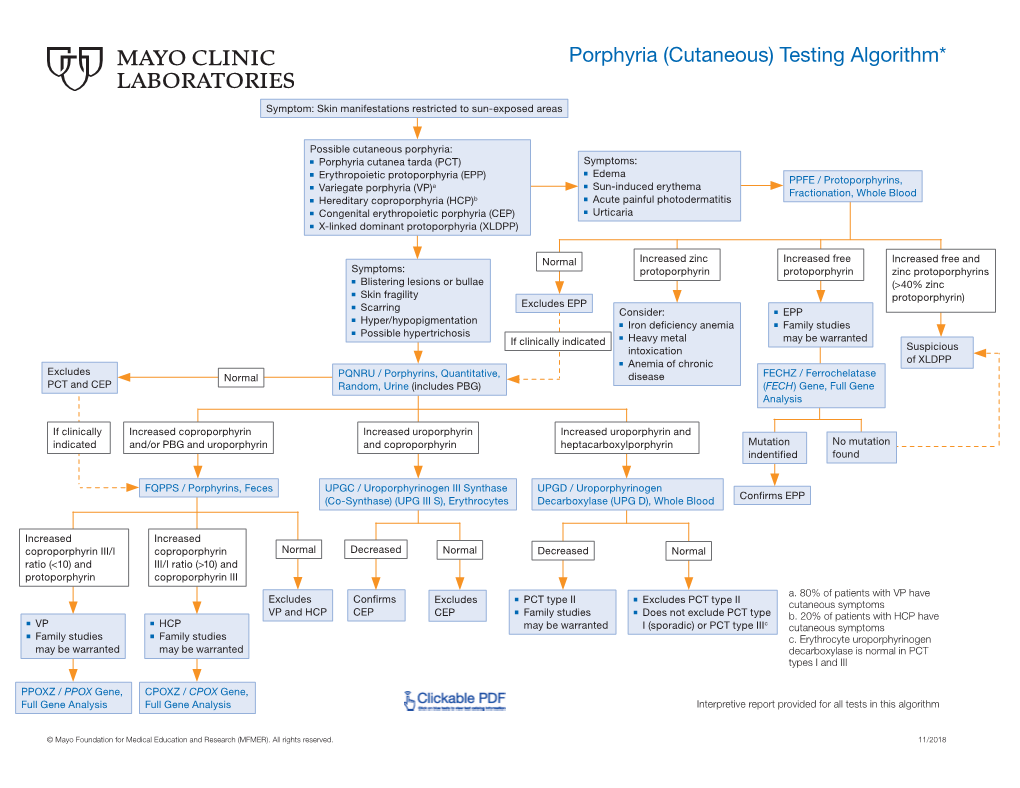
Porphyria (Cutaneous) Testing Algorithm*
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Splenectomy for HIV-Related Immune Thrombocytopenia Comparison with Results of Splenectomy for Non-HIV Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Splenectomy for HIV-Related Immune Thrombocytopenia Comparison With Results of Splenectomy for Non-HIV Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura Reginald V. N. Lord, FRACS; Maxwell J. Coleman, FRACS; Samuel T. Milliken, FRACP Objective: To determine the effectiveness and safety of tomy, with an elevation of the platelet count to greater splenectomy for patients with human immunodefi- than 1003109/L. After a median follow-up of 26.5 months, ciency virus (HIV)–related immune thrombocytopenia, all but 1 patient had a sustained complete remission with using the results of splenectomy for patients with non- no need for medical therapy for thrombocytopenia. Sple- HIV immune thrombocytopenic purpura as a control nectomy was more effective in the HIV-related throm- group for comparison. bocytopenia group than in the non-HIV immune throm- bocytopenic purpura group, with significantly higher Design: Retrospective study. platelet counts at 1 week and 1 month after splenec- tomy in the HIV group (t test, P=.02 and P=.009, respec- Setting: Tertiary care university hospital. tively). There were significantly fewer patients needing medical therapy for thrombocytopenia after splenec- Patients: Fourteen patients who underwent splenec- tomy in the HIV group (x2 test, P=.02). There were no tomy for symptomatic, medically refractory HIV- remarkable short- or long-term complications in the pa- related immune thrombocytopenia at this hospital from tients with HIV infection, including no overwhelming 1988 to 1997. During the same period, 20 patients had postsplenectomy infections. Three patients have died, and splenectomy for treatment of non-HIV immune throm- 2 patients have developed AIDS since operation. bocytopenic purpura. -

Clinical and Biochemical Characteristics and Genotype – Phenotype Correlation in Finnish Variegate Porphyria Patients
European Journal of Human Genetics (2002) 10, 649 – 657 ª 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1018 – 4813/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/ejhg ARTICLE Clinical and biochemical characteristics and genotype – phenotype correlation in Finnish variegate porphyria patients Mikael von und zu Fraunberg*,1, Kaisa Timonen2, Pertti Mustajoki1 and Raili Kauppinen1 1Department of Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, University Central Hospital of Helsinki, Biomedicum Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland; 2Department of Dermatology, University Central Hospital of Helsinki, Biomedicum Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland Variegate porphyria (VP) is an inherited metabolic disease resulting from the partial deficiency of protoporphyrinogen oxidase, the penultimate enzyme in the heme biosynthetic pathway. We have evaluated the clinical and biochemical outcome of 103 Finnish VP patients diagnosed between 1966 and 2001. Fifty-two per cent of patients had experienced clinical symptoms: 40% had photosensitivity, 27% acute attacks and 14% both manifestations. The proportion of patients with acute attacks has decreased dramatically from 38 to 14% in patients diagnosed before and after 1980, whereas the prevalence of skin symptoms had decreased only subtly from 45 to 34%. We have studied the correlation between PPOX genotype and clinical outcome of 90 patients with the three most common Finnish mutations I12T, R152C and 338G?C. The patients with the I12T mutation experienced no photosensitivity and acute attacks were rare (8%). Therefore, the occurrence of photosensitivity was lower in the I12T group compared to the R152C group (P=0.001), whereas no significant differences between the R152C and 338G?C groups could be observed. Biochemical abnormalities were significantly milder suggesting a milder form of the disease in patients with the I12T mutation. -

IS IT AIP Symptoms Checker Summary
Acute Intermittent Porphyria: Symptoms, Triggers, and Other Factors Common symptoms of acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) AIP can cause many different symptoms that tend to come and go. When someone with AIP has symptoms, the episode is called an AIP attack. A person may have certain symptoms during one attack but different symptoms during another attack. Severe abdominal pain • Severe abdominal pain is the most common symptom of AIP. More than 85% of people have abdominal pain during AIP attacks. • The pain often lasts for hours or days. • The pain tends to begin slowly and become worse. • The pain tends to be all over and not in one small area. • The pain may start in the chest or back and move to the abdomen. • Pain medicines such as Advil® (ibuprofen) or Tylenol® (acetaminophen) usually don’t help much. This is because the pain is caused by nerves. Nausea or vomiting • Nausea or vomiting is common during AIP attacks. • People with AIP often have nausea or vomiting along with abdominal pain. Constipation • Constipation is common during AIP attacks. • Loss of bladder control may go along with constipation. Dark or reddish urine • Urine that turns reddish or dark over time when exposed to light and air is common during AIP attacks. • The change in urine color is due to certain chemicals in the urine during AIP attacks. Muscle weakness • Muscle weakness is common during AIP attacks. • Muscle weakness usually begins in the arms and often in the shoulders. 1 Common symptoms of AIP (cont.) Pain in the arms, legs, back, chest, neck, or head • Abdominal pain is the most common symptom of AIP. -

Porphyria Cutanea Tarda in a Swedish Population: Risk Factors and Complications
Acta Derm Venereol 2005; 85: 337–341 CLINICAL REPORT Porphyria Cutanea Tarda in a Swedish Population: Risk Factors and Complications Ingrid ROSSMANN-RINGDAHL1 and Rolf OLSSON2 Department of 1Dermatology, and 2Internal Medicine, Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Go¨teborg, Sweden There are varying reports on the prevalence of risk factors identified (Human Gene Mutation database: www. in porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT). We reviewed 84 uwcm.ac.uk/uwcm/mg/hgmd0.html) (2). patientswithPCTinarestricteduptakeareain Additional genetic or non-genetic factors are needed Gothenburg, Sweden and evaluated different potential for overt disease. Known provoking factors are iron, risk factors for the disease and complications. Besides a alcohol, oestrogen and hepatotropic virus infection such thorough medical history, the patients were investigated as hepatitis C virus (HCV), all of which are associated with urinary porphyrin analyses, transferrin saturation, with inhibition of hepatic UROD activity (3–5). Reports ferritin and liver tests. Subsamples of patients were tested from different countries vary widely regarding the for antibodies to hepatitis C virus (n568), haemochroma- importance of different factors for the induction of the tosis gene mutations (n558) and with the oral glucose disease. For example, reports from southern Europe (6, tolerance test (n531). We found a prevalence of about 1 7), Japan (8) and the USA (5, 9) indicate a very great patient with PCT in 10 000 inhabitants. Nineteen (23%) importance of HCV for the phenotypic expression of patients reported heredity for PCT. Identified risk factors PCT, with figures varying between 56% and 85%. This is were alcohol abuse (38% of male patients), oestrogen in contrast to northern France (10), Germany (11), treatment (55% of female patients), anti-hepatitis C virus Czechoslovakia (12) and New Zealand (13), where PCT positivity (29% of male patients), diabetes (17%) or is less often associated with HCV (positivity rates impaired glucose tolerance (45% of tested patients) and varying between 0 and 23%). -

Porphyria: a Difficult Disease to Diagnose by Marelda Abney RN
1 Porphyria: A difficult disease to diagnose By Marelda Abney RN, BSN A Manuscript submitted in partial fulfillment ofthe requirement for the degree Master ofNursing Washington State University Intercollegiate College ofNursing Spokane, Washington July 2003 11 To the faculty ofWashington State University: The members ofthe committee appointed to examine the Intercollegiate College of Nursing research requirements and manuscript of MARELDA MARY ABNEY fmd it satisfactory and recommend that it be accepted. ,~~ 5ctl(.~~v~ Lorna Schumann, PhD, FAANP, ARNP ~~ 2u J:~ AhJ5uv Billie Severtsen, PhD, RN _~-/A~-t~£0 Sheila Masteller, MN, BSN, RN 111 Acknowledgements I would like to thank everyone who has supported me in one way or another in completing my manuscript and fulfilling my dream ofbecoming a family nurse practitioner. My deepest gratitude goes out to those who served on my committee for my clinical project. Dr. Billie Severtsen, committee member, whom I fIrst met in my undergraduate program. She was an inspiration then as she is now, in the ways ofmedical ethics and compassionate care. I have been forttmate to have had her be a part ofmy education from the beginning ofmy career through to the end ofthis project. Sheila Masteller, committee nlember and role model. I have been privileged to work with Sheila at Visiting Nurses Association where she is president and an exemplary leader in home health care. Her concern for the welfare ofpatients and staffhas made her the ideal example of leadership. Lorna Schumann, committee member and mentor. Lorna has always been there for me as I struggled down this path. She has listened when I just needed to talk which is a priceless gift. -

Psoriasis Findings: Causes, Consequences, and Treatments New Data Reveal More Details Concerning the Extent to Which Psoriasis Affects Individuals
Take 5 Psoriasis Findings: Causes, Consequences, and Treatments New data reveal more details concerning the extent to which psoriasis affects individuals. Psoriasis Patients Get Less Sleep.In a 16-week study presented at the 2011 AAD Meeting in New Orleans (P 3341), investigators found that psoriasis patients had an average of 12 minutes less of sleep per night than did individuals without psoriasis, which is about an hour and a half less sleep per week. Why psoriasis patients got less sleep is not fully clear, but it is speculated that itching from psoria- sis causes increased sleep disturbances. Authors also indicated that patients with psoriasis were at a 1 60 percent increased likelihood of snoring. In addition, just 47 percent of patients with psoriasis self-reported sleep adequacy, compared to 60 percent of the non-psoriatic population. Alcohol Tied to Development of Psoriasis.Alcohol can directly cause or exacerbate several skin conditions, new research indicates (Skin Therapy Lett. 2011 April; 16(4): 5-7). In particular, alcohol misuse is implicated in the development of psoriasis and discoid eczema, in addition to conferring increased susceptibility to skin and systemic infections. Researchers also noted that alcohol misuse might also 2 exacerbate rosacea, porphyria cutanea tarda, and post-adolescent acne. Patients Can Benefit From Continuous Biologic Treatment. Continuous treatment with ustekinumab (Stelara, Centocor Ortho Biotech) can have a positive impact on a patient’s life, according to new data (2011 AAD, New Orleans. P 3315). The study evaluated patients who either continued or discontinued ustekinumab therapy after 40 weeks of treatment and found a rapid loss of quality of life in patients who discontinued therapy at just 12 weeks after discontinuation. -

Skin Manifestations of Liver Diseases
medigraphic Artemisaen línea AnnalsA Koulaouzidis of Hepatology et al. 2007; Skin manifestations6(3): July-September: of liver 181-184diseases 181 Editorial Annals of Hepatology Skin manifestations of liver diseases A. Koulaouzidis;1 S. Bhat;2 J. Moschos3 Introduction velop both xanthelasmas and cutaneous xanthomas (5%) (Figure 7).1 Other disease-associated skin manifestations, Both acute and chronic liver disease can manifest on but not as frequent, include the sicca syndrome and viti- the skin. The appearances can range from the very subtle, ligo.2 Melanosis and xerodermia have been reported. such as early finger clubbing, to the more obvious such PBC may also rarely present with a cutaneous vasculitis as jaundice. Identifying these changes early on can lead (Figures 8 and 9).3-5 to prompt diagnosis and management of the underlying condition. In this pictorial review we will describe the Alcohol related liver disease skin manifestations of specific liver conditions illustrat- ed with appropriate figures. Dupuytren’s contracture was described initially by the French surgeon Guillaume Dupuytren in the 1830s. General skin findings in liver disease Although it has other causes, it is considered a strong clinical pointer of alcohol misuse and its related liver Chronic liver disease of any origin can cause typical damage (Figure 10).6 Therapy options other than sur- skin findings. Jaundice, spider nevi, leuconychia and fin- gery include simvastatin, radiation, N-acetyl-L-cys- ger clubbing are well known features (Figures 1 a, b and teine.7,8 Facial lipodystrophy is commonly seen as alco- 2). Palmar erythema, “paper-money” skin (Figure 3), ro- hol replaces most of the caloric intake in advanced al- sacea and rhinophyma are common but often overlooked coholism (Figure 11). -

Porphyria Cutanea Tarda* Fátima Mendonça Jorge Vieira 1 José Eduardo Costa Martins 2
RevABDV81N6.qxd 22.01.07 11:11 Page 573 573 Artigo de Revisão Porfiria cutânea tardia* Porphyria cutanea tarda* Fátima Mendonça Jorge Vieira 1 José Eduardo Costa Martins 2 Resumo: Trata-se de revisão sobre a porfiria cutânea tardia em que são abordados a fisio- patogenia, as características clínicas, as doenças associadas, os fatores desencadeantes, a bioquímica, a histopatologia, a microscopia eletrônica, a microscopia de imunofluorescên- cia e o tratamento da doença. Palavras-chave: Cloroquina; Fatores desencadeantes; Imunofluorescência; Porfiria cutânea tardia; Porfiria cutânea tardia/complicações; Porfiria cutânea tardia/fisiopatologia; Porfiria cutânea tardia/patologia; Porfiria cutânea tardia/terapia Abstract: This is a review article of porphyria cutanea tarda addressing pathophysiology, clinical features, associated conditions, triggering factors, biochemistry, histopathology, electronic microscopy, immunofluorescence microscopy and treatment of the disease. Keywords: Chloroquine; Fluorescent antibody technique; Porphyria cutanea tarda/compli- cations; Porphyria cutanea tarda/pathology; Porphyria cutanea tarda/pathophysiology; Porphyria cutanea tarda/therapy; Precipitating factors INTRODUÇÃO A porfiria cutânea tardia é causada pela defi- A descoberta da atividade diminuída da Urod ciência parcial da atividade enzimática da uroporfiri- na PCT levou a sua subdivisão:8 nogênio-decarboxilase (Urod), herdada ou adquirida, que resulta no acúmulo de uroporfirina (URO) e 7- Porfiria cutânea tardia esporádica (Tipo I, sinto- carboxil porfirinogênio, principalmente no fígado.1 O mática ou adquirida) – Representa percentual que termo porfiria origina-se da palavra grega porphura, varia de 72 a 84% dos casos,9-11 sendo a deficiência que significa cor roxa, e foi escolhido em função da enzimática limitada ao fígado, com atividade da Urod coloração de vermelha a arroxeada da urina de doen- eritrocitária normal.12 Não há história familiar. -

Phlebotomy As an Efficient Long-Term Treatment of Congenital
Letters to the Editor after chronic gastrointestinal bleeding that resulted in Phlebotomy as an efficient long-term treatment of iron deficiency.4 They treated her with an iron chelator, congenital erythropoietic porphyria resulting in correction of the hemolysis, decreased por- phyrin levels and improved quality of life with reduced Congenital erythropoietic porphyria (CEP, MIM photosensitivity. We recently identified three CEP sib- 263700) is a rare autosomal recessive disease caused by lings with phenotypes ranging from moderate to asymp- impaired activity of uroporphyrinogen III synthase tomatic which were modulated by iron availability, high- (UROS), the fourth enzyme of the heme biosynthetic lighting the importance of iron metabolism in the disease. 1 pathway. Accumulation of porphyrins in red blood cells, Based on these data, we prospectively treated a CEP mainly uroporphyrinogen I (URO I) and copropor- patient with phlebotomies to investigate the feasibility, phyrinogen I (COPRO I), leads to ineffective erythro- safety and efficacy of this treatment. We observed dis- poiesis and chronic hemolysis. Porphyrin deposition in continuation of hemolysis and a marked decrease in plas- the skin is responsible for severe photosensitivity result- ma and urine porphyrins. The patient reported a major ing in bullous lesions and progressive photomutilation. improvement in photosensitivity. Finally, erythroid cul- Treatment options are scarce, relying mainly on support- tures were performed, demonstrating the role of iron in ive measures and, for severe cases, on bone marrow the rate of porphyrin production. transplantation (BMT). Increased activation of the heme The study was conducted in accordance with the biosynthetic pathway by gain-of-function mutations in World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki ethi- ALAS2, the first and rate-limiting enzyme, results in a 2 cal principles for medical research involving human sub- more severe phenotype. -

Ex Vivo Gene Therapy: a “Cultured” Surgical Approach to Curing Inherited Liver Disease
Mini Review Open Access J Surg Volume 10 Issue 3 - March 2019 Copyright © All rights are reserved by Joseph B Lillegard DOI: 10.19080/OAJS.2019.10.555788 Ex Vivo Gene Therapy: A “Cultured” Surgical Approach to Curing Inherited Liver Disease Caitlin J VanLith1, Robert A Kaiser1,2, Clara T Nicolas1 and Joseph B Lillegard1,2,3* 1Department of Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA 2Midwest Fetal Care Center, Children’s Hospital of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA 3Pediatric Surgical Associates, Minneapolis, MN, USA Received: February 22, 2019; Published: March 21, 2019 *Corresponding author: Joseph B Lillegard, Midwest Fetal Care Center, Children’s Hospital of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA and Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA Introduction Inborn errors of metabolism (IEMs) are a group of inherited diseases caused by mutations in a single gene [1], many of which transplant remains the only curative option. Between 1988 and 2018, 12.8% of 17,009 pediatric liver transplants in the United States(see were primarily due to an inherited liver). disease. are identified in Table 1. Though individually rare, combined incidence is about 1 in 1,000 live births [2]. While maintenance www.optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/data/ Table 1: List of 35 of the most common Inborn Errors of Metabolism. therapies exist for some of these liver-related diseases, Inborn Error of Metabolism Abbreviation Hereditary Tyrosinemia type 1 HT1 Wilson Disease Wilson Glycogen Storage Disease 1 GSD1 Carnitine Palmitoyl Transferase Deficiency Type 2 CPT2 Glycogen Storage -

Module 01: Classification of Porphyria
MODULE 01 Classification of Porphyria Do not reprint, reproduce, modify or distribute this material without the prior written permission of Alnylam Pharmaceuticals. © 20120199 Alnylam PharmaceuticalsPharmaceuticals,, Inc.Inc. All rights reserved. -USA-00001-092018 1 Porphyria—A Rare Disease of Clinical Consequence • Porphyria is a group of at least 8 metabolic disorders1,2 – Each subtype of porphyria involves a genetic defect in a heme biosynthesis pathway enzyme1,2 – The subtypes of porphyria are associated with distinct signs and symptoms in patient populations that can differ by gender and age1,3 • Prevalence of some subtypes of porphyria may be higher than generally assumed3 Estimated Prevalence of Most Common Subtypes of Porphyria1,4 Estimated Prevalence Based on European Subtype of Porphyria and US Data Porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT) 1/10,000 (EU)1 0.118-1/20,000 (EU)1,4 Acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) 5/100,000 (US)1 Erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP) 1/50,000-75,000 (EU)1 1. Ramanujam V-MS, Anderson KE. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2015;86:17.20.1-17.20.26. 2. Puy H et al. Lancet. 2010;375:924-937. 3. Bissell DM et al. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:862-872. 4. Elder G et al. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2013;36:848-857. Do not reprint, reproduce, modify or distribute this material without the prior written permission of Alnylam Pharmaceuticals. © 2019 Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inc. All rights reserved. -USA-00001-092018 2 Classification of Porphyria Porphyria can be classified in 2 major ways1,2: 1 According to major physiological sites: liver or 2 According to major clinical manifestations1,2 bone marrow1,2 • Heme precursors originate in either the liver or Acute Versus Photocutaneous Porphyria bone marrow, which are the tissues most • Major clinical manifestations are either neurovisceral active in heme biosynthesis1,2 symptoms (eg, severe, diffuse abdominal pain) associated with acute exacerbations or cutaneous lesions resulting from phototoxicity1,2 • Acute hepatic porphyria may be somewhat of a misnomer since the clinical features may be prolonged and chronic3 1. -

Variegate Porphyria with Coexistent Decrease in Porphobilinogen Deaminase Activity
Acta Derm Venereol 2001; 81: 356–359 CLINICAL REPORT Variegate Porphyria with Coexistent Decrease in Porphobilinogen Deaminase Activity GEORG WEINLICH1, MANFRED O. DOSS2, NORBERT SEPP1 and PETER FRITSCH1 1Department of Dermatology, University of Innsbruck, Innsbruck, Austria and 2Department of Clinical Biochemistry, University of Marburg, Marburg, Germany Variegate porphyria is a rare disease caused by a de ciency of deaminase. Its activity is reduced by about 50%, resulting in protoporphyrinogen oxidase. In most cases, the clinical ndings are varying degrees of overproduction and increased urinary excre- a combination of systemic symptoms similar to those occurring in tion of delta-aminolaevulinic acid (ALA) and PBG. In AIP, acute intermittent porphyria and cutaneous lesions indistinguishable skin changes are absent, but patients suVer from episodic from those of porphyria cutanea tarda. We report on a 24-year- central or peripheral nervous system and/or psychiatric symp- old woman with variegate porphyria who, after intake of lynestrenol, toms, or acute attacks of abdominal pain (2, 4). developed typical cutaneous lesions but no viscero-neurological Variegate porphyria (VP), a rare autosomal-dominant hep- symptoms. The diagnosis was based on the characteristic urinary atic porphyria due to a de ciency of protoporphyrinogen coproporphyrin and faecal protoporphyrin excretion patterns, and (PROTO) oxidase, the related gene (PPOX ) for which has the speci c peak of plasma uorescence at 626 nm in spectro uor- been located to chromosome 1q22-23 (5, 6), is characterized ometry. Biochemical analysis revealed that most of the family by both acute neurological symptoms as in AIP and skin members, though free of clinical symptoms, excrete porphyrin lesions indistinguishable from PCT; it is thus also termed metabolites in urine and stool similar to variegate porphyria, mixed porphyria (2, 7, 8).