Unit 3 Chemical Compound Problems - Key
Complete each question on your own paper.
1. Write the symbol for each element and identify each as a metal (M) or non- metal (N).
a. barium Ba, M c. phosphorus P, N e. copper Cu, M g. potassium K, M i. sodium Na, M b. lead Pb, M d. chlorine Cl, N f. arsenic As, N h. gold Au, M j. tin Sn, M
2. What are valence electrons? Outer shell electrons that may participate in chemical activity
3. Write the symbol, number of valence electrons, and charge of each element.
a. Magnesium Mg, s2, +2 cation c. phosphorus P, s2p3, -3 anion e. oxygen O, s2p4, -2 anion g. potassium K, s1, +1, cation i. sodium Na, s1, +1, cation b. selenium Se s2p4, -2 anion d. chlorine Cl, s2p5, -1 anion f. sulfur S, s2p4, -2 anion h. silicon Si, s2p2, +/-4 j. neon Ne, s2p6, 0
4. Identify each of the elements in Number 3 as a cation or an anion. See above
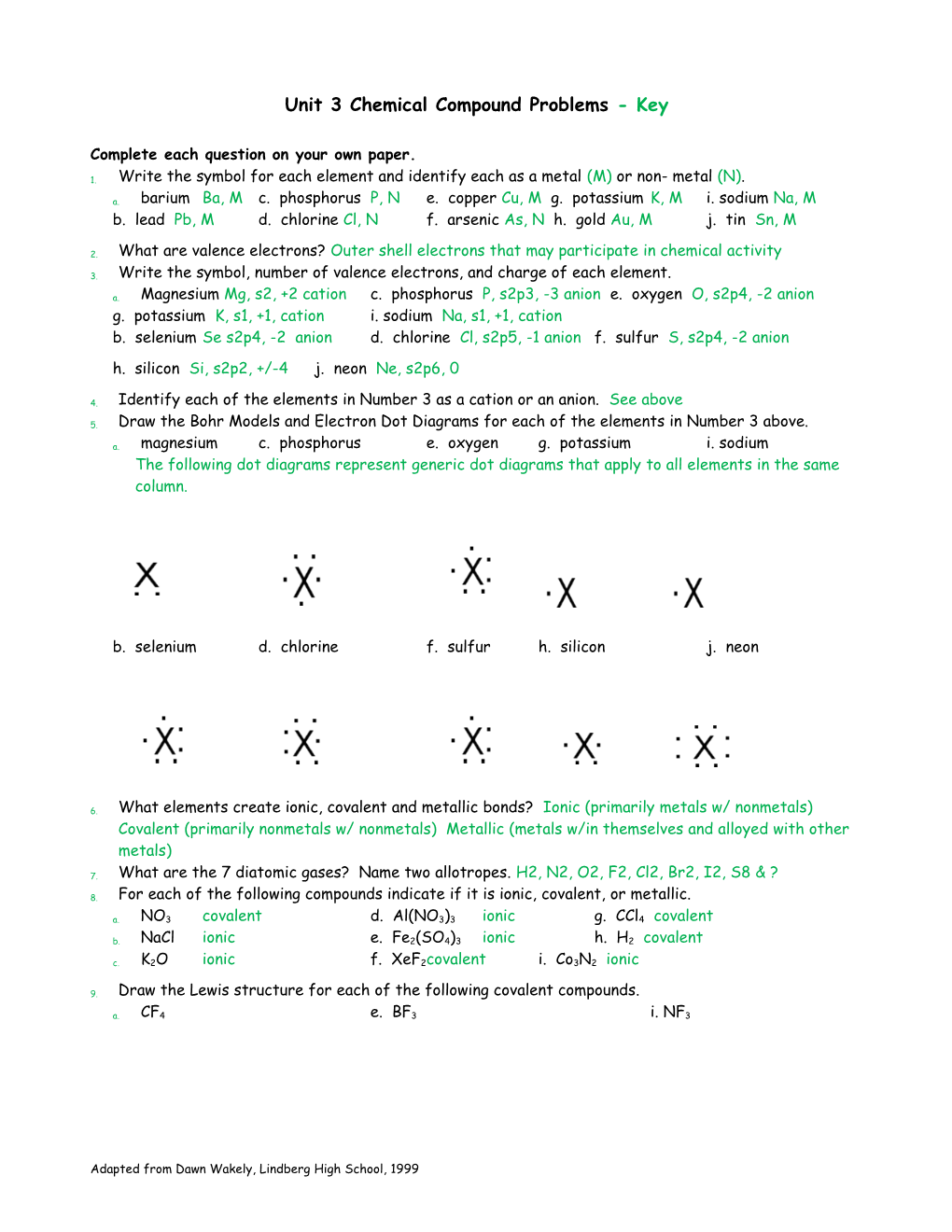
5. Draw the Bohr Models and Electron Dot Diagrams for each of the elements in Number 3 above.
a. magnesium c. phosphorus e. oxygen g. potassium i. sodium The following dot diagrams represent generic dot diagrams that apply to all elements in the same column.
b. selenium d. chlorine f. sulfur h. silicon j. neon
6. What elements create ionic, covalent and metallic bonds? Ionic (primarily metals w/ nonmetals) Covalent (primarily nonmetals w/ nonmetals) Metallic (metals w/in themselves and alloyed with other metals)
7. What are the 7 diatomic gases? Name two allotropes. H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2, S8 & ?
8. For each of the following compounds indicate if it is ionic, covalent, or metallic.
a. NO3 covalent d. Al(NO3)3 ionic g. CCl4 covalent
b. NaCl ionic e. Fe2(SO4)3 ionic h. H2 covalent
c. K2O ionic f. XeF2covalent i. Co3N2 ionic
9. Draw the Lewis structure for each of the following covalent compounds.
a. CF4 e. BF3 i. NF3
Adapted from Dawn Wakely, Lindberg High School, 1999 b. H2CS f. CH2F2 j. O2
c. PF3 g. H2S k. N2
2- - d. F2 h. carbonate ion (CO3 ) l. nitrate ion (NO3 )
10. Draw the Lewis Structure for each organic compound.
a. CH4 f. CH3OH l. CH2O q. HCOOH
a. C2H6 g. C2H5OH m. CH3CHO r. CH3COOH
b. C3H8 h. C3 H7OH n. C2H5CHO s. C2H5COOH
c. C4H10 i. C2H4 o. HCN
d. C5H12 j. C2H2 p. C2H4NH2
11. Write formulas for the following covalent compounds.
a. Chlorine dioxide e. selenium difluoride i. disulfur trioxide
ClO2 SeF2 S2O3
b. Iodine tribromide f. triphosphorus tetrabromide j. tetrasulfur hexabromide
IBr3 P3Br4 S4Br6
c. Sulfur dioxide g. dichorine monoxide k. xenon hexafluoride
SO2 Cl2O XeF6
d. Dinitrogen pentoxide h. dinitrogen triiodide l. carbon tetrachloride
N2O5 N2I3 CCl4
12. Write names for the following covalent compounds.
Adapted from Dawn Wakely, Lindberg High School, 1999 a. SiC d. OF2 g. N2O5 j. PCl3 Silicon monocarbide, oxygen difluoride, dinitrogen pentoxide, phosphorus trichloride
b. CS2 e. SO2 h. NO k. CI4 Carbon disulfide, sulfur dioxide nitrogen monoxide carbon tetra-iodide
c. NO2 f. SO3 i. P4O10 l. S2Cl6 Nitrogen dioxide sulfur trioxide tetraphosphorus deca-oxide, disulfur hexachloride
13. Write formulas for the following ionic compounds.
a. Sodium fluoride NaF e. cesium chloride CsCl2 i. Gallium sulfide Ga2S3
b. Aluminum nitride AlN f. barium bromide BaBr2 j. potassium iodide KI
c. Aluminum bromide AlBr3 g. cesium sulfide Cs2S k. strontium nitride Sr3N2
d. Magnesium sulfide MgS h. potassium oxide K2O l. aluminum iodide AlI3
14. Write formulas for the following ionic compounds.
a. scandium oxide Sc2O3 e. manganese V sulfide Mn2S5 i. iron III phosphide FeP
b. nickel II nitride Ni3N2 f. silver chloride AgCl j. mercury I nitride (Hg2)3N2
c. zinc II chloride ZnCl2 g. gold bromide AuBr3 K. mercury II nitride Hg3N2
d. nickel IV oxide NiO2 h. iron II phosphide Fe3P2 l. copper II iodide CuI2
15. Write formulas for the following ionic compounds.
a. silver nitrate AgNO3 e. iron II sulfite FeSO3 i. ammonium acetate NH4C2H3O2
b. silver nitride Ag3N f. iron II sulfide FeS k. ammonium sulfate (NH4)2SO4
c. magnesium nitrite Mg(NO2)2 g. aluminum oxide Al2O3 l. zinc II carbonate ZnCO3
d. iron II sulfate FeSO4 h. aluminum oxalate Al2(C2O4)3 m. cesium phosphate Cs3PO4
16. What is the charge on the metal of the following:
a. Al2O3 +3 d. Cu(NO3)2 +2 g. Fe(C2H3O2)2 +2 j. KC2H3O2 +1
b. ZnCO3 +2 e. Ca(OH)2 +2 h. Na2SO4 +1 k. CoC2O4 +2
c. Au(NO3)3 +3 f. Al2(SO4)3 +3 i. Sn(NO2)2 +2 l. Ag3PO4 +1
17. Name each of the following ionic compounds (Remember to place the roman numeral on transition metals.).
a. Al2O3 d. Cu(NO3)2 g. Fe(C2H3O2)2 j. KC2H3O2 Aluminum oxide copper(II) nitrate iron(II) acetate potassium acetate
b. ZnCO3 e. Ca(OH)2 h. Na2SO4 k. CoC2O4 Zinc carbonate calcium hydroxice sodium sulfate cobalt(II) oxalate
c. Au(NO3)3 f. Al2(SO4)3 i. Sn(NO2)2 l. Ag3PO4 Gold nitrate aluminum sulfate tin(II) nitrite silver phosphate
18. Identify each of the following formulas as ionic or covalent. Write the name for each.
a. MgO ionic d. NaI ionic g. N2O5 covalent j. Al2O3 ionic Magnesium oxide sodium iodide dinitrogen pentoxide aluminum oxide
b. CO covalent e. CaBr2 ionic h. S2Cl3 covalent k. PCl3 covalent Carbon monoxide calcium bromide disulfur trichloride phosphorus trichloride
c. NO2 covalent f. SO3 covalent i. Rb2O ionic l. Ga2S3 ionic Nitrogen dioxide sulfur trioxide rubidium oxide gallium sulfide
Adapted from Dawn Wakely, Lindberg High School, 1999 19. Write the name or formula for the following (both ionic and covalent compounds).
a. Aluminum chloride h. dinitrogen pentoxide o. MnO2
AlCl3 N2O5 manganese(IV) oxide
b. Cobalt II chloride i. Cobalt p. cobalt III fluoride
CoCl2 Co CoF3
c. Al2S3 j. N2O3 q. CCl4 Aluminum sulfide dinitrogen trioxide carbon tetrachloride
d. HgO k. iron II chlorate r. aluminum nitrate
Mercury(II) oxide Fe(ClO3)2 Al(NO3)3
e. CS2 l. Cr2O3 s. Ni3P2 Carbon disulfide chromium(III) oxide nickel(II) phosphide -3 f. CO m. CO3 t. NO2 Carbon monoxide carbonate ion nitrogen dioxide
-2 g. Oxygen gas n. SO3 u. PO5
O2 sulfite phosphorus pentoxide
20. Write the formula or name of the following (both ionic and covalent compounds).
a. C2O4 f. Sn(NO3)2 k. dinitrogen tetroxide
Dicarbon tetroxide tin(II) nitrate N2O4
b. Copper II chloride g. K2Cr2O7 l. potassium oxalate
CuCl2 potassium dichromate K2C2O4
c. Al(NO3)3 h. Ni2C2O4 s. Hg(NO3)2 Aluminum nitrate nickel(I) oxalate mercury(II) nitrate
d. CuCO3 i. Aluminum fluoride n. XeCl4
Copper(II) carbonate AlF3 xenon tetrachloride
e. H2CO3 j. vanadium IV carbonate o. Bi(NO3)2
Carbonic acid V(CO3)2 bismuth(II) nitrate
21. What is the difference between a(n) atom, molecule, element, compound, and a mixture? Give an example of each.
22. Give an example of the following:
a. A radical d. a nonmetal atom g. a metal atom j. a metal ion
b. A negative radical e. a compound h. an anion k. diatomic gas
c. A metal ion f. a transition metal i. A positive radical m. a mixture
23. Explain clearly the difference between Co and CO. Co is cobalt a single element. There is only one capital letter. The small o goes with the big C. CO is 2 capital letters and therefore 2 different elements. C is for carbon & O is for oxygen.
Adapted from Dawn Wakely, Lindberg High School, 1999