Brain Gym Course: Self-Funded “Brain Gym Journal” Claim Gains in Cogni�On
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

The Voice of Parents Who Have Used Rhythmic Movement Training with Their Child
The voice of parents who have used Rhythmic Movement Training with their child A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the Degree of Master of Education University of Canterbury College of Education, Health and Human Development Tessa M Grigg 2016 Table of Contents TABLE OF CONTENTS ................................................................................................................ I ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ........................................................................................................... V ABSTRACT ................................................................................................................................ VI CHAPTER 1. WHY RESEARCH RETAINED PRIMITIVE REFLEXES? ....................................... 1 1.1. AN INTRODUCTION ......................................................................................................................... 1 1.1.1. Aim of the project ................................................................................................................ 1 1.1.2. Research questions .............................................................................................................. 2 1.1.3. Researcher interest in the topic and pre-study understandings ....................................... 2 1.2. REFLEXES DEFINED ......................................................................................................................... 4 1.3. INTRODUCTION SUMMARY ............................................................................................................ -

Dyslexia: Quick Fix Or Hard Slog?
Dyslexia: quick fix or hard slog? Allan Marshall Broomfield School Sabbatical Report Allan Marshall sabbatical report 2008 1 Table of contents Executive Summary 3 Purpose 4 Background 5 Methodology 7 Findings New Zealand Government recognition of dyslexia 8 Alternative programmes available to support dyslexic children 12 Dalwood Assessment Centre and Palm Avenue School, Sydney 16 Implications 19 Conclusions 20 References 21 Allan Marshall sabbatical report 2008 2 Executive Summary Despite a great deal of effort by the MOE, schools, teachers and parents, children who are believed to be dyslexic often show little progress in reading. This is frustrating for teachers, parents and students. Lobby groups such as the Dyslexia Foundation of New Zealand (DFNZ) have worked hard to make the Ministry of Education (MOE) recognise dyslexia as a specific learning disability. The MOE acknowledged that there were still many students who were not achieving and in 2007, it announced that dyslexia was to be formally recognized as a specific learning disability. This was a shift from being non categorical. They now intend to provide specific funding for resources such as web sites, and brochures and resources for parents and teachers. The DFNZ believes that, despite the formal recognition of dyslexia as a learning disability, the MOE’s response has been slow and disappointing. If a child is diagnosed as dyslexic, there is very little clear direction about how to help the child overcome their specific reading problems. Frustrated and anxious parents often turn to expensive commercial programmes that offer ‘quick fixes’ and cures. Unfortunately, no quick fixes are available for dyslexia: dyslexia appears to be ‘for life’ and there is no ‘cure’. -

Research Into Dyslexia Provision in Wales Literature Review on the State of Research for Children with Dyslexia
Research into dyslexia provision in Wales Literature review on the state of research for children with dyslexia Research Research document no: 058/2012 Date of issue: 24 August 2012 Research into dyslexia provision in Wales Audience Local authorities and schools. Overview The Welsh Government commissioned a literature review, auditing and benchmarking exercise to respond to the recommendations of the former Enterprise and Learning Committee’s Follow-up report on Support for People with Dyslexia in Wales (2009). This work was conducted by a working group, which comprised of experts in the field of specific learning difficulties (SpLD) in Wales including the Centre for Child Development at Swansea University, the Miles Dyslexia Centre at Bangor University, the Dyscovery Centre at the University of Wales, Newport, the Wrexham NHS Trust and representatives from the National Association of Principal Educational Psychologists (NAPEP) and the Association of Directors of Education in Wales (ADEW). Action None – for information only. required Further Enquiries about this document should be directed to: information Additional Needs Branch Support for Learners Division Department for Education and Skills Welsh Government Cathays Park Cardiff CF10 3NQ Tel: 029 2082 6044 Fax: 029 2080 1044 e-mail: [email protected] Additional This document can be accessed from the Welsh Government’s copies website at http://wales.gov.uk/topics/educationandskills/publications/ researchandevaluation/research/?lang=en Related Current literacy and dyslexia provision in Wales: A report on the documents benchmarking study (2012) Digital ISBN 978 0 7504 7972 1 © Crown copyright 2012 WG16498 Contents ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS 2 I. INTRODUCTION 3 II. CURRENT DEFINITIONS OF DYSLEXIA 4 III. -
Cogmed Working Memory Training
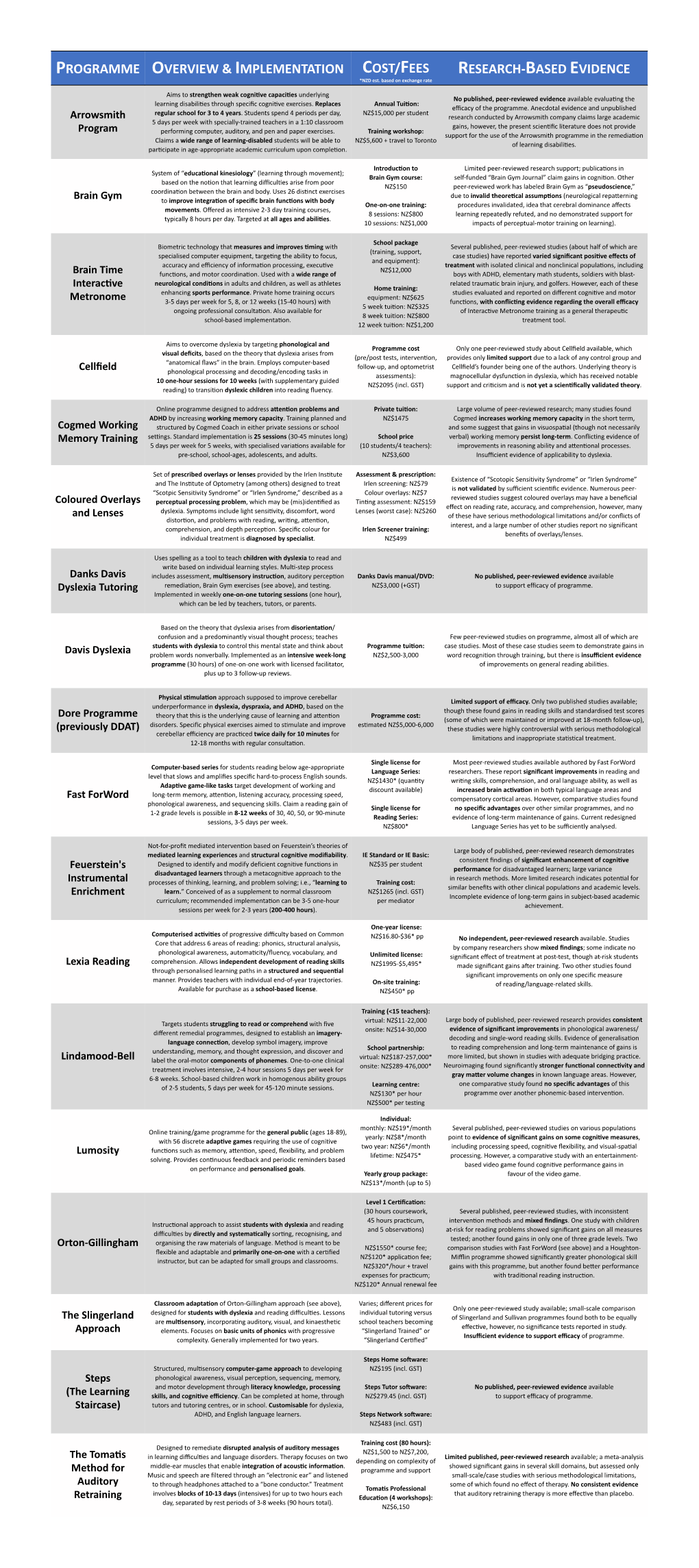
PROGRAMME OVERVIEW & IMPLEMENTATION COST/FEES RESEARCH-BASED EVIDENCE *NZD est. based on exchange rate 9/15 Aims to strengthen weak cogniOve capaciOes underlying No published, peer-reviewed evidence available evalua2ng the learning disabili2es through specific cogni2ve exercises. Replaces Annual TuiOon: efficacy of the programme. Anecdotal evidence and unpublished regular school for 3 to 4 years. Students spend 4 periods per day, NZ$15,000 per student Arrowsmith research conducted by Arrowsmith company claims large academic 5 days per week with specially-trained teachers in a 1:10 classroom gains, however, the present scien2fic literature does not provide Program performing computer, auditory, and pen and paper exercises. Training workshop: support for the use of the Arrowsmith programme in the remedia2on Claims a wide range of learning-disabled students will be able to NZ$5,600 + travel to Toronto of learning disabili2es. par2cipate in age-appropriate academic curriculum upon comple2on. IntroducOon to Limited peer-reviewed research support; publica2ons in System of “educaOonal kinesiology” (learning through movement); Brain Gym course: self-funded “Brain Gym Journal” claim gains in cogni2on. Other based on the no2on that learning difficul2es arise from poor NZ$150 peer-reviewed work has labeled Brain Gym as “pseudoscience,” coordina2on between the brain and body. Uses 26 dis2nct exercises due to invalid theoreOcal assumpOons (neurological repa\erning Brain Gym to improve integraOon of specific brain funcOons with body One-on-one training: procedures invalidated, idea that cerebral dominance affects movements. Offered as intensive 2-3 day training courses, 8 sessions: NZ$800 learning repeatedly refuted, and no demonstrated support for typically 8 hours per day. -

Looking for a Quick Fix? Controversial Therapies in the Treatment of Learning and Attention Deficit Disorders
Looking for a Quick Fix? Controversial Therapies in the Treatment of Language and Learning Disorders Cullowhee Conference – 2016 Jeffrey Black, M.D. Medical Director Luke Waites Center for Dyslexia and Learning Disorders Jeffrey L. Black, M.D. Jeffrey L. Black, M.D. I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or provider of commercial services discussed in this CME activity. I do intend to discuss an unapproved/investigative use of a commercial product/device in my presentation. One of the nation’s leading pediatric centers for the treatment of orthopedic conditions, certain related neurological disorders and learning disorders, such as dyslexia. (214) 559-7815 www.tsrhc.org 1 Jeffrey L. Black, M.D. recognize general characteristics of controversial therapies, describe common unproven therapies, and understand how to advise families. “I have an earache.” 2000 B.C. “Here, eat this root.” 1000 A.D. “That root is heathen, say a prayer.” 1850 A.D. “That prayer is superstition, drink this potion.” 1940 A.D. “That potion is snake oil, swallow this pill.” 1985 A.D. “That pill is ineffective, take this antibiotic.” 2000 A.D. “That antibiotic is artificial, here, take this root.” -- Anonymous Legal requirements for evidence-based educational practice (No Child Left Behind 2002; IDEA Reauthorization 2005). Ineffective treatments may cause harm directly (toxicity, nutrition, interrupt/delay) or indirectly (time, financial burden, guilt, inaccurate attributions). Obligation to provide information about the risks and benefits of treatments. Higher ethical standard than for adult patients because children do not decide on what treatments they receive. -

Learn-Journal-2012.Pdf
LEARN Volume 34, 2012 Learn Cover 2012_Cover 2006.qxd 23/08/2012 15:47 Page 1 Learn Journal 2012_Learn Journal 2006.qxd 23/08/2012 15:50 Page 1 LEARN JOURNAL OF THE IRISH LEARNING SUPPORT ASSOCIATION Learn Journal 2012_Learn Journal 2006.qxd 23/08/2012 15:50 Page 2 Learn Journal 2012_Learn Journal 2006.qxd 23/08/2012 15:50 Page 3 LEARN JOURNAL OF THE IRISH LEARNING SUPPORT ASSOCIATION VOLUME 34, 2012 Learn Journal 2012_Learn Journal 2006.qxd 23/08/2012 15:50 Page 4 LEARN is the Journal of the Irish Learning Support Association. It is published annually. LEARN 2013 Readers are invited to submit papers to be considered for inclusion in the 2013 issue of LEARN. Papers should reach the Editorial Committee, LEARN, ILSA, c/o Drumcondra Education Centre, Drumcondra, Dublin 9, by January 31, 2013. Papers should be relevant to some aspect of Learning Support and should not exceed 3,000 words. For information on electronic submissions please contact the administrator on our website at www.ilsa.ie Executive Committee 2011-2012 Chairperson: Catherine Sweeney, c/o ILSA, Drumcondra Education Centre, Dublin 9. Vice-Chairperson: Catherine Flanagan, Salesian College, Pallaskenry, Co. Limerick. Treasurer: Florence Gavin, c/o ILSA, Drumcondra Education Centre, Dublin 9. Minutes Secretary: Catherine Flanagan, Salesian College, Pallaskenry, Co. Limerick. Editor of ‘LEARN’: Matt Reville, c/o ILSA, Drumcondra Education Centre, Dublin 9. Editor of Newsletter : Catherine Sweeney, c/o ILSA, Drumcondra Education Centre, Dublin 9. Executive Members Margaret Egan, Mary Immaculate College, Limerick. Tony Sweeney, c/o ILSA, Drumcondra Education Centre, Dublin 9. -

A Neurodevelopmental Movement Programme for 4-8 Year Old Hearing Impaired Children in the Rural Qwaqwa Region of South Africa
A neurodevelopmental movement programme for 4-8 year old hearing impaired children in the rural QwaQwa region of South Africa Jó-MARIé VAN DER MERWE BOTHMA 23240865 Thesis submitted for the degree Philosophiae Doctor in Psychology at the POTCHEFSTROOM CAMPUS OF THE NORTH-WEST UNIVERSITY PROMOTOR : Dr. M. Dunn CO-PROMOTOR : Prof. S. Kokot NOVEMBER 2012 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The completion of this study was a culmination of the support, encouragement, love and enthusiasm of many individuals. I would therefore like to express my sincere appreciation and thanks to each of the following: My promotor, Dr. Munita Dunn, for her continued belief in me, encouragement, and support. Her contribution to this study was valuable and respected. Thank you for all your patience. My co-promotor, Professor Shirley Kokot, for her guidance and expertise in the field of neuropsychology and developmental movement programmes. Your passion in this field is contagious. Professor Martin Kidd of the Department of Statistics and Actuarial Sciences at the University of Stellenbosch for his assistance in the data analysis stage of this study. Mrs. Penny Kokot Louw, for the linguistic and technical editing of this study. The children with hearing impairment at the school who enthusiastically participated in the study. You are the ones that this is all about. Mrs. Steyn, for her permission to conduct this study at the school, as well as Mrs. Audrey Vermeulen, Mrs. Karen Kunz and the school staff, for their contribution to the collection of the data. The North West University Financial Support Services, for granting me a postgraduate bursary, which contributed to covering the financial expenses of this study. -

Behavioural Interventions to Remediate Learning Disorders: a Technical Report
Behavioural Interventions to Remediate Learning Disorders: A Technical Report 23 March 2015 George Dawson & Stephanie D'Souza Supervised by: Dr. David Moreau PhD & A/Prof. Karen Waldie PhD Centre for Brain Research and School of Psychology The University of Auckland Auckland, New Zealand Contact: [email protected] Behavioural interventions to remediate learning disorders: A technical report TABLE OF CONTENTS I Introduction ............................................................................................................ 3 II Audited Programmes .............................................................................................. 4 A Arrowsmith Programme ........................................................................................ 4 B Brain Gym ........................................................................................................... 8 C Cellfield ............................................................................................................. 17 D Cogmed Working Memory Training ........................................................................ 21 E Coloured Overlays and Lenses (including those from Irlen and The Institute of Optometry) ............................................................................................................. 30 F Danks Davis Dyslexia Tutoring .............................................................................. 34 G Davis Dyslexia ................................................................................................... -

Research Into Dyslexia Provision in Wales Literature Review on the State of Research for Children with Dyslexia
Research into dyslexia provision in Wales Literature review on the state of research for children with dyslexia PHOTO REDACTED DUE TO THIRD PARTY RIGHTS OR OTHER LEGAL ISSUES Research Research document no: 058/2012 Date of issue: 24 August 2012 Research into dyslexia provision in Wales Audience Local authorities and schools. Overview The Welsh Government commissioned a literature review, auditing and benchmarking exercise to respond to the recommendations of the former Enterprise and Learning Committee’s Follow-up report on Support for People with Dyslexia in Wales (2009). This work was conducted by a working group, which comprised of experts in the field of specific learning difficulties (SpLD) in Wales including the Centre for Child Development at Swansea University, the Miles Dyslexia Centre at Bangor University, the Dyscovery Centre at the University of Wales, Newport, the Wrexham NHS Trust and representatives from the National Association of Principal Educational Psychologists (NAPEP) and the Association of Directors of Education in Wales (ADEW). Action None – for information only. required Further Enquiries about this document should be directed to: information Additional Needs Branch Support for Learners Division Department for Education and Skills Welsh Government Cathays Park Cardiff CF10 3NQ Tel: 029 2082 6044 Fax: 029 2080 1044 e-mail: [email protected] Additional This document can be accessed from the Welsh Government’s copies website at http://wales.gov.uk/topics/educationandskills/publications/ researchandevaluation/research/?lang=en Related Current literacy and dyslexia provision in Wales: A report on the documents benchmarking study (2012) Digital ISBN 978 0 7504 7972 1 © Crown copyright 2012 WG16498 Contents ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS 2 I. -
Chloe CEN Literacy Presentation
IF READING SCIENCE IS SO ADVANCED, WHY DO SO MANY PEOPLE READ SO POORLY? Chloë Marshall 14th March 2014 Mind the gap… Seidenberg (2013) If the science is so advanced how come so many people read so poorly? Poor literacy in the UK • 18% of 15-year-olds do not reach the PISA baseline Level 2 of reading proficiency, – level at which students begin to demonstrate the reading competencies that will enable them to participate effectively and productively in life. Mind the gap… Seidenberg (2013) If the science is so advanced how come so many people read so poorly? Examines three possibilities: (a) properties of English orthography (b) how reading is taught (c) impact of language background. Plan of the talk • Interventions for children with reading difficulties • Identification of children with reading difficulties • Concluding remarks Plan of the talk • Interventions for children with reading difficulties • Identification of children with reading difficulties • Concluding remarks Interventions • Target reading itself: – Reading Recovery • Target a range of cognitive processes that underlie reading: – Phonology – Phonogame – Perception of speech sounds – Fast ForWord – Motor activity – Brain Gym, the Dore Programme – Working memory – Cogmed – Visual attention “Extra-large letter spacing improves reading in dyslexia” Zorzi et al (2012) PNAS • Phonological training: – “Although rather successful, this approach is time consuming and difficult to implement in realistic school settings, and the improvements in these subskills do not automatically improve reading” • A dyslexic child reads in 1 year the same number of words as a good reader in 2 days. • How do we get children reading more? • Manipulate print to make it more accessible Why would this work? Results • Dyslexic children were: – 20% faster – 2x more accurate when reading the altered text. -

Literature Review of Current Approaches to the Provision of Education for Children with Dyslexia
Literature Review of Current Approaches to the Provision of Education for Children with Dyslexia HM Inspectorate of Education Dely L Elliot Julia K Davidson Jon Lewin May 2007 CONTENTS Executive Summary of the key findings v 1 Overview of dyslexia 1 1.1 Introduction and Scope of the Review 1 1.2 Definition of Dyslexia 1 1.3 Background to Dyslexia 2 1.4 Causes 4 1.5 Diagnosis 5 1.6 Interventions 6 1.7 Additional Needs 8 2 Range of approaches used to teach children with Dyslexia 10 2.1 Background 10 2.2 Approaches Used to Teach Dyslexic Learners 10 2.2.1 Additional Support Strategies 11 2.2.2 Development of Phonological Skills 11 2.2.3 Facilitating a Positive Sense of Self 13 2.2.4 Intensive Remedial Instruction 15 2.2.5 Multisensory Teaching System/Approach 16 2.2.6 Partnership Between Parents and Teachers 18 2.2.7 Promotion of Dyslexia Friendly Schools 18 2.2.8 Teaching Based on Learners’ Preferred Learning Style 20 2.2.9 Use of Special Computer Software 22 2.2.10 Use of Suitable Print Size and Background Colour 23 2.2.11 Spelling and Vocabulary Training 23 2.3 Effectiveness of Teaching Approaches and Interventions 25 2.3.1 Case Studies: United Kingdom 25 2.3.2 Case Studies: International 29 3 Implications of the reviewed literature for Scottish Education 33 3.1 Conclusions and Recommendations 33 3.2 Further Recommendations: Examples of best teaching and learning practices with Dyslexic learners 34 Appendix A: A Conceptual Map of the Dyslexia Review 36 Appendix B: Review Method 37 Glossary 40 Bibliography 41 Executive Summary of the Key Findings There is a rich body of research on dyslexia as a product of over one hundred years of research. -

Dyslexia and Adhd - the Miracle Cure Pdf
FREE DYSLEXIA AND ADHD - THE MIRACLE CURE PDF Wynford Dore | 288 pages | 01 May 2013 | John Blake Publishing Ltd | 9781857826883 | English | London, United Kingdom Dyslexia and ADHD: The Miracle Cure by Wynford Dore Si quieres darte de baja, cierra tu cuenta de SlideShare. Publicado el 27 de oct. An evaluation of the Dore programme. Remarkable success is claimed for this exercise-based treatment that is designed to accelerate cerebellar development. Unfortunately, the published studies are seriously flawed. On measures where control data are available, there is no credible evidence of significant gains in literacy associated with this intervention. There are no published studies on efficacy with the clinical groups for whom the programme is advocated. It is important that family practitioners and paediatricians are aware that the claims made for this expensive treatment are misleading. Parece que ya has recortado esta diapositiva en. Inicio Explorar. Puedes cambiar tus preferencias de publicidad en cualquier momento. The Dore Programme: evaluation. Dore programme and fish oil interve Mostrar SlideShares relacionadas al final. Full Name Comment goes here. Are you sure you want to Yes No. They know how to do an amazing essay, research papers or dissertations. Scott Filostin Practical experience is an integral part of any educational process. Sin descargas. Visualizaciones Visualizaciones totales. Acciones Compartido. Insertados 0 No insertados. Dyslexia and ADHD - the Miracle Cure hay notas en la diapositiva. The Dore Programme: evaluation 1. Curing dyslexia and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder by training motor co-ordination: Miracle or myth? Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health, 43, Remarkablesuccess is claimed for an exercise-based treatment that is designed to acceleratecerebellar development.