Encor Biotechnology Inc
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Catalogue# Prot-Ra-Int: Purified Recombinant
4949 SW 41st Blvd. Suites 40 & 50 Gainesville, FL 32608 Tel: (352) 372 7022 Fax: (352) 372 7066 [email protected] Catalogue# Prot-r-a-Int: Purified recombinant human α-internexin Background: Neurofilaments are the 10 nm or intermediate filament proteins found specifically in neurons, and are composed predominantly of four major proteins called NF-L, NF-M, NF-H and α- internexin (1,2). α-internexin is the lowest molecular weight major neurofilament subunit and runs on SDS-PAGE gels at about 66 kDa, with some variability between species. Antibodies to α-internexin are useful for identifying neuronal cells and their processes in tissue sections and in tissue culture. Some neurons express only α-internexin and no other neurofilament subunit and α-internexin is expressed earlier in development than the other neurofilament subunits (1,2). Antibodies to α-internexin can also be useful in the diagnostics of neurofilament accumulations seen in certain neurological diseases, such as neurofilament inclusion body disease (3). Figure: Coomassie brilliant blue stained SDS- PAGE gel of various recombinant proteins. His- tagged full length human α-internexin, was expressed and purified from E. coli BL21 using immobilized metal affinity chromatography. 1μg of pure protein was run on each lane. The lane indicated with “α-int” contains the α-internexin protein. The other lanes show recombinant His- tagged peripherin (Peri), vimentin (Vim) and neurofilament NF-L (NF-L) as indicated. Protein molecular weight standards are in the first lane and apparent molecular weights are as indicated. Protein Characteristics: A cDNA encoding full length human α-internexin was inserted into an eukaryotic expression vector which adds an N-terminal in frame His-tag. -

Encor Biotechnology Inc
4949 SW 41st Blvd. Suites 40 & 50 Gainesville, FL 32608 Tel: (352) 372 7022 Fax: (352) 372 7066 [email protected] Catalogue RPCA-a-Int: Polyclonal Antibody to α-Internexin/NF66 The Immunogen: α-internexin is a Class IV intermediate filament originally discovered as it copurifies with other neurofilament subunits (1). α-internexin is related to but distinct from the better known neurofilament triplet proteins, NF-L, NF-M and NF-H, having similar protein sequence motifs and a similar intron organization. It is expressed only in neurons and in large amounts early in neuronal development, but is down-regulated in many neurons as development proceeds. On SDS-PAGE gels it runs with an apparent molecular weight of 64 to 66 kDa, with some species variability, although the real molecular weight is about 55 kDa. As with other neurofilament subunits the presence of highly negatively charged sequences results in reduction of SDS-PAGE mobility. Many classes of mature neurons contain α-internexin in addition to NF-L, NF-M and NF-H. In some mature neurons α-internexin is the only neurofilament subunit expressed. Antibodies to α-internexin are therefore unique probes to study and classify neuronal types and follow their processes in sections and in tissue culture. In addition the very early developmental expression of α-internexin means its presence is an early and convenient diagnostic feature of neuronal progenitors cells and other cell committed to the neuronal lineage. In addition recent studies show a marked up-regulation of α-internexin during neuronal regeneration (2). The use of antibodies to this protein in the study of brain tumors has not been examined to date, but is likely to be of interest. -

Neurofilament Proteins As Body Fluid Biomarkers of Neurodegeneration
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Multiple Sclerosis International Volume 2011, Article ID 315406, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2011/315406 Review Article Neurofilament Proteins as Body Fluid Biomarkers of Neurodegeneration in Multiple Sclerosis Melissa M. Gresle,1, 2 Helmut Butzkueven,1, 2 and Gerry Shaw3, 4 1 Department of Medicine, University of Melbourne, Parkville, Victoria 3010, Australia 2 Florey Neuroscience Institutes, Howard Florey Institute, Parkville, Victoria 3010, Australia 3 Department of Neuroscience, McKnight Brain Institute, University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, FL 32610, USA 4 EnCor Biotechnology Inc., Suite 40, 4949 SW 41st Boulevard, Gainesville, FL 32608, USA Correspondence should be addressed to Melissa M. Gresle, [email protected] Received 2 December 2010; Accepted 23 December 2010 Academic Editor: Axel Petzold Copyright © 2011 Melissa M. Gresle et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Biomarkers of axonal degeneration have the potential to improve our capacity to predict and monitor neurological outcome in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients. Neurofilament proteins, one of the major proteins expressed within neurons and axons, have been detected in cerebrospinal fluid and blood samples from MS patients and are now being actively investigated for their utility as prognostic indicators of disease progression in MS. In this paper, we summarize the current literature on neurofilament structure, assembly, and degeneration and discuss their potential utility as biomarkers for monitoring neurological decline in MS. We also discuss the need to further develop sensitive methods for assaying neurofilaments in blood to improve clinical applicability. -

Encor Biotechnology Inc
4949 SW 41st Blvd. Suites 40 & 50 Gainesville, FL 32608 Tel: (352) 372 7022 Fax: (352) 372 7066 [email protected] Catalogue# MCA-38F3: Monoclonal Antibody 38F3 to Fibrillarin/Nop1p The Immunogen: Nop1p was originally identified as a nucleolar protein of bakers yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (accession P15646). The Nop1p protein is 327 amino acids in size (34.5kDa), is essential for yeast viability, and is localized in the nucleoli (1). The systematic name for S. cerevisiae Nop1 is YDL014W, and it is now known to be part of the small subunit processome complex, involved in the processing of pre-18S ribosomal RNA. Nop1p is the yeast homologue of a protein apparently found in all eukaryotes and archea generally called fibrillarin. Fibrillarin/Nop1p is extraordinarily conserved, so that the yeast and human proteins are 67% identical, and the human protein can functionally replace the yeast protein. This means that suitably cross-reactive antibodies to Nop1p/fibrillarin, like MCA-38F3, can be used to reveal nucleoli and study fibrillarin/Nop1p in all eukaryotes and archea tested to date. Human fibrillarin has been characterized (accession P22087) and the human fibrillarin gene is located on chromosome 19 (19q13.1). Fibrillarin/Nop1p proteins have been cloned and sequenced from several other species (e.g. Mouse, accession P35550, Xenopus accession P22232, C. elegans accession Q22053, and S. pombe accession P35551. The N terminal ~80 amino acids contain multiple copies based on the peptide RGG, or arginine-glycine-glycine, sometimes referred to as GAR repeats, characteristic of the GAR family of molecules. The remaining ~240 amino acids consist of the so called fibrillarin domain. -

Encor Biotechnology Inc
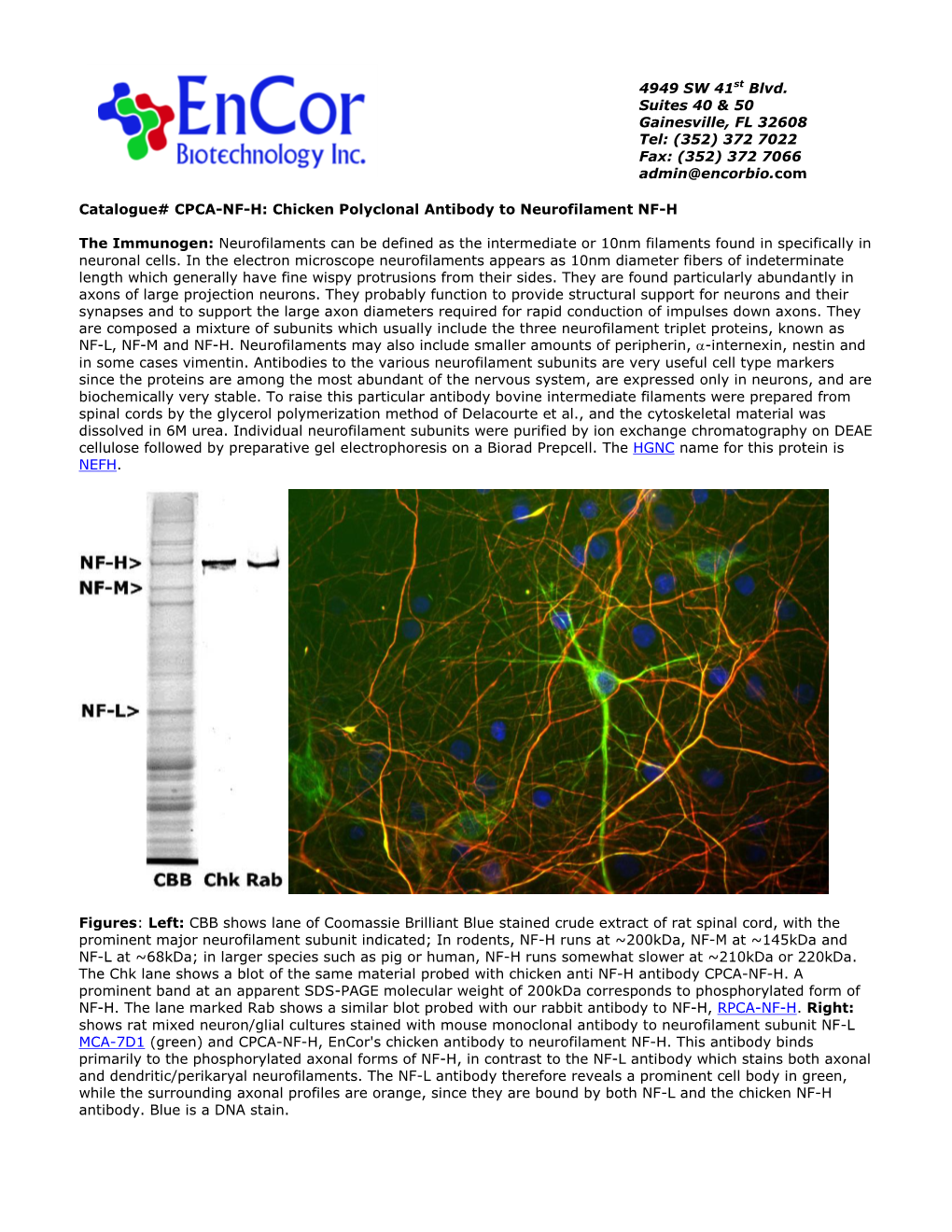
4949 SW 41st Blvd. Suites 40 & 50 Gainesville, FL 32608 Tel: (352) 372 7022 Fax: (352) 372 7066 [email protected] Catalogue# Prot-m-NF-H-bov: Purified Bovine Neurofilament Heavy Chain Background: Neurofilaments are the 10 nm or intermediate filament proteins found specifically in neurons, and are composed predominantly of four major proteins called NF-L, NF-M, NF-H and α-internexin (1). NF-H is the neurofilament heavy or high molecular weight polypeptide and runs on SDS-PAGE gels at 200-220kDa in the heavily phosphorylated axonal form. The molecule has an unusual and interesting region consisting of multiple Lysine-Serine-Proline peptides, about 40 of these in human. These peptide repeats are heavily phosphorylated on the Serine residues in axons. Enzymatic removal of these phosphate groups will increase the SDS-PAGE mobility to about 160kDa, likely due to protein conformational changes due to the removal of charge (2). Even the non-phosphorylated form runs aberrantly on SDS-PAGE, as the real molecular weight of NF-H is about 110kDa, with some variation in different species. This is likely due to an unusually high content of charged amino acids. Non-phosphorylated forms of NF-H are found in dendrites and perikarya and early in development, but the majority of NF- H in the adult is this heavily phosphorylated axonal form. Our preparation was isolated from cow spinal cord using a modification of the method of Leung and Liem (3), which purifies out the heavily phosphorylated axonal form, often referred to as pNF-H. The HGNC name for this protein is NEFH. -

Encor Biotechnology Inc
4949 SW 41st Blvd. Suites 40 & 50 Gainesville, FL 32608 Tel: (352) 372 7022 Fax: (352) 372 7066 [email protected] Catalogue# CPCA-mCherry: Chicken Polyclonal Antibody to mCherry The Immunogen: mCherry is derived from proteins originally isolated from Cnidarians (jelly fish, sea anemones and corals), and is used as a fluorescent tracer in transfection and transgenic experiments. The prototype for these fluorescent proteins is Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP), which is a ~27 kDa protein isolated originally from the jellyfish Aequoria victoria. GFP was the basis of the 2008 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, awarded to Osamu Shimomura, Martin Chalfie and Roger Tsien, specifically “for the discovery and development of the green fluorescent protein, GFP”. GFP was shown to fluoresce on contact with molecular oxygen, requiring no other cofactors, and so can be expressed in fluorescent form in essentially any prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell. The mCherry protein is derived from DsRed, a red fluorescent protein from so-called disc corals of the genus Discosoma. DsRed is similar in size and properties to GFP, but, obviously, produces a red rather than a green fluorochrome. The original DsRed was engineered extensively in the Tsien lab to prevent it from forming tetramers and dimers and to modify and improve the spectral properties (1-3). Several further cycles of mutation, directed modification and evolutionary selection produced mCherry, which has an excitation maximum at 587 nm and and emission maximum at 610 nm (4). We expressed the mCherry protein sequence shown in reference 4 in bacteria, purified out the mCherry and raised a rabbit polyclonal antibody. -

Encor Biotechnology Inc
4949 SW 41st Blvd. Suites 40 & 50 Gainesville, FL 32608 Tel: (352) 372 7022 Fax: (352) 372 7066 [email protected] Catalogue# CPCA-MAP2: Chicken Polyclonal Antibody to Microtubule associated protein 2 (MAP2) Lot 7225-4 The Immunogen: Microtubules are 25nm diameter protein rods found in most kinds of eukaryotic cells. They are polymerized from a dimeric subunit made of one a subunit and one b tubulin subunit. Microtubules are associated with a family of proteins called microtubule associated proteins (MAPs), which includes the protein t (tau) and a group of proteins referred to as MAP1, MAP2, MAP3, MAP4 and MAP5. MAP2 is made up of two ~280 kDa apparent molecular weight bands referred to as MAP2a and MAP2b. Lower molecular weight forms, usually called MAP2c and MAP2d corresponds to a pair of protein bands running at ~70 kDa on SDS-PAGE gels. All these MAP2 forms are derived from a single gene by alternate transcription, and all share a C-terminal sequence which includes either three or four microtubule binding peptide sequences, which are very similar to those found in the related microtubule binding protein t (tau). MAP2 isoforms are expressed only in neuronal cells and specifically in the perikarya and dendrites of these cells. Antibodies to MAP2 are therefore excellent markers on neuronal cells, their perikarya and neuronal dendrites. In contrast t (tau) is found predominantly in neuronal axons. The immunogen for this antibody is comprised of three peptide constructs spanning the projection domain of MAP2 (aa 377-1505), specifically our products Prot-r- MAP2-P1, Prot-r-MAP2-P2 and Prot-r-MAP2-P3. -

Encor Biotechnology Inc
4949 SW 41st Blvd. Suites 40 & 50 Gainesville, FL 32608 Tel: (352) 372 7022 Fax: (352) 372 7066 [email protected] Catalogue RPCA-FOX3: Rabbit polyclonal antibody to FOX3/NeuN: RBFOX3 The Immunogen: Fox3 is one of a family of mammalian homologues of Fox-1, which was originally discovered in C. elegans as a gene involved in sex determination. Fox is an acronym of "Feminizing locus on X". The mammalian genome contains three genes homologous to C. elegans Fox-1, called Fox1, Fox2 and Fox3. The Fox-1 protein and mammalian homologues are all about 46kDa in size, each of which includes a central highly conserved RRM type RNA recognition motif. This motif corresponds to a small ~70 amino acid structure consisting of 4 β-strands and two α-helices. An alternate name for Fox3 is hexaribonucleotide binding protein 3, and these proteins are believed to have a role in the regulation of mRNA splicing. Much interest has focused on Fox3 as a result of the recent finding that this protein corresponds to NeuN, a neuronal nuclear antigen. NeuN was first described in 1994 by Mullen et al. (2), who raised a series of monoclonal antibodies to mouse antigens with the original intent of finding species specific markers. In the event they obtained a clone, called mAb A60, which proved to bind an antigen expressed in neuronal nuclei and to a lesser extent the cytoplasm of neuronal cells, and which appeared to work on all vertebrates. A few neuronal cell types were not recognized by the antibody, such as cerebellar Purkinje cells, olfactory mitral cells and retinal photoreceptors, but no non neuronal cells were recognized. -

Encor Biotechnology Inc
4949 SW 41st Blvd. Suites 40 & 50 Gainesville, FL 32608 Tel: (352) 372 7022 Fax: (352) 372 7066 [email protected] Catalogue# MCA-Ubi-1: Ubiquitin Monoclonal Antibody Ubi-1 The Immunogen: Ubiquitin is a highly conserved globular 76 amino acid protein of about 8.5 kDa molecular weight. It has a important role in the targeting of proteins for proteolytic degradation. Proteins to be degraded are covalently coupled to the C-terminus of ubiquitin by means of ubiquitin ligases. The ubiquitin itself is frequently also ubiquitinated, producing a polyubiquitin chain. The polyubquitinated complex is then recognized by a complex of degradative enzymes which together form the proteosome. Interestingly, ubiquitin also becomes covalently bonded to many types of pathological inclusions seen in serious human disease states which appear to be resistant to normal degradation, so that ubiquitin antibodies are very useful for studies of these inclusions. For example the neurofibrillary tangles and paired helical filaments diagnostic of Alzheimer's disease, the Lewy bodies seen in Parkinson's disease, and Pick bodies found in Pick's disease are all heavily ubiquitinated and can all be readily visualized with ubiquitin antibodies of appropriate specificity. Ubi-1 has become very widely used for such studies. Left: Blots of mono and polyubiquitin (lane 1), monoubiquitin only (2), and 100 μg total wet weight of cerebellum , cortex and brain stem respectively (lane 3-5). Material was run out on 20% SDS-PAGE and transferred electrophoretically to PVDF. Right: MCA-Ubi-1 staining of cerebral cortex of an Alzheimer patient. Neurofibrillary tangles and dystrophic neurites associated with senile plaques stain strongly with this antibody. -

A Study of the Neuronal Injury Biomarkers Pnf-H and UCHL1 in Serum, CSF and Urine in a Cohort Of
bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.02.433405; this version posted March 2, 2021. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder. All rights reserved. No reuse allowed without permission. Adam W. Beck, M.D. A study of the neuronal injury biomarkers pNF-H and UCHL1 in serum, CSF and urine in a cohort of thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR) patients. Beck, Adam1, Marin, Vedrana2,5, Deng, Jay2,6, Madorsky, Irina2, Ren, Bin1, Guo, Yichen1, Neal, Dan3 and Shaw, Gerry2,4. 1Department of Surgery, Division of Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy, University of Alabama at Birmingham, 1808 7th Ave S, Birmingham, AL, 2EnCor Biotechnology Inc., 4949 SW 41st Boulevard Ste 40, Gainesville Florida 32608. 3Department of Biostatistics and 4Department of Neuroscience, University of Florida College of Medicine, 1600 SW Archer Road, Gainesville Florida 32610. Current addresses: 5Shimadzu Scientific Instruments, 7102 Riverwood Drive, Columbia, MD 21046. 6Department of Neurobiology, Duke University School of Medicine, 311 Research Drive, Durham, North Carolina 27710. Corresponding authors for clinical aspects Adam Beck MD ([email protected]) and for scientific aspects Gerry Shaw PhD ([email protected]) 1 bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.02.433405; this version posted March 2, 2021. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder. All rights reserved. No reuse allowed without permission. Adam W. Beck, M.D. Abstract A collection of longitudinal serum, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and urine samples were collected from a cohort of 50 patients undergoing thoracic endovascular aortic repairs (TEVAR). -

Cellular and Structural Neuroscience Markers SMI® Monoclonals and Β-Tubulin Antibodies
Cellular and Structural Neuroscience Markers SMI® Monoclonals and β-Tubulin Antibodies BioLegend is proud to offer SMI® monoclonal antibodies in our class of neuroscience antibody research tools. Originally developed by Dr. Ludwig Sternberger, these antibodies have become the gold standard as neural and glial markers and have an extensive publication history in scientific literature. In addition to our β-Tubulin antibodies, the SMI® product line offers researchers high quality reagents to support investigations into neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Key Features: Rat hippocampus stained with anti-GFAP (red) and anti-NF-H (822601 green). Photo courtesy of Molecular Expressions. • Antibodies specific for phosphorylated and non- phosphorlylated neurofilaments, myelin basic proteins, and GFAP. • Excellent selection of specificities for oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, and other glial cells. • Each high quality antibody is quality tested for specific, robust, and consistent performance. • Experienced technical support staff and in-house generated evaluation data. Rat cortical neurons and glia in mixed tissue culture stained with anti- NF-H (red) and GFAP (green, 840001). The nuclei are stained with Hoescht dye (blue). Photo courtesy of EnCor Biotechnology Inc. To explore the full line of products, visit: Human brain section stained with anti-GFAP (brown, 837201), counterstained with Hematoxylin (blue). biolegend.com/neuroscience_products Toll-Free Tel: (US & Canada): 1.877.BIOLEGEND (246.5343) Tel: 858.768.5800 biolegend.com 07-0092-01 World-Class Quality | Superior Customer Support | Outstanding Value Cellular and Structural Neuroscience Markers Phosphorylated Neurofilaments Non-Phosphorylated Neurofilaments Specificity Clone Reactivity Application(s) Cat. No. Specificity Clone Reactivity Application(s) Cat. No. -

Targeted Complement Inhibition at Synapses Prevents Microglial Synaptic Engulfment and Synapse Loss in Demyelinating Disease
Article Targeted Complement Inhibition at Synapses Prevents Microglial Synaptic Engulfment and Synapse Loss in Demyelinating Disease Graphical Abstract Authors Sebastian Werneburg, Jonathan Jung, Rejani B. Kunjamma, ..., Brian Popko, Daniel S. Reich, Dorothy P. Schafer Correspondence [email protected] In Brief The mechanisms underlying synaptic changes in multiple sclerosis (MS) remain unclear. Werneburg et al. identify microglia-mediated synapse engulfment and synapse loss in MS patients and multiple MS-relevant animal models. Synapse loss can occur early and prior to other MS-relevant pathology and is associated with synapse-localized complement C3. An AAV approach to inhibit C3 protects synapses and preserves circuit function. Highlights d Microglia engulf and eliminate synapses in the visual thalamus of MS patients d MS-relevant animal models show synapse engulfment and loss occur early in disease d Complement C3, but not C1q, localizes to synapses in demyelinating disease d AAV-Crry inhibits C3 and microglia-mediated synapse loss and preserves function Werneburg et al., 2020, Immunity 52, 167–182 January 14, 2020 ª 2019 Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2019.12.004 Immunity Article Targeted Complement Inhibition at Synapses Prevents Microglial Synaptic Engulfment and Synapse Loss in Demyelinating Disease Sebastian Werneburg,1 Jonathan Jung,1 Rejani B. Kunjamma,2 Seung-Kwon Ha,3 Nicholas J. Luciano,3 Cory M. Willis,4 Guangping Gao,5,6,7 Natalia P. Biscola,8 Leif.A. Havton,8,9 Stephen J. Crocker,4 Brian Popko,2