to time, be exploration of content in more Lecture-Forum (with question cards able to facilitate questions detail. or question/answer period) effectively.
Panel Audience is largely passive with Panel forum Leader must express solid set Adds different points of view to exception of expanding panel; of ground rules and have skills Expanding Panel (vacant chair— content. expanding panel not practical with to enforce them. individual can join panel when wishing groups larger than 20. to express opinion) Provides different points of view; Debate Audience is largely passive. Same as for panel. thought-provoking. Keeps participants interested and Presentation Learning points can be confusing or involved. Trainer orally presents new Presentation with Listening Teams lost. Resources can be discovered and information to the group. (participants given listening A few participants may dominate shared. assignment before presentation the discussion. Trainer should structure Learning can be observed. listening assignment with question speaker afterward) Time control is more difficult. Lots of information; fast; new clear purpose; must select Presentation with Reaction Panel Audience is largely passive; points of view; a more organized panelists from a cross-section (small group listens and forms panel reaction panel may not represent all question-and-answer format; of the group. following presentation) views of the group. reaction panel can speak. Film Reinforces content, adds Passive methods for an audience; These methods are not entertainment; video allows lights possibility of equipment problems. Prepared Videotape appropriate early in a session; to remain on; flexible start and stop never use to start a session; Slides for discussion. always introduce & de-brief a Educational T.V. film, etc.; say, “Look for___, ___, & __”; leader should set up and test equipment before
Instructional Methods 1 of 5 August 2004 POSSIBLE METHOD ADVANTAGES COMMENTS DISADVANTAGES session; have adapter plug and extra bulbs.
Trainer divides large group Keeps participants interested and Learning points can be confusing or into small groups; groups of involved. lost. 4–6 are most effective. Resources can be discovered and A few participants may dominate Small group has a short time Group Discussion (of given topic) shared. the discussion. to discuss a topic or solve a Buzz Groups (short, time-limited Learning can be observed. problem Time control is more difficult. discussion on given subject) Participants are active; allows Trainer should be able to give Inexperienced leader may be chance to hear other points of clear instructions and keep unable to use format for attitudinal view; quieter people can express discussion on target. Main purposes. viewpoints and ideas. function is judging when to cut off discussion. For idea generation and creative group thinking; all participants present many Can get all participants involved in The problem/issue must be clearly ideas as rapidly as possible collecting a lot of information. defined. on a problem or issue. Then group organizes list into Quickly generate ideas. Time control is more difficult. categories for further Brainstorming Good for problem-solving; quick Need clear trigger questions and discussion. change of pace; filler; allows all to evaluation/discussion afterwards; Do not evaluate, criticize, participate; validates ideas of somewhat over-used method; omit, or discuss contributions group. requires careful facilitation. until all are written; record in contributor’s own words; use another person to record if possible. Reading (alone or aloud) Saves time (trainees can read Written material is used to Reading with Discussion or Report. faster than trainer can talk). present new information to participants Material can be kept for later use. Can be boring if used too long Insures consistency of information. without interruption. Requires skill to select relevant material; reading skill Engaging, active; provides a Participants read at different paces. by participants. chance for in-depth insight and Difficult to measure if people are different perspectives. learning.
Instructional Methods 2 of 5 August 2004 POSSIBLE METHOD ADVANTAGES COMMENTS DISADVANTAGES May require more reading/writing skills than participants have; leader may have to fill in after reports.
ATTITUDINAL
POSSIBLE METHOD ADVANTAGES COMMENTS DISADVANTAGES Role-play Mini-role-play (See Behavioral Methods.) (See Behavioral Methods.) (See Behavioral Methods.) Playing Self “movie” Thought provoking; good for Doodling Need to relate to relevant making thoughts and opinions Requires participant self-direction. learning goals. Portraits (of self or others) more concrete, warm-up activity. Simulation Games (See Behavioral Methods.) (See Behavioral Methods.) (See Behavioral Methods.) Sustained interaction allows Time consuming; requires great Keep groups small and Task Groups quieter people to express degree of self-direction and group diverse with sustained themselves; validates participants. maturity. interaction and clear purpose. Need to provide direction and Engaging, active; good for warm- Willingness and trust of group Pantomime Skits purpose; relate method to up. necessary. relevant goals.
BEHAVIORAL
POSSIBLE METHOD ADVANTAGES COMMENTS DISADVANTAGES Role-Play Helps retention. Requires preparation time. Participants act out problem- Mini-Role-Play Allows participants to practice new May be difficult to tailor to all solving situations similar to skills in a controlled environment. situations. those they will encounter in their workplace. Participants are actively involved. Needs sufficient class time for exercise completion and feedback Trainer needs skill and Observers can impact attitude and understanding—must get behavior. Requires maturity and willingness of people into roles, give groups; requires trainer have directions, establish a climate
Instructional Methods 3 of 5 August 2004 POSSIBLE METHOD ADVANTAGES COMMENTS DISADVANTAGES of trust. Trainer needs insight into how an activity may pose a threat to some individuals; ability to help group process & excellent facilitation skills. de-brief. Use in well-formed group. Can be structured into dyad, triad, and fishbowl.
“Movie” (role-play assisted by Useful in rehearsing new skills, (Same as for role-play, intensive feedback, “more__, or less __”) behaviors. and time consuming.) Intense involvement; practice skills Competitive; requires a game and A package game requires Simulation games in problem solving and decision- possibly a consultant to help prep time for the leader to making; competitive. facilitate; time consuming. learn the rules and directions. Very concrete learning tool; Criteria must be clear; feedback Trainer should establish Tape recording with playback participant involved in judging own and assessment based on specific purpose and performance Videotape recording with playback performance. behaviors; requires equipment. criteria clearly. Participants are given Requires active participant information about a situation Information must be precise and involvement. and directed to come to a Case study kept up-to-date. decision or solve a problem Can simulate performance Needs sufficient class time for concerning the situation. Mini-case study (problem situations required after training. for small groups to analyze) participants to complete the case. Trainer needs to have Learning can be observed. Critical incident (small section of Participants can become too knowledge and skills to case stating most critical or dramatic Opportunity to apply new interested in the case content. “solve” the problem; may need knowledge; requires judgment; to design own studies; moment) Case study must be relevant to good assessment tool; participants compare approaches of learner’s needs and daily concerns. active; chance to practice skills. several groups and reinforce best solutions. Helps participant clarify and Leader needs knowledge of “In-basket” (form of case study— crystallize thoughts, opinions, Requires writing skills; must be participant’s daily “Letters, memos” etc. given to values; opportunity to apply relevant to participant. concerns/needs; ability to participant for response) knowledge to “real” situation. critique responses. Demonstration Aids comprehension and retention. Must be accurate and relevant to Participants are shown the Demonstration with practice (by Stimulates participants' interest. participants. correct steps for completing a task or are shown an example participants) Can give participants model to Written examples can require lengthy preparation time. of a correctly completed task. follow. Requires skill to model Trainer demonstrations may be
Instructional Methods 4 of 5 August 2004 POSSIBLE METHOD ADVANTAGES COMMENTS DISADVANTAGES difficult for all participants to see Allows for optional modeling of well. desired behavior; break desired behavior/skill; can be Method more effective if procedure down into simple active; good for learning simple participants are active; feedback steps; ability to provide skills. must follow immediately after feedback. practice. Different points of view and feed- Group should have enough Skills practice lab (small participant back; participant active; good for knowledge or insight to coach one Act as a resource to groups. groups practice together). translating information into skills. another.
PLANNING
POSSIBLE METHOD ADVANTAGES COMMENTS DISADVANTAGES Validates maturity and needs of Group discussion with decision- group members; members have making regarding a new action best insight into their problems and Requires mature group that can Leader serves as resource needs on-the-job; group leaves self-direct and stay on task; time Individual or group planning once directions are given. session with practical, constructive consuming. session with report and mutual goals; groups get ideas from one another.
Instructional Methods 5 of 5 August 2004