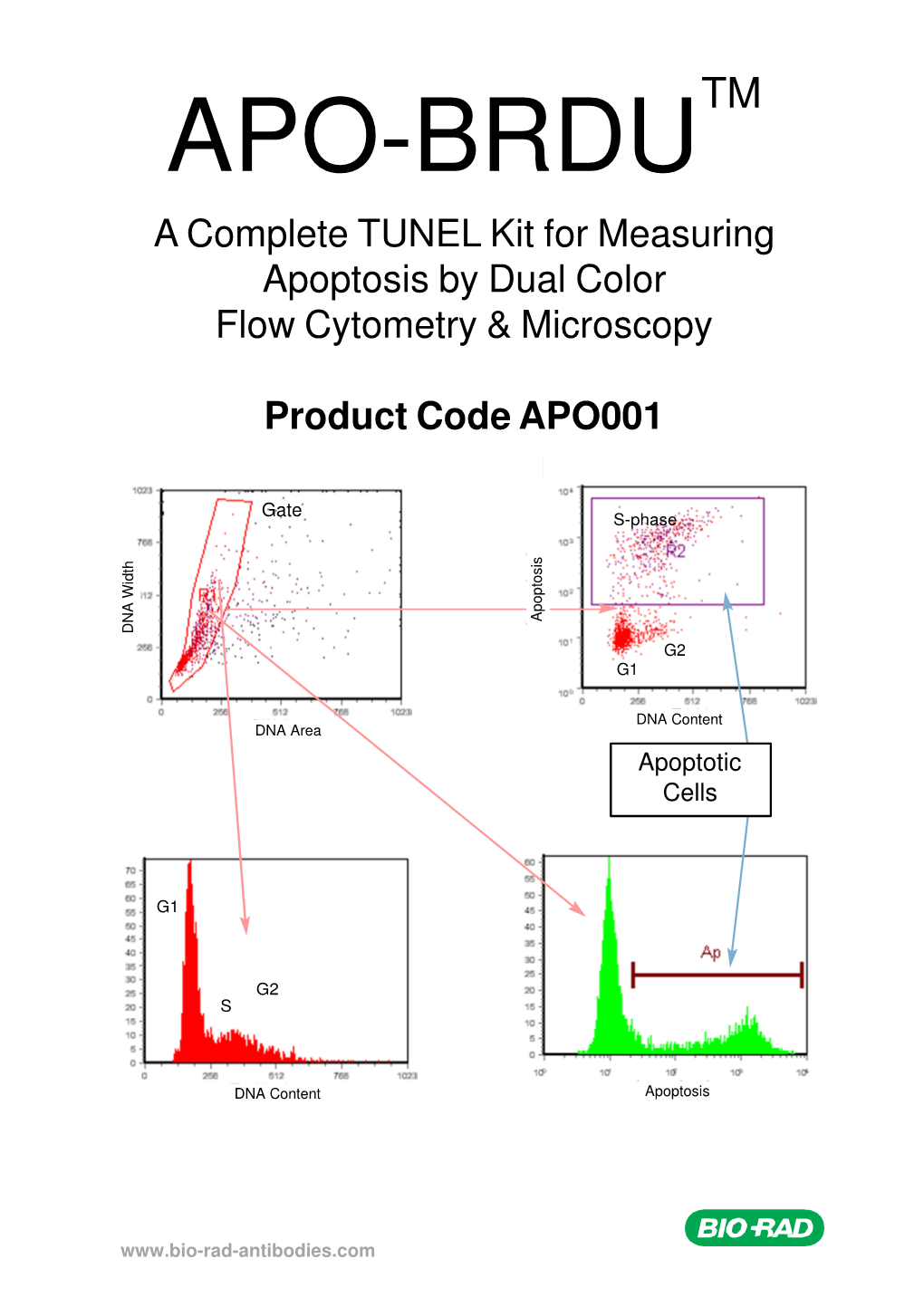
APO-BRDU TM a Complete TUNEL Kit for Measuring Apoptosis by Dual Color Flow Cytometry & Microscopy
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

APO-Brdu™ TUNEL Assay Kit Catalog No
USER GUIDE APO-BrdU™ TUNEL Assay Kit Catalog No. A23210 Pub. No. MAN0002269 Rev. A.0 Table 1. Contents and storage Material Amount Storage* Stability A35125 APO-BrdU™ TUNEL Assay Kit ≤–20°C Components Positive control cells (Component A, brown cap), fixed 5 mL human lymphoma cell line† Negative control cells (Component B, white cap), fixed When stored as directed † 5 mL human lymphoma cell line • –20°C the kit components Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (Component C, • Protect from light are stable for at least 45 µL yellow cap) 3 months. 5-Bromo-2’-deoxyuridine 5’-triphosphate (BrdUTP) 480 µL (Component D, violet cap) A35126 APO-BrdU™ TUNEL Assay Kit 2–6°C Components Anti-BrdU mouse monoclonal antibody PRB-1, Alexa 350 µL Fluor 488 conjugate (Component E, orange cap)‡ Propidium iodide/RNase A staining buffer (Component F, When stored as directed 30 mL • 2–6°C amber bottle) the kit components • Protect from light are stable for at least Reaction buffer (Component G, green cap)§ 0.6 mL • DO NOT FREEZE 3 months. Wash buffer (Component H, blue cap)‡ 120 mL Rinse buffer (Component I, red cap)‡ 120 mL *Each module can be stored under the conditions listed. For optimal storage conditions of individual components, refer to the labels on the vials. †The positive and negative control cells are suspensions of 1 × 106–2 × 106 cells/mL in 70% ethanol. ‡The antibody, wash buffer, and rinse buffer each contain 0.05% sodium azide as a preservative. Handle these materials with care. §The reaction buffer contains ≥0.2% cacodylic acid (dimethylarsenic) as a buffer. -

PDF Hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/170951 Please be advised that this information was generated on 2021-09-26 and may be subject to change. COLLECTION REVIEW Measuring Sperm DNA Fragmentation and Clinical Outcomes of Medically Assisted Reproduction: A Systematic Review and Meta- Analysis Maartje Cissen1, Madelon van Wely2*, Irma Scholten2, Steven Mansell3, Jan Peter de Bruin1, Ben Willem Mol4, Didi Braat5, Sjoerd Repping2, Geert Hamer2 1 Department of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, Jeroen Bosch Hospital, `s-Hertogenbosch, The Netherlands, 2 Center for Reproductive Medicine, Academic Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 3 Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California, Berkeley, California, United States of America, 4 The Robinson Institute/School of Paediatrics and Reproductive Health, University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, 5 Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, The Netherlands a11111 * [email protected] Abstract Sperm DNA fragmentation has been associated with reduced fertilization rates, embryo OPEN ACCESS quality, pregnancy rates and increased miscarriage rates. Various methods exist to test Citation: Cissen M, Wely Mv, Scholten I, Mansell sperm DNA fragmentation such as the sperm chromatin structure assay (SCSA), the sperm S, Bruin JPd, Mol BW, et al. (2016) Measuring chromatin dispersion (SCD) test, the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated deox- Sperm DNA Fragmentation and Clinical Outcomes yuridine triphosphate nick end labelling (TUNEL) assay and the single cell gel electrophore- of Medically Assisted Reproduction: A Systematic sis (Comet) assay. -

Radiation-Induced Double Strand Breaks and Subsequent Apoptotic DNA Fragmentation in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE 29: 769-780, 2012 Radiation-induced double strand breaks and subsequent apoptotic DNA fragmentation in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells MYRIAM GHARDI1, MARJAN MOREELS1, BERNARD CHATELAIN2, CHRISTIAN CHATELAIN2 and SARAH BAATOUT1 1Radiobiology Unit, Molecular and Cellular Biology, Belgian Nuclear Research Centre, 2 SCK•CEN, B-2400 Mol; Laboratory of Experimental Hematology and Oncology, UCL Mont-Godinne University Hospital, B-5530 Yvoir, Belgium Received September 29, 2011; Accepted November 2, 2011 DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.907 Abstract. In case of accidental radiation exposure or a nuclear apoptotic DNA fragmentation increased in a dose-dependent incident, physical dosimetry is not always complete. Therefore, manner. In conclusion, DNA DSBs and subsequent apoptotic it is important to develop tools that allow dose estimates and DNA fragmentation monitoring have potential as biomarkers determination that are based on biological markers of radiation for assessing human exposure in radiation biodosimetry. exposure. Exposure to ionizing radiation triggers a large-scale activation of specific DNA signaling and repair mechanisms. Introduction This includes the phosphorylation of γH2AX in the vicinity of a double-strand break (DSB). A DNA DSB is a cytotoxic The most critical lesion induced by ionizing radiation is form of DNA damage, and if not correctly repaired can initiate the interruption of genome integrity by DNA double-strand genomic instability, chromosome aberrations, mutations or breaks (DSBs), which represents potentially lethal damage apoptosis. Measurements of DNA DSBs and their subsequent to the cell (1-4). In response to DSB generation, histone repair after in vitro irradiation has been suggested to be of H2AX, a subfamily of histone H2A, is rapidly phosphorylated potential use to monitor cellular responses. -

TUNEL Two-Color Apoptosis Detection Kit Cat. No. L00429 (TRITC-Labeled, for Flow Cytometry)
TUNEL Two-Color Apoptosis Detection Kit Cat. No. L00429 (TRITC-labeled, for Flow Cytometry) Technical Manual No. TM0265 Version 03102011 I Description ………………………………………………………………. ………………… 1 II Key Features ……………………………………………………………. ……………….. 1 III Kit Contents ………………………………………………………. ……………………… 1 IV Storage..……………………………………………………………………………………… 2 V Protocol ……………………………………………….……………………………………. 2 VI Related Products…………………………………………………………………………… 5 VII Troubleshooting …….………………………………………………………………...……. 5 VIII Ordering Information….……………………………………………………………..…….. 6 I. DESCRIPTION TUNEL Two-Color Apoptosis Detection Kit (TRITC-labeled, for Flow Cytometry ) (Cat. No. L00429) is used for the fast detection of fragmented DNA in the nucleus during apoptosis. In this modified TUNEL assay kit, fluorescein-labeled nucleotides binds with the DNA 3´-OH ends using natural or recombinant terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT or rTdT). The fluorescence could be detectd by Flow Cytometry. II. KEY FECTURES Simplified Procedure: The kit contains ready-to-use reagents. Enhanced Sensitivity: This kit can assay the cells during the early stages of apoptosis. Enhanced Specificity: The kit can stain apoptotic cells. Streamlined Process: The entire procedure takes about 3 hours. High Veracity: The kit contains positive control reagent. III. KIT CONTENTS The TUNEL Apoptosis Detection Kit is available. L00429 is for detection using fluorescein Labeled nucleotides (TRITC-5-dUTP). Cat. No.L00429 Cat. No.L00429 Cat. No. L00429 Components 20 Assays 50 Assays 100 Assays Storage Conditions Equilibration Buffer 1 ml 2.5 ml 5.0 ml -20°C TRITC-5-dUTP 20 µl 50 µl 100 µl -20°C TdT 80 µl 200 µl 400 µl -20°C DAPI/RNase Buffer 10 ml 25 ml 50 ml -20°C DNase I (50 U/µl) 0.2 ml 0.5 ml 1 ml -20°C 1X DNase I buffer 0.2 ml 0.5 ml 1 ml 4°C Note: Controls are not provided with kit IV. -

Laboratory Evaluation of Sperm Chromatin: TUNEL Assay
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/251406945 Laboratory Evaluation of Sperm Chromatin: TUNEL Assay Article · January 2014 DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4419-6857-9_14 CITATIONS READS 5 1,361 2 authors: Rakesh K Sharma Ashok Agarwal Cleveland Clinic Cleveland Clinic 458 PUBLICATIONS 10,148 CITATIONS 1,829 PUBLICATIONS 31,891 CITATIONS SEE PROFILE SEE PROFILE Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects: SDF testing View project Research Profile View project All content following this page was uploaded by Ashok Agarwal on 27 January 2014. The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file. Laboratory Evaluation of Sperm Chromatin: TUNEL Assay 14 Rakesh Sharma and Ashok Agarwal Abstract Routine semen analysis is unable to assess alterations in sperm chromatin organization such as DNA damage. Because fertility is based not only on the absolute number of spermatozoa but also on their functional capability, methods for exploring sperm DNA stability and integrity are being used to evaluate fertility disorders. A large number of direct and indirect tests that measure sperm DNA damage have been developed. This chapter focuses on one of those tests – the terminal deoxytransferase mediated deoxyuri- dine triphosphate (dUTP) nick end-labeling or TUNEL assay – which is increasingly being used in many laboratories. Keywords 3PERMCHROMATINs45.%,ASSAYs3EMENANALYSISs,ABORATORYEVALUATION OFSPERMCHROMATINs4ERMINALDEOXYTRANSFERASEMEDIATEDDEOXYURIDINE triphosphate assay One of the possible causes of infertility in men terminal deoxytransferase mediated deoxyuri- with normal semen parameters is abnormal sperm dine triphosphate (dUTP) nick end-labeling DNA. Fortunately, a number of sperm function assay, which is otherwise called TUNEL. -

APO-Brdu™ TUNEL Assay Kit
APO-BrdU™ TUNEL Assay Kit Table 1. Contents and storage information. Material Amount Storage* Stability A35125 APO-BrdU™ TUNEL Assay Kit (A23210) ≤–20°C Components Positive control cells (Component A, brown cap), fixed human 5 mL lymphoma cell line† Negative control cells (Component B, white cap), fixed human 5 mL When stored as directed lymphoma cell line† • –20˚C the kit components Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (Component C, yellow • Protect from light are stable for at least 3 45 µL cap) months. 5-Bromo-2’-deoxyuridine 5’-triphosphate (BrdUTP) 480 µL (Component D, violet cap) A35126 APO-BrdU™ TUNEL Assay Kit (A23210) 2-6°C Components Anti-BrdU mouse monoclonal antibody PRB-1, Alexa 350 µL Fluor 488 conjugate (Component E, orange cap)‡ Propidium iodide/RNase A staining buffer (Component F, When stored as directed 30 mL • 2–6˚C amber bottle) the kit components • Protect from light are stable for at least 3 Reaction buffer (Component G, green cap)§ 0.6 mL • DO NOT FREEZE months. Wash buffer (Component H, blue cap)‡ 120 mL Rinse buffer (Component I, red cap)‡ 120 mL *Each module can be stored under the conditions listed. For optimal storage conditions of individual components, refer to the labels on the vials. †The positive and negative control cells are suspensions of 1–2 × 106 cells/mL in 70% ethanol. ‡The antibody, wash buffer, and rinse buffer each contain 0.05% sodium azide as a preservative. Handle these materials with care. §The reaction buffer contains ≥0.2% cacodylic acid (dimethylarsenic) as a buffer. Handle this material with care. -

Measures of Cell Turnover (Proliferation and Apoptosis) and Their Association with Survival in Breast Cancer1
1716 Vol. 7, 1716–1723, June 2001 Clinical Cancer Research Measures of Cell Turnover (Proliferation and Apoptosis) and Their Association with Survival in Breast Cancer1 Shuqing Liu, Susan M. Edgerton, INTRODUCTION Dan H. Moore II, and Ann D. Thor2 Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is an active process Research Institute, Evanston Northwestern Healthcare, Evanston, controlled by inducers and repressors (1, 2). The balance be- Illinois 60201 [S. L., S. M. E.]; Geraldine Brush Cancer Research tween these stimuli determines whether the cell enters prolifer- Institute of the California Pacific Medical Center, San Francisco, ation or apoptotic pathways (1). An imbalance between cell California 94115 [D. H. M.]; and Departments of Pathology and proliferation and apoptosis may contribute to tumorigenesis and Surgery, Evanston Northwestern Healthcare and Northwestern tumor progression (3, 4). Apoptosis is morphologically charac- University Medical School, Evanston, Illinois 60201 [A. D. T.] terized by nuclear condensation and cytoplasmic shrinkage. Nuclear fragments and cell-surface protuberances then separate ABSTRACT to produce apoptotic bodies that are visible microscopically. The distinct morphological features of apoptosis allow semiquanti- Our objective was to investigate the prognostic signifi- tative apoptotic body assessment using routinely processed and cance of cell turnover (apoptosis and proliferation) in breast stained histology slides (5–7). This assessment is similar to cancer patients. Apoptosis was microscopically quantitated -

Flow Cytometry of Apoptosis UNIT 18.8
Flow Cytometry of Apoptosis UNIT 18.8 This unit describes the most common methods applicable to flow cytometry that make it possible to: (1) identify and quantify dead or dying cells, (2) reveal a mode of cell death (apoptosis or necrosis), and (3) study mechanisms involved in cell death. Gross changes in cell morphology and chromatin condensation, which occur during apoptosis, can be detected by analysis with laser light beam scattering. An early event of apoptosis, dissipation of the mitochondrial transmembrane potential, can be measured using a number of fluorochromes that are sensitive to the electrochemical potential within this organelle (see Basic Protocol 1). Another early event of apoptosis, caspase activation, can be measured either directly, by immunocytochemical detection of the epitope that characterizes activated caspase (see Basic Protocol 2), or indirectly by immunocyto- chemical detection of the caspase-3 cleavage product, the p85 fragment of poly(ADP-ri- bose) polymerase (see Basic Protocol 4). Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the exterior surface of the plasma membrane can be detected by the binding of fluoresceinated annexin V (annexin V–FITC); this assay is combined with analysis of the exclusion of the plasma membrane integrity probe propidium iodide (PI; see Basic Protocol 5). Also described are methods of analysis of DNA fragmentation based either on DNA content of cells with fractional (sub-G1) DNA content (see Basic Protocol 6 and Alternate Protocol 1) or by DNA strand-break labeling (Terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase–mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling, TUNEL; or In Situ End Labeling, ISEL; see Basic Protocol 7). Still another hallmark of apoptosis is the activation of tissue transglutaminase (TGase), the enzyme that cross-links protein and thereby makes them less immunogenic. -

Identifying and Quantifying Apoptosis: Navigating Technical Pitfalls Megan M
Identifying and Quantifying Apoptosis: Navigating Technical Pitfalls Megan M. Garrity, B.S., Lawrence J. Burgart, M.D., Darren L. Riehle, B.A., C.T., Eunice M. Hill, B.S., C.T., Thomas J. Sebo, M.D., Ph.D., Thomas Witzig, M.D. Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology (MMG, LJB, DLR, EMH, TJS) and Department of Internal Medicine (TW), Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota KEY WORDS: Apoptosis, Digital image analysis, Im- Apoptosis or programmed cell death is often age morphometry, Necrosis, TUNEL assay. altered in malignancies and is frequently deter- Mod Pathol 2003;16(4):389–394 mined by the terminal transferase–mediated nick end labeling technique (TUNEL). However, Apoptosis is a physiologic form of cell death that commercially available protocols can produce serves as one aspect of tissue growth and size reg- high background and false-positive staining, ulation (1). The inhibition of apoptosis is believed which renders the distinction between apopto- to play a role in carcinogenesis in one of two ways: sis and necrosis difficult. In an attempt to de- (1) it may allow for the unchecked accumulation of velop a rapid and reproducible method for de- genetic alterations (2, 3) and (2) it may lead to tecting and quantifying apoptosis, we coupled unbalanced proliferation of tumor (4). As such, it optimization of the Apoptag Plus Peroxidase In has become an area of intense interest in oncologic Situ Apoptosis Detection kit with quantitative research. histomorphometric computer imaging software The morphologic criteria for identifying cells un- using the Bacus Laboratories Incorporated Slide dergoing apoptosis are well established and include Scanner (BLISS). -

Product Information
3159 Corporate Place Hayward, CA 94545 Glowing Products for ScienceTM www.biotium.com Revised: June 24, 2013 Product Information CF™640R TUNEL Assay Apoptosis Detection Kit a) Optional: include an extra sample to perform a negative control TUNEL reaction without TdT enzyme. Catalog Number: 30074 b) Wash cells or sections twice in PBS. Unit Size: 50 reactions c) Fix cells or tissues in 4% formaldehyde in PBS (pH 7.4) for 30 minutes at 4ºC (not required for fixed-frozen sections) Kit Contents e) Optional: store cells in 70% ethanol at -20ºC for up to two weeks, proceed Component 99965: TUNEL Equilibration Buffer, 5 mL to (f). Component 30074A: (light blue cap): TUNEL Reaction Buffer, 5 x 0.5 mL Component 99964: (white cap): TdT Enzyme, 50 uL d) Wash twice in PBS. e) Permeabilize in PBS containing 0.2% Triton X-100 for 30 minutes at room Storage and Handling temperature. Store CF™640R TUNEL Assay Kit at -20ºC. Protect TUNEL Reaction Buffer from light. Avoid subjecting TUNEL Reaction Buffer to multiple freeze/thaw cycles. TdT f) Wash twice in PBS. Enzyme is a 50% glycerol stock and will not freeze at -20ºC; keep TdT Enzyme 2.2 Preparation of paraffin tissue sections on ice during use. When stored as directed, the kit should be stable for at least 6 months from the date it is received. a) Optional: include an extra sample to perform negative control (no TdT enzyme) TUNEL labeling. CAUTION: TUNEL Equilibration Buffer and TUNEL Reaction Buffer contain b) Deparaffinize and rehydrate sections according to standard protocols. -

Click-It™ Plus TUNEL Assay for in Situ Apoptosis Detection with Alexa Fluor™ Dyes
USER GUIDE Click-iT™ Plus TUNEL Assay for in situ apoptosis detection with Alexa Fluor™ dyes Catalog Nos. C10617, C10618, C10619 Pub. No. MAN0010877 Rev. B.0 Table 1. Contents and storage Catalog No. Material Concentration Storage* C10617 C10618 C10619 TdT Reaction Buffer 8.0 mL 8.0 mL 8.0 mL 1X Solution (Component A) EdUTP nucleotide mixture 55 µL 55 µL 55 µL 50X Solution (Component B) TdT (terminal deoxynucleotidyl 3 vials (34 µL 3 vials (34 µL 3 vials (34 µL 15 U/μL in transferase) *recombinant* per vial) per vial) per vial) glycerol (Component C) Click-iT™ Plus TUNEL 10X Solution Reaction Buffer, 10X 500 µL 500 µL 500 µL in Tris-buffered (Component D) saline • ≤–20°C • Protect from ™ Click-iT Plus TUNEL light Reaction Buffer Additive 400 mg 400 mg 400 mg NA (Component E) Copper protectant (Component F) 100 µL 100 µL 100 µL NA 1 vial of 1 vial of 1 vial of Alexa Fluor™ picolyl azide dye Alexa Fluor™ 488 Alexa Fluor™ 594 Alexa Fluor™ 647 DMSO (Component G) picolyl azide picolyl azide picolyl azide Solution (25 µL) (25 µL) (25 µL) Proteinase K (Component H) 500 µL 500 µL 500 µL 25X Solution *These storage conditions are appropriate when storing the entire kit upon receipt. For optimal storage conditions for each component, see labels on individual components. NA = Not applicable. Number of assays: Sufficient material is supplied for 50 coverslips based on the protocol below. Approximate fluorescence excitation and emission maxima, in nm: Alexa Fluor™ 488 azide: 495/519 nm; Alexa Fluor™ 594 azide: 590/615 nm; Alexa Fluor™ 647 azide: 650/670 nm; Hoechst 33342: 350/461 nm, when bound to DNA. -
TUNEL Assay Kit (FITC Or HRP-DAB)
7th Edition, revised in April, 2019 (FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. DO NOT USE IT IN CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS !) TUNEL Assay Kit (FITC or HRP-DAB) Catalog No: E-CK-A332 Sizes:20 T / 50 T / 100 T Cat. Products 20T 50T 100T Storage E-CK-A332A TdT Equilibration Buffer 1.0 mL 2.5 mL 5.0 mL -20°C E-CK-A332B TdT enzyme 80 μL 200 μL 400 μL -20°C E-CK-A332C Proteinase K (50 ×) 40 μL 100 μL 200 μL -20°C E-CK-A332D fluorescein-dUTP 20 μL 50 μL 100 μL -20°C E-CK-A332E Anti-fluorescein antibody -HRP 10 μL 25 μL 50 μL -20°C E-CK-A332F DAB Concentrate (20 ×) 200 μL 500 μL 1 mL -20°C E-CK-A332G DAB Substrate 4 mL 10 mL 2× 10 mL -20°C Manual One Copy This manual must be read attentively and completely before using this product. If you have any problems, please contact our Technical Service Center for help. Phone: 240-252-7368(USA) Fax: 240-252-7376(USA) Email: [email protected] Website: www.elabscience.com Please kindly provide us the lot number (on the outside of the box) of the kit for more efficient service. Copyright ©2019-2020 Elabscience Biotechnology Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved 7th Edition, revised in April, 2019 Introduction: Elabscience® TUNEL Apoptosis Assay Kit is a highly sensitive, rapid and simple method for cell apoptosis detection. The result can be detected by fluorescence microscopy or ordinary optical microscopy. This kit is developed to detect tissue (Paraffin embedding, freezing and ultrathin section) and cells (Cell smears, cell climbing smears) in situ apoptotic detection.