Fact Sheet: Software Industry
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

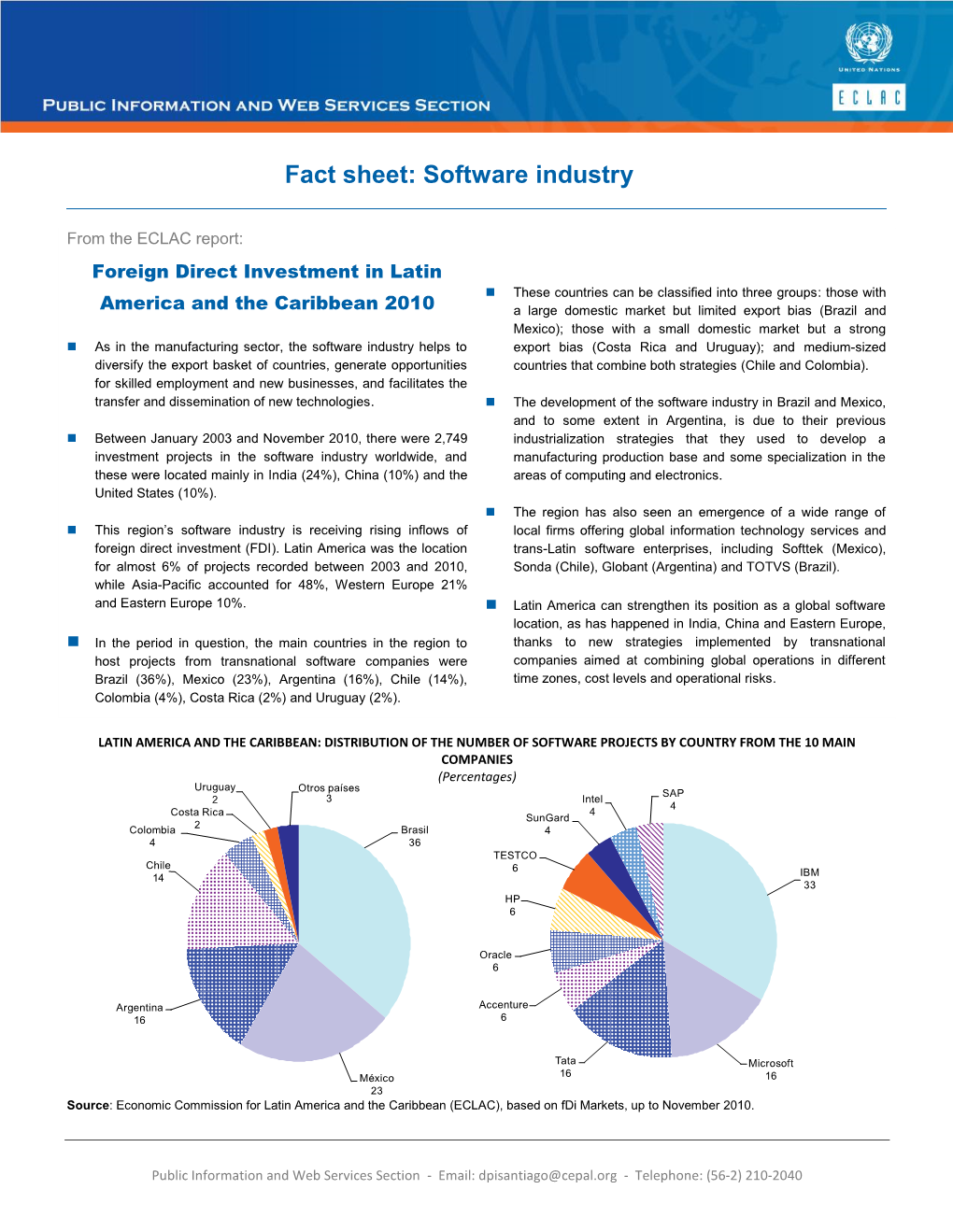
Integrated Report 2017 WELCOME This Is TOTVS Integrated Report 2017, the Third Edition of We Advanced Along Our Digital Journey, Supported by Three This Document
INTEGRATED REPORT 2017 WELCOME This is TOTVS Integrated Report 2017, the third edition of We advanced along our digital journey, supported by three this document. It voluntarily complies with Global Reporting pillars: people, clients and technology. Learn about the steps TO OUR Initiative (GRI) and International Integrated Reporting Council of this evolution and discover how we are opening ourselves INTEGRATED (IIRC) guidelines, globally approved and recognized standards, up to be together with you. covering the period from January 1 to December 31, 2017. REPORT 2017 In Chapter 10, we give a brief explanation of what an integrated In this edition, we have adopted the new version Standards, report is, to help you understand the structure of this narrative. GRI 102-1 in line with GRI Rules: Essential Option. In Chapter 11, we present the GRI Index, a way of easily find- Our aim is to tell a story of transformation and openness, on ing indicators and topics that are strategic to the company in a digital journey that goes far beyond the company’s walls. the text. Accordingly, this year, we have incorporated our stakeholders If you would like to comment on anything, make a suggestion more deeply into the report. This is to recognize that you too or ask any questions in relation to our report, please do not are ever more important players in this story. hesitate to email us at [email protected]. We want to con- We are pleased to say that 2017 was a key year for TOTVS. stantly improve. SUMÁRIO TOTVS INTEGRATED REPORT 2017 3 MESSAGE FROM THE BOARD GRI 102-10, 102-14 Value creation for investors, ethics in business and appreciation The recent renewal of our Board of Directors also warrants These are some of the aspects we have presented in this of human capital were principles embodied by TOTVS over highlighting. -

Service Power Warranty Claims Management
A Special SFGSM Analyst’s Take Ensuring Quality Customer Service Performance in the Global Insurance Segment Written by Bill Pollock ServicePower.com Enabling InsurTech Organizations to Enhance your Customer’s Experience and Boost their Bottom Line August 2018 Bill Pollock Putting Things Forward from the Perspective President & Principal of the Global Insurance Industry Consulting Analyst Strategies For GrowthSM / The results from research analyst firm, Strategies for PollockOnService Growth’s 2018 Warranty Chain Management Benchmark Survey clearly reveal that insurance organizations that have either implemented a new warranty management solution or, at the very least, upgraded their existing solution, are now experiencing an average of up to 10% improvement in warranty claims processing times, as well as commensurate upticks in customer satisfaction and the overall customer Westtown, Pennsylvania USA experience. +1 610-399-9717 As many of these implementations are now supported by [email protected] state-of-the-art Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology, those www.PollockOnService.com organizations that have taken this path benefit twice – from both the improved functionality of their “new” warranty management systems, as well as the introduction of AI technology into their business operations. A SPECIAL SFGSM ANALYST’S TAKE 1 “The insurance segment will continue to be highly dependent on the introduction of new technology into their business operations and, as a result, will be searching for vendors and solutions that will ease their -

لینک دانلود کتاب ERP for Textiles and Apparel Industry.Pdf
ERP for Textiles and Apparel Industry © 2016 by Woodhead Publishing India Pvt. Ltd. © 2016 by Woodhead Publishing India Pvt. Ltd. ERP for Textiles and Apparel Industry R. Surjit, R. Rathinamoorthy and K. J. Vishnu Vardhini WOODHEAD PUBLISHING INDIA PVT LTD New Delhi © 2016 by Woodhead Publishing India Pvt. Ltd. CRC Press Woodhead Publishing India Pvt. Ltd. Taylor & Francis Group 303, Vardaan House, 7/28, Ansari Road 6000 Broken Sound Parkway NW, Suite 300 Daryaganj, New Delhi – 110002, India Boca Raton, FL 33487-2742 © 2016 by Woodhead Publishing India Pvt. Ltd. Exclusive worldwide distribution by CRC Press an imprint of Taylor & Francis Group, an Informa business No claim to original U.S. Government works Version Date: 20160217 International Standard Book Number-13: 978-93-85059-59-9 (eBook - PDF) This book contains information obtained from authentic and highly regarded sources. Reason- able efforts have been made to publish reliable data and information, but the author and publisher cannot assume responsibility for the validity of all materials or the consequences of their use. The authors and publishers have attempted to trace the copyright holders of all material reproduced in this publication and apologize to copyright holders if permission to publish in this form has not been obtained. If any copyright material has not been acknowledged please write and let us know so we may rectify in any future reprint. Except as permitted under U.S. Copyright Law, no part of this book may be reprinted, reproduced, transmitted, or utilized in any form by any electronic, mechanical, or other means, now known or hereafter invented, including photocopying, microfilming, and recording, or in any information storage or retrieval system, without written permission from the publishers. -

Who We Are Forward Looking Disclosure
WHO WE ARE FORWARD LOOKING DISCLOSURE In addition to historical information, this release contains “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. These forward-looking statements include information about possible or assumed future results of our business and financial condition, as well as the results of operations, liquidity, plans and objectives. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terminology such as “believe,” “may,” “estimate,” “continue,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “should,” “plan,” “expect,” “predict,” “potential,” or the negative of these terms or other similar expressions. These statements include, but are not limited to, statements regarding: the persistence and intensification of competition in the IT industry; the future growth of spending in IT services outsourcing generally, application outsourcing and custom application development and offshore development services; the level of growth of demand for our services from our clients; the level of increase in revenues from our new clients; the resource utilization rates and productivity levels, the level of attrition of our IT professionals; the pricing structures we use for our client contracts; general economic and business conditions in the locations in which we operate; the levels of our concentration of revenues by vertical, geography, by client and by type of contract in the future; the continuity -

Martín Migoya – Globant CEO & Co-Founder
Personal Profile Martín Migoya – Globant CEO & Co-founder Martin has been an entrepreneur since his early youth. In 2003 he founded Globant together with 3 friends, with the aim of building a Company leader in the creation of innovative software products. Martín has served as Chairman of our board and Chief Executive Officer since 2005. As Globant CEO, Martín drove the company from a small start-up to an organization with more than 6200 professionals and presence in the US, UK, Spain, India, Brazil, Colombia, México, Perú, Chile, Uruguay and Argentina. Today, Globant is working for world class customers such as Google, Electronic Arts, NatGeo, Southwest Airlines and Coca Cola, among others. Martin is deeply passionate about inspiring future entrepreneurs, that´s why he frequently gives lectures at different events and has been a jury at the Endeavor Entrepreneurs panel and at La Red Innova. The MIT Sloan School of Management wrote a business case about Globant entitled: “Globant, Leading the IT Revolution in Latin America”, and invited Martin to give lectures to their MBA students. Harvard and Stanford also wrote business cases to study the company. Globant has become the first software development company from Latin America to do an IPO on the NYSE, in 2014. It was recognized as one of the top 10 innovative companies in South America by Fast Company and was named as a worldwide leader in Digital Strategy and Agency Service by IDC MarketScape (2016 and 2017). Martín was selected Endeavor Entrepreneur 2005 and has won a Konex Award as one of the most innovative entrepreneurs of 2008. -

Technology in Apparel Design – What Is Being Used? Melanie Carrico University of North Carolina at Greensboro, [email protected]
International Textile and Apparel Association 2013: Regeneration, Building a Forward Vision (ITAA) Annual Conference Proceedings Jan 1st, 12:00 AM Technology in apparel design – what is being used? Melanie Carrico University of North Carolina at Greensboro, [email protected] Sojin Jung Universtiy of North Carolina Thomas Turner University of North Carolina at Greensboro Linda Ohrn-McDaniel Kent State University, [email protected] Follow this and additional works at: https://lib.dr.iastate.edu/itaa_proceedings Part of the Fashion Business Commons, and the Fashion Design Commons Carrico, Melanie; Jung, Sojin; Turner, Thomas; and Ohrn-McDaniel, Linda, "Technology in apparel design – what is being used?" (2013). International Textile and Apparel Association (ITAA) Annual Conference Proceedings. 207. https://lib.dr.iastate.edu/itaa_proceedings/2013/presentations/207 This Event is brought to you for free and open access by the Conferences and Symposia at Iowa State University Digital Repository. It has been accepted for inclusion in International Textile and Apparel Association (ITAA) Annual Conference Proceedings by an authorized administrator of Iowa State University Digital Repository. For more information, please contact [email protected]. New Orleans, Louisiana 2013 Proceedings Technology in apparel design – what is being used? Melanie Carrico, Sojin Jung, Thomas Turner, University of North Carolina at Greensboro, USA Linda Ohrn-McDaniel, Kent State University, USA Keywords: software, industry, design, technology Undergraduate fashion and apparel programs strive to keep up with the changing needs of fashion industry employers, especially with respect to technology. Experience using design software is one necessary skill for fashion designers, but which software program or programs to teach is a question fashion faculty must grapple with as they strive to keep curricula current and relevant. -

Latinamerica's #1Business Gateway
LATINAMERICA’S #1 BUSINESS GATEWAY 1. BUSINESS PLATFORMS & OPPORTUNITIES FOR GLOBAL COMPANIES In the past few years, Uruguay has become a target location for Regional Corporate Centers, especially as a regional hub, where the main platforms are as follows: Although Uruguay has special attractions for the location of captive centers, it is also a privileged destination for outsourced centers focused on high-value tasks (BPO & KPO CENTERS). Many international companies choose Uruguay to provide services to other Latin American Spanish speaking countries, to Brazil, and the world. The Offshoring services exports represent 18% of total Uruguayan Exports (goods & services). 2. URUGUAY #1 in LATIN AMERICA Uruguay is the most reliable country to do business in one of the most economically attractive regions in the world. It offers a favorable business climate, social and political stability, investment grade rating and sustained GDP growth during the past 15 years. Investors distinguish Uruguay´s world-class infrastructure, and excellent quality of life for executives and their families. Uruguay´s attractive tax system for export operations, such as the free trade zones, the investment law, free port and airport; qualified and multilingual talent (Spanish, English, and Portuguese) and competitive costs are also highlighted by investors. In addition, foreign investments receive equal treatment to domestic ones, there are no restrictions on capital or profit repatriation, and companies can operate in domestic or foreign currency. SUCCCESS STORIES REGIONAL HEADQUARTERS, SHARED SERVICES CENTERS, TRADING & PROCUREMENT CENTERS Uruguay´s capital city, Montevideo, has become a hub for Regional Headquarters (HQ), Trading / Procurement Centers and Shared Services Centers (SSC), with key regional positions providing commercial services, F&A, HR management services, customer service. -

Study on the Economic Contribution of the Software Industry in Lebanon
Study on the Economic Contribution of the Software Industry in Lebanon 2 Study on the Economic Contribution of the Software Industry in Lebanon Study on the Economic Contribution of the Software Industry in Lebanon 3 TABLE OF CONTENTS ABBREVIATIONS 7 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 8 1. INTRODUCTION 11 1.1 Scope of Work 11 1.2 Methodology 11 1.3 Structure of the Report 12 1.4 The Scope of Software Activities 14 2. LEGal AND REGUlaTORY FRAMEWORK 15 2.1 Copyright Protection of the Software Industry 15 2.2 Enforcement Context 16 3. THE ICT DEVELOPMENT LEVEL 18 3.1 Access 18 3.2 Affordability 20 3.3 Capacity 21 3.4 Networked Readiness Index 22 4. THE SOFTWARE SECTOR 25 4.1 Evolution and Main Trends 25 4.2 Market Size 26 4.3 Market Structure 27 4.4 Supportive Institutions 29 5. SOFTWARE MaRKET ORIENTATION 35 5.1 Local Demand for Software 35 5.2 Foreign Demand for Lebanese Software (Exports and Subcontracting) 36 6. ASSESSING THE BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT: SWOT ANalYSIS 38 6.1 Strengths 38 6.2 Weaknesses 40 6.3 Opportunities 43 6.4 Threats 44 4 Study on the Economic Contribution of the Software Industry in Lebanon 7. ECONOMIC CONTRIBUTION OF THE SOFTWARE INDUSTRY IN LEBANON 45 7.1 Main Characteristics of Software Industry 45 7.2 The Direct Economic Effects of the Lebanese Software Industry 47 7.2.1 Economic Contribution of Software Activities to GDP 47 7.2.2 Employment Generation 51 7.2.3 Benchmarking Software Activities with Other Sectors 53 7.2.4 Export-orientated Software Industries 54 7.3 Secondary Economic Impact 55 7.3.1 Mapping the Value Chain of the Major Activities of the Software Industries 55 7.3.2 Technical Impacts on the Value Chain 56 7.3.3 Backward and Forward Linkages Generated by Software Industries 57 7.3.4 Multiplier Effect 58 7.3.5 Spin-off Effects on Business Culture 59 8. -

Who We Are Forward Looking Disclosure
WHO WE ARE FORWARD LOOKING DISCLOSURE In addition to historical information, this release contains “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. These forward-looking statements include information about possible or assumed future results of our business and financial condition, as well as the results of operations, liquidity, plans and objectives. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terminology such as “believe,” “may,” “estimate,” “continue,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “should,” “plan,” “expect,” “predict,” “potential,” or the negative of these terms or other similar expressions. These statements include, but are not limited to, statements regarding: the persistence and intensification of competition in the IT industry; the future growth of spending in IT services outsourcing generally, application outsourcing and custom application development and offshore development services; the level of growth of demand for our services from our clients; the level of increase in revenues from our new clients; the resource utilization rates and productivity levels, the level of attrition of our IT professionals; the pricing structures we use for our client contracts; general economic and business conditions in the locations in which we operate; the levels of our concentration of revenues by vertical, geography, by client and by type of contract in the future; the continuity -

Beyond Hacker Idiocy the Changing Nature of Software Community and Identity
Heckscher & Adler / The Corporation as a Collaborative Community 05-Heckscher-chap05 Revise Proof page 198 20.11.2005 12:34am 5 Beyond Hacker Idiocy The Changing Nature of Software Community and Identity Paul S. Adler Introduction Professions are often taken as prototypical of a more collegial form of community, one that can be contrasted with both traditional Gemeinschaft and modern Gesellschaft. Indeed, the collegiality of professionals doing intrinsically meaningful work stands as a prefigurative model of the com- munist utopia of a ‘free association of producers.’1 The key features of professions giving them this status are their common professional social- ization and their autonomy in economic status and in technical decision making. In reality however, professionals’ autonomy is increasingly restricted. First, a substantial and growing proportion of professionals work under heteronomous conditions, as employees of capitalist firms: engineers are the largest category of these ‘organizational professionals.’ Even without economic autonomy, professionals traditionally enjoyed considerable technical autonomy; but this technical autonomy too has been under- mined by recent trends towards the bureaucratization of professional work.2 Many observers interpret the loss of economic and technical autonomy as a sign of abject proletarianization.3 If such is indeed the future of profes- sional work, the plausibility of the central thesis of this volume would be seriously undermined. After all, professions are the occupational category most directly implicated in the trends towards knowledge-intensive and Heckscher & Adler / The Corporation as a Collaborative Community 05-Heckscher-chap05 Revise Proof page 199 20.11.2005 12:34am Beyond Hacker Idiocy solutions-oriented production that we have interpreted as driving the movement towards collaborative community. -

An Iterative Approach to Insurance Software Testing
SHIFT LEFT AN ITERATIVE APPROACH TO INSURANCE SOFTWARE TESTING THE NEED TO IMPLEMENT LARGE MISSION-CRITICAL SYSTEMS IN AN ENVIRONMENT DRIVEN BY SHORT TIMELINES AND TIGHT BUDGETS HAS LED TO TESTING AND DEVELOPMENT METHODS THAT DELIVER BUSINESS VALUE QUICKLY. These methods apply speed and incremental Shift Left testing avoids cost overruns and learning with comprehensive up-front planning project delays. It uses an iterative approach to deliver smaller, fully-tested functional units that breaks down development and test of work in significantly less time than through a activities into smaller functional units of work, classic waterfall approach. uncovering and addressing issues earlier in the timeline rather than at the end of the According to an IBM System Science Institute project. Shift Left testing also compresses report, it is 15 times costlier to fix defects in project timelines by enabling smaller hyper- the test phase of a waterfall project because focused teams to work in parallel. testing occurs later in the project development lifecycle1. $100 $15 $6.5 $1 Design Implementation Testing Maintenance FIGURE 1: IBM SYSTEM SCIENCE INSTITUTE RELATIVE COST OF FIXING DATA DEFECTS FOUND IN TESTING WERE 15 TIMES MORE COSTLY THAN IF THEY WERE FOUND DURING THE DESIGN PHASE AND TWO TIMES MORE THAN IF FOUND DURING IMPLEMENTATION. 1 ITERATIVE APPROACH Iterative development and testing methods break down the development of large applications into smaller pieces; designing, developing, and testing in repeated cycles to deliver predictable value -

Business Opportunities for Pharma Companies
BUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES FOR PHARMA COMPANIES 1 2 Table of contents Business Platforms & Opportunities for Global Companies ……………………………………………………………. 4 Pharma success stories ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………........6 Testimonials ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………9 Uruguay´s Value Proposition ……………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 11 Reliablity ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 11 Market Access ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….…. 15 Talent ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..17 Lifestyle ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 21 Incentives ............................................................................................................................................ 28 Logistics Business Models………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…... 28 Comparison between tax systems (Logistics) ..................................................................................... 32 R&D Opportunities ............................................................................................................................... 32 Annex I: Key Players - Hub Operations in Uruguay………………………………………………………………………….35 3 BUSINESS PLATFORMS & OPPORTUNITIES FOR GLOBAL COMPANIES Uruguay is the most reliable country to do business in one of the most economically attractive regions in the world. It offers a favorable business climate, social and political stability, investment grade rating and sustained GDP growth during the past 15 years. Investors distinguish Uruguay´s world-class