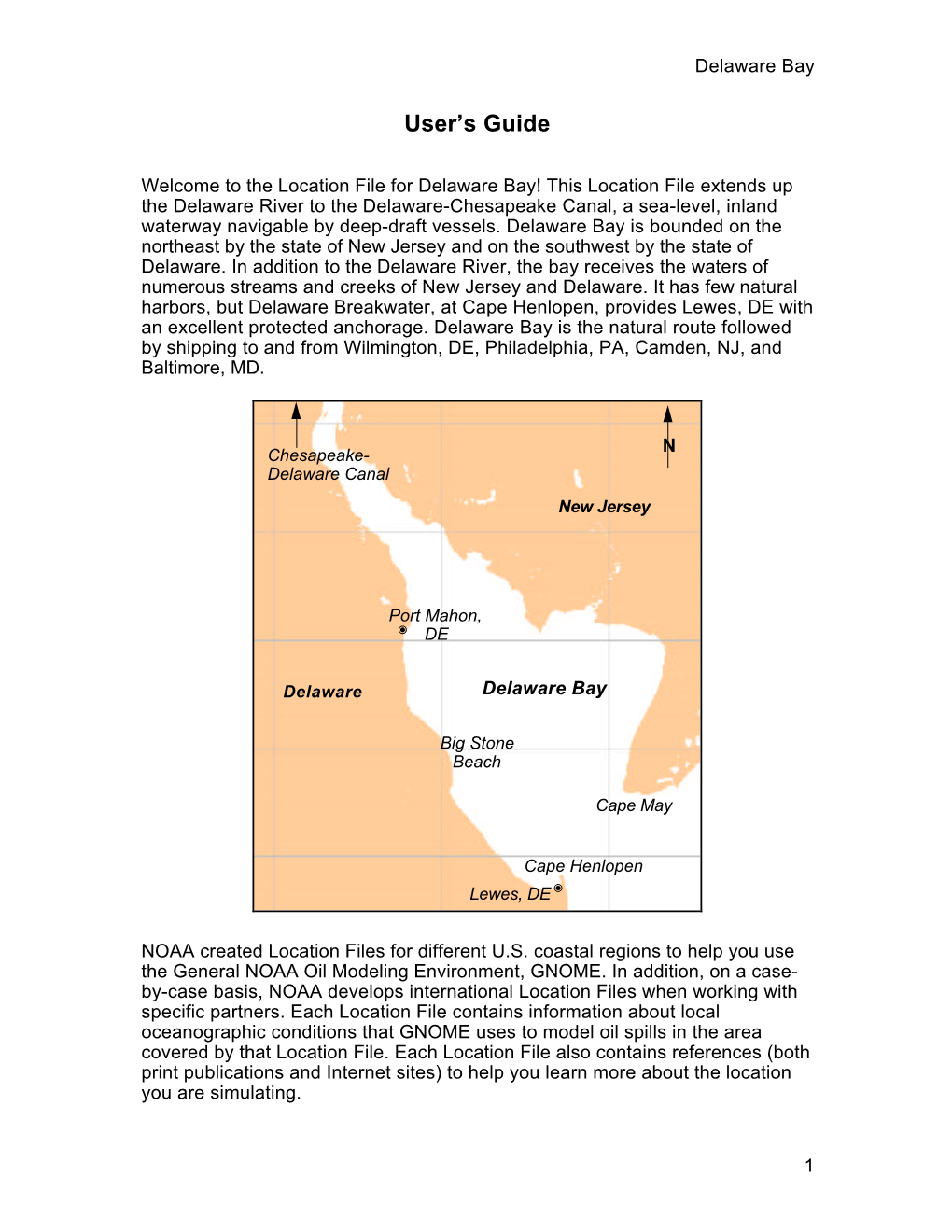
Delaware Bay GNOME User's Guide
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

THE CLIMATOLOGY of the DELAWARE BAY/SEA BREEZE By
THE CLIMATOLOGY OF THE DELAWARE BAY/SEA BREEZE by Christopher P. Hughes A dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Marine Studies Summer 2011 Copyright 2011 Christopher P. Hughes All Rights Reserved THE CLIMATOLOGY OF THE DELAWARE BAY/SEA BREEZE by Christopher P. Hughes Approved: _____________________________________________________ Dana E. Veron, Ph.D. Professor in charge of thesis on behalf of the Advisory Committee Approved: _____________________________________________________ Charles E. Epifanio, Ph.D. Director of the School of Marine Science and Policy Approved: _____________________________________________________ Nancy M. Targett, Ph.D. Dean of the College of Earth, Ocean, and Environment Approved: _____________________________________________________ Charles G. Riordan, Ph.D. Vice Provost for Graduate and Professional Education ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Dana Veron, Ph.D. for her guidance through the entire process from designing the proposal to helping me create this finished product. Daniel Leathers, Ph.D. for his continual assistance with data analysis and valued recommendations. My fellow graduate students who have supported and helped me with both my research and coursework. This thesis is dedicated to: My family for their unconditional love and support. My wonderful fiancée Christine Benton, the love of my life, who has always been there for me every step of the way. iii TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF TABLES ........................................................................................................ -

Replenishment Versus Retreat: the Cost of Maintaining Delaware's Beaches
Ocean& Coastal Management ELSEVIER Ocean & Coastal Management 44 (2001) 87-104 www.elsevier.comllocalclocecoaman Replenishment versus retreat: the cost of maintaining Delaware's beaches Heather Daniel* Graduate Colle(Je' of Moril1e SIIlt/ies, University of Delaware, Ncwark, DE /9716. USA Abstract The dynamic nature of Delaware's Atlantic coastline coupled with high shoreline property values and a growing coastal tourism industry combine to create a natural resources management problem that is particularly difllcult to address. The problem of communities threatened with storm damage and loss of recreational beaches is seriolls. Local and slate oflkials are dealing with the connicts that arise from development occurring on coastal barriers. Delaware must decide which erosion control option is the most beneficial and economically sound choice. Dehates over beach management options began with the discussion of a long~term management strategy. Beach nourishment and retreat were the primary approaches discussed during the development of H comprehensive managcment plan, entitled Beaches 2000. This plan was developed to deal with beach erosion through the year 2000. Beaches 2000 recommends a series ofactions that incorporate a variety of issues related to the management and protection of Delaware's Atlantic coastline. The recommendations arc intended to guide state and local policy regarding the statc's benches. The goal of Beaches 2000 is to cnsure that this important natural resource and tourist attraction continues to he available to the citizens of Delaware and out-or-state beach visitors. Since the publication of this document, the state has managed Delaware's shorelines through nourishment activities. Nourishment projccts have successfully maintained beach widths·. -

Delaware Bay Estuary Project Supporting the Conservation and Restoration Of
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service – Coastal Program Delaware Bay Estuary Project Supporting the conservation and restoration of the salt marshes of Delaware Bay People have altered the expansive salt marshes of Delaware Bay for centuries to farm salt hay, try to control mosquitoes, create channels for boats, to increase developable land, and other reasons all resulting in restricted tidal flow, disrupted sediment balances, or increasing erosion. Sea level rise and coastal storms threaten to further negatively impact the integrity of these salt marshes. As we alter or lose the marshes we lose the valuable habitats and ecological services they provide. tidal creek - Katherine Whittemore Addressing the all-important sediment balance of salt marshes is critical for preserving their resilience. A healthy resilient marsh may be able to keep pace with erosion and sea level rise through sediment accretion and growth Downe Twsp, NJ - Brian Marsh of vegetation. However, the delicate sediment balance of salt marshes is DBEP works to support efforts to learn more about the techniques often disrupted by barriers to tidal influence and altered drainage onto and to conserve and restore salt marshes and support the populations of fish and wildlife that rely on them. We support new and off the marsh resulting in sediment ongoing coastal resiliency initiatives and coastal planning as they starved systems, excessive mudflats, or pertain to habitat restoration and conservation. We are interested increased erosion. in finding effective tools and mechanisms for conserving and restoring salt marsh integrity on a meaningful scale and support efforts that bring partners together to approach this challenge. -

BOARD of WARDENS for PORT of PHILADELPHIA - PILOTAGE RATES Act of Nov
BOARD OF WARDENS FOR PORT OF PHILADELPHIA - PILOTAGE RATES Act of Nov. 4, 2016, P.L. 1148, No. 148 Cl. 74 Session of 2016 No. 2016-148 HB 2291 AN ACT Amending the act of May 11, 1889 (P.L.188, No.210), entitled "A further supplement to an act, entitled 'An act to establish a board of wardens for the Port of Philadelphia, and for the regulation of pilots and pilotage, and for other purposes,' approved March twenty-ninth, one thousand eight hundred and three, and for regulating the rates of pilotage and number of pilots," further providing for rates of pilotage and computation, for pilotage fees and unit charge and for charges for services. The General Assembly of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania hereby enacts as follows: Section 1. Sections 3.1 and 3.2 of the act of May 11, 1889 (P.L.188, No.210), entitled "A further supplement to an act, entitled 'An act to establish a board of wardens for the Port of Philadelphia, and for the regulation of pilots and pilotage, and for other purposes,' approved March twenty-ninth, one thousand eight hundred and three, and for regulating the rates of pilotage and number of pilots," amended May 15, 1998 (P.L.447, No.62) and June 10, 2013 (P.L.40, No.12), are amended to read: Section 3.1. For services rendered on and after January 1, 1990, retroactively, the rates of pilotage for conducting a vessel from the Capes of the Delaware to a place on the Delaware River or Bay no further upriver than the Delair Railroad Bridge between Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and Delair, New Jersey, or from a place on the river Delaware no further upriver than the Delair Railroad Bridge between Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and Delair, New Jersey, to the Capes of the Delaware, in either case, shall be computed as follows: (a) A charge, to be known as a unit charge, will be made for each pilotage, determined by length overall (in feet) multiplied by the extreme breadth (in feet) of the vessel, divided by one hundred. -

Federal Register/Vol. 63, No. 81/Tuesday, April 28
Federal Register / Vol. 63, No. 81 / Tuesday, April 28, 1998 / Rules and Regulations 23217 similar safety zones have been § 165.T01±026 Safety Zone: Fleet Week Delaware. The safety zone is necessary established for several past Fleet Week 1998 Parade of Ships, Port of New York and to protect spectators and other vessels parades of ships with minimal or no New Jersey. from the potential hazards associated disruption to vessel traffic or other (a) Location. The following are safety with the Super Loki Rocket Launch interests in the port. The Coast Guard zones: from Cape Henlopen State Park. certifies under 5 U.S.C. 605(b) that this (1) A moving safety zone including all DATES: This rule is effective May 9 and rule will not have a significant waters 500 yards ahead and astern, and May 10, 1998. economic impact on a substantial 200 yards on each side of the designated FOR FURTHER INFORMATION CONTACT: number of small entities. If, however, column of parade vessels as it transits Chief Petty Officer Ward, Project you think that your business or from the Verrazano Narrows Bridge Manager, Waterways and Waterfront organization qualifies as a small entity through the waters of the Hudson River Facilities Branch, at (215) 271±4888. to Riverbank State Park, between West and that this rule will have a significant SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: In 137th and West 144th Streets, economic impact on it, please submit a accordance with 5 U.S.C. 553, a notice Manhattan, New York. comment explaining why you think it of proposed rulemaking (NPRM) was (2) A safety zone including all waters qualifies, and in what way and to what not published for this regulation and of the Hudson River between Piers 84 degree this rule will adversely affect it. -

Remember Mid-April 1970, America Was Angry
EAaN rth Day TO Remember mid-April 1970, America was angry. The baby boomers had become cynical, mistrusting In parents, business, industry and Back in 1970, John Stenger government. This generation was especially disdainful of the so-called military-indus - and a band of students came to trial complex that President Dwight Eisenhower had warned about. The Vietnam War dragged on, filling the defense of Cape Henlopen’s the 6 o’clock news with death and destruction, and no end was in sight. The previous month, the Army had imperiled dunes charged 14 officers with suppressing the truth about the horrific My Lai massacre in Vietnam, where as many as 500 essentially unarmed civilians had been murdered by U.S. troops. The hopeful Apollo 13 moon mission had suffered an oxygen tank explosion a few days before, forcing its hasty retreat to Earth. The Cold War with the communist USSR was tense and dispiriting, and Paul McCartney had just announced the breakup of the Beatles. To many Americans, the future seemed dismal and hundreds of thousands had taken to the streets and college cam - puses to protest the nation’s various problems. Among those concerns was the environment. Decades of hellbent-for-leather industrial develop - ment with little regard for the land, oceans and air was taking an ever-greater toll. To a growing number of people, this threat trumped all others: If you can’t breathe the air, can’t eat the food, and can’t drink the water, little else mattered. Scientists and other con - cerned individuals were beginning to sound the alarm, and people were beginning to listen. -

Camden, New Jersey
COMPREHENSIVE HOUSING MARKET ANALYSIS Camden, New Jersey U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development Office of Policy Development and Research As of August 1, 2014 Bucks Mercer Montgomery Monmouth Pennsylvania Housing Market Area Chester New Jersey Ocean Delaware Philadelphia The Camden Housing Market Area (HMA) is coter minous with the Camden, NJ Metropolitan Division. Burlington Pennsylvania For purposes of this analysis, the threecounty HMA Camden is divided into three submarkets: Burlington County; Delaware Gloucester Camden County, which includes the central city of New Castle Camden; and Gloucester County. The HMA includes Salem Atlantic portions of the Joint Base McGuireDixLakehurst (Joint Base), which contains facilities for the U.S. Great Bay Delaware Bay Cumberland Air Force, U.S. Army, and U.S. Navy. Summary Economy annual rate of 0.6 percent during the for 4,075 new homes in the HMA next 3 years. Table DP1 at the end (Table 1). The 410 units currently The economy of the Camden HMA, of this report provides employment under construction and a portion of which accounts for approximately data for the HMA. the 13,800 other vacant units in the 12 percent of all jobs in New Jersey, HMA that may reenter the market weakened after expanding during Sales Market will satisfy a portion of the forecast 2012. During the 12 months ending demand. July 2014, nonfarm payrolls declined The sales housing market in the HMA is slightly soft but improving, with an by 1,900 jobs, or 0.4 percent, to an Rental Market average of 505,800 jobs compared estimated vacancy rate of 1.4 percent, with an increase of 6,450 jobs, or down from 1.6 percent in 2010. -

Cape Henlopen State Park
Cape Henlopen The State Park Point Location Map 0 0.5 1 Delaware Bay Cape Miles Henlopen The Point State Park Point Comfort Lewes Station Beach Plum Island Nature Preserve Atlantic Ocean Atlantic Delaware Bay Ocean Seaside Picnic Pavilion Nature Center Rehoboth Beach Bait & Tackle Shop Youth Camps Legend Cape May - Lewes Ferry Air Pumping Station Senator Open Park Land Food Concession D a v i d B . M c B r i d e Beach Bathhouse Forested Park Land Picnic Pavilion Umbrella Rental d Recycling Center Lighthouse Fiel Water ade Par Restricted Area Dump Station Scenic Overlook Drive enlopen Building Cabins Disc Golf Cape H Parking Tent Camping Basketball Courts Park Office d Primitive Youth a Municipalities Amphitheater o Camp R h Lewes Jetties Kayak Rental a Observation Tower n n a v Parking Surf Fishing WWII Artillery Site a S Campground Swimming Area y Fort Miles Information Hawk Watch a Historic Area (Guarded Beach) w h Restrooms Playground Horseback Riding ig The Great Dune H (Seasonal) n Showers/Bath a Trail Head m House Bike Repair Station e re Trails and Pathways F American Discovery Trail Seaside Nature Trail (0.7mi.) Bike Loop (3.3mi.) Walking Dunes Trail (2.6mi.) Gordons Pond Trail (3.2mi.) Salt Marsh Spur (1.2mi) Junction & Breakwater Primitive Biden Connector Trail Youth Camp Center Trail (5.8 mi.) Beach Vehicle Crossing Lewes-Georgetown-Cape Henlopen Rail with Trail Pedestrian Beach Crossing Pinelands Nature Trail (1.5mi.) Share the Road Park Information L e 15099 Cape Henlopen Dr. Lewes, DE 19958 w e Park Office: (302) 645-8983 -

2021-2024 CAPITAL PLAN DELAWARE STATE PARKS Blank DELAWARE STATE PARKS 2021-2024 CAPITAL PLAN
2021-2024 CAPITAL PLAN DELAWARE STATE PARKS blank DELAWARE STATE PARKS 2021-2024 CAPITAL PLAN Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control Division of Parks & Recreation blank CAPITAL PLAN CONTENTS YOUR FUNDING INVESTMENTS PARK CAPITAL FY2021 STATEWIDE STATE PARKS THE PARKS IN OUR PARKS NEEDS CAPITAL PLAN PROJECT LIST 5 Parks and 8 Capital 13 New Castle 22 Top 15 28 FY2021 CIP 32 Statewide Preserves Funds For County Major Needs Request Projects Parks 6 Accessible 16 Kent County 25 Top Needs 29 Project to All 9 Land and at Each Park Summary Water 17 Sussex Chart Conservation County Fund 30 Planning, 19 Preserving Design, and 10 Statewide Delaware’s Construction Pathway and Past Timeline Trail Funds 20 Partner/ 11 Recreational Friends Trails Projects Program 12 Outdoor Recreation, Parks and Trails Grant Program Delaware State Parks Camping Cabins Tower 3 interior at Delaware Seashore State Park DELAWARE YOUR STATE PARKS STATE PARKS by the The mission of Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control's (DNREC) Division of Parks & Recreation is to provide Numbers: Delaware’s residents and visitors with safe and enjoyable recreational opportunities and open spaces, responsible stewardship of the lands and the cultural and natural resources that we have 6.2 been entrusted to protect and manage, and resource-based interpretive and educational services. million+ visitors PARKS, PRESERVES, AND 17 ATTRACTIONS Parks The Division of Parks & Recreation operates and maintains 17 state parks in addition to related preserves and -

NJMA Brochure
What’s the tallest lighthouse in New Jersey? . .# 21 What’s the name of NJ’s Official Tall Ship? . .# 26 How many shipwrecks are along the NJ coast? . .# 14 1) New Jersey was almost called the “Maritime State” 12) The Spanish may have been the first Europeans to attempt instead of the “Garden State” according to NJ Governor settlement of what is now New Jersey – the 1525 voyage of Driscoll in his 1953 veto of a bill to put the words “Garden Quejo sent by Ayllon northward received reports of coastline State” on each NJ license plate. from as far north as the Deer River (may have been the 2) New Jersey is home to Governor William Newell who Hudson River). initiated what would become the United States Life 13) Hoboken was the departure point for most American Saving Service in 1871 and the United States Coast Guard troops headed to France for World War I – “Heaven, Hell in 1915. The anti-immigrant member of the No Nothing or Hoboken” was a common saying of Dough Boys of the Party is credited for developing the Beach Apparatus Drill American Expeditionary Forces. that saved over 177,000 lives – ironically, many of whom 14) There are over 4,800 shipwrecks in the waters along were immigrants. the New Jersey coast focused on the Atlantic Ocean, 3) Joseph Francis Life-Car was invented and Delaware Bay and Delaware River. demonstrated in New Jersey. The original car used in the (njmaritimemuseum.org/shipwreck-database) 1850 wreck of the Ayrshire off “Squan Beach” became 15) The Delaware River flows 419 miles from New York’s one of the top ten exhibits at the Smithsonian Catskill Mountains into the Delaware Bay. -

Underwater Archaeological Investigation of the Roosevelt Inlet Shipwreck (7S-D-91A) Volume 1: Final Report
UNDERWATER ARCHAEOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE ROOSEVELT INLET SHIPWRECK (7S-D-91A) VOLUME 1: FINAL REPORT State Contract No. 26-200-03 Federal Aid Project No. ETEA-2006 (10) Prepared for: Delaware Department of State Division of Historical and Cultural Affairs 21 The Green Dover, Delaware 19901 And for the Federal Highway Administration and Delaware Department of Transportation By: APRIL 2010 www.searchinc.com UNDERWATER ARCHAEOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE ROOSEVELT INLET SHIPWRECK (7S-D-91A) State Contract No. 26-200-03 Federal Aid Project No. ETEA-2006 (10) Prepared for Delaware Department of State Division of Historical and Cultural Affairs 21 The Green Dover, Delaware 19901 And for the Federal Highway Administration and Delaware Department of Transportation By SOUTHEASTERN ARCHAEOLOGICAL RESEARCH, INC. Michael Krivor, M.A., RPA Principal Investigator AUTHORED BY: MICHAEL C. KRIVOR, NICHOLAS J. LINVILLE, DEBRA J. WELLS, JASON M. BURNS, AND PAUL J. SJORDAL APRIL 2010 www.searchinc.com Underwater Archaeological Investigations of the Roosevelt Inlet Shipwreck FINAL REPORT ABSTRACT In the fall of 2004, a dredge struck an eighteenth-century wreck site during beach replenishment, resulting in thousands of artifacts being scattered along the beach in Lewes, Delaware. Local residents informed archaeologists with the Delaware Department of State (State) Division of Historical and Cultural Affairs (Division) about the artifacts, and investigations were undertaken to locate the source of the historic material. Approximately 40,000 artifacts from Lewes Beach were recovered by archaeologists from the Division as well as many private citizens who donated their artifacts to the Delaware Department of State. In consultation with the U.S. -

Camden, New Jersey
COMPREHENSIVE HOUSING MARKET ANALYSIS Camden, New Jersey U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development Office of Policy Development and Research As of May 1, 2017 Summary Economy homes that may reenter the market likely will satisfy part of the forecast Housing Market Area Although payrolls are still below demand. their 2006 peak, job growth in the Camden HMA since 2015 has been Rental Market strong. During the 12 months ending Pennsylvania Bucks Mercer The overall rental housing market in Monmouth April 2017, nonfarm payrolls in the Montgomery HMA increased by 12,900 jobs, or the HMA is slightly soft, with an Chester New Jersey Philadelphia Ocean estimated vacancy rate of 7.3 percent, Delaware Burlington 2.5 percent. State-based incentives down from 8.6 percent in April 2010. Delaware Camden established in 2013 engendered strong Gloucester job growth in the manufacturing and Despite relatively high levels of apart- Salem ment construction activity since 2013, Atlantic the transportation and utilities sectors New Castle Cumberland and significant commercial construc- the apartment market is balanced, with Delaware Bay Atlantic Ocean tion activity in the city of Camden. a vacancy rate of 4.7 percent as of the The Camden Housing Market Area Job gains are expected to continue first quarter of 2017 (Axiometrics, Inc.). (HMA) is coterminous with the Camden, during the 3-year forecast period, During the forecast period, demand is NJ Metropolitan Division in South albeit at a more modest pace of 7,900 expected for 2,725 new market-rate New Jersey and comprises Burlington, jobs, or 1.5 percent, annually.