Gamma-Linolenic Acid (GLA)
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Types of Gene Effects Governing the Inheritance of Oleic and Linoleic Acids in Peanut (Arachis Hypogaea L.)
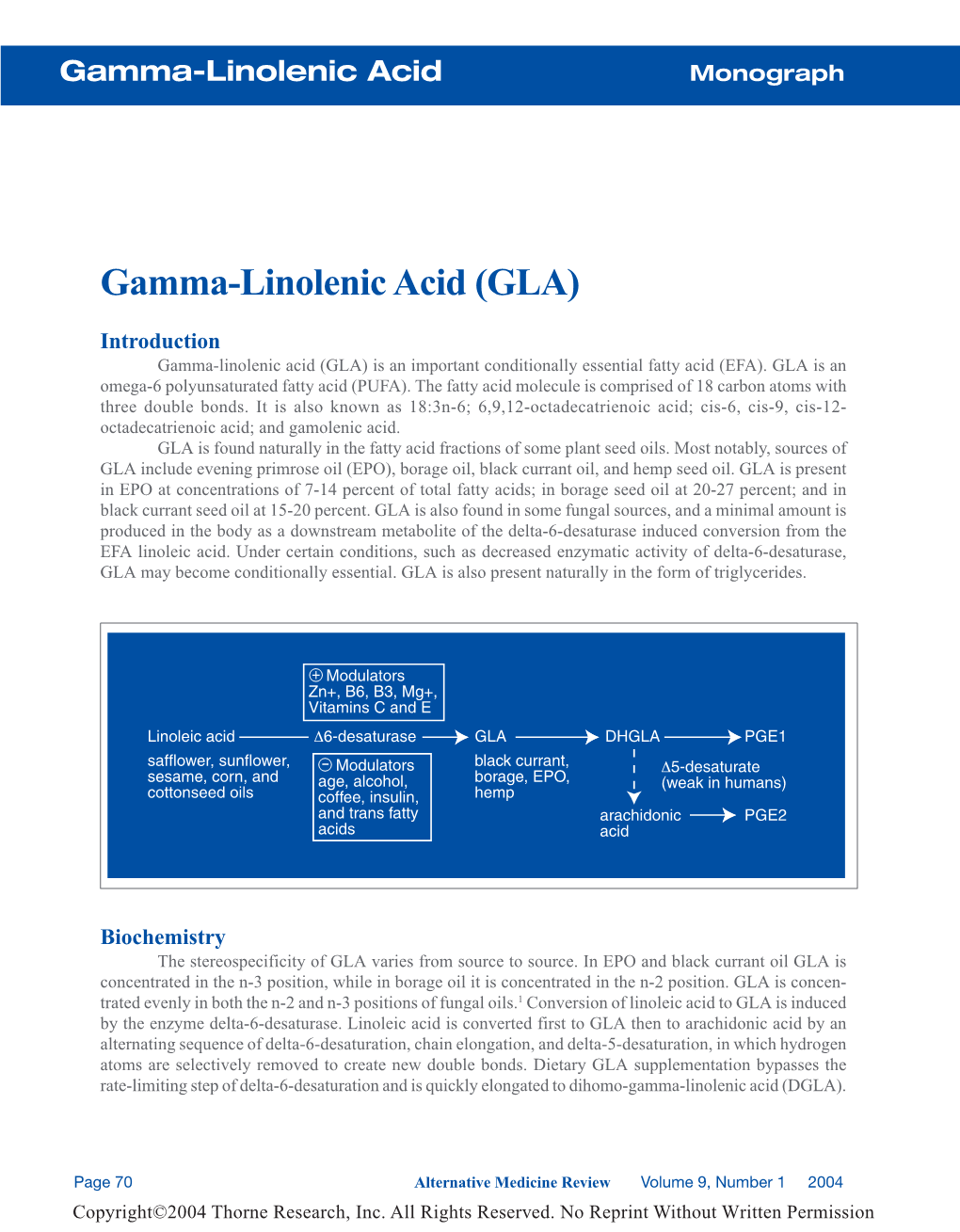
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 11(67), pp. 13147-13152, 21 August, 2012 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/AJB DOI:10.5897/AJB12.1498 ISSN 1684-5315 ©2012 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Types of gene effects governing the inheritance of oleic and linoleic acids in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Nattawut Singkham1, Sanun Jogloy1*, Bhalang Suriharn1, Thawan Kesmala1, Prasan Swatsitang2, Prasit Jaisil1, Naveen Puppala3 and Aran Patanothai1 1Department of Plant Science and Agricultural Resources, Faculty of Agriculture, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, 40002, Thailand. 2Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Science, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, 40002, Thailand. 3Agricultural Science Center at Clovis, New Mexico State University, Clovis, New Mexico, 88101, USA. Accepted 3 August, 2012 Oleic and linoleic acids are major fatty acids in peanut determining the quality and shelf-life of peanut products. A better understanding on the inheritance of these characters is an important for high-oleic breeding programs. The objective of this research was to determine the gene actions for oleic acid, linoleic acid, the ratio of oleic to linoleic acids (O/L ratio) and percentage oil (% oil) in peanut. Georgia- 02C, SunOleic 97R (high-oleic genotypes) and KKU 1 (low-oleic genotypes) were used as parents to generate P1, P2, F2, F3, BC11S and BC12S. The entries were planted in a randomized complete block design with four replications in the rainy season (2008) and the dry season (2008/2009). Gas liquid chromatography (GLC) was used to analyze fatty acid compositions. The data were used in generation means analysis to understand gene effects. The differences in season, generation and generation season interactions were significant for oleic acid in the crosses Georgia-02C KKU 1 and SunOleic 97R KKU 1. -

Use of Gamma-Linolenic Acid and Related Compounds for the Manufacture of a Medicament for the Treatment of Endometriosis
~" ' MM II II II II I II Ml Ml Ml I II I II J European Patent Office ooo Ats*% n i © Publication number: 0 222 483 B1 Office_„. europeen des brevets © EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION © Date of publication of patent specification: 18.03.92 © Int. CI.5: A61 K 31/20, A61 K 31/1 6, A61K 31/23 © Application number: 86307533.9 @ Date of filing: 01.10.86 Use of gamma-linolenic acid and related compounds for the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of endometriosis. © Priority: 02.10.85 GB 8524276 © Proprietor: EFAMOL HOLDINGS PLC Efamol House Woodbridge Meadows @ Date of publication of application: Guildford Surrey GU1 1BA(GB) 20.05.87 Bulletin 87/21 @ Inventor: Horrobin, David Frederick © Publication of the grant of the patent: c/o Efamol Ltd, Efamol House Woodbridge 18.03.92 Bulletin 92/12 Meadows Guildford, Surrey, GU1 1BA(GB) © Designated Contracting States: Inventor: Casper, Robert AT BE CH DE ES FR GB GR IT LI LU NL SE University Hospital 339 Windermere Road London Ontario N6A 5AS(CA) © References cited: EP-A- 0 003 407 EP-A- 0 115 419 © Representative: Miller, Joseph EP-A- 0 132 089 J. MILLER & CO. Lincoln House 296-302 High EP-A- 0 181 689 Holborn London WC1V 7JH(GB) J. GYNECOL. OBSTET. BIOL. REPROD. vol. 10, no. 5, 1981, pages 465-471 Masson, Paris, FR PH. CALLGARIS et al.: "Endometriose de la paroi abdominale" 00 00 CLINICAL OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY, 00 vol. 23, no. 3, Sept. 1980, pages 895-900 J.C. WEED: "Prostaglandins as related to en- CM dometriosis" CM CM Note: Within nine months from the publication of the mention of the grant of the European patent, any person may give notice to the European Patent Office of opposition to the European patent granted. -

Role of Arachidonic Acid and Its Metabolites in the Biological and Clinical Manifestations of Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome
International Journal of Molecular Sciences Review Role of Arachidonic Acid and Its Metabolites in the Biological and Clinical Manifestations of Idiopathic Nephrotic Syndrome Stefano Turolo 1,* , Alberto Edefonti 1 , Alessandra Mazzocchi 2, Marie Louise Syren 2, William Morello 1, Carlo Agostoni 2,3 and Giovanni Montini 1,2 1 Fondazione IRCCS Ca’ Granda-Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Pediatric Nephrology, Dialysis and Transplant Unit, Via della Commenda 9, 20122 Milan, Italy; [email protected] (A.E.); [email protected] (W.M.); [email protected] (G.M.) 2 Department of Clinical Sciences and Community Health, University of Milan, 20122 Milan, Italy; [email protected] (A.M.); [email protected] (M.L.S.); [email protected] (C.A.) 3 Fondazione IRCCS Ca’ Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Pediatric Intermediate Care Unit, 20122 Milan, Italy * Correspondence: [email protected] Abstract: Studies concerning the role of arachidonic acid (AA) and its metabolites in kidney disease are scarce, and this applies in particular to idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS). INS is one of the most frequent glomerular diseases in childhood; it is characterized by T-lymphocyte dysfunction, alterations of pro- and anti-coagulant factor levels, and increased platelet count and aggregation, leading to thrombophilia. AA and its metabolites are involved in several biological processes. Herein, Citation: Turolo, S.; Edefonti, A.; we describe the main fields where they may play a significant role, particularly as it pertains to their Mazzocchi, A.; Syren, M.L.; effects on the kidney and the mechanisms underlying INS. AA and its metabolites influence cell Morello, W.; Agostoni, C.; Montini, G. -

On Fatty Acid Composition and Shelf Life of Broiler Chicken Meat Hilal Ürüşan1* • Canan Bölükbaşı2
Alinteri J. of Agr. Sci. (2020) 35(1): 29-35 http://dergipark.gov.tr/alinterizbd e-ISSN: 2587-2249 http://www.alinteridergisi.com/ [email protected] DOI: 10.28955/alinterizbd.737995 RESEARCH ARTICLE The Influence of Turmeric Powder (Curcuma longa) on Fatty Acid Composition and Shelf Life of Broiler Chicken Meat Hilal Ürüşan1* • Canan Bölükbaşı2 1Atatürk University, Erzurum Vocational High School, Department of Plant and Animal Production, Erzurum/Turkey 2Atatürk University, Faculty of Agriculture, Department of Animal Science, Erzurum/Turkey ARTICLE INFO ABSTRACT Article History: The objective of this study was to determine the appropriate concentration of dietary Received: 21.03.2019 supplementation of turmeric powder, and its effect on thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) Accepted: 03.02.2020 and fatty acid composition in thigh and breast meat of broiler chickens. Three hundred fifty (175 Available Online: 15.05.2020 male and 175 female), one day old Ross-308 broiler chicks were used in this study. A corn-soybean Keywords: meal based diet containing different levels of turmeric powder (0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 g/kg) and a single dose of chlortetracycline (10 mg/kg) was used. The result revealed that dietary supplementation of Broiler 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 g/kg of turmeric powder decreased TBARS in thigh meat at 5th day when compared Turmeric with control. The addition of 4 g/kg turmeric powder to the basal diet increased DHA, SFA and omega- TBARS 3 in breast meat. DHA and SFA were increased by dietary 2 g/kg turmeric powder in thigh meats. Fatty acid composition Under the conditions of this experiment, it was concluded that turmeric powder may positive effects Antioxidant on tissue fatty acid compositions and shelf life of meat (TBARS). -

The Chemical Composition, Botanical Characteristic and Biological Activities of Borago Officinalis: a Review
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by Elsevier - Publisher Connector Asian Pac J Trop Med 2014; 7(Suppl 1):: S22-S28 S22 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine journal homepage:www.elsevier.com/locate/apjtm Document heading doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60199-1 The chemical composition, botanical characteristic and biological activities of Borago officinalis: a review 1 2 1 Majid Asadi-Samani , Mahmoud Bahmani , Mahmoud Rafieian-Kopaei * 1Medical Plants Research Center, Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences, Shahrekord, Iran 2Razi Herbal Medicines Research Center, Lorestan University of Medical Sciences, Khorramabad, Iran ARTICLE INFO ABSTRACT Article history: Borago officinalis Borage ( ) is an annual herb which is cultivated for medicinal and culinary uses, Received 2 Jun 2014 although it is commercially cultivated for borage seed oil. Borage seed oil is the plant rich in the Received in revised form 23 Aug 2014 gamma-linolenic acid (26%-38%) which is used as dietary or food supplement. Other than seed oil Accepted 17 Sep 2014 it contains a lot of fatty acids such as linoleic acid (35%-38%), oleic acid (16%-20%), palmitic acid Available online 26 Sep 2014 (10%-11%), stearic acid (3.5%-4.5%), eicosenoic acid (3.5%-5.5%) and erucic acid (1.5%-3.5%). It is used for the treatment of various diseases such as multiple sclerosis, diabetes, heart diseases, arthritis and eczema. In this study different aspects of borage such as plant characteristics,’ production, applications in traditional medicine, clinical considerations, its effects on patients Keywords: blood and urine biochemistry, and also the effect of the its products on liver and kidney Borage performance tests are presented using published articles in scientific sites. -

Gamma-Linolenic Acid Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
ARTIIRIl'IS & RI1EIJMhl'ISM Vol. 39, Yo. 11. November 1996. pp 1808-1817 1808 0 19Y6, American Collegc of Rhcumatology ____ -. .. ~ - GAMMA-LINOLENIC ACID TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial ROBERT B. ZURIER. RONALD G. ROSSETTI, ERIC W. JACOBSON, DEBORAH M. DEMAKCO. NANCY Y. LIU. JOSEPH E. TEMMING. BERNADETTE M. WHITE, and MICIIAEL LAPOSATA Objective. To assess the clinical efticacy and ad- GLA is available as a component of several plant seed verse effects of y-linolenic acid (GLA),a plant seed oils and is usually taken in far lower doses than were oil-derived unsaturated fatty acid that suppresses in- used in this trial. It is not approved in the United States flammation and joint tissue injury in animal models, in for the treatment of any condition, and should not be the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis (RA). viewed as therapy for any disease. Further controlled Methods. Fifty-six patients with active RA were studies of its use in RA are warranted. randomized to treatment groups in a 6-month, double- blind trial of GLA versus placebo. This was followed by Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA; 18:3 06) is an a 6-month, single-blind trial during which all patients essential fatty acid (Figure 1) found in certain plant seed received GLA. Patients were treated with 2.8 gm/day of oils. It is metabolizcd to dihomo-y-linolcnic acid GLA as the free fatty acid or with sunflower seed oil (DGLA; 20:3 06). the immediate precursor of prosta- (placebo) administered in identical capsules. glandin E, (PGE,), an cicosanoid with known antiin- Resulrs. -

Protective Effect of Borage Seed Oil and Gamma Linolenic Acid on DNA: in Vivo and in Vitro Studies
Protective Effect of Borage Seed Oil and Gamma Linolenic Acid on DNA: In Vivo and In Vitro Studies Inmaculada Tasset-Cuevas1*, Zahira Ferna´ndez-Bedmar2, Marı´a Dolores Lozano-Baena3, Juan Campos- Sa´nchez2, Antonio de Haro-Bailo´ n3, Andre´s Mun˜ oz-Serrano2,A´ ngeles Alonso-Moraga2 1 Departamento de Bioquı´mica y Biologı´a Molecular, Facultad de Medicina, Instituto Maimo´nides de Investigaciones Biome´dicas de Co´rdoba (IMIBIC/Universidad de Co´rdoba), Co´rdoba, Espan˜a, 2 Departamento de Gene´tica, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de Co´rdoba, Co´rdoba, Espan˜a, 3 Instituto de Agricultura Sostenible, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientı´ficas, Co´rdoba, Espan˜a Abstract Borage (Borago officinalis L.) seed oil has been used as a treatment for various degenerative diseases. Many useful properties of this oil are attributed to its high gamma linolenic acid content (GLA, 18:3 v-6). The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the safety and suitability of the use of borage seed oil, along with one of its active components, GLA, with respect to DNA integrity, and to establish possible in vivo toxic and in vitro cytotoxic effects. In order to measure these properties, five types of assays were carried out: toxicity, genotoxicity, antigenotoxicity, cytotoxicity (using the promyelocytic leukaemia HL60 cell line), and life span (in vivo analysis using the Drosophila model). Results showed that i) Borage seed oil is not toxic to D. melanogaster at physiological concentrations below 125 ml/ml and the studies on GLA indicated non-toxicity at the lowest concentration analyzed ii) Borage seed oil and GLA are DNA safe (non-genotoxic) and antimutagenic compared to hydrogen peroxide, thereby confirming its antioxidant capacity; iii) Borage seed oil and GLA exhibited cytotoxic activity in low doses (IC50 of 1 ml/ml and 0.087 mM, respectively) iv) Low doses of borage seed oil (0.19%) increased the health span of D. -

Curcumin Boosts DHA in the Brain: Implications for the Prevention of Anxiety Disorders
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by Elsevier - Publisher Connector Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1852 (2015) 951–961 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Biochimica et Biophysica Acta journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bbadis Curcumin boosts DHA in the brain: Implications for the prevention of anxiety disorders Aiguo Wu a, Emily E. Noble a,EthikaTyagia,ZheYinga, Yumei Zhuang a, Fernando Gomez-Pinilla a,b,⁎ a Department of Integrative Biology and Physiology, University of California at Los Angeles, 621 Charles E. Young Drive Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA b Department of Neurosurgery, UCLA Brain Injury Research Center, David Geffen School of medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA article info abstract Article history: Dietary deficiency of docosahexaenoic acid (C22:6 n-3; DHA) is linked to the neuropathology of several cognitive Received 3 September 2014 disorders, including anxiety. DHA, which is essential for brain development and protection, is primarily obtained Received in revised form 17 November 2014 through the diet or synthesized from dietary precursors, however the conversion efficiency is low. Curcumin Accepted 2 December 2014 (diferuloylmethane), which is a principal component of the spice turmeric, complements the action of DHA in Available online 27 December 2014 the brain, and this study was performed to determine molecular mechanisms involved. We report that curcumin α Keywords: enhances the synthesis of DHA from its precursor, -linolenic acid (C18:3 n-3; ALA) and elevates levels of DHA synthesis enzymes involved in the synthesis of DHA such as FADS2 and elongase 2 in both liver and brain tissues. -

Leveraging CAM to Treat Depression and Anxiety
Amanda E. Olagunju, DO; Leveraging CAM to treat Heidi Gaddey, MD Department of Family Medicine, Langley Hospital, depression and anxiety Langley Air Force Base, VA (Dr. Olagunju); Department of Family Medicine, David Grant Conventional medications and psychotherapy are still Medical Center, Travis Air Force Base, CA (Dr. Gaddey) first-line treatments, but certain complementary and amanda.olagunju@gmail. alternative strategies have value as adjunctive measures. com The authors reported no potential conflict of interest relevant to this article. The views expressed in this article lmost 8% of Americans ages ≥ 12 years have depression are those of the authors and do not PRACTICE necessarily reflect the official policy and 19.1% of Americans ages ≥ 18 years have experienced or position of the US government or any other agency, organization, RECOMMENDATIONS 1,2 an anxiety disorder in the past year. Furthermore, sui- employer, or company. ❯ Consider standardized A cide, which can result from depression and anxiety, is the 10th preparations of St. John’s leading cause of death in the United States, claiming about 40,000 wort for the treatment of 3 mild to moderate depression to 49,000 lives per year since 2012, with increasing yearly rates. in certain patients. A While multiple conventional medication and therapy treatments are available, patients remain interested in complementary and ❯ Encourage patients with alternative medicine (CAM) options. According to the National depression or anxiety to engage in exercise and Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, more than 30% 4 meditation to help with of American adults use CAM treatments. symptom management. A This article provides an overview of the evidence for com- monly used CAM treatments for unipolar depression and anxiety ❯ Consider methylfolate in adults. -

Linoleic Acid: the Code of Life?
Journal of ISSN: 2581-7310 Inno Volume 1: 2 Health Science and Development J Health Sci Dev 2018 Linoleic Acid: The Code of Life? Joseph Eldor1* 1Joseph Eldor, Theoretical Medicine Institute, Jerusalem, Israel Abstract Article Information Intralipid® 20% is made up of 20% Soybean Oil, 1.2% Egg Yolk Article Type: : Research Phospholipids, 2.25% Glycerine, and Water for Injection. The major Article Number: JHSD114 component fatty acids are linoleic acid (44-62%), oleic acid (19-30%), Received Date: 30 August, 2018 palmitic acid (7-14%), a-linolenic acid (4-11%) and stearic acid (1.4- Accepted Date: 26 September, 2018 5.5%). It means that the various effects of Intralipid are based 63% to Published Date: 10 September, 2018 92% on linoleic acid and oleic acid. *Corresponding author: Joseph Eldor, Theoretical Are these 2 fatty acids the Code of Life? Medicine Institute, Jerusalem, Israel, Tel: +972-2-5835528; Email: csen_international(at)csen.com Linoleic acid has effects on the mitochondria. Linoleic acid has effects on Cancer. Linoleic acid has effects on Aging. Citation: Eldor J (2018) Linoleic Acid: The Code of Life?. Keywords Linoleic acid, Oleic acid, Intralipid, Mitochondria, Cancer, J Health Sci Dev Vol: 1, Issu: 2 (18-32). Aging. The Basis of Intralipid Copyright: © 2018 Eldor J. This is an open-access article Intralipid® 20% (A 20% I.V. Fat Emulsion) Pharmacy Bulk Package distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, is a sterile, non-pyrogenic fat emulsion intended as a source of calories distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the and essential fatty acids for use in a pharmacy ad- mixture program. -

Borage Oil Abstracts
Research Borage Oil Abstracts Clinical and experimental study on the long-term effect of dietary gamma-linolenic acid on plasma lipids, platelet aggregation, thromboxane formation, and prostacyclin production Effects of a dietary intake of the polyunsaturated omega-6 essential fatty acids (EFAs) linoleic and gamma-linolenic acids (GLA) on blood lipids, platelet function, and vascular prostacyclin production were studied 12 hyperlipidemic patients (doses of 3 g/day) and 12 male Wistar rats (doses of 3 mg/kg/day) for 4 months. In humans, GLA supplementation decreased plasma triglyceride (TG) levels by 48% (p < 0.001) and increased HDL-cholesterol concentration by 22% (p < 0.01). Total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol levels were significantly decreased by omega-6 EFAs. Platelet aggregation induced by low concentrations of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and epinephrine, and serum thromboxane B2 decreased by 45% both in humans and animals after GLA supplementation. Bleeding time increased 40% (p , 0.01). In rats, vascular prostacyclin production measured by radioimmunoassay of 6-keto-PGF1 alpha was enhanced by GLA intake. These effects of omega- 6 EFAs may contribute to cardiovascular protection and prevention of the atherosclerotic disease. Guivernau M, Meza N, Barja P, Roman O. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 1994 Nov;51(5):311-316. Dietary fatty acid supplementation alters stress reactivity and performance in man Certain dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids, gamma linolenic (18:3n-6) and eicosapentaenoic (20:5n-3) acid, attenuate cardiovascular reactivity to stress in rats. To study their effects on cardiovascular reactivity to acute stress in man, 30 men were randomly assigned to one of three groups and given 28 day supplements of borage oil (containing 18:3n-6), fish oil (containing 20:5n-3), or olive oil (placebo). -

Ibuprofen Alters Epoxide Hydrolase Activity and Epoxy-Oxylipin Metabolites Associated with Different Metabolic Pathways in Murine Livers
Ibuprofen alters epoxide hydrolase activity and epoxy-oxylipin metabolites associated with different metabolic pathways in murine livers Shuchita Tiwari University of California, Davis Jun Yang University of California, Davis Christophe Morisseau University of California, Davis Blythe Durbin-Johnson University of California, Davis Bruce Hammock University of California, Davis Aldrin Gomes ( [email protected] ) University of California, Davis Research Article Keywords: sex difference, ibuprofen, liver, microsomal epoxide hydrolase, oxylipin, soluble epoxide hydrolase Posted Date: November 30th, 2020 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-109297/v1 License: This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Read Full License Version of Record: A version of this preprint was published at Scientic Reports on March 29th, 2021. See the published version at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86284-1. Ibuprofen alters epoxide hydrolase activity and epoxy-oxylipin metabolites associated with different metabolic pathways in murine livers 1 2 2 3 Shuchita Tiwari , Jun Yang , Christophe Morisseau , Blythe Durbin-Johnson , Bruce D. Hammock2 and Aldrin V. Gomes1, 4, * 1Department of Neurobiology, Physiology, and Behavior, University of California, Davis, CA, USA. 2Department of Entomology and Nematology, and Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of California, Davis, CA 95616, USA. 3Department of Public Health Sciences, University of California, Davis, CA, USA. 4Department of Physiology and Membrane Biology,