Analysis of Methanol and Ethanol in Virgin Olive Oil
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
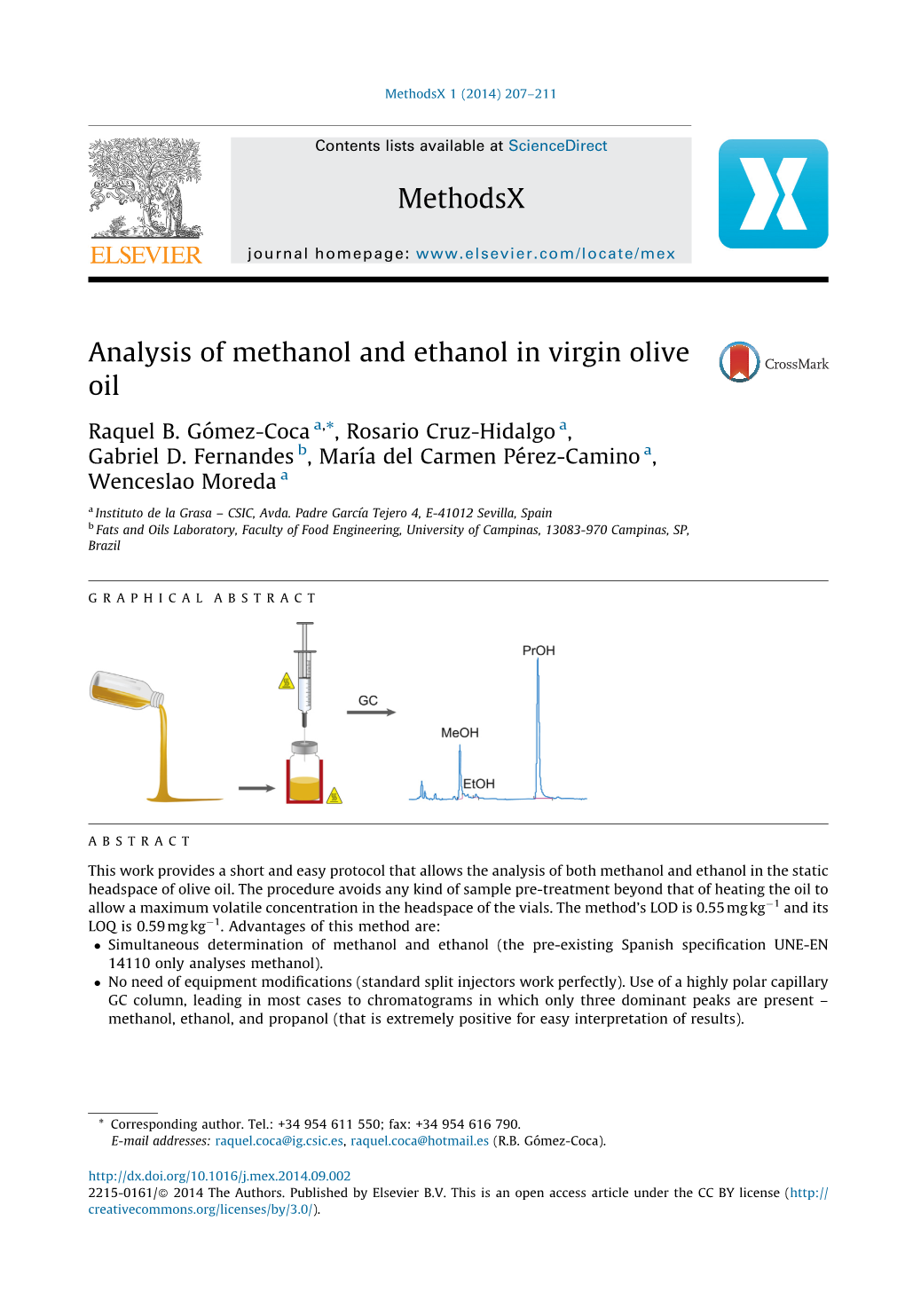
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Cultivated Olive Diversification at Local and Regional Scales
Cultivated Olive Diversification at Local and Regional Scales: Evidence From the Genetic Characterization of French Genetic Resources Bouchaib Khadari, Ahmed El Bakkali, Laïla Khadari, Christine Tollon-Cordet, Christian Pinatel, Guillaume Besnard To cite this version: Bouchaib Khadari, Ahmed El Bakkali, Laïla Khadari, Christine Tollon-Cordet, Christian Pinatel, et al.. Cultivated Olive Diversification at Local and Regional Scales: Evidence From theGe- netic Characterization of French Genetic Resources. Frontiers in Plant Science, Frontiers, 2019, 10, 10.3389/fpls.2019.01593. hal-02620852 HAL Id: hal-02620852 https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-02620852 Submitted on 26 May 2020 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci- destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents entific research documents, whether they are pub- scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, lished or not. The documents may come from émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de teaching and research institutions in France or recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires abroad, or from public or private research centers. publics ou privés. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution| 4.0 International License ORIGINAL RESEARCH published: 24 December 2019 doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01593 Cultivated Olive Diversification at Local and Regional Scales: Evidence From the Genetic Characterization of French Genetic Resources Bouchaib Khadari 1,2*, Ahmed El Bakkali 3, Laila Essalouh -

Olive Oil: Chemistry and Technology, Second Edition
Analysis and Authentication Franca Angerosa*, Christine Campestre**, Lucia Giansante* * CRA-Istituto Sperimentale per la Elaiotecnica, Viale Petruzzi, 65013 Città Sant’Angelo (PE) – ITALY, ** Dipartimento di Scienze del Farmaco, Università degli Studi G. D’Annunzio, Via dei Vestini, 31, 66100 Chieti - ITALY Introduction Olive oil, differently from most vegetable oils, is obtained by means of some technological operations which have the purpose to liberate the oil droplets from the cells of olive flesh. Due to its mechanical extraction, it is a natural juice and preserves its unique composition and its delicate aroma, and therefore can be consumed with- out further treatments. However, a refining process is necessary for making edible lampante virgin olive oils. Lampante oils cannot be directly consumed because of the presence of organoleptic defects or because chemical-physical constants exceeding the limits established by International Organizations. Consumers are becoming continuously more aware of potential health and thera- peutic benefits of virgin olive oils and their choice is oils of high quality which pre- serve unchanged the aromatic compounds and the natural elements that give the typical taste and flavor. Because of the steady increasing demand and its high cost of production virgin olive oil demands a higher price than other vegetable oils. Therefore, there is a great temptation to mix it with less expensive vegetable oils and olive residue oils. On the other hand even refined olive oils, due to high mono-unsaturated fatty acids content and other properties, often have prices higher than those of olive residue oil or seed oils. Thus, there are attempts to partially or totally substitute both virgin and refined olive oils with pomace oil, seed oils, or synthetic products prepared from olive oil fatty acids recovered as by-products in the refining process. -

Extra Virgin Olive Oils
Extra Virgin Olive Oils: French A L’Olivier Founded by a chemist in 1822, A L’Olivier is France’s most esteemed producer of specialty oils and vinegars. The picturesque Parisian shop still sells beautifully presented products in glass bottles, rustic stoneware crocks, and colorful tins. Olive Oil- A L’Olivier extra virgin olive oils are fragrant and fruity, with sweet, mild olive flavor. A L'Olivier Black and Fruity Extra Virgin Olive Oil Tin 250 ml 6 / case A L'Olivier Extra Virgin Olive Oil 250 ml 6 / case 500 ml 6 / case 1 L 6 / case A L'Olivier Extra Virgin Olive Oil Mini Drum 750 ml 6 / case A L’Olivier Extra Virgin Olive Oil Spray 200 ml 6 / case A L'Olivier Extra Virgin Olive Oil White Stoneware Crock 500 ml 6 / case Arnaud Arnaud Extra Virgin Olive Oil Salonenque, Blanquette, Verdale, Picholine, and Grossane olives 500 ml 12 / case Castelines From their orchards near Les Beaux, Jean Benoit and Catherine Hugues hand-pick a variety of olives just before they begin to blacken. These young olives are used to produce an olive oil that is light and delicate, with aromas of fresh grass and flavors of artichokes and almonds. Castelines also produces Late Harvest Fruite Noir olive oil, using only perfectly ripened native olives. The black olives are stored and lightly fermented to create a pleasantly sweet oil, with hints of truffle. Castelines Extra Virgin Olive Oil Salonenque, Aglandau, Grossane and Verdale olives 500 ml 6 / case 750 ml 6 / case Castelines Late Harvest Olive Oil (Fruite Noir) Salonenque, Aglandau, Grossane and Verdale olives 500 ml 6 / case Le Château d’Estoublon Le Château d’Estoublon Single Varietal Extra Virgin Olive Oil: Picholine 100% Picholine olives 500 ml 6 / case Le Château d’Estoublon Extra Virgin Olive Oil AOP: Vallée des Baux de Provence Béruguette, Bouteillan, Grossane, Salonenque and Picholine olives 500 ml 6 / case . -

Press Release
1 INDIAN OLIVE ASSOCIATION PHD House, 4/2, Siri Institutional Area, August Kranti Marg, New Delhi 110016 Phone: 2686380104 (4 lines), Fax: 911126855450, Email: [email protected] PRESS RELEASE Generous Micro Nutrients Discovered in Olive Pomace Oil New Delhi, August 2013: Blasting myths and contradicting assertions of food writers and nutritionists, a pioneering laboratory study in Italy recently discovered that the humble olive pomace oil actually contains generous quantities of antioxidants in the form of tocopherols (vitamin E). Tests in one sample of refined olive pomace oil found vitamin E present at the astounding level of 370 mg / kg. To understand the enormity of this discovery in context, Safflower (Kardi) Oil’s vitamin E content is 310 mg/kg, Palm Oil 145 mg/kg, Groundnut Oil 143 mg/kg, Corn Oil 130 mg/kg, Soyabean 84 mg/kg, Vanaspati 74 mg/kg. Virgin olive oil, being the first press and thus raw juice of the fruit contains a host of antioxidants in generous quantities including vitamins A, D, E and K. It was earlier presumed that olive pomace oil did not contain antioxidants as these were lost in the solvent extraction process. Olive pomace oil is procured through solvent extraction of the residue after the first press of olives which produces virgin olive oil. This solvent extracted product is then refined to become refined olive pomace oil. Food critics and nutritionists have long professed olive pomace oil to have no micro-nutrients. While they acknowledged that olive pomace oil, like virgin olive oil, was high in “good” monounsaturated fat, they held that olive pomace oil was devoid of nutrients. -

12.2% 130000 155M Top 1% 154 5300
We are IntechOpen, the world’s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 5,300 130,000 155M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 154 TOP 1% 12.2% Countries delivered to most cited scientists Contributors from top 500 universities Selection of our books indexed in the Book Citation Index in Web of Science™ Core Collection (BKCI) Interested in publishing with us? Contact [email protected] Numbers displayed above are based on latest data collected. For more information visit www.intechopen.com Chapter 12 From the Olive Flower to the Drupe: Flower Types, Pollination, Self and Inter-Compatibility and Fruit Set Catherine Breton and André Bervillé Additional information is available at the end of the chapter http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/55312 1. Introduction 1.1. Frame of the chapter Although the tree development directs the olive tree yield we focus here to describe the main phases, stages and key steps from blossoming to harvest. The olive tree produces much more flowers than all other trees, however, fruit set and final harvest are limited by several parameters. Most articles in literature deal with the physiological aspects of the transformation of the olive flower into the drupe. Little attention has been given to genetic involvements that underlay the physiology and the biochemistry. A comprehensive survey of the literature as much as we can is given with genetic commentaries based upon recent genetic progresses made in the field. The olive tree derived from the oleaster and the oleaster belongs to an intertropical (Asian, African) genus and a major difference between northern species (Fraxinus, Syringa, Ligus‐ trum) is the bare axillary buds at the basis of leaves. -

Evaluation of Extra-Virgin Olive Oils Shelf Life Using an Electronic Tongue
CORE Metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk Provided by Universidade do Minho: RepositoriUM Eur Food Res Technol (2017) 243:597–607 DOI 10.1007/s00217-016-2773-2 ORIGINAL PAPER Evaluation of extra‑virgin olive oils shelf life using an electronic tongue—chemometric approach Nuno Rodrigues1,2 · Luís G. Dias3,4 · Ana C. A. Veloso5,6 · José A. Pereira7 · António M. Peres8 Received: 3 March 2016 / Accepted: 8 August 2016 / Published online: 6 September 2016 © Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2016 Abstract Physicochemical quality parameters, olfactory gustatory sensorial parameters. Linear discriminant mod- and gustatory–retronasal positive sensations of extra-vir- els, based on subsets of 5–8 electronic tongue sensor sig- gin olive oils vary during storage leading to a decrease in nals, selected by the meta-heuristic simulated annealing the overall quality. Olive oil quality decline may prevent variable selection algorithm, allowed the correct classifica- the compliance of olive oil quality with labeling and sig- tion of olive oils according to the light exposition condi- nificantly reduce shelf life, resulting in important economic tions and/or storage time (sensitivities and specificities for losses and negatively condition the consumer confidence. leave-one-out cross-validation: 82–96 %). The predictive The feasibility of applying an electronic tongue to assess performance of the E-tongue approach was further evalu- olive oils’ usual commercial light storage conditions and ated using an external independent dataset selected using storage time was evaluated and compared with the discrim- the Kennard–Stone algorithm and, in general, better clas- ination potential of physicochemical or positive olfactory/ sification rates (sensitivities and specificities for exter- nal dataset: 67–100 %) were obtained compared to those achieved using physicochemical or sensorial data. -

Total and Sustainable Valorisation of Olive Pomace Using a Fractionation Approach
applied sciences Article Total and Sustainable Valorisation of Olive Pomace Using a Fractionation Approach Tânia B. Ribeiro 1,2 , Ana L. Oliveira 1, Cristina Costa 2, João Nunes 1, António A. Vicente 3 and Manuela Pintado 1,* 1 CBQF-Centro de Biotecnologia e Química Fina–Laboratório Associado, Escola Superior de Biotecnologia, Universidade Católica Portuguesa, Rua Diogo Botelho 1327, 4169-005 Porto, Portugal; [email protected] or [email protected] (T.B.R.); [email protected] (A.L.O.); [email protected] (J.N.) 2 Centre Bio R&D Unit, Association BLC3-Technology and Innovation Campus, Rua Nossa Senhora da Conceição, 2, Lagares, 3405-155 Oliveira do Hospital, Portugal; [email protected] 3 Centro de Engenharia Biológica, Universidade do Minho, Campus Gualtar, 4710-057 Braga, Portugal; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +351-22-55-800-44 Received: 14 August 2020; Accepted: 23 September 2020; Published: 28 September 2020 Abstract: Olive pomace management represents a great concern to the olive oil industry. This work focused on the development of a “zero waste” strategy for olive pomace based on a fractionation approach resulting in the obtention of different value-added fractions. The physicochemical composition of edible fractions obtained (liquid and pulp) was analysed. The potential use as a solid biofuel of the non-edible fraction (stones) was evaluated. High amounts of hydroxytyrosol (513.61–625.76 mg/100 g dry weight) were present in the liquid fraction. Pulp fraction was demonstrated to be a good source of fibre (53–59% dry weight) with considerable antioxidant activity both from free and bound phenolics. -

Additive, Synergistic, and Antagonistic Effects
molecules Article Influence of Olive Pomace Blending on Antioxidant Activity: Additive, Synergistic, and Antagonistic Effects M. Antónia Nunes , Filip Reszczy ´nski,Ricardo N. M. J. Páscoa , Anabela S. G. Costa, Rita C. Alves * and Maria Beatriz P. P. Oliveira REQUIMTE/LAQV, Department of Chemical Sciences, Faculty of Pharmacy of University of Porto, R. Jorge Viterbo Ferreira n◦. 228, 4050-313 Porto, Portugal; [email protected] (M.A.N.); [email protected] (F.R.); [email protected] (R.N.M.J.P.); [email protected] (A.S.G.C.); [email protected] (M.B.P.P.O.) * Correspondence: [email protected] Abstract: Food innovation is moving rapidly and comprises new categories of food products and/or ingredients with a natural and ecological origin. Monocultivar olive pomaces, individually or combined, can be a source of natural bioactive compounds suitable for food or cosmetic applications. This work aimed to assess the phenolics content and antioxidant activity of four monocultivar olive pomaces (Arbosana, Koroneiki, Oliana, and Arbequina) and forty-nine blends prepared with different proportions of each. Additive, synergistic, and antagonistic effects were studied. Among the monocultivar pomaces, Koroneiki and Arbosana were the richest in total phenolics (~15 mg gallic acid eq./g). Most of the interactions found in the blends were additive or synergistic, while very few antagonistic effects were observed. The best results were obtained for those blends where the Koroneiki variety predominated: (i) 90% Koroneiki, 4.75% Oliana, 3.75% Arbequina, 1.5% Arbosana; (ii) 65% Koroneiki, 29% Oliana, 3.25% Arbequina, 2.75% Arbosana; and (iii) 85% Koroneiki, 8.75% Citation: Nunes, M.A.; Reszczy´nski, Arbequina, 3.5% Arbosana, 2.75% Oliana. -

Olive Oil Production in the Var Region of France, May, 1995
Olive Oil Production in the Var Region of France, May, 1995 In the south of France there are approximately 60 oil mills and cooperatives processing and retailing local olive oil today. They have a long history and tell the story of when olives were the dominant agricultural crop of the area. The Var region is at the center of what was once a thriving olive oil empire producing thousands of tons of olive oil each year. A devastating freeze in 1956 killed all of the olive trees down to the ground and most farmers replanted with the more profitable wine grapes for which France is so well known. Most of the mills in the region today still use the low technology stone mills and decantation processes their ancestors used. Unfortunately they have trouble finding enough olives nearby to sell much more than just to local residents, who bring their own olives for pressing. Mills that have modern equipment supplement their investment by bringing in olives from Spain and selling olive crafts, soaps, and canned table fruit in stores and restaurants adorned with antique processing equipment. Statistically, France is not a major producer of olive oil, processing an estimated 2,500 to 3,500 tons of olives in 1994. The Var region Chamber of Commerce economic development bulletin lists 11,136 farms in the region with an average size of just under 20 acres each. Vineyards represent 43% of the land and 47% of the earnings, cut flower production occurs on 1% of the land and represents 36% of the earnings. -

Class-Action Lawsuit
Case 2:13-cv-06326-LDW-WDW Document 1 Filed 11/13/13 Page 1 of 30 PageID #: 1 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE EASTERN DISTRICT OF NEW YORK SARA WEISBLUM and ANTOINETTE BAZIKOS, individually and on behalf of all others similarly situated, Civil Action No. Plaintiffs, CLASS ACTION COMPLAINT v. SIROB IMPORTS INC. Defendant. Plaintiffs Sara Weisblum and Antoinette Bazikos (“Plaintiffs”) by their attorneys, make the following allegations pursuant to the investigations of counsel and upon information and belief, except as to the allegations specifically pertaining to themselves or their counsel, which are based on personal knowledge. NATURE OF THE ACTION 1. This is a class action against Sirob Imports Inc. (“Defendant”) for misbranding edible oil products sold to consumers. Defendant markets oils for human consumption under the “Kalamata” brand as “100% Pure olive oil.” But Defendant’s “100% Pure olive oil” is nothing of the sort. Instead of “olive oil,” Defendant’s product consists of an industrially produced, chemically derived fat known as “olive-pomace oil” or “olive-residue oil” (hereafter “Pomace Oil”). 2. Pomace Oil is extracted from olive pomace using a combination of carcinogenic chemical solvents and high temperatures. Olive pomace is a waste byproduct of the olive oil making process consisting of leftover olive skins and pits, among other things. Unsurprisingly, Case 2:13-cv-06326-LDW-WDW Document 1 Filed 11/13/13 Page 2 of 30 PageID #: 2 because Pomace Oil is obtained only through chemical solvent treatments and high temperatures, it does not appear in pure olive oil. And, as a factual and legal matter, Pomace Oil is not olive oil. -

Evaluation of Fatty Acid and Sterol Profiles, California Olive Oil, 2016/17 Season
Evaluation of Fatty Acid and Sterol Profiles, California Olive Oil, 2016/17 Season Evaluation of Fatty Acid and Sterol Profiles California Olive Oil 2016/17 Season Submitted to the Olive Oil Commission of California June 2017 Evaluation of Fatty Acid and Sterol Profiles, California Olive Oil, 2016/17 Season Evaluation of Fatty Acid and Sterol Profiles, California Olive Oil, 2016/17 Season SUMMARY At the request of the Olive Oil Commission of California (OOCC), the UC Davis Olive Center collected California olive oil samples produced in the 2016/17 Season and analyzed fatty acid and sterol profiles. The study team collected 70 single-variety samples of olive oil from California commercial producers. Samples that were found to be outside one or more parameters at the UC Davis laboratory were sent to Modern Olives Laboratory (Woodland, CA) for retesting. Both laboratories agreed that 61 of 70 samples (87 percent) were within the fatty acid and sterol parameters required in California. Nine samples (13 percent) were outside at least one fatty acid or sterol parameter. The Commission may wish to recommend modifications to California olive oil standards so that fatty acid and sterol profile standards accommodate all olive oil produced in California and assess new and advanced methods to analyze olive oil purity with the potential to cost less, be more accurate, and minimize laboratory variability. BACKGROUND The Olive Oil Commission of California requested the UC Davis Olive Center to collect data on the fatty acid and sterol profile of California olive oils from commercial samples. The Commission requested that the Olive Center collect at least 70 samples from a wide range of varieties and counties. -

Identification of Tyrosyl Oleate As a Novel Olive Oil Lipophenol With
antioxidants Article Identification of Tyrosyl Oleate as a Novel Olive Oil Lipophenol with Proliferative and Antioxidant Properties in Human Keratinocytes Cinzia Benincasa 1 , Chiara La Torre 2,†, Alessia Fazio 2,†, Enzo Perri 1, Maria Cristina Caroleo 2,†, Pierluigi Plastina 2,*,† and Erika Cione 2,† 1 CREA Research Centre for Olive, Fruit and Citrus Crops, 87036 Arcavacata di Rende, CS, Italy; [email protected] (C.B.); [email protected] (E.P.) 2 Department of Pharmacy, Health and Nutritional Sciences, University of Calabria, 87036 Arcavacata di Rende, CS, Italy; [email protected] (C.L.T.); [email protected] (A.F.); [email protected] (M.C.C.); [email protected] (E.C.) * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +39-0984-493128 † Department of Excellence 2018–2022. Abstract: Lipophenols are an emerging subclass of phenolic compounds characterized by the pres- ence of a lipid moiety. Recently, hydroxytyrosyl oleate (HtyOle), a derivative of hydroxytyrosol, has been identified in olive oil and by-products. Furthermore, HtyOle possesses anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and tissue regenerating properties. In this work, the potential occurrence of tyrosyl oleate (TyOle) in olive oil was investigated based on the hypothesis that its precursors tyrosol and Citation: Benincasa, C.; La Torre, C.; oleic acid, both present in relatively high amount can be coupled together. Moreover, TyOle effects Fazio, A.; Perri, E.; Caroleo, M.C.; have been investigated in human keratinocytes to verify its proliferative and antioxidant properties. Plastina, P.; Cione, E. Identification The quantitative determination of TyOle was carried out by the external standard method in liquid of Tyrosyl Oleate as a Novel Olive chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (LC/MS), in negative mode using multiple reac- Oil Lipophenol with Proliferative tion monitoring (MRM).