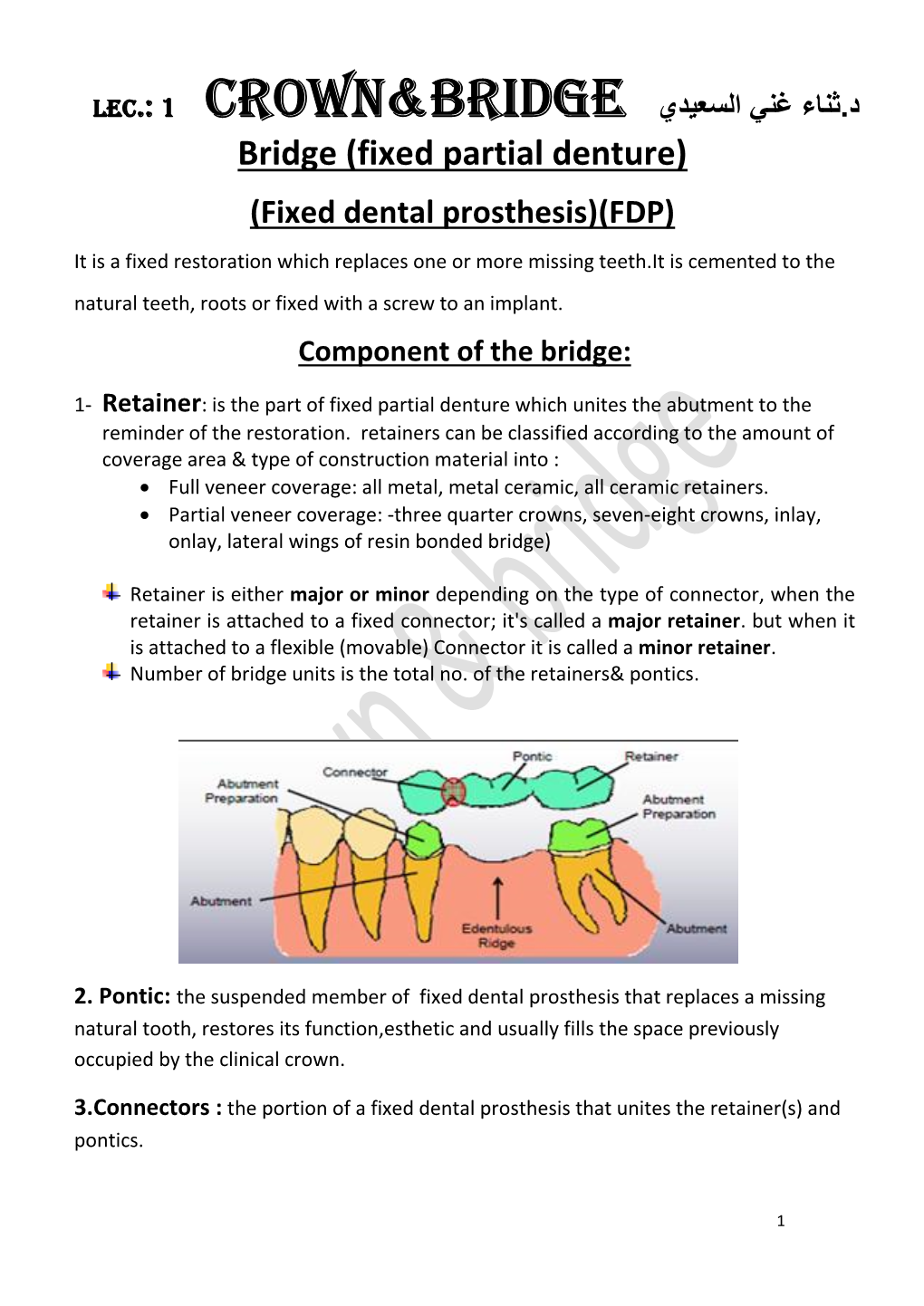
Lec.: 1 Crown&Bridge
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Dentistry: Advanced Research Kalghoum I, Et Al
Dentistry: Advanced Research Kalghoum I, et al. Dentistry Adv Res: DTAR-133. Case Report DOI: 10.29011/2574-7347. 100033 All Ceramic Bonded Bridge: Clinical Procedure and Requirements Imen Kalghoum1, Ines Azzouzi1, Amina Khiari1, Dalenda Hadyaoui2*, Belhssan Harzallah2, Mounir Cherif2 1DDM, Department of Fixed Prosthodontics, Faculty of Dental Medicine, Monastir, Tunisia 2Professor, Department of Fixed Prosthodontics, Faculty of Dental Medicine, Monastir, Tunisia *Corresponding author: Dalenda Hadyaoui, Professor, Department of Fixed Prosthodontics, Faculty of Dental Medicine, Mona- stir, Tunisia. Tel: +21655967860; Email: [email protected] Citation: Kalghoum I, Azzouzi I, Khiari A, Hadyaoui D, Harzallah B, et al. (2017) All Ceramic Bonded Bridge: Clinical Procedure and Requirements. Dentistry Adv Res: DTAR-133. DOI: 10.29011/2574-7347. 100033 Received Date: 05 September, 2017; Accepted Date: 18 September, 2017; Published Date: 25 September, 2017 Abstract One of the basic principles of tooth preparation for fixed prosthodontics is conservation of tooth structure. This is the ma- jor advantage of bonded bridge as an alternative to implant retained restorations in the esthetic zone. Especially used for juvenile patient who do not come into consideration for implant therapy?. This article describes the use of an all ceramic resin-bonded bridge as a conservative and esthetic solution for the replacement of 2 mandibular incisors for a 17 -year female patient. Keywords: All Ceramic Resin Bonded Bridge; Esthetic Pros- alumina ceramic, -

Biodental Engineering V
BIODENTAL ENGINEERING V PROCEEDINGS OF THE 5TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON BIODENTAL ENGINEERING, PORTO, PORTUGAL, 22–23 JUNE 2018 Biodental Engineering V Editors J. Belinha Instituto Politécnico do Porto, Porto, Portugal R.M. Natal Jorge, J.C. Reis Campos, Mário A.P. Vaz & João Manuel R.S. Tavares Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal CRC Press/Balkema is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an informa business © 2019 Taylor & Francis Group, London, UK Typeset by V Publishing Solutions Pvt Ltd., Chennai, India All rights reserved. No part of this publication or the information contained herein may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, by photocopying, recording or otherwise, without written prior permission from the publisher. Although all care is taken to ensure integrity and the quality of this publication and the information herein, no responsibility is assumed by the publishers nor the author for any damage to the property or persons as a result of operation or use of this publication and/or the information contained herein. Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data Names: International Conference on Biodental Engineering (5th: 2018: Porto, Portugal), author. | Belinha, Jorge, editor. | Jorge, Renato M. Natal editor. | Campos, J.C. Reis, editor. | Vaz, Mario A.P., editor. | Tavares, Joao Manuel R.S., editor. Title: Biodental engineering V: proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Biodental Engineering, Porto, Portugal, 22–23 June 2018 / editors, J. Belinha, R.M. Natal Jorge, J.C. Reis Campos, Mario A.P. Vaz & Joao Manuel R.S. Tavares. Description: London, UK; Boca Raton, FL: Taylor & Francis Group, [2019] | Includes bibliographical references and index. -

HIV/ I S and Its Significance for the Ental Profession Remember To
JOURNAL OF THE CANADIAN DENTAL ASSOCIATION December 2007/JanuaryJC 2008, Vol. 73, No. 10 DAwww.cda-adc.ca/jcda Remember to Register for the ODA Annual Spring Meeting in Conjunction with CDA in Toronto pril 10-12, 2008 HIV/I�S and its Significance for the Dental Profession PM40064661 R09961 ���JCDA • www.cda-adc.ca/jcda • December 2007/January 2008, Vol. 73, No. 10 • 861 Essential reading for Canadian dentists Straumann p/u Nov 07, p. 750 E/F 4/C December 2007/January 2008, Vol. 73, No. 10 Publisher Canadian Dental Association Mission Statement Editor-In-Chief The Canadian Dental Association is the national voice for dentistry, dedicated to Dr. John P. O’Keefe the advancement and leadership of a unified profession and to the promotion of Writer/Editor optimal oral health, an essential component of general health. Emilie Adams Assistant Editor Natalie Blais A S S O C I AT E E DITORS Coordinator, French Dr. Michael J. Casas Translation Dr. Anne Charbonneau Nathalie Upton Dr. Mary E. McNally Coordinator, Publications Rachel Galipeau Writer, Electronic Media EDITORIAL CONSULTANTS David Shaw Dr. James L. Armstrong Dr. Robert J. Hawkins Dr. Richard B. Price Manager, Design & Production Dr. Catalena Birek Dr. Asbjørn Jokstad Dr. N. Dorin Ruse Barry Sabourin Dr. Gary A. Clark Dr. Richard Komorowski Dr. Kathy Russell Dr. Jeff Coil Dr. Ernest W. Lam Dr. George K.B. Sándor Graphic Designer Dr. Pierre C. Desautels Dr. Gilles Lavigne Dr. Benoit Soucy Janet Cadeau-Simpson Dr. Terry Donovan Dr. James L. Leake Dr. David J. Sweet All statements of opinion and Dr. -

Herbert T. Shillingburg, Jr
Herbert T. Shillingburg, Jr, DDS David Ross Boyd Professor Emeritus Department of Fixed Prosthodontics University of Oklahoma College of Dentistry Oklahoma City, Oklahoma with David A. Sather, DDS Edwin L. Wilson, Jr, DDS, MEd Joseph R. Cain, DDS, MS Donald L. Mitchell, DDS, MS Luis J. Blanco, DMD, MS James C. Kessler, DDS Illustrations by Suzan E. Stone Quintessence Publishing Co, Inc Chicago, Berlin, Tokyo, London, Paris, Milan, Barcelona, Istanbul, Moscow, New Delhi, Prague, São Paulo, and Warsaw Cover design based on a photograph of Monument Valley on the Navajo Reservation in northern Arizona taken at sunrise by Dr Herbert T. Shillingburg, Jr. Contents Dedication vii Authors viii Preface ix Acknowledgments x 1 An Introduction to Fixed Prosthodontics 1 2 Fundamentals of Occlusion 13 3 Articulators 27 4 Interocclusal Records 35 5 Articulation of Casts 45 6 Treatment Planning for Single-Tooth Restorations 71 7 Treatment Planning for the Replacement of Missing Teeth 81 8 Fixed Partial Denture and Implant Con!gurations 99 9 Principles of Tooth Preparations 131 10 Preparations for Full Coverage Crowns 149 11 Preparations for Partial Coverage Crowns 165 12 Preparations for Intracoronal Restorations 193 13 Preparations for Severely Debilitated Teeth 203 14 Preparations for Periodontally Weakened Teeth 229 15 Provisional Restorations 241 16 Fluid Control and Soft Tissue Management 269 291 17 Impressions 325 18 Working Casts and Dies 343 19 Wax Patterns 363 20 Investing and Casting 383 21 Cementation and Bonding 413 22 Esthetic Considerations 425 23 All-Ceramic Restorations 447 24 Metal-Ceramic Restorations 471 25 Pontics and Edentulous Ridges 493 26 Solder Joints and Other Connectors 517 27 Restoration of Osseointegrated Dental Implants 531 28 Single-Tooth Implant Restoration 543 29 Multiple-Tooth Implant Restoration Index 555 Dedication In Memoriam Constance Murphy Shillingburg 1938–2008 This book is dedicated to the loving memory of Constance surgeries later in life, she was the most optimistic person I Murphy Shillingburg. -

RETENTION of a POSTERIOR RESIN-BONDED Flxed PARTIAL DENTURE Wlth a Modlfled DESIGN - an in Vltro STUDY
RETENTION OF A POSTERIOR RESIN-BONDED FlXED PARTIAL DENTURE WlTH A MODlFlED DESIGN - AN IN VlTRO STUDY. Marcia Helena Marangoni Rubo A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Science Graduate Department of Dentistry University of Toronto O Copyright by Marcia Helena Marangoni Rubo 1998 National übrary Bibliothèque nationale du Canada Acquisitions and Acquisitions et Bibliographie Services services bibliographiques 395 Wellington Street 395. rue Wellington OttawaON K1AW OttawaON K1AW Canada Canada The author has granted a non- L'auteur a accordé une licence non exclusive licence allowing the exclusive permettant a la National Library of Canada to Bibliothèque nationale du Canada de reproduce, loan, distriiute or sell reproduire, prêter, distribuer ou copies of this thesis in microfom, vendre des copies de cette thèse sous papa or electronic formats. la forme de miaofiche/nlm, de reproduction sur papier ou sur format électronique. The author retains ownership of the L'auteur conserve la propriété du copyright in this thesis. Neither the droit d'auteur qui protège cette thèse. thesis nor substantial extracts fiom it Ni la thèse ni des extraits substantiels may be printed or otherwise de celle-ci ne doivent être imprimés reproduced without the author's ou autrement reproduits sans son permission. autorisation. Retention of a Posterior ResinBonded Fixed Partial Denture with a Modified Design - an in vitro study. Marcia Helena Marangoni Rubo Degree of Master of Science Graduate Department of Dentistry University of Toronto 1998 Abstract ln vitro retention of a RBFPD made wlh a modified design (MD) was compared to that of a curent design (CD) using five experimental groups (G). -

Article-NOVEMBER ISSUE Final
A REVIEW ON RESIN BONDED PROSTHESIS Dr. Tanmay Biswas*, Dr. Anindita Majumder*, Dr. (Prof) T.K Giri**, Dr. (Prof) S. Mukharjee *** Abstract Resin bonded bridges are a minimally invasive option for replacing missing teeth. The minimal-preparation, resin retained adhesive bridge may be considered to be an ideal choice of fixed prosthesis to replace a single missing tooth, especially in the anterior region. Many dental practitioners do not use adhesive bridges because of concerns over high failure rates. This article highlights advantages, disadvantages, types of framework and bridge designs and clinical procedure which may improve outcome, with a special mention of all ceramic resin bonded bridges. Key Words Resin bonded bridges, adhesive bridge, bridge design, minimally invasive, all ceramic resin bonded bridges. INTRODUCTION Resin bonded or resin retained bridges (RBBs/RRBs) are minimally invasive fixed prostheses which rely on composite resin cements for retention. These restorations were first described in the 1970s and since this time they have evolved significantly. The first type of RBB was the Rochette Bridge, which relied on the retention generated by resin cement tags through a characteristic perforated metal retainer. However, longevity of this type of restoration was limited and in an effort to address this, methods of altering the surface of the metal retainer to enhance micromechanical retention were developed.2The term 'Maryland Bridge' resulted from the development of a type of electrochemical etching at the University of Maryland. More recently bridge retention has been enhanced by the development of resin cements which bond chemically to both the tooth surface and the metal alloy. -

Peaceful Bridging RS Carlson* ISSN Private Practice, Carlson Bridge Technologies, Inc., Hawaiia, USA 2573-6191
Open Access Journal of Oral Health and Craniofacial Science Research Article Peaceful Bridging RS Carlson* ISSN Private Practice, Carlson Bridge Technologies, Inc., Hawaiia, USA 2573-6191 In our past 200 years we have seen the advancing development of Dental Arts and *Address for Correspondence: Dr. RS Carlson, Private Practice, Carlson Bridge Technologies, Science though discoveries by its practitioners. Perhaps it will do some good to review Inc., Hawaiia, USA, Tel: (808) 735-0282; Email: the basis upon which ixed tooth replacement has evolved—that is the prosthetic [email protected] crown. Submitted: 27 November 2018 Approved: 04 December 2018 Prior to 1871, before the irst manufactured foot-treadle dental engine was Published: 05 December 2018 introduced in America, the restoration of structurally compromised teeth was with hand cutting instruments and bands of metal or wires that were place about the tooth Copyright: © 2018 Carlson RS. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative remanents. Although crude and only for the very wealthy, they seemed to be secure Commons Attribution License, which permits enough to last sometime—temporarily or permanently depending upon the time in unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction service. Since life expectancy at this time was less than 35 years, even “temporary”—a in any medium, provided the original work is year or more—would work well. properly cited We show here in our graphic igure 1, a page from the Dental Cosmos. In it we see the art of “engrafting” a metal crown about a tooth with minimal reduction/preparation. When the electric dental drill was patented by G. -

GPT-9 the Academy of Prosthodontics the Academy of Prosthodontics Foundation
THE GLOSSARY OF PROSTHODONTIC TERMS Ninth Edition GPT-9 The Academy of Prosthodontics The Academy of Prosthodontics Foundation Editorial Staff Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms Committee of the Academy of Prosthodontics Keith J. Ferro, Editor and Chairman, Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms Committee Steven M. Morgano, Copy Editor Carl F. Driscoll, Martin A. Freilich, Albert D. Guckes, Kent L. Knoernschild and Thomas J. McGarry, Members, Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms Committee PREFACE TO THE NINTH EDITION prosthodontic organizations regardless of geographic location or political affiliations. Acknowledgments are recognized by many of “The difference between the right word and the almost right the Academy fellowship, too many to name individually, with word is the difference between lightning and a lightning bug.” whom we have consulted for expert opinion. Also recognized are dMark Twain Gary Goldstein, Charles Goodacre, Albert Guckes, Steven Mor- I live down the street from Samuel Clemens’ (aka Mark Twain) gano, Stephen Rosenstiel, Clifford VanBlarcom, and Jonathan home in Hartford, Connecticut. I refer to his quotation because he Wiens for their contributions to the Glossary, which have spanned is a notable author who wrote with familiarity about our spoken many decades. We thank them for guiding us in this monumental language. Sometimes these spoken words are objectionable and project and teaching us the objectiveness and the standards for more appropriate words have evolved over time. The editors of the evidence-based dentistry to be passed on to the next generation of ninth edition of the Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms ensured that the dentists. spoken vernacular is represented, although it may be nonstandard in formal circumstances. -

Prosthodontic Management of True Generalised Microdontia in Pituitary Dwarfism – a Case Report
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-ISSN: 2279-0853, p-ISSN: 2279-0861.Volume 18, Issue 9 Ser.12 (September. 2019), PP 59-61 www.iosrjournals.org Prosthodontic Management of True Generalised Microdontia in Pituitary Dwarfism – A Case Report Dr. Mohammed Ibrahim Mathar1,Dr. Shaik Mohamed Shamsudeen2,Dr.Mohammed Ziauddeen Mustafa 3Dr. Pramod Punchiri Sadan4 Dr. Syed Shujaulla5 1. Assistant professor, Dept. of Prosthetic Dental Science, Al-Rass College of Dentistry, Qassim University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. 2. Assistant professor, Department of Dental Diagnostic Science ,College of Dentistry, King Khalid University,Abha, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. 3. Assistant Professor, Dept. of Prosthetic Dental Science, College of Dentistry, Al-Zulfi, Majmaah University,Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. 4. Associate Professor, Dept. of Prosthetic Dental Science, College of Dentistry,Qassim University, Buraidah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. 5. Assistant Professor, Dept. of Prosthetic Dental Science,College of Dentistry,Qassim University, Buraidah,Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Corresponding Author: Dr.Mohammed Ibrahim Mathar M.D.S.,Dr. Shaik Mohamed ShamsudeenM.D.S., Abstract: Abnormalities in size & number of teeth are occasionally recorded in clinical cases. True generalized microdontia is a rare case in which all the teeth are smaller than normal. True generalized microdontia markedly influence on physical, functional & psychological maturation of the affected individual. Thorough evaluation, proper counseling & careful treatment planning employing -

Ceramic Bonded Bridge: Clinical Procedure and Requirements
Case Report Adv Dent & Oral Health Volume 6 Issue 1 - October 2017 Copyright © All rights are reserved by Dalenda Hadyaoui DOI: 10.19080/ADOH.2017.06.555678 All Ceramic Bonded Bridge: Clinical Procedure and Requirements Imen kalghoum2, Ines Azzouzi1, Amina Khiari2, Dalenda Hadyaoui2*, Belhssan Harzallah2 and Mounir cherif2 1Department of Fixed Prosthodontics, Faculty of dental medicine, Tunisia 2Professor, Department of Fixed Prosthodontics, Faculty of dental medicine, Tunisia Submission: September 06, 2017; Published: October 25, 2017 *Corresponding author: Dalenda Hadyaoui, Professor, Department of Fixed Prosthodontics, Faculty of dental medicine, Monastir, Tunisia, Email: Abstract bonded bridge as an alternative to implant retained restorations in the esthetic zone. Especially used for juvenile patient who do not come into considerationOne of the for basic implant principles therapy? of tooth This articlepreparation describes for fixedthe use prosthodontics of an all ceramic is conservation resin-bonded of bridge tooth asstructure. a conservative This is and the estheticmajor advantage solution for of the replacement of 2 mandibular incisors for a 17 -year female patient. Keywords: All ceramic resin bonded bridge; Lithium discilicate; Mini invasive restoration; RBFPD; Esthetic prostheses Introduction This clinical report presents resin bonded prosthesis as a The frequency of teeth trauma permanent denture reaches prosthesis for the replacement of a missing mandible anterior 10-35% of the general population, especially, for the central viable treatment alternative to conventional fixed or removable tooth fabricated from lithium dislocate ceramic (IPS Emax CAD) mandibular incisors (3, 8 à 13, 3%) [1]. As a result, the need as a provisional solution. preparation is challenging because of their small axial. -

Dental Lamina March 2018.Cdr
VOL. 4 NO. 2, DECEMBER 2017 Dr. Mridula Goswami Published at : Plot No. 6, Industrial Area, NIT Faridabad, Haryana Printed at : Prabhakar Press, Plot No. 6, Industrial Area, NIT Faridabad, Haryana VOL. 4 NO. 2 DECEMBER 2017 Dental Lamina - Journal of Dental Sciences Vol. 4, No. 2, December 2017 Oral diseases are closely linked to lifestyle. Dental health encompasses the likelihood of making healthy choices in relation to diet, smoking, tobacco, oral hygiene and utilization of dental health services.3 A rise in the use of sugary diet, especially bakery products and carbonated drinks increase prevalence of Dental caries. Making choices that support and care for your body everyday and making them part of your lifestyle will help you to have a healthy life and a healthy mouth. Unfortunately more and more people living busy lifestyles are relying on caffeine and sugar to keep them going and then turning to food and alcohol to help them relax. With modern technology and the need to get more done people are staying up later, not getting enough sleep or quality sleep and feeling exceedingly stressed on a daily basis. No amount of good oral hygiene practices can make up for the affects of poor lifestyle habits. This would be like thinking that you can stay up really late every night then thinking you can make up the lost sleep hours by sleeping late on the weekends. The damage has already been done. Balancing stress, diet/nutrition, sleep quality, hydration, tooth brushing and flossing are the keys to dental health. It has to be a total body package, aimed at achieving balance and harmony throughout the body as a whole. -

(IJDSIR) P Age 34
ISSN: 2581-5989 PubMed - National Library of Medicine - ID: 101738774 International Journal of Dental Science and Innovative Research (IJDSIR) IJDSIR : Dental Publication Service Available Online at: www.ijdsir.com Volume – 2, Issue – 4, July – August - 2019, Page No. : 34 - 39 Resin Bonded Fixed Prosthesis a Conservative Approach to Replace Missing Teeth in the Aesthetic Zone – A Clinical Case Report 1Dr Nazish Baig, Professor and PG Guide in Dept of Prosthodontics CSMSS Dental College, Aurangabad 2Dr Yusuf Shaikh, 2nd Year PG Student Dept of Prosthodontics CSMSS dental College, Aurangabad 3Dr Babita Yashwanti, HOD and Professor in Dept of Prosthodontics CSMSS Dental College, Aurangabad Corresponding Author: Dr Yusuf Shaikh, 2nd Year PG Student Dept of Prosthodontics CSMSS dental College, Aurangabad Type of Publication: Case Report Conflicts of Interest: Nil Abstract Restoring the missing central incisors in the maxillary jaw Keywords: Resin bonded fixed partial denture, Maryland is one of the most difficult esthetic challenges in dentistry. Bridge, Missing central incisor. A space in the maxillary anterior region of the dental arch Introduction can produce a psychological impact on the young patient. There are various treatment options available for the Resin bonded bridges are highly effective treatment option replacement of the missing mandibular anterior incisors in these situations to restore the oral function and such as implant, removable partial denture and fixed aesthetics and result in high levels of patient satisfaction. partial denture. Removable partial denture may cause the Maryland bridges are the type of resin bonded bridge with bone resorption and attending of the interdental papillaein certain advantages over conventional dental prosthesis long term use however it can be used as interim prosthesis such as minimal removal of the tooth structure, minimal for initial esthetics.