Ecological Succession Notes
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

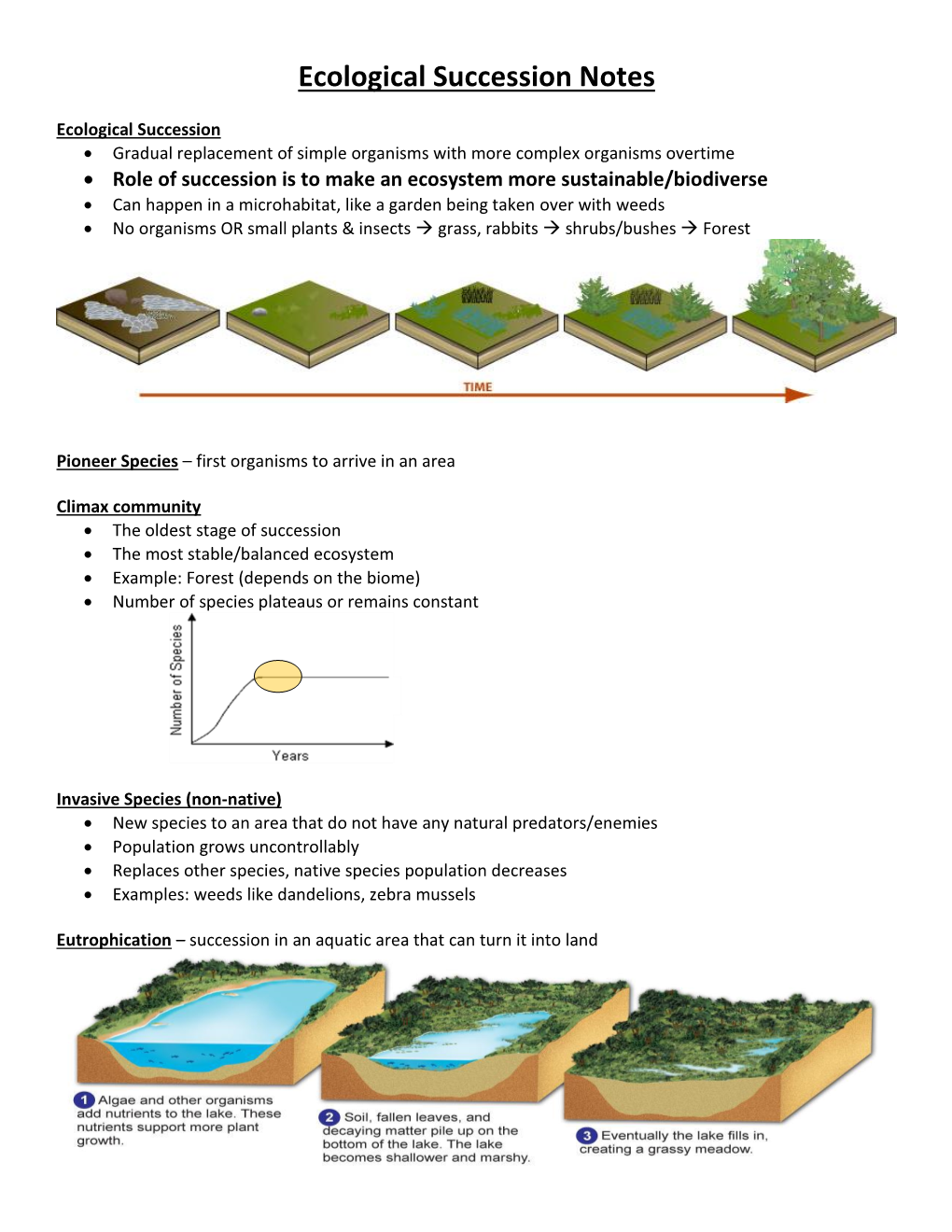
Variety of Organisms in an Ecosystem Or Biome Climax Community
Lessons for 5th Six Weeks (Weeks 4-6) 1) Copy the following vocabulary words onto a blank sheet of paper. Biodiversity – variety of organisms in an ecosystem or biome Climax community – dominant community of plants and animals that come to live in an area Ecological succession – the changing sequence of communities that live in an ecosystem during a given time period Limiting factor – a condition or resource that keeps a population at a certain size Microhabitat – a small or specialized habitat within a larger habitat Niche – the unique role or job of an organism in an ecosystem Pioneer species – first organisms to live in an area Primary succession – a process that develops a biotic community in a previously uninhabited and barren habitat with little or no soil Secondary succession – a process started by an event that reduces an already established ecosystem to a smaller population of species Sustainability – ability to maintain ecological processes over long periods of time; ability of an ecosystem to maintain its structure and function over time 2) Copy the following notes onto a blank sheet of paper. TEK 7.10A - Observe and describe how different environments, including microhabitats in schoolyards and biomes, support different varieties of organisms. Observe, Describe HOW DIFFERENT ENVIRONMENTS SUPPORT DIFFERENT VARIETIES OF ORGANISMS Including, but not limited to: • Different environments o Microhabitats in schoolyards o Biomes • Support different varieties of organisms through o Providing for basic needs . Possible examples may include: 7th Grade Science - Watson . Climate . Vegetation . Location . Water TEK 7.10B - Describe how biodiversity contributes to the sustainability of an ecosystem. -

Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis
TIEE Teaching Issues and Experiments in Ecology - Volume 1, January 2004 ISSUES – FIGURE SET Ecology of Disturbance Charlene D'Avanzo, School of Natural Sciences Hampshire College, Amherst, MA, 01002 [email protected] Controlled fire, © Konza Prairie LTER, Manhattan, KS {www.konza.ksu.edu/ gallery/hulbert.jpg} Figure Set 1: Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis Purpose: To illustrate the intermediate disturbance hypothesis with 2 field experiments. Teaching Approach: "Pairs Share" Cognitive Skills: (see Bloom's Taxonomy) — comprehension, interpretation, application, analysis Student Assessment: Take home or in class essay quiz © 2004 – Charlene D’Avanzo and the Ecological Society of America. Teaching Issues and Experiments in Ecology, TIEE Volume 1 © 2004 - Ecological Society of America (www.tiee.ecoed.net). page 2 Charlene D’Avanzo TIEE Volume 1, January 2004 BACKGROUND W. Sousa (1979) In this study, Wayne Sousa tested the intermediate disturbance hypothesis proposed by Connell (1978). In the 70's and 80's ecologists hotly debated factors explaining high diversity in tropical regions and bottom of the deep sea. Popular ideas included: the time hypothesis (older communities are more diverse), the competition hypothesis (in agreeable climates where biological and not physical factors prevail, interspecific competition and niche partitioning results in high diversity), and the environmental stability hypothesis (relatively unchanging physical variables allow more species to exist). Connell questioned all of these and reasoned instead that highest species diversity exists under conditions of intermediate disturbance. He proposed that in recently disturbed communities a few early colonizing species prevail; similarly after a long time diversity is also low, but these few are long-living and competitively dominant organisms. -

ZOOLOGY Principles of Ecology Community
Paper : 12 Principles of Ecology Module : 20 Community: Community characteristics, types of biodiversity, diversity index, abundance, species richness, vertical and horizontal stratification: Part IV Development Team Principal Investigator: Prof. Neeta Sehgal Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Co-Principal Investigator: Prof. D.K. Singh Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Paper Coordinator: Prof. D.K. Singh Department of Zoology, University of Delhi Content Writer: Dr. Haren Ram Chiary and Dr. Kapinder Kirori Mal College, University of Delhi Content Reviewer: Prof. K.S. Rao Department of Botany, University of Delhi 1 Principles of Ecology ZOOLOGY Community: Community characteristics, types of biodiversity, diversity index, abundance, species richness, vertical and horizontal stratification: Part IV Description of Module Subject Name ZOOLOGY Paper Name Zool 12, Principles of Ecology Module Name/Title Community Module Id M20, Community characteristics, types of biodiversity, diversity index, abundance, species richness, vertical and horizontal stratification : Part-IV Keywords Succession, Primary succession, secondary succession, Sera, Climax community, Hydrosere, Lithosere, theories of climax community Contents 1. Learning Objective 2. Introduction 3. History of study of succession 4. Ecological succession and types: Primary and secondary succession 5. Stages of Primary and secondary succession 6. Process of succession in Hydrosere 7. Process of succession in Lithosere 8. Theories of climax community 9. Summary 2 Principles -

Unit 6 - Evolution Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts a and B-1
Unit 6 - Evolution Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a food web in an ecosystem. 1. If the population of hawks in this area increases, their prey populations might decrease. Later, with fewer prey, the hawk population might decrease. The prey populations might then increase. This is an example of A) an ecosystem that is completely out of balance B) how ecosystems maintain stability over time C) interaction between biotic and abiotic factors within an ecosystem D) ecological succession in an ecosystem 2. Missing from the diagram of this ecosystem are the A) biotic factors and decomposers B) abiotic factors and decomposers C) autotrophs, only D) heterotrophs, only 3. Which row in the chart below best identifies the relationships between the mice and the wheat? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 4. All of Earth's water, land, and atmosphere within 5. The study of the interactions between organisms and which life exists is known as their interrelationships with the physical environment is known as A) a population B) a community C) a biome D) the biosphere A) ecology B) cytology C) embryology D) physiology Page 1 Unit 6 - Evolution 6. The science of ecology is best defined as the study of 8. The graph below represents some changes in the number of individuals in a particular population in a A) the classification of plants and animals stable ecosystem over a period of time. -

Chapter 5 Species Interactions, Ecological Succession, and Population Control How Do Species Interact?
Chapter 5 Species interactions, Ecological Succession, and Population Control How do species interact? Give some limited resources that organisms need in order to survive. Food, shelter, space, mate to reproduce, water, light air How might species interact to get these limited resources? Competition Have you ever competed with another organism to get what you wanted/needed? Interspecific competition is between different species. Intraspecific competition is between a single species. Competition Species need to compete because their niches overlap and they end up sharing the limited resources. When the word “share” is used here, it doesn’t mean equal sharing. Species like to reduce or avoid competition, so they resource partition. Competition Resource partitioning is a way for organisms to share a resource by using the resource at different times or using different parts of the resource. Predator/Prey interactions Predator is the hunter and feeds on the prey (the hunted) This interaction has a strong effect on population sizes. Predator/Prey interactions pg 134- 135 Give a way predators capture their prey. What are some ways prey avoid predators? Birds of prey (predators) and prey Google search ‘Birds of Prey’ – the Nature Conservancy has a great site Google search ‘bluebird, robin, sparrow’ Answer: 1. What differences do you notice regarding placement of the eyes in each group? 2. How might the difference in eye placement benefit each group of birds? What is mimicry? • Mimicry is the similarity of one species to another species which protects one or both organisms. Can be in appearance, behavior, sound, scent and even location. Who are the players? Mimics can be good tasting (easy targets) so they need to gain protection by looking like something bad tasting or dangerous. -

Mechanism of Ecological Succession
Environmental Biology Prof.(Dr.) Punam Jeswal Head M.Sc semester IV Botany Department MECHANISM OF ECOLOGICAL SUCCESSION ECOLOGICAL SUCCESSION Ecological succession is the gradual and continuous change in the species composition and community structure over time in the same area. Environment is always kept on changing over a period of time due to - i) Variations in climatic and physiographic factors and ii) The activities of the species of the communities themselves. These influences bring changes in the existing community which is sooner or later replaced by another community developed one after another. This process continues and successive communities develop one after another over the same area, until the terminal final community again becomes more or less stable for a period of time. The occurrence of definite sequence of communities over a period of time in the same area is known as Ecological Succession. Succession is a unidirectional progressive series of changes which leads to the established of a relatively stable community. Hult (1885), while studying communities of Southern Sweden used for the first time the term succession for the orderly changes in the communities. Clements (1907, 1916) put forth various principles that governed the process of succession, and while studying plant communities, defined succession as ' the natural process by which the same locality becomes successively colonized by different groups or communities of plants. According to E.P. Odum (1971), the ecological succession is an orderly process of community change in a unity area. It is the process of changes in species composition in an ecosystem over time. In simple terms, it is the process of ecosystem development in nature. -

Is Ecological Succession Predictable?
Is ecological succession predictable? Commissioned by Prof. dr. P. Opdam; Kennisbasis Thema 1. Project Ecosystem Predictability, Projectnr. 232317. 2 Alterra-Report 1277 Is ecological succession predictable? Theory and applications Koen Kramer Bert Brinkman Loek Kuiters Piet Verdonschot Alterra-Report 1277 Alterra, Wageningen, 2005 ABSTRACT Koen Kramer, Bert Brinkman, Loek Kuiters, Piet Verdonschot, 2005. Is ecological succession predictable? Theory and applications. Wageningen, Alterra, Alterra-Report 1277. 80 blz.; 6 figs.; 0 tables.; 197 refs. A literature study is presented on the predictability of ecological succession. Both equilibrium and nonequilibrium theories are discussed in relation to competition between, and co-existence of species. The consequences for conservation management are outlined and a research agenda is proposed focusing on a nonequilibrium view of ecosystem functioning. Applications are presented for freshwater-; marine-; dune- and forest ecosystems. Keywords: conservation management; competition; species co-existence; disturbance; ecological succession; equilibrium; nonequilibrium ISSN 1566-7197 This report can be ordered by paying € 15,- to bank account number 36 70 54 612 by name of Alterra Wageningen, IBAN number NL 83 RABO 036 70 54 612, Swift number RABO2u nl. Please refer to Alterra-Report 1277. This amount is including tax (where applicable) and handling costs. © 2005 Alterra P.O. Box 47; 6700 AA Wageningen; The Netherlands Phone: + 31 317 474700; fax: +31 317 419000; e-mail: [email protected] No part of this publication may be reproduced or published in any form or by any means, or stored in a database or retrieval system without the written permission of Alterra. Alterra assumes no liability for any losses resulting from the use of the research results or recommendations in this report. -

Chapter 5 Hmdscience.Com EN Online Vir Onmental Science Work Ecosystems How
DO NOT EDIT--Changes must be made through “File info” printcode=a Chapter 5 Section 1 Energy Flow in Ecosystems How Section 2 The Cycling of Matter Section 3 How Ecosystems Change Why It Matters Ecosystems This frog gets the energy it needs to survive by eating other organisms, such as damselflies. Frogs and damselflies are both consumers in an aquatic food chain. Work How does energy continue to be transferred in this food chain? CASESTUDY Learn how pollutants, like the pesticide DDT, are transferred through a food chain in the case study DDT in an Aquatic Food Chain on page 120. Online enVirOnmental Science HMDScience.com Go online to access additional resources, including labs, worksheets, multimedia, and resources in Spanish. Inc. Cosmos Blank/Photo Researchers, ©A. 116 DO NOT EDIT--Changes must be made through “File info” printcode=a Section 1 Energy Flow in Objectives Describe how energy is transferred from the sun Ecosystems to producers and then to consumers. organisms need energy to survive, grow, and reproduce. Different organisms Describe one way in which get energy from different sources, but the ultimate source of energy for almost all consumers depend on producers. organisms on earth is the sun. Identify two types of consumers. Explain how energy transfer in a Life Depends on the Sun food web is more complex than Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when organisms use sunlight energy transfer in a food chain. to make sugar in a process called photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, plants, algae, and some bacteria capture light energy from the sun and Explain why an energy pyramid use it to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen, as is a representation of trophic shown in Figure 1.1. -

Chapter 15 Communities and Ecosystems Rosech15 0104043 437-474 2P 11/18/04 3:07 PM Page 439
RoseCh15_0104043_437-474_2p 11/18/04 2:32 PM Page 437 15 The feeding relationships between species can often be complicated. Communities and Ecosystems hen scientists first began studying bio- dioxide levels, which are covered in Chapter 16 logical communities, they were so fasci- (The Biosphere and the Physical Environment). Wnated with the interactions and The coordination and integration of biological dependencies between species that they saw the bi- communities has vast implications for the Earth. ological community as a superorganism. Whole For this reason, there are few biological topics as species were viewed as organs that performed spe- important for the future of life on Earth as the func- cific functions for the complete ecological superor- tioning of ecosystems. In this chapter, we survey ganism. The integration and communication how ecosystems function, from the flow of energy in between these “organs” was thought to be deliber- Module 15.1 (Energy Flow) and the recycling of nu- ate and well tuned. One way to think of this idea is trients in Module 15.15 (Ecosystems) to the porten- to imagine a stitched-together Frankenstein, each tous problem of the fragility of ecosystems. In sewn-on body part a distinct species. Modules 15.8 (Community Organization) and 15.4 Today biologists find the analogy between bio- (Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Communities), logical communities and organisms superficial. To we consider the factors that determine the number be sure, there are populations within communities of species in a community. Surprisingly, in some that are highly dependent on each other. And it is communities predation and environmental distur- also true that biological communities and their bance may promote increased species diversity. -

Early Successional Habitat
Early Successional Habitat January 2007 Fish and Wildlife Habitat Management Leaflet Number 41 Introduction Change is a characteristic of all natural systems. Directional change in the make-up and appearance of natural communities over time is commonly known as ecological succession. This change begins with a dis- turbance to the existing community, followed by plant colonization or regrowth. Materials (snags, soils, and disturbance-adapted seeds and other organisms) that are left behind after a disruptive event serve as biolog- ical legacies; that is, potential reservoirs of life, facili- tating the recovery of the habitat and biological com- munity. Through complex interactions, the disturbances, cli- mate, and soils of an ecological site are reflected in NRCS a plant community that is unique to that site. In a Early successional habitats are highly dynamic, highly healthy ecosystem, the plant community is in a state productive seral stages with uniquely adapted animal of dynamic (or ever changing) equilibrium exhibiting communities. variability in species composition and successional stages following disturbance. This variability creates valuable wildlife habitat because different wildlife Early successional habitats form soon after a distur- species are adapted to different plant species and suc- bance. Early successional plants are generally her- cessional stages. Over evolutionary time, plants and baceous annuals and perennials that quickly occupy animals have developed traits that allow them to sur- disturbed sites. They reproduce seeds that are distur- vive, exploit, and even depend on disturbances. For bance adapted or can be widely dispersed by wind, example, some plants require fire to produce seeds or water, or animals. Early successional communities flowers, and some fish depend on regular flooding to are characterized by high productivity and provide create and maintain their streambed habitat. -

Ecosystem Succession: Who/What Is Where and When
Ecosystem Succession: Who/What is Where and When Dennis Baldocchi ESPM Un ivers ity o f Ca liforn ia, Ber ke ley ESPM 111 Ecosystem Ecology Succession • From the Latin, succedere, to follow after • Orderly process of community development that is directional and predictable • Results from the modification of physical environment by the community – Succession is community-controlled even though the physical environment determines the pattern , rate of change and limits • Culminates in a stabilized ecosystem in which biomass and symbiotic function between organisms are maintained per unity of available energy flow – Eugene P Odum, 1969, Science ESPM 111 Ecosystem Ecology Succession • Primary Succession – After severe disturbance that remove or bury products of the ecosystem • Secondary Succession – After disturbance on a vegetated site. Most above ground live biomass may be disturbed but soil organic matter and plant propagules remain • Gap Phase Succession – Mortality and Tree fall for gap in canopy for new vegetation to invade and establish itself ESPM 111 Ecosystem Ecology Dynamic Sequence of Vegetation • Initial Conditions – Equilibrium • Disturbance • Colonization/Recruitment • Recovery • Competition • Succession – Primary – Secondary – Gap Succession • Climax – New Eq uilibri u m ESPM 111 Ecosystem Ecology Disturbance • Relativelyyp Discrete event, in time and space, that alters the structure of populations, communities and ecosystems and causes changes in resource availability and the ppyhysical environment. Chapin et al. ESPM 111 -

Short Term Shifts in Soil Nematode Food Web Structure and Nutrient Cycling Following Sustainable Soil Management in a California Vineyard
SHORT TERM SHIFTS IN SOIL NEMATODE FOOD WEB STRUCTURE AND NUTRIENT CYCLING FOLLOWING SUSTAINABLE SOIL MANAGEMENT IN A CALIFORNIA VINEYARD A Thesis presented to the Faculty of California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Science in Agriculture with a Specialization in Soil Science by Holly M. H. Deniston-Sheets April 2019 © 2019 Holly M. H. Deniston-Sheets ALL RIGHTS RESERVED ii COMMITTEE MEMBERSHIP TITLE: Short Term Shifts in Soil Nematode Food Feb Structure and Nutrient Cycling Following Sustainable Soil Management in a California Vineyard AUTHOR: Holly M. H. Deniston-Sheets DATE SUBMITTED: April 2019 COMMITTEE CHAIR: Cristina Lazcano, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Natural Resources & Environmental Sciences COMMITTEE MEMBER: Bwalya Malama, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Natural Resources & Environmental Sciences COMMITTEE MEMBER: Katherine Watts, Ph.D Assistant Professor of Chemistry and Biochemistry iii ABSTRACT Short term shifts in soil nematode food web structure and nutrient cycling following sustainable soil management in a California vineyard Holly M. H. Deniston-Sheets Evaluating soil health using bioindicator organisms has been suggested as a method of analyzing the long-term sustainability of agricultural management practices. The main objective of this study was to determine the effects of vineyard management strategies on soil food web structure and function, using nematodes as bioindicators by calculating established nematode ecological indices. Three field trials were conducted in a commercial Pinot Noir vineyard in San Luis Obispo, California; the effects of (i) fertilizer type (organic and inorganic), (ii) weed management (herbicide and tillage), and (iii) cover crops (high or low water requirements) on nematode community structure, soil nutrient content, and crop quality and yield were analyzed.